Certificate management functions comprise the management and distribution of certificates and TrustLists for OPC UA Applications. An application that provides the certificate management functions is called CertificateManager. GDS and CertificateManager will typically be combined in one application. The basic concepts regarding Certificate management are described in OPC 10000-2.
There are two primary models for Certificate management: PullManagement and PushManagement. In PullManagement, the application acts as a Client and uses the Methods on the CertificateManager to request and update Certificates and TrustLists. The application is responsible for ensuring the Certificates and TrustLists are kept up to date. In PushManagement the application acts as a Server and exposes Methods which the CertificateManager can call to update the Certificates and TrustLists as required.
The CertificateManager is intended to work in conjunction with different Certificate management services such as Active Directory. The CertificateManager provides a standard OPC UA based information model that all OPC UA Applications can support without needing to know the specifics of a particular Certificate management system.
The CertificateManager should support the following features:
- Onboarding (first time setup for a device/application);
- Renewal (renewing expired or compromised certificates);
- TrustList Update (updating the TrustLists including the Revocation Lists);
- Revocation (removing a device/application from the system).
Although it is generally assumed that Client applications will use the Pull model and Server applications will use the Push model, this is not required.
OPC 10000-21 defines the complete process to automatically authenticate and onboard new Devices that depends on the Devices having support built in by the Manufacturer. If this support is not present, Devices and OPC UA Applications shall be manually onboarded using the mechanisms defined in this document.
During manual onboarding, the CertificateManager shall be able to operate in a mode where any Client is allowed to connect securely with any valid Certificate and user credentials are used to determine the rights a Client has; this eliminates the need to configure TrustLists before connecting to the CertificateManager for application setup, Application vendors may decide to build the interaction with the CertificateManager as a separate component, e.g. as part of an administration application with access to the OPC UA configuration of this Application. This is transparent for the CertificateManager and will not be considered further in the rest of this chapter.
Clients shall only connect to a CertificateManager which the Client has been configured to trust. This may require an out of band configuration step which is completed prior to starting the manual onboarding process.
This standard does not define how to administer a CertificateManager but a CertificateManager shall provide an integrated system that includes both push and PullManagement.
CertificateManagers restrict access to many of the features they provide. These restrictions are described either by referring to well-known Roles which a Session must have access to or by referring to Privileges which are assigned to Sessions using mechanisms other than the well-known Roles. The well-known Roles used for CertificateManagers are listed in Table 18.
Table 18 – Well-known Roles for a CertificateManager
|
Name |
Description |
|
CertificateAuthorityAdmin |
This Role grants rights to request or revoke any Certificate, update any TrustList or assign CertificateGroups to OPC UA Applications. |
|
RegistrationAuthorityAdmin |
This Role grants rights to approve Certificate Signing requests or NewKeyPair requests. |
|
SecurityAdmin |
This Role grants the right to change the security configuration of a CertificateManager. |
The well-known Roles for Server managed by a CertificateManager are listed in Table 19.
Table 19 – Well-known Roles for Server managed by a CertificateManager
|
Name |
Description |
|
SecurityAdmin |
For PushManagement, this Role grants the right to change the security configuration of a Server managed by a CertificateManager. |
The Privileges used in for CertificateManagers are listed in Table 20.
Table 20 – Privileges for a CertificateManager
|
Name |
Description |
|
ApplicationSelfAdmin |
This Privilege grants an OPC UA Application the right to renew its own Certificate or read its own CertificateGroups and TrustLists. The Certificate used to create the SecureChannel is used to determine the identity of the OPC UA Application. |
|
ApplicationAdmin |
This Privilege grants rights to request or renew Certificates, read TrustLists or CertificateGroups for one or more OPC UA Applications. The Certificate used to create the SecureChannel is used to determine the identity of the OPC UA Application and the set of OPC UA Applications that it is authorized to manage. |
PullManagement is performed by using the CertificateManager information model, in particular the Methods defined in 7.9. The interactions between Application and CertificateManager during PullManagement are illustrated in Figure 13.
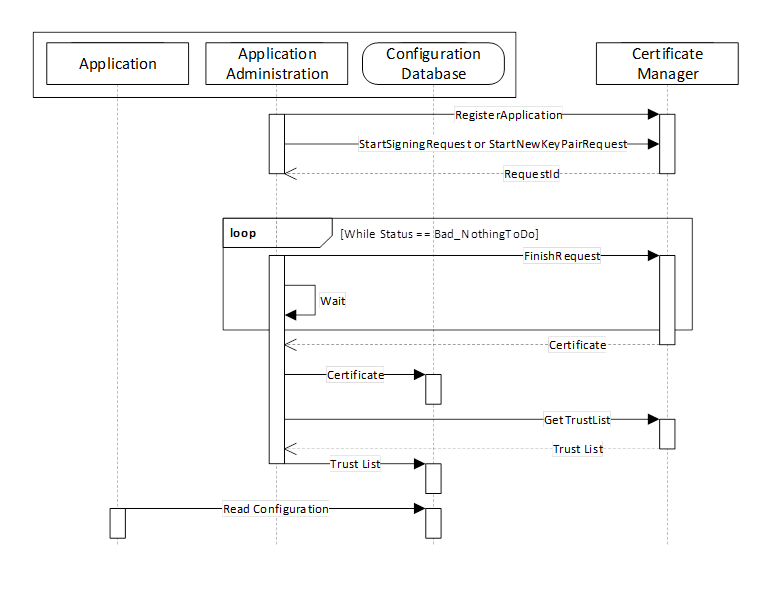
Figure 13 – The Pull Management Model for Certificates
The Application Administration component may be part of the Client or Server or a standalone utility that understands how the application persists its configuration information in its Configuration Database.
A similar process is used to renew certificates or to periodically update TrustList.
Security in PullManagement requires an encrypted channel and authorized credentials. These credentials may be user credentials for a CertificateAuthorityAdmin or application credentials determined by the Certificate used to create the SecureChannel. Examples of the application credentials include Certificates previously issued to the application being accessed, Device Certificates issued by the Registrar defined in OPC 10000-21 or Certificates issued to an application with access to the ApplicationAdmin Privilege (see 6.2).
The CertificateManager shall ensure that any application with a Certificate issued by the CertificateManager may connect securely to the CertificateManager using that Certificate (i.e. all CAs and CRLs needed to verify a Certificate are added to the CertificateManager’s TrustList).
Before a Client provides any secrets associated with credentials to a CertificateManager it needs to know that it can trust the CertificateManager. This can be done by an administrator that adds the CertificateManager to the Client TrustList before the Client attempts to connect to the CertificateManager. If the Client finds a CertificateManager on a network via mDNS or other insecure mechanism it could trust the CertificateManager if it has some independently acquired information that allows it to trust the CertificateManager. For example, the DNS address of the CertificateManager could be provided by a trusted authority and this address appears in the Certificate of the CertificateManager being used and the address was used to connect.
Once the Client finds a CertificateManager that it can trust, it needs to provide credentials that allows the CertificateManager to know that it can issue Certificates. The Certificate used by the Client can be the credential if there is an out of band process to provide the Certificate to the CertificateManager. The CertificateManager could provide a one-time password to the Client via email or other mechanisms.
The CertificateManager can only issue Certificates to authenticated Clients. There are a number of ways to authenticate Clients:
- The CertificateManager is pre-configured with information about the Client Certificate that allows the CertificateManager to know that the Client can request Certificates even if anonymous user credentials are used. The Client may be a DCA authenticated by a Registrar (see OPC 10000-21), a Client with a previously issued Certificate, or a Client authorized to create Certificates on behalf of other applications.
- The CertificateManager may have a manual process where an administrator reviews each request before issuing a Certificate.
- The Client provides user credentials. A Client shall not provide a secret (e.g. a password) to an untrusted CertificateManager.
PushManagement is targeted at applications that can be configured with a CertificateManager or agent acting as a Client. The Methods defined in 7.10 are used to create a CertificateRequest which can be passed onto the registration authority managed by the CertificateManager. After the registration authority signs the Certificate, the new Certificate is pushed to the Server with the UpdateCertificate Method.
There are two use cases for PushManagement:
- Management of a Server via the ServerConfiguration Object (see 7.10.4);
- Management of a Server, Client or non-OPC UA application via an ApplicationConfiguration Object (see 7.10.16).
The second use case requires a Server acting as a proxy for the application being managed.
The interactions between an Application and CertificateManager during PushManagement are illustrated in Figure 14.
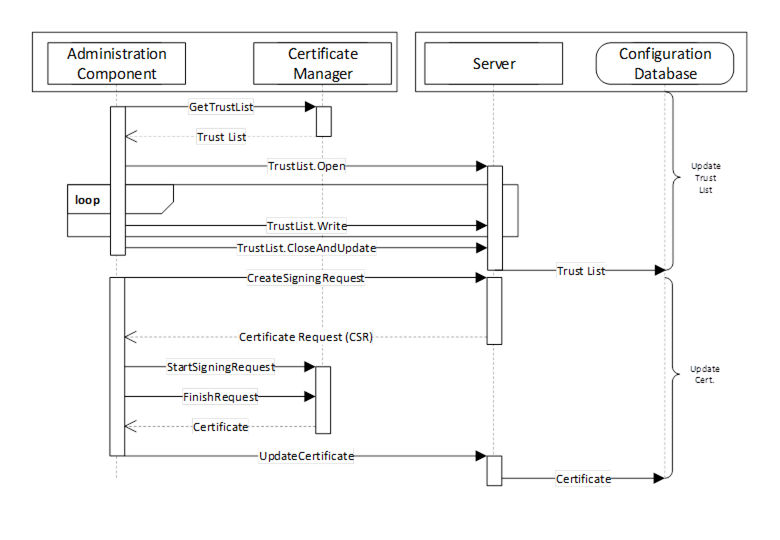
Figure 14 – The Push Certificate Management Model
The Administration Component may be part of the CertificateManager or a standalone utility that uses OPC UA to communicate with the CertificateManager (see 7.3 for a more complete description of the interactions required for this use case). The Configuration Database is used by the Server to persist its configuration information. The RegisterApplication Method (or internal equivalent) is assumed to have been called before the sequence in the diagram starts.
A similar process is used to renew certificates or to periodically update TrustList. In Figure 14 the TrustList update is shown to happen first. This is necessary to ensure any CRLs are provided to the Server before the new Certificate is updated. The TrustList update may be skipped If the current TrustList allows the Server to validate the new Certificate.
Security when using the PushManagement model requires an encrypted channel and a Client with access to the SecurityAdmin Role. For example, SecurityAdmin Role could be mapped to user credentials for an administrator or to a ApplicationInstance Certificate issued to a configuration tool. OPC 10000-21 defines a mechanism to install administrative Client Certificates into the Server TrustList.
Application Setup is the initial installation of an OPC UA Server or Client into a system in which a GDS is available and managing Certificates. Applications using a Client interface can be setup using the PullManagement. Applications using a Server interface can be setup using the PushManagement.
PushManagement and PullManagement are also integrated into OPC 10000-21 which specifies how new Devices can be authenticated when they are added to the network. Once a Device is authenticated the Device is trusted and can use the push or PullManagement without additional administrator credentials.
OPC UA Servers that do not support OPC 10000-21 typically auto-generate a self-signed Certificate when they first start. They may also have a pre-configured TrustList with Applications that are allowed to setup the Server. For example, a machine vendor may use a CA that is used to issue Certificates to Applications used by their field technicians.
For embedded devices, the Server should allow any Client that provides the proper SecurityAdmin credentials to create the secure connection needed for setup using PushManagement. Once the Server has been given its initial TrustList the Server should then restrict access to those Clients with Certificates in the TrustList. A vendor specific process for setup is required if a device restricts the Clients allowed to connect securely.
See Annex G for more specific instructions on how to provision an application when OPC 10000-21 is not used.
In this workflow the OPC UA Application that gets Certificates from the CertificateManager is the Client that executes the workflow and the CertificateManager is the Server processing the request in the workflow.
The Application is authenticated with the Certificate signed by the CertificateManager (or the Certificate assigned during registration). The UserTokenType is always Anonymous using the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege.
The workflow for PullManagement is shown in Figure 15 and the steps are described in Table 21. The two options for the key pair creation are described in Figure 16. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
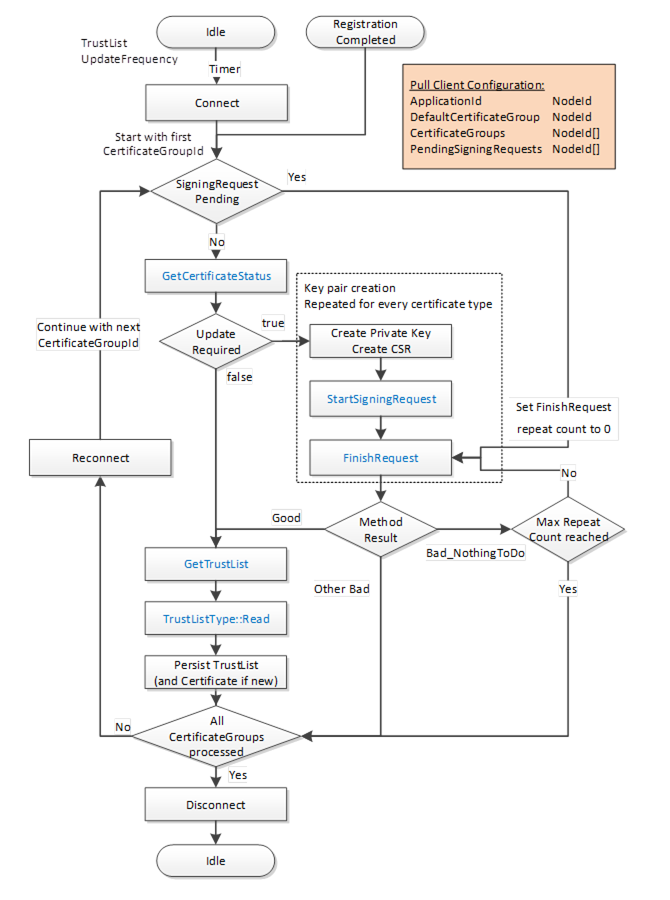
Figure 15 – Certificate Pull Management Workflow
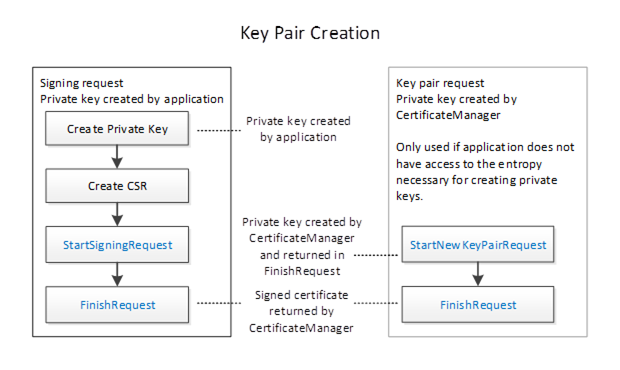
Figure 16 – The Pull Management Options for Key Pair Creation
The steps of the PullManagement workflow are described in detail in Table 21.
