The following paragraphs describe the elements of the ADI Information Model. All elements of the ADI Information Model defined by this specification belong to OPC-ADI namespace unless otherwise specified. OPC-ADI namespace is identified by the following URI:
http://opcfoundation.org/UA/ADI/
Figure 2 illustrates the overview of the ADI object model. It illustrates main components of the object model in the OPC-UA notation as described in Appendix D of [OPC 10000-3].
AnalyserDeviceType, AnalyserChannelType, StreamType, AccessorySlotType and AccessoryType represent the main building blocks of the object model. They are described in detail in dedicated paragraphs of this specification. Object of type AnalyserDeviceType is the topmost Object of the ADI object model. It represents an abstract type which shall be subtyped for different types of analyser devices. Subtypes of AnalyserDeviceType are described in 5.2.1.3.
This specification does not attempt to define all Parameters for analysers or their components. Instead, it aims to provide a set of mandatory and optional Parameters which are common for all analysers or analysers within the same class (type). Additionally, this specification defines placeholders (FunctionalGroups) where instrument vendors can expose their custom Parameters.
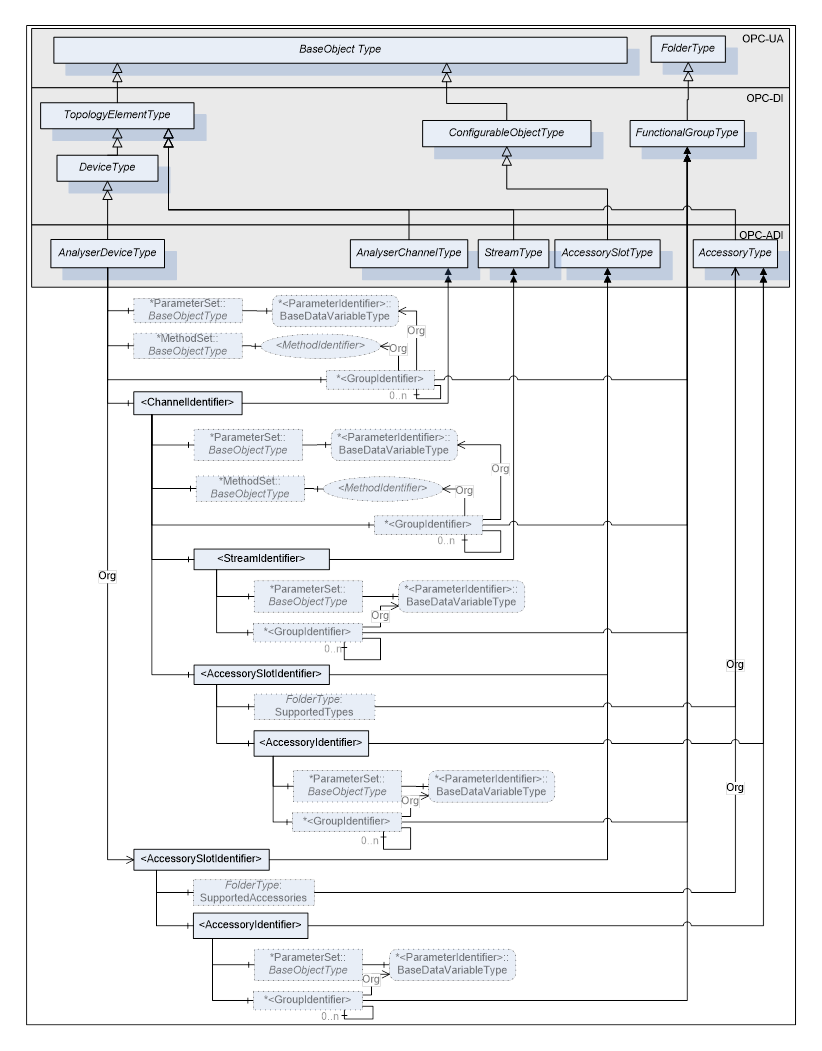
Figure 2 - Object Model Overview
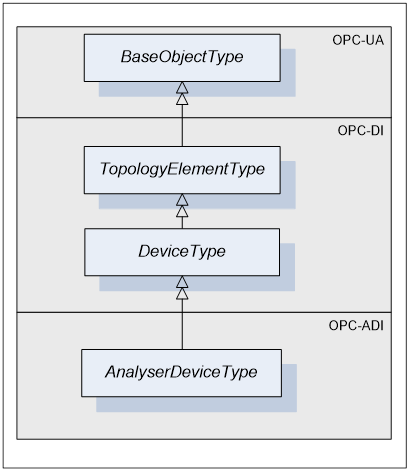
AnalyserDeviceType defines the general structure of an AnalyserDevice Object. Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the inheritance hierarchy and detailed composition of AnalyserDeviceType. It is formally defined in Table 1.
AnalyserDeviceType is a subtype of DeviceType [OPC 10000-100] and as such can have Parameters which are kept in an Object called ParameterSet. Parameters represented by <ParameterIdentifier > and their list called ParameterSet are inherited from DeviceType.
