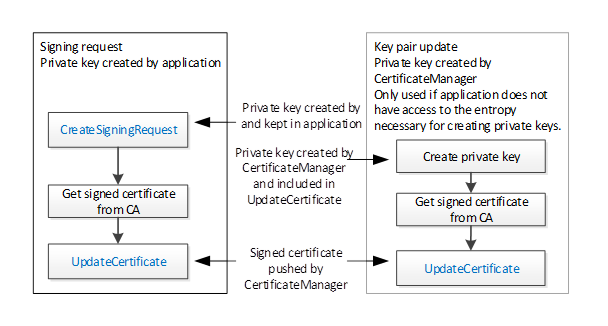
In this workflow the CertificateManager is the Client that executes the steps and the OPC UA Application is the Server that is processing the request in the sequence. The workflow is started if the CertificateManager determines that an update is required.
The workflow for PushManagement is shown in Figure 18. The two options for the key pair creation are described in Figure 19. The boxes with blue text indicate Method calls.
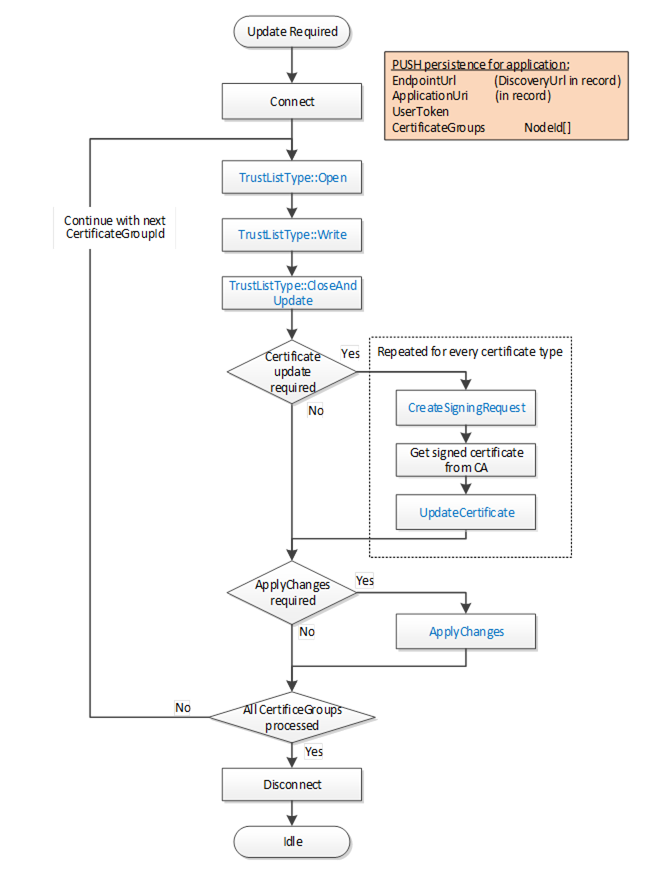
Figure 18 – The Certificate Push Management Workflow