Table 21 – Certificate Pull Management Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Certificate management begin options |
The following options are possible to start the PullManagement.
|
|
Connect |
Create a connection for option (2). For the connection management with the CertificateManager the Services OpenSecureChannel, CreateSession and ActivateSession are used to create a connection with MessageSecurityMode SignAndEncrypt and an Anonymous user. The default CertificateGroup from the Client configuration is used to establish the connection. Application authentication is used by the CertificateManager to allow OPC UA Applications to access the necessary resources to update themselves using the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege. |
|
Required information |
The OPC UA Application requires the following information to execute the PullManagement workflow
|
|
SigningRequestPending |
If one or more signing requests are pending for a CertificateGroup, the FinishRequest Method is called directly with the ApplicationId and the RequestId for the pending signing request. The repeat count is set to 0 in this case. |
|
GetCertificateStatus |
The Method GetCertificateStatus is called with the ApplicationId and the CertificateGroupId to check if a certificate update is required. This is repeated for each CertificateType needed for the CertificateGroup. |
|
Update Required |
If GetCertificateStatus returns updateRequired set to True for one or more combinations of CertificateGroup and CertificateType, the process for key pair creation is started for the affected combinations. |
|
Create CSR |
The application creates a certificate signing request (CSR). It is strongly recommended, that the OPC UA Application creates a new private key for each signing request. |
|
StartSigningRequest |
The Method StartSigningRequest is called for each CertificateGroup and CertificateType together with the CSR to request a signed Certificate from the CertificateManager. Each Method call requires its own CSR. As alternative for OPC UA Applications who do not have access to a cryptographically sufficient entropy source, the Method StartNewKeyPairRequest can be used. In this case the private key is created by the CertificateManager. Both Methods return a RequestId that can be passed to the FinishRequest Method. The repeat count for FinishRequest is set to a small number like 2. |
|
FinishRequest |
The Method FinishRequest is called to check the results of a previous StartSigningRequest or StartNewKeyPairRequest. The following results are possible:
|
|
GetTrustList |
If all Certificates for a CertificateGroup are up-to-date, the TrustList is checked for updates by calling the Method GetTrustList. The Method returns the NodeId of the TrustList Object for the CertificateGroup. The LastUpdateTime of TrustList Object indicates when the contents of the TrustList changed. When using PullManagement, the Client should check this Property before downloading the TrustList. |
|
TrustListType::Read |
The NodeId of the TrustList Object returned by GetTrustList is used to open the TrustList for reading and to read the current content of the TrustList. |
|
Persist TrustList |
If a TrustList update or Certificate updates are available, they are persisted for further use by the OPC UA Application. They must be persisted at the same time to ensure a consistent setup. |
|
Repeat for all CertificateGroups |
Repeat the process for all CertificateGroups |
|
Disconnect |
Disconnect from CertificateManager. |
There are a few common workflows that a CertificateManager, as a Client, executes against the ServerConfiguration Object or a BaseApplicationConfiguration Object in the ManagedApplications Folder.
This workflow is started if the CertificateManager determines that an update to one or more Certificates used for an existing Endpoints is required. It is shown in Figure 17. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
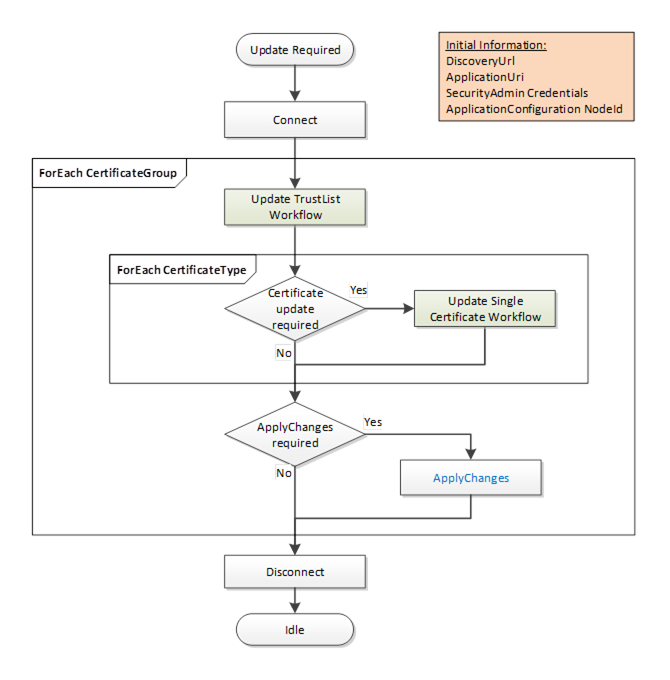
Figure 17 – PushManagement Update Multiple Certificates Workflow
The steps of the workflow are described in Table 22.
Table 22 – PushManagement Update Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Initial Conditions |
The update is triggered when the CertificateManager becomes aware that one or more Certificates need to be updated. Possible trigger mechanisms include:
The CertificateManager needs to have a DiscoveryUrl for the Server and should already trust at least one existing Certificate. It also needs the NodeId of the ApplicationConfigurationType instance being updated or the ApplicationUri for the Application being updated. This is either the well-known ServerConfiguration Object or one of the ApplicationConfigurationType instances in the ManagedApplications Folder. The list of CertificateGroups to update may be specified by an administrator or discovered by browsing a ApplicationConfigurationType instance. Only CertificateGroups with an ApplicationCertificateType Purpose are considered. The CertificateManager needs credentials that will have access to the SecurityAdmin Role on the Server. |
|
Connect |
The CertificateManager creates a secure connection using encryption and a Session with the Server. The Session requires access to the SecurityAdmin Role or equivalent. Possible credentials used to authenticate the CertificateManager are: |
|
Update TrustList Workflow |
The steps involved in updating the Certificate are described in the Update TrustList workflow. For each CertificateGroup the TrustList is updated first. The updates shall include all issuers and CRLs needed to validate new Certificates assigned to the CertificateGroup. If the CertificateManager needs to connect using an Endpoint associated with the CertificateGroup then the TrustList update shall include all Certificates needed to trust the CertificateManager. An application being configured via the ManagedApplications Folder does not need to trust the CertificateManager |
|
Certificate Update Required? |
For each CertificateType in a CertificateGroup the CertificateManager must determine if an update is required. This is usually based on any of the checks that triggered the workflow in the first place. For example, a Certificate close to its expiry date needs to be updated. |
|
Update Single Certificate Workflow |
The steps involved in updating the Certificate are described in the Update Single Certificate workflow. The Certificate update process may take time or require approval by an administrator so the CertificateManager may start multiple updates in parallel. |
|
Apply Changes Required? |
For each CertificateGroup it may be necessary to call ApplyChanges once the Certificate Update workflow completes. ApplyChanges is required if one or more of the Methods calls returns applyChangesRequired=TRUE. This step may cause the Server to close its Endpoints and force all Clients to reconnect. If this happens the CertificateManager may need to use the new Certificate to re-establish a Session with the Server. |
|
Disconnect |
Disconnect from Server. |
The Update TrustList workflow starts if the CertificateManager determines that an update to an existing TrustList is required. This update can be part of another workflow or a standalone workflow. It is shown in Figure 18. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
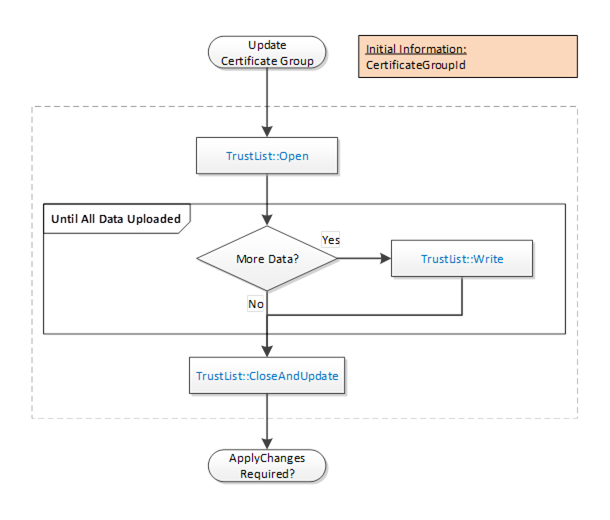
Figure 18 – PushManagement Update TrustList Workflow
The steps of the PushManagement Update TrustList workflow are described in Table 23.
Table 23 – PushManagement Update TrustList Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Initial Conditions |
The update is triggered when the CertificateManager needs to update a TrustList as part of a larger workflow. The CertificateGroupId is determined by the containing workflow. |
|
TrustList::Open |
The TrustList is opened for writing. The new TrustList is serialized into stream of bytes. |
|
TrustList::Write |
The stream of bytes is written to the Server in one or more blocks. The size of a block shall not exceed the value specified by the MaxByteStringLength Property. |
|
TrustList::CloseAndUpdate |
The CertificateManager closes the TrustList and tells the Server to apply changes. The Server may set the applyChangesRequired =TRUE to indicate that ApplyChanges needs to be called. If required, ApplyChanges is called by the containing workflow. |
The Update Single Certificate workflow is part of the Update Certificates workflow in 7.7.2. It starts when the CertificateManager determines that an update to a Certificate assigned to a CertificateGroup is required. It is shown in Figure 19. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
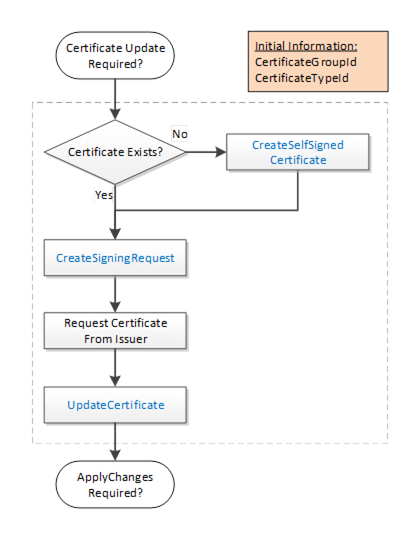
Figure 19 – PushManagement Update Certificate Workflow
The steps of the workflow are described in Table 24.
Table 24 – PushManagement Update Certificate Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Initial Conditions |
The update is triggered when the CertificateManager needs to update a Certificate as part of a larger workflow. The CertificateGroupId and CertificateTypeId are determined by the containing workflow. |
|
Certificate Exists? |
An existing Certificate may not be assigned to the CertificateType slot or it may not have field values that meet the requirements of the CertificateManager. If a useable Certificate does not exist a new self-signed Certificate is generated. |
|
CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
This Method creates a new self-signed Certificate using field values provided by the CertificateManager. This Method may not be implemented by all Servers. If this Method is available, it allows the CertificateManager to specify all of the key fields, such as the DNS names, in the Certificate. This is important when the CertificateManager configures Endpoints as described in 7.7.5. |
|
CreateSigningRequest |
This Method creates a new CertificateRequest that is signed with a PrivateKey owned by the Server. If requested, the Server generates a new PrivateKey but uses the field values from the existing Certificate. Some Servers may not have the resources to generate PrivateKeys. This step is skipped when this is the case. |
|
Request Certificate from Issuer. |
The CertificateManager requests a new Certificate from the Issuer. The CertificateManager generates a PrivateKey on behalf the Server if the Server cannot generate its own PrivateKeys. |
|
UpdateCertificate |
This Method allows the CertificateManager to upload a new Certificate and PrivateKey (if not generated by the Server) to the Server. The Server may set the applyChangesRequired =TRUE to indicate that ApplyChanges needs to be called. |
The Create Endpoint workflow starts if the CertificateManager determines it needs to create a new Endpoint. This update is always part of another workflow. It is shown in Figure 20. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
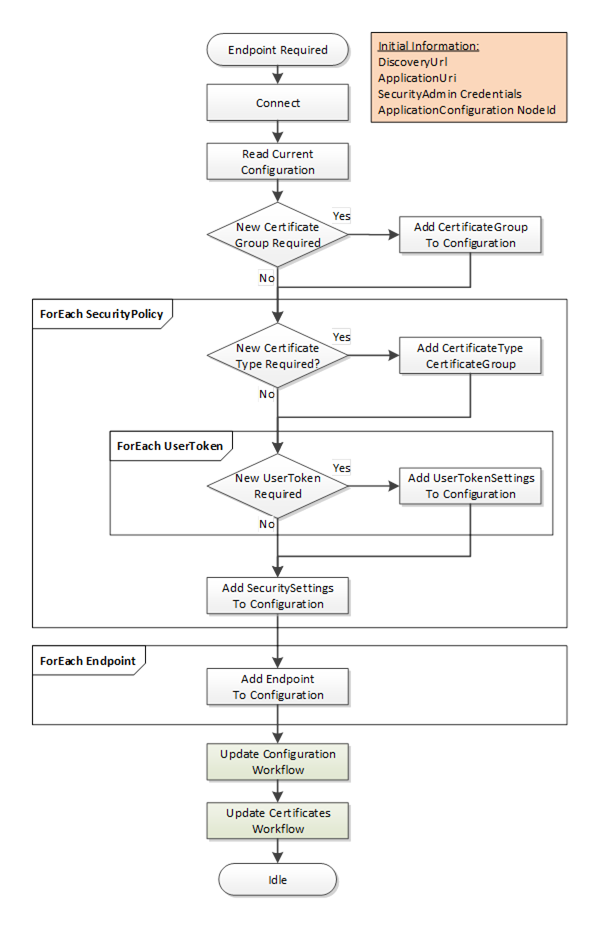
Figure 20 – PushManagement Create Endpoint Workflow
The steps of the workflow are described in Table 25.
Table 25 – PushManagement Create Endpoint Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Initial Conditions |
The workflow is triggered when an administrator decides that a new Endpoint needs to be created and instructs the CertificateManager to create it. The CertificateManager needs to have a DiscoveryUrl for the Server and should already trust at least one existing Certificate. It also needs the NodeId of the ApplicationConfigurationType instance being updated or the ApplicationUri for the Application being updated. This is either the well-known ServerConfiguration Object or one of the ApplicationConfigurationType instances in the ManagedApplications Folder. The CertificateManager needs credentials that will have access to the SecurityAdmin Role on the Server. |
|
Connect |
This is described in Table 22. |
|
Read Current Configuration |
The current configuration needs to be read from the ConfigurationFile Object which is a component of the ApplicationConfiguration instance. The ConfigurationVersion is needed when updating the configuration. Existing SecuritySettings, UserTokenSettings and CertificateGroups may be used by the new Endpoint. The current configuration is extended with new records as required. When updating the configuration a list of UpdateTargets is needed. Only records referenced by the UpdateTargets are processed. |
|
New CertificateGroup Required? |
Checks if a new CertificateGroup is required. |
|
Add CertificateGroup |
A new CertificateGroup is added to the configuration. An UpdateTarget with UpdateType=INSERT is created for the new CertificateGroup. The Path is ‘CertificateGroups.[n]’ where n is the index in the list of CertificateGroups currently in the configuration. The Name of the new record can be any value which is unique within the configuration and the CertificateGroups Object on the ApplicationConfiguration instance. It is used to create the BrowseName for the new CertificateGroup Object. |
|
New CertificateType Required? |
Checks if a new CertificateType is required. |
|
Add CertificateType to CertificateGroup. |
A new CertificateType is added to a CertificateGroups. If the CertificateGroup already exists, an UpdateTarget with UpdateType=REPLACE is created for the CertificateGroup. The Path is ‘CertificateGroups.[n]’ where n is the index in the list of CertificateGroups currently in the configuration. No additional UpdateTarget is needed if the CertificateGroup is a new CertificateGroup added in the previous step. |
|
New UserToken Required? |
Checks if a new UserToken is required. |
|
Add UserTokenSettings to Configuration. |
A new UserTokenSettings is added to the configuration. An UpdateTarget with UpdateType= INSERT is created. The Path is ‘UserTokenSettings.[n]’ where n is the index in the list of UserTokenSettings currently in the configuration. A new IssuedTokenType may also require a new AuthorizationServices record to be created as well. The Name of the new record can be any value which is unique within the configuration. It is not saved by the Server. |
|
Add SecuritySettings to Configuration. |
A new SecuritySettings is added to the configuration. An UpdateTarget with UpdateType= INSERT is created. The Path is ‘SecuritySettings.[n]’ where n is the index in the list of SecuritySettings currently in the configuration. The Name of the new record can be any value which is unique within the configuration. It is not saved by the Server. |
|
Add Endpoint to Configuration. |
A new Endpoint is added to the configuration. If the ApplicationConfiguration instance represents a Server then the Endpoint is an instance of ServerEndpointDataType and added to the ServerEndpoints list in the configuration. If the ApplicationConfiguration instance represents a Client then the Endpoint is an instance of EndpointDataType and added to the ClientEndpoints list in the configuration. An UpdateTarget with UpdateType= INSERT is created. The Path is ‘ServerEndpoints.[n]’ or ‘ClientEndpoints.[n]’ where n is the index in the appropriate list currently in the configuration. The Name of the new record can be any value which is unique within the configuration. It is not saved by the Server. |
|
Update Configuration Workflow |
The update configuration is uploaded to the Server. It is described in 7.7.6. |
|
Update Configuration Workflow |
The update configuration is uploaded to the Server. After this step completes the CertificateManager disconnects from the Server. It is described in 7.7.6. |
|
Update Certificates Workflow |
Once new CertificateGroups and CertificateTypes are added to the configuration it is possible to use the Update Certificates workflow to populate the TrustLists and issue Certificates. If this step is skipped, any Endpoints that reference the CertificateGroups missing Certificates will not be enabled. An Endpoint that has a valid Certificate but an empty TrustList will exist but no connections will be possible. The TOFU mode used during Application Setup (see G.2) only applies when a Server is configured for the first time. It is described in 7.7.2. |
The Update Configuration workflow is always part of another workflow. It is shown in Figure 21. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
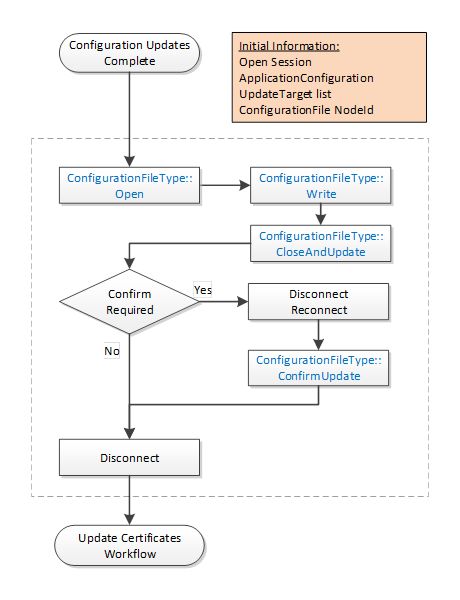
Figure 21 – PushManagement Update Configuration Workflow
The steps of the workflow are described in Table 26.