TopologyElementType [OPC 10000-100] introduced a component called MethodSet, which can be used to organize Methods exposed to the Client. AnalyserDeviceType takes advantage of that inherited component and groups all of its Methods under MethodSet.
DeviceType also introduces FunctionalGroups identified by <GroupIdentifier> that expose its Parameters in an organized fashion reflecting the structure of the device. AnalyserDeviceType can have any number of FunctionalGroups.
AnalyserDeviceType defines three mandatory FunctionalGroups:
- Configuration - used to organize Parameters representing the high-level configuration items of the analyser, which are expected to be modified by end users.
- Status - used to organize Parameters which describe the general health of the analyser.
- FactorySettings - used to organize Parameters, which describe the factory settings of the analyser that are not expected to be modified by end users.
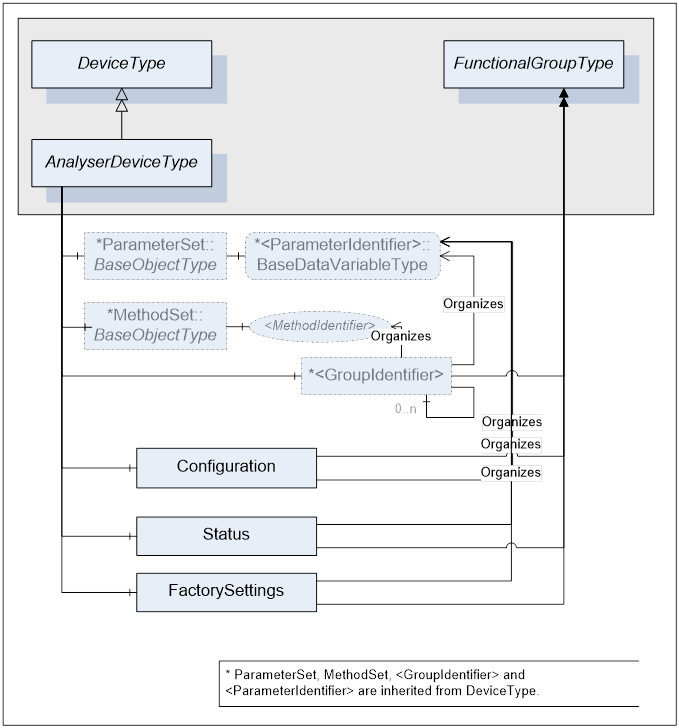
Figure 4 – AnalyserDeviceType Components
The AnalyserDevice Object that represents an analyser has one or more AnalyserChannels. AnalyserChannel is described in clause 5.2.2. The AnalyserChannel Node instances are identified by <ChannelIndentifier> browse name.
AnalyserDevice Object has zero or more Objects of type AccessorySlotType and identified by <AccessorySlotIdentifier>. AccessorySlotType is described in clause5.2.4. AccessorySlot Objects represent physical locations on the analyser where the analytical accessory can be mounted. Accessories currently mounted on the analyser device as well as the supported accessories for the accessory slot are represented as components of the AccessorySlot Object. For details refer to clause 5.2.3.
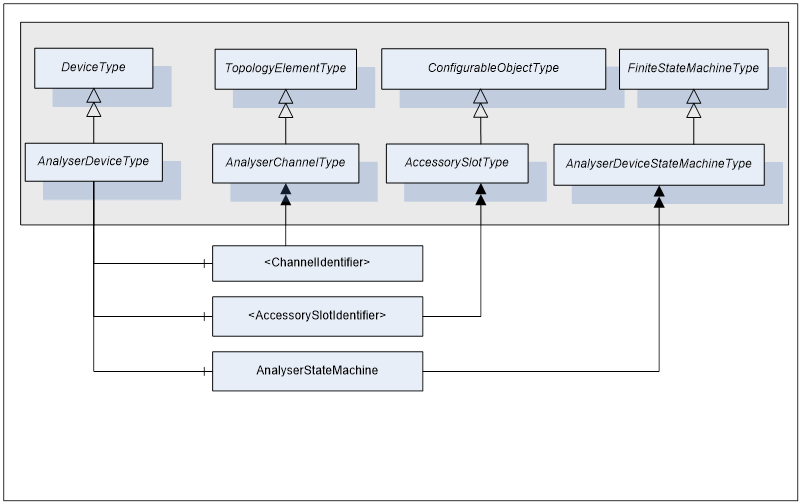
Figure 5 - AnalyserDeviceType Components cont.
AnalyserDeviceType does not expose any mandatory Parameters to report or manipulate the state of an analyser device. Instead, AnalyserDevice states are exposed through the AnalyserStateMachine component of type AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType. For details on AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType see clause 5.3.2.
