If a Server supports PushManagement it is required to support an information model as part of its AddressSpace. It shall support the ServerConfiguration Object shown in Figure 23.
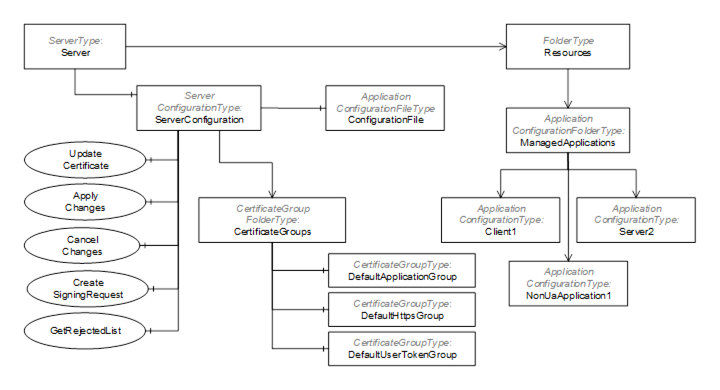
Figure 23 – The AddressSpace for the Server that supports Push Management
The ServerConfiguration Object is used to manage the Server. The ManagedApplications Folder collects ApplicationConfiguration Objects for other applications which the Server is able to manage. For example, a Server may have associated Client applications that do not support PushManagement so the Server can become a proxy for these Clients.
The CertificateGroups and TrustLists used by a Server may be updated as part of a transaction where multiple Methods are invoked, however, no changes will have any effect until ApplyChanges is called (see 7.10.9). These transactions are created automatically and the Server returns applyChangesRequired =TRUE in a Method response to tell the Client that a transaction is active. Servers that do not support transactions return applyChangesRequired =FALSE and apply any changes before returning a Method response.
If a Method called within a transaction fails (e.g. a parameter was invalid) the transaction state shall not change and all previous changes are applied when ApplyChanges is called.
Once a transaction is created, a Server shall queue the changes in the order that they were requested within the current Session. When ApplyChanges is called the Server verifies that all the changes are consistent and can be applied without errors. If any errors are found then all changes are discarded. If no errors are found, the Server applies all changes.
Using the ApplicationConfigurationFileType to update the configuration blocks the creation of new transactions. Methods that would normally create a new transaction shall return Bad_TransactionPending if a configuration update via a file is in progress (see 7.10.20).
If errors occur, they are reported in the TransactionDiagnostics Object (see 7.10.3).
The life cycle of a transaction is shown in Figure 24.
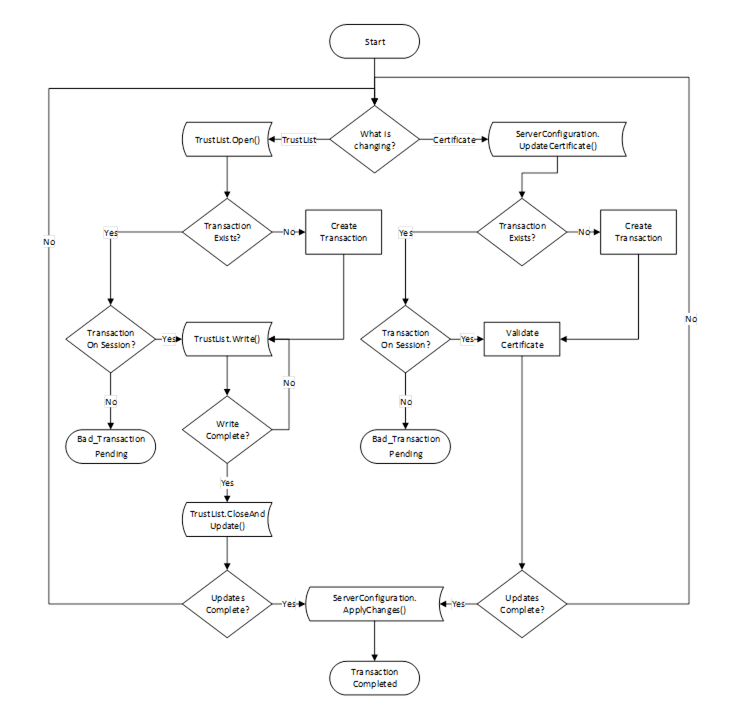
Figure 24 – The Transaction Lifecycle when using PushManagement
Servers that implement the transaction model shall support the CancelChanges Method and always set applyChangesRequired to TRUE.
Servers that support the transaction model are expected to support exactly one active transaction. Once a transaction has started in Session all other Sessions will not be able to modify TrustLists or Certificates. Transactions are automatically cancelled when the Session that created it is closed or when the CancelChanges Method is called.
If the transaction model is not supported and applyChangesRequired is TRUE then the behaviour of the Server for multiple changes is undefined.
If applyChangesRequired is FALSE then any changes are applied before the Method response is sent.
This type defines a concrete ObjectType which represents the configuration of the local Server that supports PushManagement. The ServerConfiguration Object (see 7.10.4) is the single instance of this Object that appears in the Server AddressSpace.
Its components are defined in Table 87.