Table 26 – PushManagement Update Configuration Workflow Steps
|
Step |
Description |
|
Initial Conditions |
The workflow starts when a CertificateManager has completed updates to a local copy of the ApplicationConfiguration. A Session with SecurityAdmin access rights exists. The ConfigurationFile Object belongs to the ApplicationConfiguration being updated. It may be the Server that the CertificateManager is connected to or another application being managed by the Server. |
|
ConfigurationFileType::Open |
The ConfigurationFile is opened for writing. The new configuration is serialized into stream of bytes. |
|
ConfigurationFileType::Write |
The stream of bytes is written to the Server in one or more blocks. The size of a block shall not exceed the value specified by the MaxByteStringLength Property. |
|
ConfigurationFileType::CloseAndUpdate |
The CertificateManager closes the ConfigurationFile and tells the Server to apply changes. The CertificateManager provides a list of update targets which indicate what records in the configuration have changed. Records that are not referenced by an update target may be omitted. Note that when referencing existing the records the names provided by the Server when the configuration was downloaded shall be used. The names are associated with ConfigurationVersion and may change if the ConfigurationVersion changes. An error occurs if the ConfigurationVersion in the configuration does not match the current ConfigurationVersion known to the Server. The Server may return an UpdateId to indicate that ConfirmUpdate shall be called. |
|
Confirm Required? |
Checks if a new ConfirmUpdate needs to be called. |
|
Disconnect/Reconnect |
The CertificateManager closes the connection and waits at least the RestartDelayTime period but no longer than the RevertAfterTime period. |
|
ConfigurationFileType::ConfirmUpdate |
This Method tells the Server that the changes can be made permanent because the CertificateManager could reconnect. |
|
Disconnect |
Disconnect from Server. This step may be skipped instead of re-connecting when the Update Certificates workflow starts. |
The common information model defines types that are used in both the Push and the Pull Model.
This type defines a FileType that can be used to access a TrustList.
The CertificateManager uses this type to implement the Pull Model.
Servers use this type when implementing the Push Model.
An instance of a TrustListType shall restrict access to appropriate users or applications. This may be a CertificateManager administrative user that can change the contents of a TrustList, it may be an administrative user that is reading a TrustList to deploy to an Application host or it may be an Application that can only access the TrustList assigned to it.
The TrustList file is a UA Binary encoded stream containing an instance of TrustListDataType (see 7.8.2.8).
The Size Property inherited from FileType has no meaning for TrustList and returns the error code defined in OPC 10000-20.
When a Client opens the file for writing the Server will not actually update the TrustList until the CloseAndUpdate Method is called. Simply calling Close will discard the updates. The bit masks in TrustListDataType structure allow the Client to only update part of the TrustList.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 27.
Table 27 – TrustListType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:FileType defined in OPC 10000-20. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:LastUpdateTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:UpdateFrequency |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ActivityTimeout |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultValidationOptions |
TrustListValidationOptions |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:OpenWithMasks |
Defined in 7.8.2.2. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CloseAndUpdate |
Defined in 7.8.2.5. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:AddCertificate |
Defined in 7.8.2.6. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:RemoveCertificate |
Defined in 7.8.2.7. |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
The LastUpdateTime indicates when the TrustList was last updated. The LastUpdateTime shall reflect changes made using the TrustList Object Methods. A TrustList Object in a CertificateManager shall also reflect changes made in other ways.
The LastUpdateTime of a TrustList Object in a CertificateManager allows Clients using the PullManagement to know whether the TrustList has changed since the last time they accessed it. The LastUpdateTime of a TrustList Object in the ServerConfiguration allows administration Clients to verify the date of TrustLists. If a Server is not able to determine the LastUpdateTime after an event such as a restart, then the LastUpdateTime shall be DateTime.MinValue.
The UpdateFrequency Property specifies how often the TrustList shall be checked for changes. When the CertificateManager specifies this value, all Clients that read a copy of the TrustList should connect to the CertificateManager and check for updates to the TrustList within 2 times the UpdateFrequency. The choice of UpdateFrequency depends on how quickly system changes are required to be detected and the performance constraints of the system. UpdateFrequencies that are too long create security risks because of out of date CRLs. UpdateFrequencies that are too short negatively impact system performance. If the TrustList Object is contained within a ServerConfiguration Object then this Property is not present.
The ActivityTimeout Property specifies the maximum elapsed time between the calls to Methods on the TrustList Object after Open or OpenWithMasks is called. If this time elapses the TrustList is automatically closed by the Server and any changes are discarded. The default value is 60 000 milliseconds (1 minute).
The DefaultValidationOptions Property specifies the default options to use when validating Certificates with the TrustList. The TrustListValidationOptions DataType is defined in 7.8.2.10. This Property may be updated by Clients with access to the SecurityAdmin Role.
If auditing is supported, the CertificateManager shall generate the TrustListUpdated AuditEventType (see 7.8.2.13) when the TrustList is updated via the CloseAndUpdate (see 7.8.2.5), AddCertificate (see 7.8.2.6), RemoveCertificate (see 7.8.2.7) or ApplyChanges (see 7.10.9) Methods. The Event is only raised once after the asynchronous update process completes.
The Open Method is inherited from FileType which is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The Open Method shall not support modes other than Read (0x01) and the Write + EraseExisting (0x06). If other modes are requested the return code is Bad_NotSupported.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending if Open is called with the Write Mode bit set. If the Server supports transactions, then the Server creates a new transaction or continues an existing transaction if Open is called with the Write Mode bit set.
If the SecureChannel is not authenticated the Server shall return Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient.
Method Result Codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
The mode is not supported. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
The TrustList cannot be opened because it is part of a transaction is in progress. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
The OpenWithMasks Method allows a Client to read only a portion of the TrustList.
This Method can only be used to read the TrustList.
After calling this Method, the Client calls Read one or more times to get the TrustList. If the Server is able to detect out of band changes to theTrustList before the Client calls the Close Method, then the next Read returns Bad_InvalidState. If the Server cannot detect out of band changes it shall ensure the Client receives a consistent snapshot.
For PullManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
For PushManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
OpenWithMasks(
[in] UInt32 masks
[out] UInt32 fileHandle
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
masks |
The parts of the TrustList that are include in the file to read. The masks are defined in 7.8.2.9. |
|
fileHandle |
The handle of the newly opened file. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
The TrustList cannot be opened because it is part of a transaction that is in progress. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 28 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the OpenWithMasks Method.
Table 28 – OpenWithMasks Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:OpenWithMasks |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The Read Method is inherited from FileType which is defined in OPC 10000-5.
If the Server is able to detect out of band changes to the TrustList before the Client calls the Close Method, then this Method returns Bad_InvalidState.
Additional Method Result Codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The state of the TrustList has changed. |
The CloseAndUpdate Method closes the TrustList and applies the changes to the TrustList. It can only be called if the TrustList was opened for writing. If the Close Method is called any cached data is discarded and the TrustList is not changed.
If only part of the TrustList is being updated the Server creates a new TrustList that includes the existing TrustList plus any updates and validates the new TrustList.
The Server shall verify that every Certificate in the new TrustList is valid using the validation process defined in OPC 10000-4. If an invalid Certificate is found the Server shall return an error and shall not replace the existing TrustList.
If the Server does not support transactions, it applies the changes immediately and sets applyChangesRequired to FALSE. If the Server supports transactions, then the Server creates a new transaction or continues an existing transaction and sets applyChangesRequired to TRUE.
If a transaction exists on the current Session, the Server does not update the TrustList until ApplyChanges (see 7.10.9) is called. Any Clients that read the TrustList before ApplyChanges is called will receive the existing TrustList before the transaction started.
If any errors occur, the new TrustList shall be discarded.
When the TrustList changes the Server shall re-evaluate the Certificate associated with any open Sessions and SecureChannels. Sessions or SecureChannels with an untrusted or revoked Certificate shall be closed. This process may not complete before the Method returns and could take a significant amount of time on systems with limited resources.
The structure uploaded includes a mask (see 7.8.2.9) which specifies which fields are updated. If a bit is not set then the associated field is not changed.
For PullManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
For PushManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CloseAndUpdate(
[in] UInt32 fileHandle
[out] Boolean applyChangesRequired
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
fileHandle |
The handle of the previously opened file. |
|
applyChangesRequired |
If TRUE the ApplyChanges Method (see 7.10.9) shall be called before the new TrustList will be used by the Server. If FALSE the TrustList is now in use. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_CertificateInvalid |
The Server could not validate one or more Certificates in the TrustList. This may be returned after the first failed validation check. |
|
Bad_RequestTooLarge |
The changes would result in a TrustList that exceeds the MaxTrustListSize for the Server. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
Table 29 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CloseAndUpdate Method.
Table 29 – CloseAndUpdate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CloseAndUpdate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The AddCertificate Method allows a Client to add a single Certificate to the TrustList. The Server shall verify that the Certificate using the validation process defined in OPC 10000-4. If an invalid Certificate is found the Server shall return an error and shall not update the TrustList.
This Method will return a validation error if the Certificate is issued by a CA and the Certificate for the issuer is not in the TrustList.
This Method cannot provide CRLs so issuer Certificates cannot be added with this Method. Instead, CA Certificates and their CRLs shall be managed with the Write Method on the containing TrustList Object.
This Method cannot be called if the containing TrustList Object is open.
This Method returns Bad_TransactionPending if a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9).
This Method returns Bad_NotWritable if the TrustList Object is read only.
For PullManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
For PushManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
AddCertificate(
[in] ByteString certificate
[in] Boolean isTrustedCertificate
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded Certificate to add. |
|
isTrustedCertificate |
If TRUE the Certificate is added to the trustedCertificates list. If FALSE Bad_CertificateInvalid is returned. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_CertificateInvalid |
The certificate to add is invalid. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The Open Method was called with write access and the CloseAndUpdate Method has not been called. |
|
Bad_RequestTooLarge |
The changes would result in a TrustList that exceeds the MaxTrustListSize for the Server. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
Transaction has started and ApplyChanges or CancelChanges has not been called. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_NotWritable |
The TrustList Object is open for read only |
Table 30 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the AddCertificate Method.
Table 30 – AddCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:AddCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The RemoveCertificate Method allows a Client to remove a single Certificate from the TrustList. It returns Bad_InvalidArgument if the thumbprint does not match a Certificate in the TrustList.
If the Certificate is a CA Certificate that has CRLs then all CRLs for that CA are removed as well.
This Method returns Bad_CertificateChainIncomplete if the Certificate is a CA Certificate needed to validate another Certificate in the TrustList.
This Method returns Bad_TransactionPending if a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9).
This Method returns Bad_NotWritable if the TrustList Object is read only. For PullManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Session that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
For PushManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Session that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
RemoveCertificate(
[in] String thumbprint
[in] Boolean isTrustedCertificate
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Thumbprint |
The CertificateDigest of the Certificate to remove. |
|
isTrustedCertificate |
If TRUE the Certificate is removed from the Trusted Certificates List. If FALSE the Certificate is removed from the Issuer Certificates List. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificate to remove was not found. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The Open Method was called with write access and the CloseAndUpdate Method has not been called. |
|
Bad_CertificateChainIncomplete |
The Certificate is needed to validate another Certificate in the TrustList. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
Transaction has started and ApplyChanges or CancelChanges has not been called. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_NotWritable |
The TrustList Object is open for read only. |
Table 31 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the RemoveCertificate Method.
Table 31 – RemoveCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:RemoveCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This type defines a DataType which stores the TrustList of a Server. Its values are defined in Table 32.
Table 32 – TrustListDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TrustListDataType |
Structure |
Subtype of the Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|
specifiedLists |
UInt32 |
A bit mask which indicates which lists contain information. The TrustListMasks enumeration in 7.8.2.9 defines the allowed values. |
|
trustedCertificates |
ByteString[] |
The list of Application and CA Certificates which are trusted. |
|
trustedCrls |
ByteString[] |
The CRLs for the Certificates in the trustedCertificates list. |
|
issuerCertificates |
ByteString[] |
The list of CA Certificates which are necessary to validate Certificates. |
|
issuerCrls |
ByteString[] |
The CRLs for the CA Certificates in the issuerCertificates list. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 33.
Table 33 – TrustListDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This is a DataType that defines the values used for the SpecifiedLists field in the TrustListDataType. Its values are defined in Table 34.
Table 34 – TrustListMasks Enumeration
|
Name |
Value |
Description |
|
None |
0 |
No fields are provided. |
|
TrustedCertificates |
1 |
The TrustedCertificates are provided. |
|
TrustedCrls |
2 |
The TrustedCrls are provided. |
|
IssuerCertificates |
4 |
The IssuerCertificates are provided. |
|
IssuerCrls |
8 |
The IssuerCrls are provided. |
|
All |
15 |
All fields are provided. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 35.
Table 35 – TrustListMasks Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListMasks |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the Enumeration DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:EnumValues |
0:EnumValueType [] |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This DataType defines flags for TrustListValidationOptions is formally defined in Table 36.
Table 36 – TrustListValidationOptions Values
|
Value |
Bit No. |
Description |
|
SuppressCertificateExpired |
0 |
Ignore errors related to the validity time of the Certificate. |
|
SuppressHostNameInvalid |
1 |
Ignore mismatches between the host name or ApplicationUri. |
|
SuppressRevocationStatusUnknown |
2 |
Ignore errors if the revocation list cannot be found for the issuer of the Certificate. |
|
SuppressIssuerCertificateExpired |
3 |
Ignore errors if an issuer has an expired Certificate. |
|
SuppressIssuerRevocationStatusUnknown |
4 |
Ignore errors if the revocation list cannot be found for any issuer of issuer Certificates. |
|
CheckRevocationStatusOnline |
5 |
Check the revocation status online. |
|
CheckRevocationStatusOffline |
6 |
Check the revocation status offline. |
If CheckRevocationStatusOnline is set, the Certificate validation process defined in OPC 10000-4 will look for the authorityInformationAccess extension to find an OCSP (RFC 6960) endpoint which can be used to determine if the Certificate has been revoked.
If the OCSP endpoint is not reachable then the Certificate validation process looks for offline CRLs if the CheckRevocationStatusOffline bit is set. Otherwise, validation fails.
The revocation status flags only have meaning for issuer Certificates and are used when validating Certificates issued by that issuer.
The default value for this DataType only has the CheckRevocationStatusOffline bit set.
The TrustListValidationOptions representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 37.
Table 37 – TrustListValidationOptions Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListValidationOptions |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:UInt32 DataType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OptionSetValues |
0:LocalizedText [] |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This SystemOffNormalAlarmType is raised by the Server when the UpdateFrequency elapses and the TrustList has not been updated. This alarm automatically returns to normal when the TrustList is updated.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 38.
Table 38 – TrustListOutOfDateAlarmType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListOutOfDateAlarmType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the SystemOffNormalAlarmType defined in OPC 10000-9. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:TrustListId |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:LastUpdateTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:UpdateFrequency |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
TrustListId Property specifies the NodeId of the out-of-date TrustList Object.
LastUpdateTime Property specifies when the TrustList was last updated.
UpdateFrequency Property specifies how frequently the TrustList is updated.
This event is raised when a Method that changes the TrustList is called
It is raised when CloseAndUpdate, AddCertificate or RemoveCertificate Method on a TrustListType Object is called.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 39.
Table 39 – TrustListUpdateRequestedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListUpdateRequestedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
This event is raised when a TrustList is successfully changed.
This is the result of a CloseAndUpdate Method on a TrustListType Object or the result of a ApplyChanges Method on the ServerConfigurationType Object being called.
It shall also be raised when the AddCertificate or RemoveCertificate Method causes an update to the TrustList.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined inTable 40.
Table 40 – TrustListUpdatedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TrustListUpdatedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:TrustListId |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The TrustListId Property is the NodeId of the TrustList Object that was changed.
This ObjectType is used for Objects which represent CertificateGroups in the AddressSpace. A CertificateGroup is a context that contains a TrustList and one or more CertificateTypes that can be assigned to an application. This ObjectType allows an application which has multiple TrustLists and/or ApplicationInstance Certificates to express them in its AddressSpace.
A CertificateManager can have many CertificateGroups which manage CertificateTypes and TrustLists for the applications in the system.
A Server has one or more CertificateGroups which specify the CertificateTypes and TrustLists managed by the Server. Typically, there is a mapping between a CertificateGroup in a Server and a CertificateGroup in the CertificateManager. The mechanisms for creating that mapping are outside the scope of this specification.
This type is defined in Table 41.
Table 41 – CertificateGroupType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateGroupType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:TrustList |
|
0:TrustListType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateTypes |
0:NodeId[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Purpose |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:CertificateExpired |
|
0:CertificateExpirationAlarmType |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasCondition |
ObjectType |
0:CertificateExpirationAlarmType |
|
|
|
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:TrustListOutOfDate |
|
0:TrustListOutOfDateAlarmType |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:GetRejectedList |
Defined in 7.8.3.2. |
Optional |
||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
The TrustList Object is the TrustList associated with the CertificateGroup.
The CertificateTypes Property specifies the NodeIds of the CertificateTypes which may be assigned to applications which belong to the CertificateGroup. For example, a CertificateGroup with the NodeId of RsaMinApplicationCertificateType (see 7.8.4.8) and the NodeId RsaSha256ApplicationCertificate (see 7.8.4.9) specified allows an OPC UA Application to have one ApplicationInstance Certificates for each type. If this list is empty then the CertificateGroup does not allow Certificates to be assigned to Applications (i.e. a UserToken CertificateGroup only exists to allow the associated TrustList to be read or updated). All CertificateTypes for a given CertificateGroup shall be subtypes of a single common type (see Purpose in 7.8.3.4).
The Purpose Property specifies the allowed CertificateTypes. It shall be a direct subtype of CertificateType. See 7.8.3.4 for more details.
The CertificateExpired Object is an Alarm which is raised when a Certificate associated with the CertificateGroup is about to expire. If multiple Certificates are about to expire an Alarm for each Certificate is raised. The CertificateExpirationAlarmType is defined in OPC 10000-9.
The TrustListOutOfDate Object is an Alarm which is raised when the TrustList has not been updated within the period specified by the UpdateFrequency (see 7.8.2.1). The TrustListOutOfDateAlarmType is defined in 7.8.2.11.
The GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates that have been rejected by the Server when using the TrustList associated with the CertificateGroup. It can be used to track activity or allow administrators to move a rejected Certificate into the TrustList. This Method shall only be present on CertificateGroups which are part of the ServerConfiguration Object defined in 7.10.4.
GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates that have been rejected by the Server.
No rules are defined for how the Server updates this list or how long a Certificate is kept in the list. It is recommended that every valid but untrusted Certificate be added to the rejected list as long as storage is available. Servers can delete entries from the list returned if the maximum message size is not large enough to allow the entire list to be returned.
Servers only add Certificates to this list that have no unsuppressed validation errors but are not trusted.
For PullManagement, this Method is not present on the CertificateGroup.
For PushManagement, this Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
GetRejectedList(
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificates |
The DER encoded form of the Certificates rejected by the Server. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 42 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetRejectedList Method.
Table 42 – GetRejectedList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:GetRejectedList |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This type is used for Folders which organize CertificateGroups in the AddressSpace. This type is defined in Table 43.
Table 43 – CertificateGroupFolderType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateGroupFolderType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:DefaultApplicationGroup |
|
0:CertificateGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:DefaultHttpsGroup |
|
0:CertificateGroupType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:DefaultUserTokenGroup |
|
0:CertificateGroupType |
Optional |
|
0:Organizes |
Object |
0:<AdditionalGroup> |
|
0:CertificateGroupType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
The DefaultApplicationGroup Object represents the default CertificateGroup for Applications. It is used to access the default Application TrustList and to define the CertificateTypes allowed for the Certificates used by the application when communicating with peers:
- For OPC UA Applications and CertificateManagers these CertificateTypes specify what is allowed for ApplicationInstance Certificates. They shall specify one or more subtypes of ApplicationCertificateType (see 7.8.4.2).
- For NonUaApplications, these CertificateTypes specify what is allowed for the NonUaApplications Certificates. They shall specify one or more subtypes of CertificateType (see 7.8.4.1 and Table 99).
The DefaultHttpsGroup Object represents the default CertificateGroup for HTTPS communication. It is used to access the default HTTPS TrustList and to define the CertificateTypes allowed for the HTTPS Certificate. This Object shall specify the HttpsCertificateType NodeId (see 7.8.4.3) as a single entry in the CertificateTypes list or it shall specify one or more subtypes of HttpsCertificateType.
This DefaultUserTokenGroup Object represents the default CertificateGroup for validating user credentials. It is used to access the default user credential TrustList and to define the CertificateTypes allowed for user credentials Certificate. This Object shall leave CertificateTypes list empty.
Any additional CertificateGroups shall have a BrowseName where the Name is unique within the CertificateGroupFolder.
This type is used to serialize a single CertificateGroup configuration. It is defined in Table 44.
This type is used as part of the ApplicationConfigurationDataType defined in 7.10.19 which allows multiple of CertificateGroups in a Server to be updated at once.
The Name of the record is the name portion of the BrowseName of the associated CertificateGroup Object in the AddressSpace.
It may not be possible to delete CertificateGroups such as DefaultApplicationGroup.
Note that when a new CertificateGroup is added, Clients need to browse the CertificateGroups folder to discover the NodeId assigned by the Server that is needed for Certificate management Methods.
Each element in the CertificateTypes list shall be unique and not abstract. The set of permitted CertificateTypes is defined by the ApplicationConfigurationFileType Object (see 7.10.20).
When the CertificateTypes list is updated, if an element already exists it is not changed, if an element does not exist a new CertificateType is added. If existing CertificateTypes are not in the list they are deleted if no Certificate is assigned. The update is rejected if a Certificate is assigned to a deleted CertificateType. The DeleteCertificate Method is used to remove Certificates.
The Purpose imposes restrictions on the allowed CertificateTypes. The update to the CertificateGroup is rejected if the Purpose is changed and the CertificateTypes are not consistent.
The set of permitted Purposes is defined by the ApplicationConfigurationFileType Object (see 7.10.20).
This type is defined in Table 44.
Table 44 – CertificateGroupDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
CertificateGroupDataType |
Structure |
Subtype of BaseConfigurationRecordDataType. |
|
Purpose |
0:NodeId |
This value specifies the purpose of the CertificateGroup. It shall be a direct subtype of CertificateType. All CertificateTypes shall be the CertificateType or a subtype of the CertificateType indicated by the Purpose. For example, if the Purpose is ApplicationCertificate Type then the CertificateGroup is used to specify Certificates used as ApplicationInstance Certificate. A NULL value is not valid. |
|
CertificateTypes |
0:NodeId[] |
The list of CertificateTypes supported by the CertificateGroup. At least one element shall be provided. |
|
IsCertificateAssigned |
0:Boolean[] |
A list of flags indicating whether the CertificateType has a Certificate assigned. The length of this list shall be the same as the CertificateTypes list. This value is ignored during an update. |
|
ValidationOptions |
TrustListValidationOptions |
The validation options that are used when validating Certificates associated with the TrustList. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 45.
Table 45 – CertificateGroupDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateGroupDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This type is an abstract base type for types that describe the purpose of a Certificate. This type is defined in Table 46.
Table 46 – CertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
0:ApplicationCertificateType |
Defined in 7.8.4.2. |
||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
0:HttpsCertificateType |
Defined in 7.8.4.3. |
||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is an abstract base type for types that describe the purpose of an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. This type is defined in Table 47.
Table 47 – ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationCertificateType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the CertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
||||||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
0:RsaMinApplicationCertificateType |
Defined in 7.8.4.8. |
|||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
0:RsaSha256ApplicationCertificateType |
Defined in 7.8.4.9. |
|||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
0:EccApplicationCertificateType |
Defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This type is used to describe Certificates that are intended for use as HTTPS Certificates. This type is defined in Table 48.
Table 48 – HttpsCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:HttpsCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:CertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates that are intended to identify users. This type is defined in Table 48.
Table 49 – UserCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:UserCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:CertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates that are intended for use as TLS Certificates. This type is defined in Table 48.
Table 50 – TlsCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TlsCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:CertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe a Certificates that is a TLS server Certificate. This type is defined in Table 51.
Table 51 – TlsServerCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TlsServerCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:TlsCertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe a Certificates that is a TLS client Certificate. This type is defined in Table 52.
Table 52 – TlsClientCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TlsClientCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:TlsCertificateType defined in 7.8.4. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an RSA key size of 1024 or 2048 bits. All Applications which support the Basic128Rsa15 and Basic256 profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 53.
Table 53 – RsaMinApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:RsaMinApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:ApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.2 |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an RSA key size of 2048, 3072 or 4096 bits. All Applications which support the Basic256Sha256 profile (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 54.
Table 54 – RsaSha256ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:RsaSha256ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:ApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.2 |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC Public Key. Applications which support the ECC profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 55.
Table 55 – EccApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:ApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.2. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC nistP256 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC NIST P256 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type or a Certificate of the EccNistP384ApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.12. This type is defined in Table 56.
Table 56 – EccNistP256ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccNistP256ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC nistP384 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC NIST P384 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 57.
Table 57 – EccNistP384ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccNistP384ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC brainpoolP256r1 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC brainpoolP256r1 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type or a Certificate of the EccBrainpoolP384r1ApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.14. This type is defined in Table 58.
Table 58 – EccBrainpoolP256r1ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccBrainpoolP256r1ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC brainpoolP384r1 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC brainpoolP384r1 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 59.
Table 59 – EccBrainpoolP384r1ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccBrainpoolP384r1ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC curve25519 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC curve25519 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 60.
Table 60 – EccCurve25519ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccCurve25519ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type is used to describe Certificates intended for use as an ApplicationInstanceCertificate. They shall have an ECC curve448 Public Key. Applications which support the ECC curve448 curve profiles (see OPC 10000-7) shall have a Certificate of this type. This type is defined in Table 61.
Table 61 – EccCurve448ApplicationCertificateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EccCurve448ApplicationCertificateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:EccApplicationCertificateType defined in 7.8.4.10. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
This type defines a FileType that can be used to access the configuration associated with an Object.
The file is a stream containing an instance of UABinaryFileDataType serialized using one of the DataEncodings defined in OPC 10000-6. The DataEncoding used depends on the DataEncoding used for the messages sent to the Server. The body of the UABinaryFileDataType shall be an instance of the DataType specified by the SupportedDataType Property.
An instance of a ConfigurationFileType shall restrict access to appropriate users or applications. This should be ConfigureAdmin, SecurityAdmin or an equivalent administrative Role.
The Open Method shall not support modes other than Read (0x01) and Read + Write (0x03).
When a Client opens the file for reading and writing, the Client shall follow the following steps.
- Read the existing configuration with the FileType Read Method.
- Set the position to the beginning of the file with the FileType SetPosition Method.
- Write the changes with the FileType Write Method.
- Apply the changes with the CloseAndUpdate Method.
Servers shall automatically Close ConfigurationFiles if there are no calls to Methods on the ConfigurationFile Object within the time specified by the ActivityTimeout Property.
The Size Property inherited from FileType has no meaning for ConfigurationFile and returns the error code defined in OPC 10000-20.
When the CloseAndUpdate Method is called the Server will validate the configuration and then schedules the update. The Server returns initial results in the CloseAndUpdate response and may return additional errors after applying the changes in the response to ConfirmUpdate.
If CloseAndUpdate succeeds it returns a UpdateId that is used to confirm that the Client can connect after the update by calling the ConfirmUpdate Method. If it is not necessary to call ConfirmUpdate, the Server returns a empty value for the UpdateId.
Table 62 – ConfigurationFileType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ConfigurationFileType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 0:FileType defined in OPC 10000-20. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:LastUpdateTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CurrentVersion |
0:VersionTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ActivityTimeout |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SupportedDataType |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CloseAndUpdate |
Defined in 7.8.5.2. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:ConfirmUpdate |
Defined in 7.8.5.3. |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
|||||
The LastUpdateTime Property indicates when the configuration was last updated. The LastUpdateTime shall reflect changes made using the ConfigurationFile Object Methods. A ConfigurationFile Object should also reflect changes made in other ways.
The CurrentVersion Property is the value of the Version for the currently active configuration.
The ActivityTimeout Property specifies the maximum elapsed time between the calls to Methods on the ConfigurationFile Object after Open is called. If this time elapses the ConfigurationFile is automatically closed by the Server and any changes are discarded. The default value is 60 000 milliseconds (1 minute).
The SupportedDataType Property specifies the NodeId of the DataType that is put into the body of the UABinaryFileDataType during reading and writing. Any DataType shall be a subtype of BaseConfigurationDataType which is defined in 7.8.5.4.
The CloseAndUpdate Method validates the configuration and returns any validation errors.
The ConfirmUpdate Method is used to confirm that the Client can reconnect after the changes were applied.
The CloseAndUpdate Method closes the ConfigurationFile and applies the changes to the configuration. It can only be called if the ConfigurationFile was opened for writing. If the Close Method is called any cached data is discarded and the configuration is not changed.
The Client may partially update the configuration by specifying one or more targets. Each target refers to a component of the configuration that will be inserted, updated or deleted. The Server shall attempt to apply all changes. If any errors occur then all changes are rolled back.