Table 87 –ServerConfigurationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerConfigurationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ProductUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationType |
0:ApplicationType |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationNames |
0:LocalizedText[] |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ServerCapabilities |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SupportedPrivateKeyFormats |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxTrustListSize |
0:UInt32 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MulticastDnsEnabled |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:HasSecureElement |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SupportsTransactions |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InApplicationSetup |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:UpdateCertificate |
See 7.10.5. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
See 7.10.6. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:DeleteCertificate |
See 7.10.7. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:GetCertificates |
See 7.10.8. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:ApplyChanges |
See 7.10.9. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CancelChanges |
See 7.10.11. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:CreateSigningRequest |
See 7.10.10. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:GetRejectedList |
See 7.10.12. |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
0:ResetToServerDefaults |
See 7.10.13. |
Optional |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:CertificateGroups |
|
0:CertificateGroupFolderType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:TransactionDiagnostics |
|
0:TransactionDiagnosticsType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:ConfigurationFile |
|
0:ApplicationConfigurationFileType |
Optional |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
The ApplicationUri Property specifies the ApplicationUri assigned to the application.
The ProductUri Property specifies the ProductUri for the application that appears in the ApplicationDescription.
The ApplicationType Property specifies whether the Application is a Client, a Server or both. Applications which do not support OPC UA specify an ApplicationType of Client. Note that non-OPC UA applications often have network endpoints, however, from the perspective of the CertificateManager, the applications are not Servers.
The ApplicationNames Property is a list of localized names for the application that may be used to when registering with a GDS.
The ServerCapabilities Property specifies the capabilities from Annex D which the Server supports. The value is the same as the value reported to the LocalDiscoveryServer when the Server calls the RegisterServer2 Service.
The SupportedPrivateKeyFormats specifies the PrivateKey formats supported by the Server. Possible values include “PEM” (see RFC 5958), “PFX” (see PKCS #12) or “PKCS8” (see PKCS #8). The array is empty if the Server does not allow external Clients to update the PrivateKey.
The MaxTrustListSize is the maximum size of the TrustList in bytes. 0 means no limit. The default is 65 535 bytes.
If MulticastDnsEnabled is TRUE then the application announces itself using multicast DNS. It can be changed by writing to the Variable.
If HasSecureElement is TRUE then the application has access to hardware based secure storage for the PrivateKeys associated with its Certificates.
If the SupportsTransactions Property is TRUE, the Server supports the transaction lifecyle defined in 7.10.2. If it is FALSE or not present, the Server only supports delaying application of changes until ApplyChanges is called.
If the InApplicationSetup Property is TRUE then the application is in the application setup state described in G.2.
The UpdateCertificate Method is used to update a Certificate.
The CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method creates a new self-signed Certificate assigned to a CertificateType in a CertificateGroup.
The DeleteCertificate Method deletes Certificate that is currently assigned to a CertificateType in a CertificateGroup.
The GetCertificates Method returns the Certificates assigned to each of the CertificateTypes in a CertificateGroup.
The ApplyChanges Method is used complete changes made to CertificateGroups and/or TrustLists within the context of a transaction.
The CancelChanges Method is used to cancel an existing transaction.
The CreateSigningRequest Method asks the Server to create a PKCS #10 encoded Certificate Request that is signed with the Server’s private key.
The GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates which have been rejected by the Server. It can be used to track activity or allow administrators to move a rejected Certificate into the TrustList. This Method is the a shortcut for the GetRejectedList Method (see 7.8.3.2) on the DefaultApplicationGroup CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.3).
The ResetToServerDefaults Method is used reset the application security configuration to a default state.
The CertificateGroups Object organizes the CertificateGroups supported by the application. It is described in 7.8.4.10. All applications shall support the DefaultApplicationGroup and may support the DefaultHttpsGroup or the DefaultUserTokenGroup. Applications may support additional CertificateGroups depending on their requirements. For example, a Server with two network interfaces should have a different TrustList for each interface. The second TrustList would be represented as a new CertificateGroupType Object organized by CertificateGroups Folder.
The TransactionDiagnostics Object reports detailed error information for the current or most recently completed transaction. The TransactionDiagnostics Object is only visible to Clients with access to the SecurityAdmin Role.
The ConfigurationFile Object allows the current configuration to be read and updated.
This Object allows access to the Server’s configuration and it is the target of an HasComponent reference from the Server Object defined in OPC 10000-5.
This Object and its immediate children shall be visible (i.e. browse access is available) to users who can access the Server Object. The children of the CertificateGroups Object should only be visible to Clients with access to the SecurityAdmin Role.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 88.
Table 88 – ServerConfiguration Object Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerConfiguration |
||||
|
TypeDefinition |
0:ServerConfigurationType defined in 7.10.3. |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
|||||
UpdateCertificate is used to update a Certificate.
There are the following two use cases for this Method:
- The PrivateKey is already known to the Server (i.e. it was created with the CreateSigningRequest (see 7.10.10) or CreateSelfSignedCertificate (see 7.10.6) Method).
- The PrivateKey was created outside the Server and is updated with this Method.
The Server shall follow the validation process defined in OPC 10000-4 on the Certificate and all of the issuer Certificates. Note that the validation process requires that the TrustList associated with the CertificateGroup already contain the Issuer Certificates and any CRLs or that the issuers support online CRL checks. This Method may be called within the context of an ApplicationConfiguration Object (see 7.10.14) which means the Certificate may be used by a Client or a non-OPC UA application. Not all of the steps in the validation process will apply.
The Server shall report an error if the PublicKey does not match the existing Certificate and the PrivateKey was not provided.
If the Server returns applyChangesRequired =FALSE then it is indicating that it is able to satisfy the requirements specified for the ApplyChanges Method.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
UpdateCertificate(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] ByteString certificate
[in] ByteString[] issuerCertificates
[in] String privateKeyFormat
[in] ByteString privateKey
[out] Boolean applyChangesRequired
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup Object which is affected by the update. If null the DefaultApplicationGroup is used. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The type of Certificate being updated. The set of permitted types is specified by the CertificateTypes Property belonging to the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded Certificate which replaces the existing Certificate. |
|
issuerCertificates |
The issuer Certificates required to verify the signature on the new Certificate. |
|
privateKeyFormat |
The format of the Private Key (PKCS #12 encoded and PKCS #8 Base64 encoded DER (see RFC 5958) ). If the privateKey is not specified the privateKeyFormat is null or empty. |
|
privateKey |
The Private Key encoded in the privateKeyFormat. |
|
applyChangesRequired |
Indicates that the ApplyChanges Method shall be called before the new Certificate will be used. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateTypeId or certificateGroupId is not valid. |
|
Bad_CertificateInvalid |
The Certificate is invalid or the format is not supported. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
The PrivateKey is invalid or the format is not supported. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityChecksFailed |
Some failure occurred verifying the integrity of the Certificate. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 89 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the UpdateCertificate Method.
Table 89 – UpdateCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:UpdateCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method creates a new self-signed Certificate and associates it with a CertificateGroup.
This Method allows an administration Client to create a Certificate used by the Server. The Purpose of the CertificateGroup specifies what the Certificate is used for. For example, a CertificateGroup that contains ApplicationInstance Certificates would only contain Certificates that are valid ApplicationInstance Certificates as defined in OPC 10000-6.The new Certificate shall be an instance of the certificateTypeId.
If a Certificate is already assigned to the CertificateType slot then a Bad_InvalidState error is returned.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending. If the SecureChannel is not authenticated the Server shall return Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient.
The Server shall continue an existing transaction or create a new transaction if an existing transaction does not exist.
The Server may use an existing PrivateKey or create a new PrivateKey. If a Server cannot generate PrivateKeys for the specified CertificateType then the Server shall return Bad_NotSupported.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CreateSelfSignedCertificate (
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] String subjectName
[in] String[] dnsNames
[in] String[] ipAddresses
[in] UInt16 lifetimeInDays
[in] UInt16 keySizeInBits
[out] ByteString certificate
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The CertificateType that the new Certificate is assigned to. |
|
subjectName |
The subjectName to use with the Certificate. For HttpsCertificateTypes the subjectName shall be specified and have the dnsName or IP Address as the common name. For ApplicationCertificateTypes the subjectName may be omitted and the Server creates a suitable default based on the Server’s ApplicationIdentity (see 7.10.21) |
|
dnsNames |
The list of DNS names that appear in the subjectAltName. There shall be at least one entry in dnsName or IP address lists. |
|
ipAddresses |
The list of IP Addresses that appear in the subjectAltName. There shall be at least one entry in dnsName or IP address lists. |
|
lifetimeInDays |
The lifetime of the Certificate in days. The validity period shall begin 1 day prior to calling this Method. |
|
keySizeInBits |
The size of the PublicKey and PrivateKey in bits. The certificateTypeId limits the values that may be set. A value of 0 indicates that a suitable default value is used. |
|
certificate |
The DER encoded form of the Certificate created by the Server. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
There is already a Certificate assigned to the CertificateType slot. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
A Certificate cannot be created that matches the parameters provided. |
|
Bad_OutOfRange |
The keySizeInBits is not supported. |
Table 42 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method.
Table 90 – CreateSelfSignedCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration CreateSelfSignedCertificate |
|||||
DeleteCertificate Method a Certificate that is associated with a CertificateGroup.
If no Certificate is assigned to the CertificateType slot then a Bad_InvalidState error is returned.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending. If the SecureChannel is not authenticated the Server shall return Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient.
The Server shall continue an existing transaction or create a new transaction if a transaction does not exist.
Certificates that are referenced by EndpointDescriptions shall not be deleted. This determination happens when ApplyChanges is called. ApplyChanges is always required when this Method is called.
The Server is responsible for managing the lifetime of the PrivateKeys associated with the Certificate. When the Certificate is deleted, the Server should delete the associated PrivateKey if no longer needed.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
DeleteCertificate(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The CertificateType for the Certificate to be deleted. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
There is no Certificate assigned to the CertificateType slot. |
Table 42 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the DeleteCertificate Method.