Updating the configuration will often require the endpoints to be closed and all active Sessions be interrupted. When the new configuration is applied it is possible that a configuration error made the Server unreachable. The restartDelayTime argument is used to delay the restart process to give the Client a chance to receive results from the CloseAndUpdate call. The revertAfterTime argument is used to automatically restore the previous configuration if the Client is not able to reconnect and call the ConfirmUpdate Method.
If auditing is supported, the Server shall generate the ConfigurationUpdatedAuditEventType (see 7.8.5.8) when the configuration is updated. This may occur before CloseAndUpdate completes or when the update is scheduled to occur based on the restartDelayTime.
Signature
CloseAndUpdate(
[in] 0:UInt32 fileHandle
[in] 0:VersionTime versionToUpdate
[in] 0:ConfigurationUpdateTargetType[] targets
[in] 0:Duration revertAfterTime
[in] 0:Duration restartDelayTime
[out] 0:StatusCode[] updateResults
[out] 0:VersionTime newVersion
[out] 0:Guid updateId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
fileHandle |
The handle of the previously opened file. |
|
versionToUpdate |
Specifies the version of the configuration that the Client believes it is updating. If the CurrentVersion is not the same a Bad_InvalidState error is returned. |
|
targets |
The list of targets to update. There must be at least one target. Contents of the file which are not referenced by a target are ignored. |
|
revertAfterTime |
How long the Server should wait before reverting the configuration changes if ConfirmUpdate is not called after CloseAndUpdate returns a response. The revertAfterTime countdown starts after the restartDelayTime time elapses. After getting a response, the Client must wait at least restartDelayTime before attempting to reconnect but no longer than restartDelayTime + revertAfterTime. |
|
restartDelayTime |
How long the Server should wait before applying the configuration changes if applying the configuration changes will interrupt active Sessions. Clients set this value based on how long it takes for them to receive the response to the Method. |
|
updateResults |
The result for each target update operation. The length and order of the array shall match the targets array. If any element is not Good then then no changes are applied and the Method return code is Uncertain. |
|
newVersion |
The new ConfigurationVersion. If it is NULL, then no changes were applied. |
|
updateId |
An id to passed into ConfirmUpdate to tell the Server that the update was successful. If this value is a NULL Guid then ConfirmUpdate does not need to be called. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Uncertain |
Errors occurred processing individual targets. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The versionToUpdate does not match the CurrentVersion. |
|
Bad_ChangesPending |
|
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Operation Result Codes (Returned in UpdateResults)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NoEntryExists |
An existing record was not found. |
|
Bad_EntryExists |
Another record with the same name was found. |
|
Good_EntryInserted |
A new record was created successfully, |
|
Good_EntryReplaced |
An existing record was updated successfully, |
|
Bad_NoDeleteRights |
A record exists but it cannot be deleted. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
A field in the record cannot be changed to the value specified. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The target definition is not valid. |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The maximum number of supported elements would be exceeded. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The current state of the record does not allow the operation. For example, a CertificateGroup has Certificates assigned. |
Table 29 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CloseAndUpdate Method.
Table 63 – CloseAndUpdate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CloseAndUpdate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The ConfirmUpdate Method allows a Client to confirm that it can connect after the configuration has been applied. The Client shall disconnect from the Server and reconnect before calling ConfirmUpdate. The RevertAfterTime parameter passed to the CloseAndUpdate Method specifies how long the Server shall wait for confirmation.
If the Server could not apply all changes then the return code is Bad_TransactionFailed and no changes were applied.
If the Method is called too soon the Server returns Bad_InvalidState.
The permissions needed to call this method shall be specified by the subtype and should require one of the administrator Roles.
Signature
ConfirmUpdate(
[in] 0:Guid updateId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
updateId |
The id returned by CloseAndUpdate. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_TransactionFailed |
An error occurred applying the changes and they have been rolled backed and the ConfigurationVersion does not change. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The updateId is not valid or is no longer valid. Any transaction associated with the updateId has been rolled back. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The Server has not had a chance to apply the changes and the Client needs to wait and call the Method again. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 28 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ConfirmUpdate Method.
Table 64 – ConfirmUpdate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ConfirmUpdate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This DataType is the base DataType used to serialize configurations. It is defined in Table 65.
Table 65 – BaseConfigurationDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
BaseConfigurationDataType |
Structure |
|
|
ConfigurationVersion |
0:VersionTime |
This field is ignored when updating the configuration. |
|
ConfigurationProperties |
0:KeyValuePair[] |
Additional configuration properties |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 66.
Table 66 – BaseConfigurationDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:BaseConfigurationDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
||||||
This DataType is the base DataType for a named record contained within a configuration. It is defined in Table 67.
Table 67 – BaseConfigurationRecordDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
BaseConfigurationRecordDataType |
Structure |
|
|
Name |
0:String |
The name of the record used when updating or deleting a single record. If the record corresponds to an Object in the AddressSpace then this shall be the Name portion of the BrowseName. If the record does not have a matching Object, then Name is only unique within an instance of a configuration file. For these cases, the Server may generate new names each time the ConfigurationVersion changes. The names may be persisted by the Server with the ConfigurationVersion or may be generated with an algorithm that produces the same value given a fixed set of records. Which behaviour to use is defined by the subtype. |
|
RecordProperties |
0:KeyValuePair[] |
Additional record properties |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 66.
Table 68 – BaseConfigurationRecordDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
||||||
This is a DataType that defines a target for an update operation It allows the Client to specify the type of update operation (insert, replace or delete).
The Path field defines the path to the target record of the update operation within the configuration. Only fields which are subtypes of BaseConfigurationRecordDataType are valid targets of the path.
The UpdateType specifies that operation to be performed.
Examples of paths:
- CertificateGroups.[1]
- ApplicationIdentity
- UserTokenSettings.[2]
The ConfigurationUpdateTargetType is defined in Table 69.
Table 69 – ConfigurationUpdateTargetType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ConfigurationUpdateTargetType |
Structure |
|
|
Path |
0:String |
A path to the target record for the update operation. The path uses the DataType FieldPath syntax defined in OPC 10000-6.
|
|
UpdateType |
0:ConfigurationUpdateType |
The type of update. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 70.
Table 70 – ConfigurationUpdateTargetType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ConfigurationUpdateTargetType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
||||||
This is a DataType that defines the values used for the UpdateType field in the ConfigurationUpdateTargetType. Its values are defined in Table 71.
The update operation is applied to a target within the configuration identified by a path (see 7.8.5.6). The Replace and Delete operations use the Name field in the Structure to match a target with an existing record. For Insert operations no existing record with the same Name may exist. For Delete operations the contents of the record are ignored.
Table 71 – ConfigurationUpdateType Enumeration
|
Name |
Value |
Description |
|
Insert |
1 |
The target is added. An error occurs if a name conflict occurs. |
|
Replace |
2 |
The existing record is updated. An error occurs if a name cannot be matched to an existing record. |
|
InsertOrReplace |
3 |
The existing record is updated. New records are created if the name does not match an existing record. |
|
Delete |
4 |
Any existing record is deleted. An error occurs if the name cannot be matched to an existing record. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 72.
Table 72 – ConfigurationUpdateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ConfigurationUpdateType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the Enumeration DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:EnumValues |
0:EnumValueType [] |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
||||||
This event is raised when a configuration been updated.
The SourceNode Property for Events of this type shall be assigned to the NodeId for the Node that owns the configuration (usually the parent of the ConfigurationFile Object). The SourceName for Events of this type shall be the BrowseName of the configuration owner.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 73.
Table 73 – ConfigurationUpdatedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ConfigurationUpdatedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OldVersion |
0:VersionTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:NewVersion |
0:VersionTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Configuration Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The DataType Property specifies the DataType of the configuration that was updated.
The GlobalDiscoveryServer AddressSpace used for Certificate management is shown in Figure 22. Most of the interactions between the GlobalDiscoveryServer and Application administrator or the Client will be via Methods defined on the Directory folder.
Figure 22 – The Certificate Management AddressSpace for the GlobalDiscoveryServer
This ObjectType is the TypeDefinition for the root of the CertificateManager AddressSpace. It provides additional Methods for Certificate management which are shown in Table 74.
Table 74 – CertificateDirectoryType ObjectType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:CertificateDirectoryType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the 2:DirectoryType defined in 6.5.3. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:Organizes |
Object |
2:CertificateGroups |
|
0:CertificateGroup FolderType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:StartSigningRequest |
Defined in 7.9.3. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:StartNewKeyPairRequest |
Defined in 7.9.4. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:FinishRequest |
Defined in 7.9.5. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:RevokeCertificate |
Defined in 7.9.6. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:GetCertificateGroups |
Defined in 7.9.7. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:GetCertificates |
Defined in 7.9.8. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:GetTrustList |
Defined in 7.9.9. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:GetCertificateStatus |
Defined in 7.9.10. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
2:CheckRevocationStatus |
Defined in 7.9.11. |
Optional |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
|||||
The CertificateGroups Object organizes the CertificateGroups supported by the CertificateManager. It is described in 7.8.4.10. CertificateManagers shall support the DefaultApplicationGroup and may support the DefaultHttpsGroup or the DefaultUserTokenGroup. CertificateManagers may support additional CertificateGroups depending on their requirements. For example, a CertificateManager with multiple Certificate Authorities would represent each as a CertificateGroupType Object organized by CertificateGroups Folder. Clients could then request Certificates issued by a specific CA by passing the appropriate NodeId to the StartSigningRequest or StartNewKeyPairRequest Methods.
CertificateGroups assigned by the CertificateManager to specific applications are persisted by PullManagement Clients. These Clients use the NodeIds to relate their local configuration to the CertificateGroup in the CertificateManager.
The StartSigningRequest Method is used to request a new a Certificate that is signed by a CA managed by the CertificateManager. This Method is recommended when the caller already has a private key.
The StartNewKeyPairRequest Method is used to request a new Certificate that is signed by a CA managed by the CertificateManager along with a new private key. This Method is used only when the caller does not have a private key and cannot generate one.
The FinishRequest Method is used to check that a Certificate request has been approved by an entity with access to the RegistrationAuthorityAdmin Role. If successful the Certificate and Private Key (if requested) are returned.
The GetCertificateGroups Method returns a list of NodeIds for CertificateGroupType Objects that can be used to request Certificates or TrustLists for an Application.
The GetCertificates Method returns a list of Certificates assigned to the Application for a CertificateGroup.
The GetTrustList Method returns a NodeId of a TrustListType Object that belongs to a CertificateGroup assigned to an Application.
The GetCertificateStatus Method checks whether the Application has to update the Certificate identified in the call.
The CheckRevocationStatus Method checks the revocation status of a Certificate.
StartSigningRequest is used to initiate a request to create a Certificate which uses the private key which the caller currently has. The new Certificate is returned in the FinishRequest response.
Signature
StartSigningRequest(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] ByteString certificateRequest
[out] NodeId requestId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application record by the CertificateManager. |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup which provides the context for the new request. If null the CertificateManager shall choose the DefaultApplicationGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The NodeId of the CertificateType for the new Certificate. If null the CertificateManager shall generate a Certificate based on the value of the certificateGroupId argument. |
|
certificateRequest |
A CertificateRequest used to prove possession of the Private Key. It is a PKCS #10 encoded blob in DER format. If the CertificateRequest is for an ApplicationInstance Certificate then it shall include all fields required by OPC 10000-6 such as the subjectAltName. |
|
requestId |
The NodeId that represents the request. This value is passed to FinishRequest. |
The call returns the NodeId that is passed to the FinishRequest Method.
The certificateGroupId parameter allows the caller to specify a CertificateGroup that provides context for the request. If null the CertificateManager shall choose the DefaultApplicationGroup. If the Application does not currently belong to the requested CertificateGroup the CertificateManager shall verify that the Application is allowed to join the CertificateGroup and then, if permitted, add the Application to the CertificateGroup. The CertificateGroup verification and assignment may occur anytime before FinishRequest returns success.
The set of available CertificateGroups are found in the CertificateGroups folder described in 7.9.2. The CertificateGroups allowed for an Application are returned by the GetCertificateGroups Method (see 7.9.7).
The certificateTypeId parameter specifies the type of Certificate to return. The permitted values are specified by the CertificateTypes Property of the Object specified by the certificateGroupId parameter.
The certificateRequest parameter is a DER encoded CertificateRequest. The subject, subjectAltName and Public Key are copied into the new Certificate.
If the certificateTypeId is a subtype of ApplicationCertificateType the subject conforms to the requirements defined in OPC 10000-6. The public key length shall meet the length restrictions for the CertificateType. If the certificateType is a subtype of HttpsCertificateType the Certificate common name (CN=) shall be the same as a domain from a DiscoveryUrl which uses HTTPS and the subject shall have an organization (O=) field.
The ApplicationUri shall be specified in the CSR. The CertificateManager shall return Bad_CertificateUriInvalid if the stored ApplicationUri for the Application is different from what is in the CSR.
The subject in the CSR may be ignored by the CertificateManager. The CertificateManager may update the subject to comply with policy requirements and to ensure global uniqueness.
Any bits set in basicConstraints or extendedKeyUsage fields in the CSR are ignored by the CertificateManager. The CertificateManager uses values that are appropriate and compliant with requirements defined for Application Instance Certificates in OPC 10000-6.
For Servers, the list of domain names shall be specified in the CSR. The domains shall include the domain(s) in the DiscoveryUrls known to the CertificateManager.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Session that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
If auditing is supported, the CertificateManager shall generate the CertificateRequested AuditEventType (see 7.9.12) if this Method succeeds or fails.
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more of the certificateGroupId, certificateTypeId or certificateRequest arguments is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_RequestNotAllowed |
The current configuration of the CertificateManager does not allow the request. The text associated with the error should indicate the exact reason. |
|
Bad_CertificateUriInvalid |
The ApplicationUri was not specified in the CSR or does not match the Application record. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
The signing algorithm, public algorithm or public key size are not supported by the CertificateManager. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 75 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the StartSigningRequest Method.
Table 75 – StartSigningRequest Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:StartSigningRequest |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This Method is used to start a request for a new Certificate and Private Key. The Certificate and Private Key. are returned in the FinishRequest response.
Signature
StartNewKeyPairRequest(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] String subjectName
[in] String[] domainNames
[in] String privateKeyFormat
[in] String privateKeyPassword
[out] NodeId requestId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application Instance by the CertificateManager. |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup which provides the context for the new request. If null the CertificateManager shall choose the DefaultApplicationGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The NodeId of the CertificateType for the new Certificate. If null the CertificateManager shall generate a Certificate based on the value of the certificateGroupId argument. |
|
subjectName |
The subject to use for the Certificate. If not specified the ApplicationName and/or domainNames are used to create a suitable default value. The format of the subject is a sequence of name value pairs separated by a ‘/’. The name shall be one of ‘CN’, ‘O’, ‘OU’, ‘DC’, ‘L’, ‘S’ or ‘C’ and shall be followed by a ‘=’ and then followed by the value. The value may be any printable character except for ‘”’. If the value contains a ‘/’ or a ‘=’ then it shall be enclosed in double quotes (‘”’). |
|
domainNames |
The domain names to include in the Certificate. If not specified the DiscoveryUrls are used to create suitable defaults. |
|
privateKeyFormat |
The format of the private key. The following values are always supported: PFXPKCS #12 encoded PEMPKCS #8 Base64 encoded DER (see RFC 5958). |
|
privateKeyPassword |
The password to use for the private key. |
|
requestId |
The NodeId that represents the request. This value is passed to FinishRequest. |
The call returns the NodeId that is passed to the FinishRequest Method.
The certificateGroupId parameter allows the caller to specify a CertificateGroup that provides context for the request. If null the CertificateManager shall choose the DefaultApplicationGroup. If the Application does not currently belong to the requested CertificateGroup the CertificateManager shall verify that the application is allowed to join the CertificateGroup and then, if permitted, add the Application to the CertificateGroup.