Table 91 – DeleteCertificate Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:DeleteCertificate |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration DeleteCertificate |
|||||
GetCertificates returns the Certificates assigned to CertificateTypes associated with a CertificateGroup.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
GetCertificates(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[out] NodeId[] certificateTypeIds
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The identifier for the CertificateGroup. |
|
certificateTypeIds |
The CertificateTypes that currently have a Certificate assigned. The length of this list is the same as the length as certificates list. An empty list if the CertificateGroup does not have any CertificateTypes. |
|
certificates |
A list of DER encoded Certificates assigned to CertificateGroup. The certificateType for the Certificate is specified by the corresponding element in the certificateTypes parameter. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The certificateGroupId is not valid. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 92 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetCertificates Method.
Table 92 – GetCertificates Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:GetCertificates |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server ServerConfiguration GetCertificates |
|||||
ApplyChanges is used to apply pending Certificate and TrustList updates and to complete a transaction as described in 7.10.2.
ApplyChanges returns Bad_InvalidState if any TrustList is still open for writing. No changes are applied and ApplyChanges can be called again after the TrustList is closed.
If a Session is closed or abandoned then the transaction is closed and all pending changes are discarded.
If ApplyChanges is called and there is no active transaction then the Server returns Bad_NothingToDo. If there is an active transaction, however, no changes are pending the result is Good and the transaction is closed.
When a Server Certificate or TrustList changes active SecureChannels are not immediately affected. This ensures the caller of ApplyChanges can get a response to the Method call. Once the Method response is returned the Server shall force existing SecureChannels affected by the changes to renegotiate and use the new Server Certificate and/or TrustLists.
Servers may close SecureChannels without discarding any Sessions or Subscriptions. This will seem like a network interruption from the perspective of the Client and the Client reconnect logic (see OPC 10000-4) allows them to recover their Session and Subscriptions. Note that some Clients may not be able to reconnect because they are no longer trusted.
Other Servers do a complete shutdown. In this case, the Server shall advertise its intent to interrupt connections by setting the SecondsTillShutdown and ShutdownReason Properties in the ServerStatus Variable.
If a TrustList change only affects UserIdentity associated with a Session then Servers shall re-evaluate the UserIdentity and if it is no longer valid the Session and associated Subscriptions are closed.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from the Session that created the transaction and has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
ApplyChanges();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
There is no active transaction. |
|
Bad_BadSessionIdInvalid |
The session is not valid for the active transaction. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
TrustList(s) are open for writing and changes cannot be applied. |
Table 93 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ApplyChanges Method.
Table 93 – ApplyChanges Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplyChanges |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
|
CreateSigningRequest Method asks the Server to create a PKCS #10 DER encoded Certificate Request that is signed with the Server’s private key. The Certificate Request can be then used to request a Certificate from a CA.
Servers shall support a least one active and one new key pair for each combination of certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId. If this Method is called multiple times with the same certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId then any previously generated new key pair, that has not been made active, is discarded. If a key pair is made active by a call to UpdateCertificate then the previously active key pair is deleted if it is no longer used.
If Certificate associated with the certificateGroupId and certificateTypeId is deleted or replaced via CreateSelfSignedCertificate (see 7.10.6) or DeleteCertificate (see 7.10.7) then the new key pair is discarded.
The new key pair created with CreateSigningRequest shall be persisted and shall be available for UpdateCertificate even if it is called from a different Session.
This Method shall be called from an encrypted SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CreateSigningRequest(
[in] NodeId certificateGroupId
[in] NodeId certificateTypeId
[in] String subjectName
[in] Boolean regeneratePrivateKey
[in] ByteString nonce
[out] ByteString certificateRequest
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificateGroupId |
The NodeId of the CertificateGroup Object which is affected by the request. If null the DefaultApplicationGroup is used. |
|
certificateTypeId |
The type of Certificate being requested. The set of permitted types is specified by the CertificateTypes Property belonging to the CertificateGroup. |
|
subjectName |
The subject name to use in the Certificate Request. If not specified the SubjectName from the current Certificate is used. The format of the subjectName is defined in 7.9.4. |
|
regeneratePrivateKey |
If TRUE the Server shall create a new Private Key which it stores until the matching signed Certificate is uploaded with the UpdateCertificate Method. Previously created Private Keys may be discarded if UpdateCertificate was not called before calling this method again. If FALSE the Server uses its existing Private Key. |
|
nonce |
Additional entropy which the caller shall provide if regeneratePrivateKey is TRUE. It shall be at least 32 bytes long. |
|
certificateRequest |
The PKCS #10 DER encoded Certificate Request. If the CertificateRequest is for an ApplicationInstance Certificate then it shall include all fields required by OPC 10000-6 such as the subjectAltName. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more of the certificateTypeId, certificateGroupId, nonce, or subjectName paremeters is not valid. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_TransactionPending |
There is already a transaction active for another session. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not encrypted. |
Table 94 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CreateSigningRequest Method.
Table 94 – CreateSigningRequest Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CreateSigningRequest |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
CancelChanges is used to tell the Server to discard changes to the TrustLists or Certificates which were waiting for the Client to ApplyChanges.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from the Session that created the transaction and has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
CancelChanges();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 93 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the CancelChanges Method.
Table 95 – CancelChanges Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:CancelChanges |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server ServerConfiguration Transactions |
|
GetRejectedList Method returns the list of Certificates that have been rejected by the Server.
No rules are defined for how the Server updates this list or how long a Certificate is kept in the list. It is recommended that every valid but untrusted Certificate be added to the rejected list as long as storage is available. Servers should omit older entries from the list returned if the maximum message size is not large enough to allow the entire list to be returned.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
GetRejectedList(
[out] ByteString[] certificates
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
certificates |
The DER encoded form of the Certificates rejected by the Server. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 96 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetRejectedList Method.
Table 96 – GetRejectedList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:GetRejectedList |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The ResetToServerDefaults Method resets an application configuration to its default settings.
If the application is running on a Device that supports OPC 10000-21, the Device is placed in a state where the Onboarding process has to restart. If the Device does not support OPC 10000-21, the Server repeats the Application Setup process described in Annex G.
If the application is a Server, after this Method completes the Server shall set the ServerState to SHUTDOWN and the shutdownReason to a localized message that warns Clients that their credentials may not work when the Server restarts. The Server should set the secondsTillShutdown to a time that gives the Client a chance to receive the response to this Method.
Note that the default configuration for a application is set by configuration and is not necessarily the “factory default”. For example, a machine builder could update the default configuration to ensure that the application can still communicate with other applications within the machine after the reset.
The mechanisms for setting the default configuration are vendor specific.
This Method shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Signature
ResetToServerDefaults ();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
|
Bad_SecurityModeInsufficient |
The SecureChannel is not authenticated. |
Table 97 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ResetToServerDefaults Method.
Table 97 – ResetToServerDefaults Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
0:ResetToServerDefaults |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|
|
Server ServerConfiguration ResetToServerDefaults |
|
The ApplicationConfigurationType ObjectType defines a model which represents the configuration of another application. A Server acting as a proxy will add the Objects that represent the application it manages to the ManagedApplications Object (see 7.10.16).
Table 98 – ApplicationConfigurationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the ServerConfigurationType defined in 7.10.3. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Enabled |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ProductUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:ApplicationType |
0:ApplicationType |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:IsNonUaApplication |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:KeyCredentials |
|
0:KeyCredentialConfigurationFolderType |
Optional |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:AuthorizationServices |
|
0:AuthorizationServicesConfigurationFolderType |
Optional |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
The Enabled Property indicates whether the application is enabled. If FALSE the application will not run. If TRUE the Application runs.
The KeyCredentials Folder that contains credentials assigned to the application. It is described in 8.6.
The AuthorizationServices Folder contains the AuthorizationServiceConfiguration Objects which the application supports. It is described in 9.7.
If ApplicationType is Client then the ApplicationsNames Property shall not be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be “NA” or “RCP”.
If ApplicationType is Server or ClientAndServer then the ApplicationsNames Property shall be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be set”.
If ApplicationType is DiscoveryServer then the ApplicationsNames Property shall not be present and the ServerCapabilities shall be “LDS”.
For NonUaApplications, the ApplicationType shall be Client, the ApplicationsNames shall not be present, the ServerCapabilities shall be “NA” and MulticastDnsEnabled shall be FALSE.
The IsNonUaApplication Property indicates that the application is a NonUaApplication.
Additional requirements for some components inherited from ServerConfigurationType are specified in Table 99.
Table 99 – ApplicationConfigurationType Component Requirements
|
Component |
OPC UA Client |
OPC UA Server |
LDS |
NonUaApplication |
|
0:ApplicationUri |
Required |
Required |
Required |
Optional. The syntax and conventions for the URI may not conform to the requirements for OPC UA ApplicationUris. |
|
0:ApplicationType |
“Client” |
“Server“ or “ClientAndServer“ |
“DiscoveryServer“ |
“Client“ |
|
0:IsNonUaApplication |
Omitted or FALSE |
Omitted or FALSE |
Omitted or FALSE |
TRUE |
|
0:ApplicationNames |
Omitted |
Required |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:ServerCapabilities |
“NA” or “RCP” |
Required |
“LDS” |
“NA” |
|
0:MulticastDnsEnabled |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“TRUE” or “FALSE” |
“FALSE” |
|
0:AuthorizationServices |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:KeyCredentials |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Omitted |
|
0:InApplicationSetup |
Optional |
Optional |
Omitted |
Optional |
The application may require software updates. In this case, the software update model described in OPC 10000-100 specifies an instance of the SoftwareUpdateType that may be added to the ApplicationConfiguration instance.
A Folder for ApplicationConfiguration Objects which a Server exposes in its AddressSpace.
Table 100 – ApplicationConfigurationFolderType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFolderType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:Organizes |
Object |
0:<ApplicationName> |
|
0:ApplicationConfigurationType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
This Object allows access to the application configurations and it is the target of an Organizes reference from the Resources Object defined in OPC 10000-22.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 101.
Table 101 – ManagedApplications Object Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ManagedApplications |
||||
|
TypeDefinition |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFolderType defined in 7.10.15. |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Managed Application Configuration |
|||||
This type defines an ObjectType which represents the diagnostics for the last transaction (see 7.10.1. If no transaction has started the values of all Variables have a status of Bad_OutOfService. All existing results are discarded when a new transaction starts.