The set of available CertificateGroups are found in the CertificateGroups folder described in 7.9.2. The CertificateGroups allowed for an application are returned by the GetCertificateGroups Method (see 7.9.7).
The certificateTypeId parameter specifies the type of Certificate to return. The permitted values are specified by the CertificateTypes Property of the Object specified by the certificateGroupId parameter.
The subjectName parameter is a sequence of X.500 name value pairs separated by a ‘/’. For example: CN=ApplicationName/OU=Group/O=Company.
If the certificateType is a subtype of ApplicationCertificateType the Certificate subject shall have an organization (O=) or domain name (DC=) field. The public key length shall meet the length restrictions for the CertificateType. The domain name field specified in the subject is a logical domain used to qualify the subject that is not necessarily the same as a domain or IP address in the subjectAltName field of the Certificate. The common name (CN=) field shall be specified and should be the ApplicationName or a suitable equivalent.
If the certificateType is a subtype of HttpsCertificateType the Certificate common name (CN=) shall be the same as a domain from a DiscoveryUrl which uses HTTPS and the subject shall have an organization (O=) field.
If the subjectName is blank or null the CertificateManager generates a suitable default.
The requested subject may be ignored by the CertificateManager. The CertificateManager may update the subject to comply with policy requirements and to ensure global uniqueness.
The domainNames parameter is list of domains to be includes in the Certificate. If it is null or empty the GDS uses the DiscoveryUrls of the Server to create a list. For Clients the domainNames are omitted from the Certificate if they are not explicitly provided.
The privateKeyFormat specifies the format of the private key returned. All CertificateManager implementations shall support “PEM” and “PFX”. If PFX is used the packet shall include the Certificate and the PrivateKey.
The privateKeyPassword specifies the password on the private key. The CertificateManager shall not persist this information and shall discard it once the new private key is generated.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Session that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
If auditing is supported, the CertificateManager shall generate the CertificateRequested AuditEventType (see 7.9.12) if this Method succeeds or fails.
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NodeIdUnknown |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application (deprecated). |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more of the certificateGroupId, certificateTypeId, subjectName, domainNames or privateKeyFormat parameters is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_RequestNotAllowed |
The current configuration of the CertificateManager does not allow the request. The text associated with the error should indicate the exact reason. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 76 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the StartNewKeyPairRequest Method.
Table 76 – StartNewKeyPairRequest Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:StartNewKeyPairRequest |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
FinishRequest is used to finish a certificate request started with a call to StartNewKeyPairRequest or StartSigningRequest.
Signature
FinishRequest (
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId requestId
[out] ByteString certificate
[out] ByteString privateKey
[out] ByteString[] issuerCertificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application Instance by the GDS. |
|
requestId |
The NodeId returned by StartNewKeyPairRequest or StartSigningRequest. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded Certificate. |
|
privateKey |
The private key encoded in the format requested. If a password was supplied the blob is protected with it. This field is null if no private key was requested. |
|
issuerCertificates |
The Certificates required to validate the new Certificate. |
This call is passes the NodeId returned by a previous call to StartNewKeyPairRequest or StartSigningRequest.
It is expected that a Client will periodically call this Method until an entity with access to the RegistrationAuthorityAdmin Role has approved the request.
If the Client experiences a network failure while waiting for a completed request it may receive a Bad_InvalidArgument error when it calls the Method again. Recovering from this error is done by:
- If the Client originally called StartSigningRequest it can retrieve the Certificate by calling GetCertificates (see 7.9.8).
- If the Client originally called StartNewKeyPairRequest it shall restart the process by calling StartNewKeyPairRequest again.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Session that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2). In addition, the Client Certificate shall be the same as the one used to call StartSigningRequest or StartNewKeyPairRequest.
If auditing is supported, the CertificateManager shall generate the CertificateDeliveredAuditEventType (see 7.9.13) if this Method succeeds.
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The requestId is does not reference to a valid request for the Application. |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
There is nothing to do because request has not yet completed. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_RequestNotAllowed |
The CertificateManager rejected the request. The text associated with the error should indicate the exact reason. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 77 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the FinishRequest Method.
Table 77 – FinishRequest Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:FinishRequest |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
RevokeCertificate is used to revoke a Certificate issued by the CertificateManager.
When a Certificate is revoked it shall be removed from any TrustLists that it is in and TrustLists with the issuer Certificate shall be updated with the new CRL.
Certificates assigned to an Application are automatically revoked when the UnregisterApplication Method is called (see 6.5.8).
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
If auditing is supported, the CertificateManager shall generate the CertificateRevokedAuditEventType on success.
Signature
RevokeCertificate (
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] ByteString certificate
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application by the CertificateManager. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded Certificate to revoke. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificate is not a Certificate for the specified Application that was issued by the CertificateManager. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 78 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the RevokeCertificate Method.
Table 78 – RevokeCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:RevokeCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager RevokeCertificate |
|||||
GetCertificateGroups returns the CertificateGroups assigned to Application.
Signature
GetCertificateGroups(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[out] NodeId[] certificateGroupIds
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application by the GDS. |
|
certificateGroupIds |
An identifier for the CertificateGroups assigned to the Application. |
A CertificateGroup provides a TrustList and one or more CertificateTypes which may be assigned to an Application.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 79specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetCertificateGroups Method.
Table 79 – GetCertificateGroups Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:GetCertificateGroups |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
GetCertificates returns the Certificates assigned to the application and associated with the CertificateGroup.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
Signature
GetCertificates(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[out] NodeId[] certificateTypeIds
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application by the GDS. |
|
certificateGroupId |
An identifier for the CertificateGroup that the Certificates belong to. If null, the CertificateManager shall return the Certificates for all CertificateGroups assigned to the Application. |
|
certificateTypeIds |
The CertificateTypes that currently have a Certificate assigned. The length of this list is the same as the length as certificates list. |
|
certificates |
A list of DER encoded Certificates assigned to Application. This list only includes Certificates that are currently valid. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateGroupId is not recognized or not valid for the Application. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 80 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetCertificates Method.
Table 80 – GetCertificates Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:GetCertificates |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager GetCertificates |
|||||
GetTrustList is used to retrieve the NodeId of a TrustList assigned to an application.
Signature
GetTrustList(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[out] NodeId trustListId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application by the GDS. |
|
certificateGroupId |
An identifier for a CertificateGroup that the Application belongs to. If null, the CertificateManager shall return the trustListId for a suitable default group for the Application. |
|
trustListId |
The NodeId for a TrustList Object that can be used to download the TrustList assigned to the Application. |
Access permissions also apply to the TrustList Objects which are returned by this Method. This TrustList includes any Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) associated with issuer Certificates in the TrustList.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateGroupId parameter is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 81 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetTrustList Method.
Table 81 – GetTrustList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:GetTrustList |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
GetCertificateStatus is used to check if an Application has to update its Certificate.
If this Method is called for a CertificateGroup which the application does not belong to then the Method shall return updateRequired =TRUE.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the CertificateAuthorityAdmin Role, the ApplicationAdmin Privilege, or the ApplicationSelfAdmin Privilege (see 7.2).
Signature
GetCertificateStatus(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[out] Boolean updateRequired
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned to the Application Instance by the GDS. |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup which provides the context. If null the CertificateManager shall choose the DefaultApplicationGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The NodeId of the CertificateType for the Certificate. If null the CertificateManager shall select a Certificate based on the value of the certificateGroupId argument. |
|
updateRequired |
TRUE if the Application has to request a new Certificate from the GDS. FALSE if the Application can keep using the existing Certificate. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId does not refer to a registered Application. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateGroupId or certificateTypeId parameter is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 82 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetCertificateStatus Method.
Table 82 – GetCertificateStatus Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:GetCertificateStatus |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
CheckRevocationStatus Method is used to check the revocation status of an Certificate.
Clients or Servers may use this Method if the issuer Certificate has a crlDistributionPoint extension, an authorityInformationAccess extension (see RFC 6960) or the TrustList is configured to require online Certificate revocation checks (see 7.8.2.1).
The CertificateManager will typically use a protocol such as OCSP (see RFC 6960) to verify the Certificate status using the endpoint in the CDP extension, however, it may also optimize performance by maintaining a cache of recently verified Certificate and/or maintaining its own offline CRLs. The validityTime parameter provides guidance on how long a result can be kept in a local cache.
The caller shall perform all validation checks other than the revocation status check (see OPC 10000-4) on the Certificate before calling this Method. The CertificateManager shall check the Signature on the Certificate and may do additional validation.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel.
Signature
CheckRevocationStatus (
[in] ByteString certificate
[out] StatusCode certificateStatus
[out] UtcTime validityTime
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
INPUTS |
|
|
certificate |
The DER encoded form of the Certificate to check. |
|
OUTPUTS |
|
|
certificateStatus |
The first error encountered when validating the Certificate. |
|
validityTime |
When the result expires and should be rechecked. DateTime.MinValue is this is unknown. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 83 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CheckRevocationStatus Method.
Table 83 – CheckRevocationStatus Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
2:CheckRevocationStatus |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager CheckRevocationStatus |
|||||
This event is raised when a new certificate request has been accepted or rejected by the CertificateManager.
This can be the result of a StartNewKeyPairRequest or StartSigningRequest Method calls.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 84.
Table 84 – CertificateRequestedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
2:CertificateRequestedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:CertificateGroup |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:CertificateType |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The CertificateGroup Property specifies the CertificateGroup that was affected by the update.
The CertificateType Property specifies the type of Certificate that was updated.
This event is raised when a certificate is delivered by the CertificateManager to a Client.
This is the result of a FinishRequest Method completing successfully.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 85.
Table 85 – CertificateDeliveredAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
2:CertificateDeliveredAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:CertificateGroup |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:CertificateType |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The CertificateGroup Property specifies the CertificateGroup that was affected by the update.
The CertificateType Property specifies the type of Certificate that was updated.
This event is raised when a certificate is revoked by the CertificateManager.
This is the result of a RevokeCertificate Method completing successfully.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 86.
Table 86 – CertificateRevokedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
2:CertificateRevokedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
GDS Certificate Manager Pull Model |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
If a Server supports PushManagement it is required to support an information model as part of its AddressSpace. It shall support the ServerConfiguration Object shown in Figure 23.
Figure 23 – The AddressSpace for the Server that supports Push Management
The ServerConfiguration Object is used to manage the Server. The ManagedApplications Folder collects ApplicationConfiguration Objects for other applications which the Server is able to manage. For example, a Server may have associated Client applications that do not support PushManagement so the Server can become a proxy for these Clients.
The CertificateGroups and TrustLists used by a Server may be updated as part of a transaction where multiple Methods are invoked, however, no changes will have any effect until ApplyChanges is called (see 7.10.9). These transactions are created automatically and the Server returns applyChangesRequired =TRUE in a Method response to tell the Client that a transaction is active. Servers that do not support transactions return applyChangesRequired =FALSE and apply any changes before returning a Method response.
If a Method called within a transaction fails (e.g. a parameter was invalid) the transaction state shall not change and all previous changes are applied when ApplyChanges is called.
Once a transaction is created, a Server shall queue the changes in the order that they were requested within the current Session. When ApplyChanges is called the Server verifies that all the changes are consistent and can be applied without errors. If any errors are found then all changes are discarded. If no errors are found, the Server applies all changes.
Using the ApplicationConfigurationFileType to update the configuration blocks the creation of new transactions. Methods that would normally create a new transaction shall return Bad_TransactionPending if a configuration update via a file is in progress (see 7.10.20).
If errors occur, they are reported in the TransactionDiagnostics Object (see 7.10.3).
The life cycle of a transaction is shown in Figure 24.
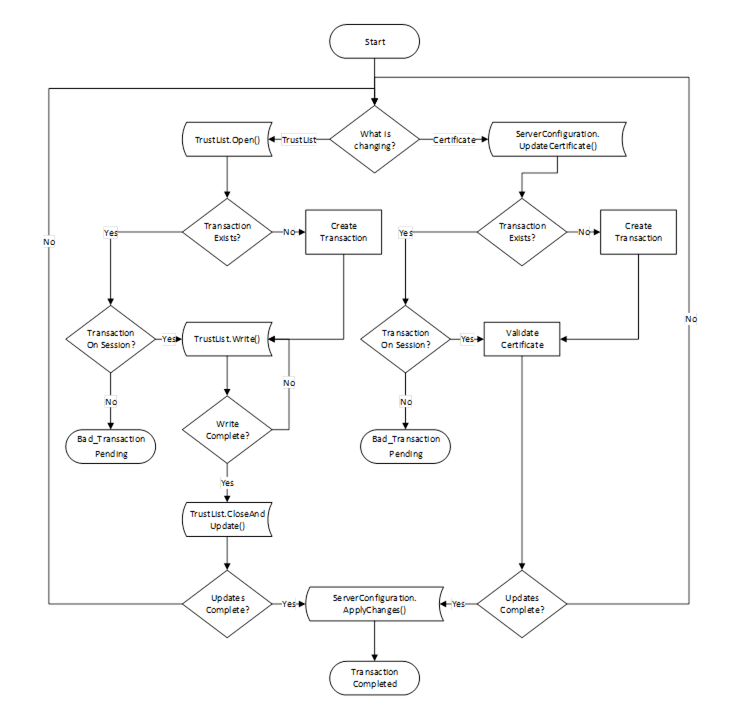
Figure 24 – The Transaction Lifecycle when using PushManagement
Servers that implement the transaction model shall support the CancelChanges Method and always set applyChangesRequired to TRUE.
Servers that support the transaction model are expected to support exactly one active transaction. Once a transaction has started in Session all other Sessions will not be able to modify TrustLists or Certificates. Transactions are automatically cancelled when the Session that created it is closed or when the CancelChanges Method is called.
If the transaction model is not supported and applyChangesRequired is TRUE then the behaviour of the Server for multiple changes is undefined.
If applyChangesRequired is FALSE then any changes are applied before the Method response is sent.
This type defines a concrete ObjectType which represents the configuration of the local Server that supports PushManagement. The ServerConfiguration Object (see 7.10.4) is the single instance of this Object that appears in the Server AddressSpace.
Its components are defined in Table 87.
Table 87 –ServerConfigurationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerConfigurationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ProductUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationType |
0:ApplicationType |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationNames |
0:LocalizedText[] |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ServerCapabilities |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SupportedPrivateKeyFormats |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxTrustListSize |
0:UInt32 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MulticastDnsEnabled |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:HasSecureElement |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SupportsTransactions |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InApplicationSetup |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:UpdateCertificate |
See 7.10.5. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
See 7.10.6. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:DeleteCertificate |
See 7.10.7. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:GetCertificates |
See 7.10.8. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:ApplyChanges |
See 7.10.9. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CancelChanges |
See 7.10.11. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CreateSigningRequest |
See 7.10.10. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:GetRejectedList |
See 7.10.12. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:ResetToServerDefaults |
See 7.10.13. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:CertificateGroups |
|
0:CertificateGroupFolderType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:TransactionDiagnostics |
|
0:TransactionDiagnosticsType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:ConfigurationFile |
|
0:ApplicationConfigurationFileType |
Optional |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
The ApplicationUri Property specifies the ApplicationUri assigned to the application.
The ProductUri Property specifies the ProductUri for the application that appears in the ApplicationDescription.
The ApplicationType Property specifies whether the Application is a Client, a Server or both. Applications which do not support OPC UA specify an ApplicationType of Client. Note that non-OPC UA applications often have network endpoints, however, from the perspective of the CertificateManager, the applications are not Servers.
The ApplicationNames Property is a list of localized names for the application that may be used to when registering with a GDS.
The ServerCapabilities Property specifies the capabilities from Annex D which the Server supports. The value is the same as the value reported to the LocalDiscoveryServer when the Server calls the RegisterServer2 Service.