Table 102 – TransactionDiagnosticsType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TransactionDiagnosticsType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:StartTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:EndTime |
0:UtcTime |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Result |
0:StatusCode |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AffectedTrustLists |
0:NodeId [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AffectedCertificateGroups |
0:NodeId [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Errors |
0:TransactionErrorType [] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
|||||
The StartTime Property indicates when transaction started. It has a status of Bad_OutOfService if a transaction has not started
The EndTime Property indicates when transaction ended. It has a value of DateTime.MinValue if the transaction has not completed.
The Result Property indicates the overall transaction result. It has a status of Bad_InvalidState if a transaction has started but not completed. If the transaction has completed the status is Good and the value is the StatusCode that was returned from the ApplyChanges Method. If the CancelChanges Method was called the value is Bad_RequestCancelledByClient.
The AffectedTrustLists Property specifies the NodeIds of the TrustLists that are included in the transaction. It is updated each time as soon as a TrustList is added to the transaction.
The AffectedCertificateGroups Property specifies the NodeIds of the CertificateGroups are included in the transaction. It is updated each time as soon as a CertificateGroup is added to the transaction.The Errors Property has a list of errors that occurred when the changes were applied. Empty if no errors occurred. The TransactionErrorType is defined in 7.10.18.
This type defines a DataType which stores an error that occurred when processing a transaction. Its values are defined in Table 103.
Table 103 – TransactionErrorType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TransactionErrorType |
Structure |
Subtype of the Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|
targetId |
NodeId |
The NodeId of the Object that had the error. It is either a TrustListId or a CertificateGroupId. |
|
error |
StatusCode |
The code describing the error. |
|
message |
LocalizedText |
A description of the error. It should include enough information to allow the Client to understand which Certificate(s) and/or CRL(s) are the source of the problem. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 104.
Table 104 – TransactionErrorType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:TransactionErrorType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server PushManagement Transactions |
||||||
This is the DataType used to serialize application configurations. It is defined in Table 105.
The fields that are used depend on the ApplicationType.
Each ServerEndpoint has a unique combination of NetworkName and Port. Each ClientEndpoint has a unique combination of NetworkName and Port.
At least one CertificateGroup linked to a ServerEndpoint (see 7.10.23) shall have a CertificateType slot compatible with the Server Certificate used for the current Session. If no such slot exists the configuration update is rejected. The TrustList associated with that CertificateGroup shall trust the Client Certificate used for the current Session.
Updates to the configuration are applied in the following order:
- ApplicationIdentity
- CertificateGroups
- UserTokenSettings
- SecuritySettings
- ServerEndpoints
- ClientEndpoints
- AuthorizationServices
While processing a single record type updates are applied in the order they appear in the array.
Client shall put updates in this order: Delete => Insert => Replace.
For Insert/Replace operations, a record name shall never appear more than once.
References to other records by name are only verified after all records have been processed.
Table 105 – ApplicationConfigurationDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ApplicationConfigurationDataType |
Structure |
|
|
ApplicationIdentity |
0:ApplicationIdentityDataType |
The application identity used to create new Certificates. |
|
CertificateGroups |
0:CertificateGroupDataType [] |
The list CertificateGroups. |
|
ServerEndpoints |
0:ServerEndpointDataType [] |
A list of Server Endpoints. Not specified for Clients. |
|
ClientEndpoints |
0:EndpointDataType [] |
A list of Client Endpoints which allow reverse connections. Not specified for Servers. |
|
SecuritySettings |
0:SecuritySettingsDataType [] |
A list of security settings. Not specified for Clients. |
|
UserTokenSettings |
0:UserTokenSettingsDataType [] |
A list of settings for UserTokenPolicies. Not specified for Clients. |
|
AuthorizationServices |
0:AuthorizationServiceConfigurationDataType [] |
List of AuthorizationServices supported by a Server. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 106.
Table 106 – ApplicationConfigurationDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationDataType DataType defined in 7.8.5.4 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Application Configuration Management |
||||||
A File Object that supports the reading and writing of an ApplicationConfiguration defined in 7.10.19.
If a transaction is in progress (see 7.10.9) on another Session then the Server shall return Bad_TransactionPending if Open is called with Write Mode bit set.
Open is called with Write Mode bit set then new transactions (see 7.10.2) cannot be started. The block on new transactions lasts until the update was applied or rolled back. This may occur when ConfirmUpdate is called.
Methods that update the configuration shall be called from an authenticated SecureChannel and from a Client that has access to the SecurityAdmin Role (see 7.2).
Table 107 – ApplicationConfigurationFileType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationConfigurationFileType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the ConfigurationFileType defined in 7.8.5.1. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AvailableNetworks |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:AvailablePorts |
0:NumericRange |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxEndpoints |
0:UInt16 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:MaxCertificateGroups |
0:UInt16 |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:SecurityPolicyUris |
0:UriString[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:UserTokenTypes |
0:UserTokenPolicy[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateTypes |
0:NodeId[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateGroupPurposes |
0:NodeId[] |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
|||||
The AvailableNetworks Property specifies the valid values for NetworkName for an Endpoint (see 7.10.22).