The SupportedPrivateKeyFormats specifies the PrivateKey formats supported by the Server. Possible values include “PEM” (see RFC 5958), “PFX” (see PKCS #12) or “PKCS8” (see PKCS #8). The array is empty if the Server does not allow external Clients to update the PrivateKey.
The MaxTrustListSize is the maximum size of the TrustList in bytes. 0 means no limit. The default is 65 535 bytes.
If MulticastDnsEnabled is TRUE then the application announces itself using multicast DNS. It can be changed by writing to the Variable.
If HasSecureElement is TRUE then the application has access to hardware based secure storage for the PrivateKeys associated with its Certificates.
If the SupportsTransactions Property is TRUE, the Server supports the transaction lifecyle defined in 7.10.2. If it is FALSE or not present, the Server only supports delaying application of changes until ApplyChanges is called.
If the InApplicationSetup Property is TRUE then the application is in the application setup state described in G.2.
The UpdateCertificate Method is used to update a Certificate.
The CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method creates a new self-signed Certificate assigned to a CertificateType in a CertificateGroup.
The DeleteCertificate Method deletes Certificate that is currently assigned to a CertificateType in a CertificateGroup.
The GetCertificates Method returns the Certificates assigned to each of the CertificateTypes in a CertificateGroup.
The ApplyChanges Method is used complete changes made to CertificateGroups and/or TrustLists within the context of a transaction.
The CancelChanges Method is used to cancel an existing transaction.
The CreateSigningRequest Method asks the Server to create a PKCS #10 encoded Certificate Request that is signed with the Server’s private key.
The GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates which have been rejected by the Server. It can be used to track activity or allow administrators to move a rejected Certificate into the TrustList. This Method is the a shortcut for the GetRejectedList Method (see 7.8.3.2) on the DefaultApplicationGroup CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.3).
The ResetToServerDefaults Method is used reset the application security configuration to a default state.
The CertificateGroups Object organizes the CertificateGroups supported by the application. It is described in 7.8.4.10. All applications shall support the DefaultApplicationGroup and may support the DefaultHttpsGroup or the DefaultUserTokenGroup. Applications may support additional CertificateGroups depending on their requirements. For example, a Server with two network interfaces should have a different TrustList for each interface. The second TrustList would be represented as a new CertificateGroupType Object organized by CertificateGroups Folder.
The TransactionDiagnostics Object reports detailed error information for the current or most recently completed transaction. The TransactionDiagnostics Object is only visible to Clients with access to the SecurityAdmin Role.
The ConfigurationFile Object allows the current configuration to be read and updated.
This Object allows access to the Server’s configuration and it is the target of an HasComponent reference from the Server Object defined in OPC 10000-5.
This Object and its immediate children shall be visible (i.e. browse access is available) to users who can access the Server Object. The children of the CertificateGroups Object should only be visible to Clients with access to the SecurityAdmin Role.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 88.
Table 88 – ServerConfiguration Object Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerConfiguration |
||||
|
TypeDefinition |
0:ServerConfigurationType defined in 7.10.3. |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
UpdateCertificate is used to update a Certificate.
There are the following two use cases for this Method:
- The PrivateKey is already known to the Server (i.e. it was created with the CreateSigningRequest (see 7.10.10) or CreateSelfSignedCertificate (see 7.10.6) Method).
- The PrivateKey was created outside the Server and is updated with this Method.
The Server shall follow the validation process defined in OPC 10000-4 on the Certificate and all of the issuer Certificates. Note that the validation process requires that the TrustList associated with the CertificateGroup already contain the Issuer Certificates and any CRLs or that the issuers support online CRL checks. This Method may be called within the context of an ApplicationConfiguration Object (see 7.10.14) which means the Certificate may be used by a Client or a non-OPC UA application. Not all of the steps in the validation process will apply.
The Server shall report an error if the PublicKey does not match the existing Certificate and the PrivateKey was not provided.
If the Server returns applyChangesRequired =FALSE then it is indicating that it is able to satisfy the requirements specified for the ApplyChanges Method.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
UpdateCertificate(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] ByteString certificate
[in] ByteString[] issuerCertificates
[in] String privateKeyFormat
[in] ByteString privateKey
[out] Boolean applyChangesRequired
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup Object which is affected by the update. If null the DefaultApplicationGroup is used. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The type of Certificate being updated. The set of permitted types is specified by the CertificateTypes Property belonging to the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded Certificate which replaces the existing Certificate. |
|
issuerCertificates |
The issuer Certificates required to verify the signature on the new Certificate. |
|
privateKeyFormat |
The format of the Private Key (PKCS #12 encoded and PKCS #8 Base64 encoded DER (see RFC 5958) ). If the privateKey is not specified the privateKeyFormat is null or empty. |
|
privateKey |
The Private Key encoded in the privateKeyFormat. |
|
applyChangesRequired |
Indicates that the ApplyChanges Method shall be called before the new Certificate will be used. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateTypeId or certificateGroupId is not valid. |
|
Bad_CertificateInvalid |
The Certificate is invalid or the format is not supported. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
The PrivateKey is invalid or the format is not supported. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityChecksFailed |
Some failure occurred verifying the integrity of the Certificate. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 89 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the UpdateCertificate Method.
Table 89 – UpdateCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:UpdateCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method creates a new self-signed Certificate and associates it with a CertificateGroup.
This Method allows an administration Client to create a Certificate used by the Server. The Purpose of the CertificateGroup specifies what the Certificate is used for. For example, a CertificateGroup that contains ApplicationInstance Certificates would only contain Certificates that are valid ApplicationInstance Certificates as defined in OPC 10000-6.The new Certificate shall be an instance of the certificateTypeId.
If a Certificate is already assigned to the CertificateType slot then a Bad_InvalidState error is returned.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending. If the SecureChannel is not authenticated the Server shall return Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient.
The Server shall continue an existing transaction or create a new transaction if an existing transaction does not exist.
The Server may use an existing PrivateKey or create a new PrivateKey. If a Server cannot generate PrivateKeys for the specified CertificateType then the Server shall return Bad_NotSupported.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CreateSelfSignedCertificate (
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] String subjectName
[in] String[] dnsNames
[in] String[] ipAddresses
[in] UInt16 lifetimeInDays
[in] UInt16 keySizeInBits
[out] ByteString certificate
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The CertificateType that the new Certificate is assigned to. |
|
subjectName |
The subjectName to use with the Certificate. For HttpsCertificateTypes the subjectName shall be specified and have the dnsName or IP Address as the common name. For ApplicationCertificateTypes the subjectName may be omitted and the Server creates a suitable default based on the Server’s ApplicationIdentity (see 7.10.21) |
|
dnsNames |
The list of DNS names that appear in the subjectAltName. There shall be at least one entry in dnsName or IP address lists. |
|
ipAddresses |
The list of IP Addresses that appear in the subjectAltName. There shall be at least one entry in dnsName or IP address lists. |
|
lifetimeInDays |
The lifetime of the Certificate in days. The validity period shall begin 1 day prior to calling this Method. |
|
keySizeInBits |
The size of the PublicKey and PrivateKey in bits. The certificateTypeId limits the values that may be set. A value of 0 indicates that a suitable default value is used. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded form of the Certificate created by the Server. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
There is already a Certificate assigned to the CertificateType slot. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
A Certificate cannot be created that matches the parameters provided. |
|
Bad_OutOfRange |
The keySizeInBits is not supported. |
Table 42 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method.
Table 90 – CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
|||||
DeleteCertificate Method a Certificate that is associated with a CertificateGroup.
If no Certificate is assigned to the CertificateType slot then a Bad_InvalidState error is returned.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending. If the SecureChannel is not authenticated the Server shall return Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient.
The Server shall continue an existing transaction or create a new transaction if a transaction does not exist.
Certificates that are referenced by EndpointDescriptions shall not be deleted. This determination happens when ApplyChanges is called. ApplyChanges is always required when this Method is called.
The Server is responsible for managing the lifetime of the PrivateKeys associated with the Certificate. When the Certificate is deleted, the Server should delete the associated PrivateKey if no longer needed.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
DeleteCertificate(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The CertificateType for the Certificate to be deleted. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
There is no Certificate assigned to the CertificateType slot. |
Table 42 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the DeleteCertificate Method.
Table 91 – DeleteCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:DeleteCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration DeleteCertificate |
|||||
GetCertificates returns the Certificates assigned to CertificateTypes associated with a CertificateGroup.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
GetCertificates(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[out] NodeId[] certificateTypeIds
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeIds |
The CertificateTypes that currently have a Certificate assigned. The length of this list is the same as the length as certificates list. An empty list if the CertificateGroup does not have any CertificateTypes. |
|
certificates |
A list of DER encoded Certificates assigned to CertificateGroup. The certificateType for the Certificate is specified by the corresponding element in the certificateTypes parameter. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateGroupId is not valid. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 92 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetCertificates Method.
Table 92 – GetCertificates Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:GetCertificates |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration GetCertificates |
|||||
ApplyChanges is used to apply pending Certificate and TrustList updates and to complete a transaction as described in 7.10.2.
ApplyChanges returns Bad_InvalidState if any TrustList is still open for writing. No changes are applied and ApplyChanges can be called again after the TrustList is closed.
If a Session is closed or abandoned then the transaction is closed and all pending changes are discarded.
If ApplyChanges is called and there is no active transaction then the Server returns Bad_NothingToDo. If there is an active transaction, however, no changes are pending the result is Good and the transaction is closed.
When a Server Certificate or TrustList changes active SecureChannels are not immediately affected. This ensures the caller of ApplyChanges can get a response to the Method call. Once the Method response is returned the Server shall force existing SecureChannels affected by the changes to renegotiate and use the new Server Certificate and/or TrustLists.
Servers may close SecureChannels without discarding any Sessions or Subscriptions. This will seem like a network interruption from the perspective of the Client and the Client reconnect logic (see OPC 10000-4) allows them to recover their Session and Subscriptions. Note that some Clients may not be able to reconnect because they are no longer trusted.
Other Servers do a complete shutdown. In this case, the Server shall advertise its intent to interrupt connections by setting the SecondsTillShutdown and ShutdownReason Properties in the ServerStatus Variable.
If a TrustList change only affects UserIdentity associated with a Session then Servers shall re-evaluate the UserIdentity and if it is no longer valid the Session and associated Subscriptions are closed.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from the Session that created the transaction and has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
ApplyChanges();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
There is no active transaction. |
|
Bad_BadSessionIdInvalid |
The session is not valid for the active transaction. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
TrustList(s) are open for writing and changes cannot be applied. |
Table 93 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ApplyChanges Method.
Table 93 – ApplyChanges Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplyChanges |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
|
CreateSigningRequest Method asks the Server to create a PKCS #10 DER encoded Certificate Request that is signed with the Server’s private key. The Certificate Request can be then used to request a Certificate from a CA.
Servers shall support a least one active and one new key pair for each combination of certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId. If this Method is called multiple times with the same certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId then any previously generated new key pair, that has not been made active, is discarded. If a key pair is made active by a call to UpdateCertificate then the previously active key pair is deleted if it is no longer used.
If Certificate associated with the certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId is deleted or replaced via CreateSelfSignedCertificate (see 7.10.6) or DeleteCertificate (see 7.10.7) then the new key pair is discarded.
The new key pair created with CreateSigningRequest shall be persisted and shall be available for UpdateCertificate even if it is called from a different Session.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CreateSigningRequest(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] String subjectName
[in] Boolean regeneratePrivateKey
[in] ByteString nonce
[out] ByteString certificateRequest
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup Object which is affected by the request. If null the DefaultApplicationGroup is used. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The type of Certificate being requested. The set of permitted types is specified by the CertificateTypes Property belonging to the CertificateGroup. |
|
subjectName |
The subject name to use in the Certificate Request. If not specified the SubjectName from the current Certificate is used. The format of the subjectName is defined in 7.9.4. |
|
regeneratePrivateKey |
If TRUE the Server shall create a new Private Key which it stores until the matching signed Certificate is uploaded with the UpdateCertificate Method. Previously created Private Keys may be discarded if UpdateCertificate was not called before calling this method again. If FALSE the Server uses its existing Private Key. |
|
nonce |
Additional entropy which the caller shall provide if regeneratePrivateKey is TRUE. It shall be at least 32 bytes long. |
|
certificateRequest |
The PKCS #10 DER encoded Certificate Request. If the CertificateRequest is for an ApplicationInstance Certificate then it shall include all fields required by OPC 10000-6 such as the subjectAltName. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more of the certificateTypeId, certificateGroupId, nonce, or subjectName paremeters is not valid. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 94 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CreateSigningRequest Method.
Table 94 – CreateSigningRequest Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CreateSigningRequest |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
CancelChanges is used to tell the Server to discard changes to the TrustLists or Certificates which were waiting for the Client to ApplyChanges.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from the Session that created the transaction and has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CancelChanges();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 93 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CancelChanges Method.
Table 95 – CancelChanges Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:CancelChanges |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server ServerConfiguration Transactions |
|
GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates that have been rejected by the Server.
No rules are defined for how the Server updates this list or how long a Certificate is kept in the list. It is recommended that every valid but untrusted Certificate be added to the rejected list as long as storage is available. Servers should omit older entries from the list returned if the maximum message size is not large enough to allow the entire list to be returned.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
GetRejectedList(
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificates |
The DER encoded form of the Certificates rejected by the Server. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 96 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetRejectedList Method.
Table 96 – GetRejectedList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:GetRejectedList |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The ResetToServerDefaults Method resets an application configuration to its default settings.
If the application is running on a Device that supports OPC 10000-21, the Device is placed in a state where the Onboarding process has to restart. If the Device does not support OPC 10000-21, the Server repeats the Application Setup process described in Annex G.
If the application is a Server, after this Method completes the Server shall set the ServerState to SHUTDOWN and the shutdownReason to a localized message that warns Clients that their credentials may not work when the Server restarts. The Server should set the secondsTillShutdown to a time that gives the Client a chance to receive the response to this Method.
Note that the default configuration for a application is set by configuration and is not necessarily the “factory default”. For example, a machine builder could update the default configuration to ensure that the application can still communicate with other applications within the machine after the reset.
The mechanisms for setting the default configuration are vendor specific.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
ResetToServerDefaults ();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 97 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ResetToServerDefaults Method.
Table 97 – ResetToServerDefaults Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:ResetToServerDefaults |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server ServerConfiguration ResetToServerDefaults |
|
The ApplicationConfigurationType ObjectType defines a model which represents the configuration of another application. A Server acting as a proxy will add the Objects that represent the application it manages to the ManagedApplications Object (see 7.10.16).
Table 98 – ApplicationConfigurationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the ServerConfigurationType defined in 7.10.3. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Enabled |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ProductUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationType |
0:ApplicationType |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:IsNonUaApplication |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:KeyCredentials |
|
0:KeyCredentialConfigurationFolderType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:AuthorizationServices |
|
0:AuthorizationServicesConfigurationFolderType |
Optional |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
The Enabled Property indicates whether the application is enabled. If FALSE the application will not run. If TRUE the Application runs.
The KeyCredentials Folder that contains credentials assigned to the application. It is described in 8.6.
The AuthorizationServices Folder contains the AuthorizationServiceConfiguration Objects which the application supports. It is described in 9.7.
If ApplicationType is Client then the ApplicationsNames Property shall not be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be “NA” or “RCP”.
If ApplicationType is Server or ClientAndServer then the ApplicationsNames Property shall be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be set”.
If ApplicationType is DiscoveryServer then the ApplicationsNames Property shall not be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be “LDS”.
For NonUaApplications, the ApplicationType shall be Client, the ApplicationsNames shall not be present, the ServerCapabilities shall be “NA” and MulticastDnsEnabled shall be FALSE.
The IsNonUaApplication Property indicates that the application is a NonUaApplication.
Additional requirements for some components inherited from ServerConfigurationType are specified in Table 99.