The AvailablePorts Property the range of ports that may be specified for an Endpoint. If it is empty then all Ports are valid.
The SecurityPolicyUris Property is a list of URIs that may be used in a SecuritySettings (see 7.10.24). If empty then all URIs are supported.
The UserTokenTypes Property is the list of UserTokenTypes that may be used in a UserTokenSetting (see 7.10.24). If empty then all UserTokenTypes are supported. The PolicyId, IssuerEndpointUrl and SecurityPolicyUrl fields in the UserTokenPolicy Structure are not used and are always ignored. There may only be one combination of TokenType and IssuedTokenType in the list.
The CertificateTypes Property is a list of CertificateTypeIds that may be used in a CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.4). It shall have at least one element specified.
The CertificateGroupPurposes Property is a list of Purposes that may be used in a CertificateGroup (see 7.8.3.4). It shall have at least one element specified.
The MaxEndpoints Property specifies the maximum total number of Endpoints (Client plus Server) that may be defined. 0 means no limit.
The MaxCertificateGroups Property specifies the maximum number of CertificateGroups that may be defined. 0 means no limit.
This type is used to serialize the ApplicationIdentity configuration. It is defined in Table 108.
The ApplicationIdentity affects Certificates, CertificateRequests and ApplicationDescriptions created by a Client or Server. When the ApplicationIdentity is changed, existing Certificates are not affected, however, they may no longer be valid for use by the application because the ApplicationUri does not match the ApplicationUri in the Certificate. Applications shall continue to use the invalid Certificates which allows the configuration Client, which is aware of the mismatch, to complete the process needed to update Certificates. The new ApplicationUri shall be used in any subsequent signing requests.
Table 108 – ApplicationIdentityDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ApplicationIdentityDataType |
Structure |
|
|
ApplicationUri |
0:UriString |
The Uri that identifies the application. |
|
ApplicationNames |
0:LocalizedText[] |
The human readable names for the application in multiple locales. |
|
AdditionalServers |
0:ApplicationDescription[] |
The list of additional Servers returned by FindServers. This is typically used to provide information about other Servers in a redundant set. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 109.
Table 109 – ApplicationIdentityDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ApplicationIdentityDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize a single Endpoint configuration. It is defined in Table 110.
The DiscoveryUrls associated with the Endpoint. They are reported as part of the ApplicationDescription returned by FindServers (see OPC 10000-4) and by QueryApplications (6.5.10). If multiple Endpoints are specified the DiscoveryUrls from each Endpoint are collected into a single list with any duplicates removed. If this list is empty the Endpoint is not included in the ApplicationDescription returned by FindServers or QueryApplications.
The DiscoveryUrls returned to Clients includes one of the URLs in the DiscoveryUrls list based on the EndpointUrl filter provided in the FindServers Request. If the filter provided is not one of the DiscoveryUrls then the first entry in the DiscoveryUrls list is returned.
NetworkName and Port specify the information the application needs listen for incoming connections. Only one Endpoint may be specified for each combination of NetworkName and Port.
Table 110 – EndpointDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
EndpointDataType |
Structure |
|
|
DiscoveryUrls |
0:UriString[] |
The list of DiscoveryUrls. The domain portion of the URLs may include DNS names or IP addresses that the application cannot access because they are only resolvable on the other side of a NAT firewall. For this reason, the application shall not attempt to validate the domains or the ports. EndpointUrls that are used for reverse connect have the ‘rcp+’ prefix (see 6.5.5). |
|
NetworkName |
0:String |
The name of the network interface or the IP address the application should bind to when listening on these EndpointUrls. The default value is an empty String. In this case the application binds to all available IPs. The name is either one of the AvailableNetworks Property on the ApplicationConfigurationFile Object or a valid IPv4 or IPv6 address. |
|
Port |
0:UInt16 |
The port to bind to when listening for incoming requests. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 111.
Table 111 – EndpointDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:EndpointDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize a single Endpoint configuration for a Server. It is defined in Table 112.
The information in the Endpoint is used to generate a list of EndpointDescriptions that could be returned by the Server when GetEndpoints is called. The basic algorithm generates an EndpointDescription for each valid combination of SecurityPolicyUri, SecurityMode and Certificate (specified in the SecuritySettings). The EndpointDescription returned to Clients includes one of the URLs in the EndpointUrls list based on the EndpointUrl filter provided in the GetEndpoints Request. If the filter provided is not one of the EndpointUrls then the first entry in the EndpointUrls list is returned.
The complete set of EndpointDescriptions is built by repeating the process for all enabled Endpoints.
The UserTokenSettings array may specify a UserTokenPolicy with a SecurityPolicyUri. Any UserTokenSetting that is not valid for ServerCertificate associated with a generated EndpointDescription is rejected.
The Server chooses unique values for PolicyIds in UserTokenPolicies when building the EndpointDescriptions.
The ReverseConnectUrls are the URLs that the Server connects to and sends a ReverseHello. The EndpointDescriptions generated from the ServerEndpoint are available to Clients connecting via the socket.