Table 99 – ApplicationConfigurationType Component Requirements
|
Component |
OPC UA Client |
OPC UA Server |
LDS |
NonUaApplication |
|
0:ApplicationUri |
Required |
Required |
Required |
Optional. The syntax and conventions for the URI may not conform to the requirements for OPC UA ApplicationUris. |
|
0:ApplicationType |
“Client” |
“Server“ or “ClientAndServer“ |
“DiscoveryServer“ |
“Client“ |
|
0:IsNonUaApplication |
Omitted or FALSE |
Omitted or FALSE |
Omitted or FALSE |
TRUE |
|
0:ApplicationNames |
Omitted |
Required |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:ServerCapabilities |
“NA” or “RCP” |
Required |
“LDS” |
“NA” |
|
0:MulticastDnsEnabled |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“FALSE” |
|
0:AuthorizationServices |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:KeyCredentials |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:InApplicationSetup |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Optional |
The application may require software updates. In this case, the software update model described in OPC 10000-100 specifies an instance of the SoftwareUpdateType that may be added to the ApplicationConfiguration instance.
A Folder for ApplicationConfiguration Objects which a Server exposes in its AddressSpace.
Table 100 – ApplicationConfigurationFolderType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFolderType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:Organizes |
Object |
0:<ApplicationName> |
|
0:ApplicationConfigurationType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
This Object allows access to the application configurations and it is the target of an Organizes reference from the Resources Object defined in OPC 10000-22.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 101.
Table 101 – ManagedApplications Object Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ManagedApplications |
||||
|
TypeDefinition |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFolderType defined in 7.10.15. |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
This type defines an ObjectType which represents the diagnostics for the last transaction (see 7.10.1. If no transaction has started the values of all Variables have a status of Bad_OutOfService. All existing results are discarded when a new transaction starts.
Table 102 – TransactionDiagnosticsType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TransactionDiagnosticsType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:StartTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:EndTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Result |
0:StatusCode |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AffectedTrustLists |
0:NodeId [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AffectedCertificateGroups |
0:NodeId [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Errors |
0:TransactionErrorType [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
|||||
The StartTime Property indicates when transaction started. It has a status of Bad_OutOfService if a transaction has not started
The EndTime Property indicates when transaction ended. It has a value of DateTime.MinValue if the transaction has not completed.
The Result Property indicates the overall transaction result. It has a status of Bad_InvalidState if a transaction has started but not completed. If the transaction has completed the status is Good and the value is the StatusCode that was returned from the ApplyChanges Method. If the CancelChanges Method was called the value is Bad_RequestCancelledByClient.
The AffectedTrustLists Property specifies the NodeIds of the TrustLists that are included in the transaction. It is updated each time as soon as a TrustList is added to the transaction.
The AffectedCertificateGroups Property specifies the NodeIds of the CertificateGroups are included in the transaction. It is updated each time as soon as a CertificateGroup is added to the transaction.The Errors Property has a list of errors that occurred when the changes were applied. Empty if no errors occurred. The TransactionErrorType is defined in 7.10.18.
This type defines a DataType which stores an error that occurred when processing a transaction. Its values are defined in Table 103.
Table 103 – TransactionErrorType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TransactionErrorType |
Structure |
Subtype of the Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|
targetId |
NodeId |
The NodeId of the Object that had the error. It is either a TrustListId or a CertificateGroupId. |
|
error |
StatusCode |
The code describing the error. |
|
message |
LocalizedText |
A description of the error. It should include enough information to allow the Client to understand which Certificate(s) and/or CRL(s) are the source of the problem. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 104.
Table 104 – TransactionErrorType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TransactionErrorType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
||||||
This is the DataType used to serialize application configurations. It is defined in Table 105.
The fields that are used depend on the ApplicationType.
Each ServerEndpoint has a unique combination of NetworkName and Port. Each ClientEndpoint has a unique combination of NetworkName and Port.
At least one CertificateGroup linked to a ServerEndpoint (see 7.10.23) shall have a CertificateType slot compatible with the Server Certificate used for the current Session. If no such slot exists the configuration update is rejected. The TrustList associated with that CertificateGroup shall trust the Client Certificate used for the current Session.
Updates to the configuration are applied in the following order:
- ApplicationIdentity
- CertificateGroups
- UserTokenSettings
- SecuritySettings
- ServerEndpoints
- ClientEndpoints
- AuthorizationServices
While processing a single record type updates are applied in the order they appear in the array.
Client shall put updates in this order: Delete => Insert => Replace.
For Insert/Replace operations, a record name shall never appear more than once.
References to other records by name are only verified after all records have been processed.
Table 105 – ApplicationConfigurationDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ApplicationConfigurationDataType |
Structure |
|
|
ApplicationIdentity |
0:ApplicationIdentityDataType |
The application identity used to create new Certificates. |
|
CertificateGroups |
0:CertificateGroupDataType [] |
The list CertificateGroups. |
|
ServerEndpoints |
0:ServerEndpointDataType [] |
A list of Server Endpoints. Not specified for Clients. |
|
ClientEndpoints |
0:EndpointDataType [] |
A list of Client Endpoints which allow reverse connections. Not specified for Servers. |
|
SecuritySettings |
0:SecuritySettingsDataType [] |
A list of security settings. Not specified for Clients. |
|
UserTokenSettings |
0:UserTokenSettingsDataType [] |
A list of settings for UserTokenPolicies. Not specified for Clients. |
|
AuthorizationServices |
0:AuthorizationServiceConfigurationDataType [] |
List of AuthorizationServices supported by a Server. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 106.
Table 106 – ApplicationConfigurationDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationDataType DataType defined in 7.8.5.4 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Application Configuration Management |
||||||
A File Object that supports the reading and writing of an ApplicationConfiguration defined in 7.10.19.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending if Open is called with Write Mode bit set.
Open is called with Write Mode bit set then new transactions (see 7.10.2) cannot be started. The block on new transactions lasts until the update was applied or rolled back. This may occur when ConfirmUpdate is called.
Methods that update the configuration shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Table 107 – ApplicationConfigurationFileType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFileType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the ConfigurationFileType defined in 7.8.5.1. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AvailableNetworks |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AvailablePorts |
0:NumericRange |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxEndpoints |
0:UInt16 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxCertificateGroups |
0:UInt16 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SecurityPolicyUris |
0:UriString[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:UserTokenTypes |
0:UserTokenPolicy[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateTypes |
0:NodeId[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateGroupPurposes |
0:NodeId[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
|||||
The AvailableNetworks Property specifies the valid values for NetworkName for an Endpoint (see 7.10.22).
The AvailablePorts Property the range of ports that may be specified for an Endpoint. If it is empty then all Ports are valid.
The SecurityPolicyUris Property is a list of URIs that may be used in a SecuritySettings (see 7.10.24). If empty then all URIs are supported.
The UserTokenTypes Property is the list of UserTokenTypes that may be used in a UserTokenSetting (see 7.10.24). If empty then all UserTokenTypes are supported. The PolicyId, IssuerEndpointUrl and SecurityPolicyUrl fields in the UserTokenPolicy Structure are not used and are always ignored. There may only be one combination of TokenType and IssuedTokenType in the list.
The CertificateTypes Property is a list of CertificateTypeIds that may be used in a CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.4). It shall have at least one element specified.
The CertificateGroupPurposes Property is a list of Purposes that may be used in a CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.4). It shall have at least one element specified.
The MaxEndpoints Property specifies the maximum total number of Endpoints (Client plus Server) that may be defined. 0 means no limit.
The MaxCertificateGroups Property specifies the maximum number of CertificateGroups that may be defined. 0 means no limit.
This type is used to serialize the ApplicationIdentity configuration. It is defined in Table 108.
The ApplicationIdentity affects Certificates, CertificateRequests and ApplicationDescriptions created by a Client or Server. When the ApplicationIdentity is changed, existing Certificates are not affected, however, they may no longer be valid for use by the application because the ApplicationUri does not match the ApplicationUri in the Certificate. Applications shall continue to use the invalid Certificates which allows the configuration Client, which is aware of the mismatch, to complete the process needed to update Certificates. The new ApplicationUri shall be used in any subsequent signing requests.
Table 108 – ApplicationIdentityDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ApplicationIdentityDataType |
Structure |
|
|
ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
The Uri that identifies the application. |
|
ApplicationNames |
0:LocalizedText[] |
The human readable names for the application in multiple locales. |
|
AdditionalServers |
0:ApplicationDescription[] |
The list of additional Servers returned by FindServers. This is typically used to provide information about other Servers in a redundant set. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 109.
Table 109 – ApplicationIdentityDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationIdentityDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize a single Endpoint configuration. It is defined in Table 110.
The DiscoveryUrls associated with the Endpoint. They are reported as part of the ApplicationDescription returned by FindServers (see OPC 10000-4) and by QueryApplications (6.5.10). If multiple Endpoints are specified the DiscoveryUrls from each Endpoint are collected into a single list with any duplicates removed. If this list is empty the Endpoint is not included in the ApplicationDescription returned by FindServers or QueryApplications.
The DiscoveryUrls returned to Clients includes one of the URLs in the DiscoveryUrls list based on the EndpointUrl filter provided in the FindServers Request. If the filter provided is not one of the DiscoveryUrls then the first entry in the DiscoveryUrls list is returned.
NetworkName and Port specify the information the application needs listen for incoming connections. Only one Endpoint may be specified for each combination of NetworkName and Port.
Table 110 – EndpointDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
EndpointDataType |
Structure |
|
|
DiscoveryUrls |
0:UriString[] |
The list of DiscoveryUrls. The domain portion of the URLs may include DNS names or IP addresses that the application cannot access because they are only resolvable on the other side of a NAT firewall. For this reason, the application shall not attempt to validate the domains or the ports. EndpointUrls that are used for reverse connect have the ‘rcp+’ prefix (see 6.5.5). |
|
NetworkName |
0:String |
The name of the network interface or the IP address the application should bind to when listening on these EndpointUrls. The default value is an empty String. In this case the application binds to all available IPs. The name is either one of the AvailableNetworks Property on the ApplicationConfigurationFile Object or a valid IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Port |
0:UInt16 |
The port to bind to when listening for incoming requests. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 111.
Table 111 – EndpointDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EndpointDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize a single Endpoint configuration for a Server. It is defined in Table 112.
The information in the Endpoint is used to generate a list of EndpointDescriptions that could be returned by the Server when GetEndpoints is called. The basic algorithm generates an EndpointDescription for each valid combination of SecurityPolicyUri, SecurityMode and Certificate (specified in the SecuritySettings). The EndpointDescription returned to Clients includes one of the URLs in the EndpointUrls list based on the EndpointUrl filter provided in the GetEndpoints Request. If the filter provided is not one of the EndpointUrls then the first entry in the EndpointUrls list is returned.
The complete set of EndpointDescriptions is built by repeating the process for all enabled Endpoints.
The UserTokenSettings array may specify a UserTokenPolicy with a SecurityPolicyUri. Any UserTokenSetting that is not valid for ServerCertificate associated with a generated EndpointDescription is rejected.
The Server chooses unique values for PolicyIds in UserTokenPolicies when building the EndpointDescriptions.
The ReverseConnectUrls are the URLs that the Server connects to and sends a ReverseHello. The EndpointDescriptions generated from the ServerEndpoint are available to Clients connecting via the socket.
Table 112 – ServerEndpointDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ServerEndpointDataType |
Structure |
|
|
EndpointUrls |
0:UriString[] |
The list of EndpointUrls that may be return ed in an EndpointDescription. |
|
SecuritySettingNames |
0:String[] |
The names of the SecuritySettings used to build the EndpointDescriptions. |
|
TransportProfileUri |
0:UriString |
The TransportProfileUri. |
|
UserTokenSettingNames |
0:String[] |
The names of the UserTokenSettings used to build the UserTokenPolicies that appear in the EndpointDescriptions. |
|
ReverseConnectUrls |
0:String[] |
A list of URLs that a Server connects to and waits for incoming Client connections. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 113.
Table 113 – ServerEndpointDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerEndpointDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:EndpointDataType defined in 7.10.22. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to specify the SecuritySettings for a Server Endpoint. It is defined in Table 114.
The CertificateGroup specifies one or more Certificates that are assigned to a Server. When generating EndpointDescriptions any SecurityPolicyUris (other than None) that are not valid for one of the Certificates associated with the CertificateGroup are ignored.
If a SecurityPolicyUri is valid for more than one Certificate in the CertificateGroup, then an EndpointDescription is generated for each Certificate.
EndpointDescriptions generated with a None SecurityMode only use the SecurityPolicyUris and the CertificateGroupName to restrict the SecurityPolicies that may be used in the UserTokenPolicies.
Table 114 – SecuritySettingsDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
SecuritySettingsDataType |
Structure |
|
|
SecurityModes |
0:MessageSecurityMode[] |
The list of SecurityModes. |
|
SecurityPolicyUris |
0:String[] |
The list of SecurityPolicyUris. |
|
CertificateGroupName |
0:String |
The name of the CertificateGroup in the CertificateGroups list. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 115.
Table 115 – SecuritySettingsDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:SecuritySettingsDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize the configuration for a UserTokenPolicy. It is defined in Table 116.
The UserTokenSettingsDataType in the is used to configure how to validate UserIdentityTokens.
If a CertificateGroup is specified it refers to the TrustList used to verify credentials by either verifying that an X509IdentityToken is trusted or by using a Certificate in the TrustList to verify the Signature on an IssuedIdentityToken. The CertificateGroup is not specified for UserName or Anonymous TokenTypes.
The KeyCredentialName is only specified for IssuedIdentityTokens and refers to a KeyCredential needed to access network resources used to validate IssuedIdentityTokens.
Table 116 – UserTokenSettingsDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
UserTokenSettingsDataType |
Structure |
|
|
TokenType |
0:UserTokenType |
The type of UserIdentityToken |
|
IssuedTokenType |
0:String |
A URI identifying the type of IssuedIdentityToken (i.e. JWT). |
|
IssuerEndpointUrl |
0:String |
An optional string which depends on the Authorization Service. The meaning of this value depends on the IssuedTokenType. Further details for the different Token types are defined in OPC 10000-6. |
|
SecurityPolicyUri |
0:String |
The SecurityPolicy to use when encrypting or signing the UserIdentityToken when it is passed to the Server in the ActivateSession request. For X509 UserIdentityTokens this value shall specify the SecurityPolicy that matches the Certificates that the Server will accept. For other UserIdentityTokens this value shall specify the SecurityPolicy to use when the SecureChannel uses SecurityPolicy = None. |
|
CertificateGroupName |
0:String |
The name of the corresponding entry in the CertificateGroups list of the ApplicationConfiguration. It contains the TrustList used to verify an X509IdentityToken. Only specified if the TokenType is an X509IdentityToken. |
|
AuthorizationServiceName |
0:String |
The name of the corresponding entry in the AuthorizationServices list of the ApplicationConfiguration. This is the AuthorizationService which issues tokens accepted by the Server. Only specified if the TokenType is an IssuedIdentityToken. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 117.
Table 117 – UserTokenSettingsDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:UserTokenSettingsDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This event is raised when the UpdateCertificate Method is called.
If a PrivateKey was one of the InputArguments then that argument is set to NULL before generating this Event.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 118.
Table 118 – CertificateUpdateRequestedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateUpdateRequestedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
This event is raised when a Certificate is actually changed as a result of a Method call.
This is the result of a successful call to UpdateCertificate or ApplyChanges on a ServerConfigurationType Object. No Event is raised if the Method call fails. If ApplyChanges affects multiple Certificates then this Event is raised for each changed Certificate.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 119.
Table 119 – CertificateUpdatedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateUpdatedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateGroup |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateType |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The SourceNode Property for Events of this type shall be assigned to the NodeId of the Object with the Method that triggered the Event.
The CertificateGroup Property specifies the CertificateGroup that was affected by the update.
The CertificateType Property specifies the type of Certificate that was updated.