Table 112 – ServerEndpointDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ServerEndpointDataType |
Structure |
|
|
EndpointUrls |
0:UriString[] |
The list of EndpointUrls that may be return ed in an EndpointDescription. |
|
SecuritySettingNames |
0:String[] |
The names of the SecuritySettings used to build the EndpointDescriptions. |
|
TransportProfileUri |
0:UriString |
The TransportProfileUri. |
|
UserTokenSettingNames |
0:String[] |
The names of the UserTokenSettings used to build the UserTokenPolicies that appear in the EndpointDescriptions. |
|
ReverseConnectUrls |
0:String[] |
A list of URLs that a Server connects to and waits for incoming Client connections. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 113.
Table 113 – ServerEndpointDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:ServerEndpointDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:EndpointDataType defined in 7.10.22. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to specify the SecuritySettings for a Server Endpoint. It is defined in Table 114.
The CertificateGroup specifies one or more Certificates that are assigned to a Server. When generating EndpointDescriptions any SecurityPolicyUris (other than None) that are not valid for one of the Certificates associated with the CertificateGroup are ignored.
If a SecurityPolicyUri is valid for more than one Certificate in the CertificateGroup, then an EndpointDescription is generated for each Certificate.
EndpointDescriptions generated with a None SecurityMode only use the SecurityPolicyUris and the CertificateGroupName to restrict the SecurityPolicies that may be used in the UserTokenPolicies.
Table 114 – SecuritySettingsDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
SecuritySettingsDataType |
Structure |
|
|
SecurityModes |
0:MessageSecurityMode[] |
The list of SecurityModes. |
|
SecurityPolicyUris |
0:String[] |
The list of SecurityPolicyUris. |
|
CertificateGroupName |
0:String |
The name of the CertificateGroup in the CertificateGroups list. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 115.
Table 115 – SecuritySettingsDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:SecuritySettingsDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This type is used to serialize the configuration for a UserTokenPolicy. It is defined in Table 116.
The UserTokenSettingsDataType in the is used to configure how to validate UserIdentityTokens.
If a CertificateGroup is specified it refers to the TrustList used to verify credentials by either verifying that an X509IdentityToken is trusted or by using a Certificate in the TrustList to verify the Signature on an IssuedIdentityToken. The CertificateGroup is not specified for UserName or Anonymous TokenTypes.
The KeyCredentialName is only specified for IssuedIdentityTokens and refers to a KeyCredential needed to access network resources used to validate IssuedIdentityTokens.
Table 116 – UserTokenSettingsDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
UserTokenSettingsDataType |
Structure |
|
|
TokenType |
0:UserTokenType |
The type of UserIdentityToken |
|
IssuedTokenType |
0:String |
A URI identifying the type of IssuedIdentityToken (i.e. JWT). |
|
IssuerEndpointUrl |
0:String |
An optional string which depends on the Authorization Service. The meaning of this value depends on the IssuedTokenType. Further details for the different Token types are defined in OPC 10000-6. |
|
SecurityPolicyUri |
0:String |
The SecurityPolicy to use when encrypting or signing the UserIdentityToken when it is passed to the Server in the ActivateSession request. For X509 UserIdentityTokens this value shall specify the SecurityPolicy that matches the Certificates that the Server will accept. For other UserIdentityTokens this value shall specify the SecurityPolicy to use when the SecureChannel uses SecurityPolicy = None. |
|
CertificateGroupName |
0:String |
The name of the corresponding entry in the CertificateGroups list of the ApplicationConfiguration. It contains the TrustList used to verify an X509IdentityToken. Only specified if the TokenType is an X509IdentityToken. |
|
AuthorizationServiceName |
0:String |
The name of the corresponding entry in the AuthorizationServices list of the ApplicationConfiguration. This is the AuthorizationService which issues tokens accepted by the Server. Only specified if the TokenType is an IssuedIdentityToken. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 117.
Table 117 – UserTokenSettingsDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:UserTokenSettingsDataType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseConfigurationRecordDataType defined in 7.8.5.5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Server Endpoint Management |
||||||
This event is raised when the UpdateCertificate Method is called.
If a PrivateKey was one of the InputArguments then that argument is set to NULL before generating this Event.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 118.
Table 118 – CertificateUpdateRequestedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateUpdateRequestedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
This event is raised when a Certificate is actually changed as a result of a Method call.
This is the result of a successful call to UpdateCertificate or ApplyChanges on a ServerConfigurationType Object. No Event is raised if the Method call fails. If ApplyChanges affects multiple Certificates then this Event is raised for each changed Certificate.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 119.
Table 119 – CertificateUpdatedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
0:CertificateUpdatedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the 0:AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateGroup |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:CertificateType |
0:NodeId |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Push Model for Global Certificate and TrustList Management |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantic is defined in OPC 10000-5.
The SourceNode Property for Events of this type shall be assigned to the NodeId of the Object with the Method that triggered the Event.
The CertificateGroup Property specifies the CertificateGroup that was affected by the update.
The CertificateType Property specifies the type of Certificate that was updated.