Table 1 - AnalyserDeviceType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the DeviceType defined in [OPC 10000-100] |
||||||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
SpectrometerDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.6.1 |
|||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.8.1 |
|||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
AcousticSpectrometerDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.9.1 |
|||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
MassSpectrometerDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.7.1 |
|||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
ChromatographDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.10.1 |
|||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
NMRDeviceType |
Defined in Clause 5.2.11.1 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Configuration |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Status |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
FactorySettings |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<ChannelIdentifier> |
|
AnalyserChannelType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<AccessorySlotIdentifier> |
|
AccessorySlotType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyserStateMachine |
|
AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyserDeviceType.MethodSet |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GetConfiguration |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
SetConfiguration |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GetConfigDataDigest |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
CompareConfigDataDigest |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
ResetAllChannels |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
StartAllChannels |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
StopAllChannels |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
AbortAllChannels |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GotoOperating |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GotoMaintenance |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
AnalyserDeviceType is a subtype of DeviceType defined in [OPC 10000-100] and as such it inherits DeviceType’s characteristics. For a complete definition of the DeviceType see [OPC 10000-100].
The AnalyserDeviceType ObjectType is abstract. There will be no instances of an AnalyserDeviceType itself, but there will be instances of sub-types of this type. In this specification, the term AnalyserDevice generically refers to an instance of any ObjectType derived from the AnalyserDeviceType ObjectType.
All AnalyserDevices have Attributes and Properties that they inherit from the DeviceType. For those elements, the same rules as defined for Device Objects in [OPC 10000-100] apply.
The sub types of the AnalyserDeviceType are illustrated in Figure 6. Each of these sub type may be further sub typed.
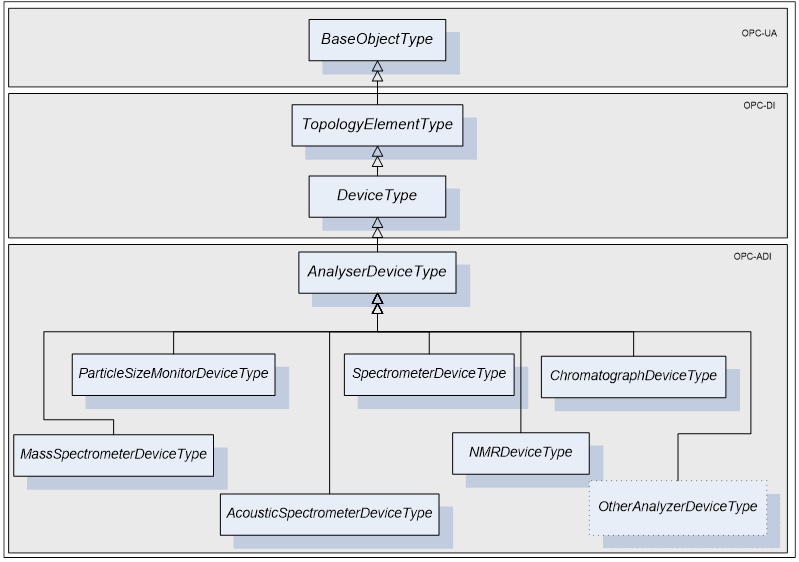
Figure 6 - AnalyserDeviceType Hierarchy
The AnalyserDeviceType is derived from the DeviceType as an Abstract type. It is sub-typed for each one of the analyser classes. Six sub-types are introduced:
Table 2 –AnalyserDeviceType Sub-type definition
|
AnalyserDeviceType |
Description |
|
SpectrometerDeviceType |
A light spectrometer is an optical instrument used to measure Properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum (IR/NIR/VIS/UV), typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify chemical composition of sample materials. The use of analytical techniques to determine process control parameters from spectra allows a wide range of industrial applications. This type covers FTIR, diode array, etc. |
|
AcousticSpectrometerDeviceType |
An acoustic spectrometer uses sound wave emission and advanced pattern recognition software to predict the physical Properties of powders and particulates. This type of analyser uses high frequency sounds emitted by all physical and chemical processes (particle impact, turbulent gas flow, gas evolution, fermentation, cavitation and multiphase flow). It is a non-invasive technique which is responding to dynamic event making it suitable for process control. |
|
MassSpectrometerDeviceType |
A mass spectrometer is an analytical instrument used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It is most generally used to find the composition of a physical sample by generating a mass spectrum representing the masses of sample components. A wide range of industrial process control applications are therefore possible, such as the online control of solvent drying. |
|
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType |
Particle size can be determined by light scattering (e.g. Focus Beam Reflectance Measurement) or other Methods. This type of analyser can be used to implement particle monitoring technique for in-line real-time measurement of particle size. A wide range of industrial process control applications are therefore possible such as the online control of crystallizers |
|
ChromatographDeviceType |
Chromatography is the collective term for a family of techniques for the separation of mixtures. It involves passing a mixture dissolved in a "mobile phase" through a stationary phase, which separates the analyte to be measured from other molecules in the mixture and allows it to be isolated. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. Preparative chromatography seeks to separate the components of a mixture for further use (and is thus a form of purification). Analytical chromatography normally operates with smaller amounts of material and seeks to measure the relative proportions of analytes in a mixture. The two are not mutually exclusive |
|
NMRDeviceType |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectrometers |
|
|
|
Parameters defined for the AnalyserDeviceType are described in the following tables. The tables correspond to mandatory FunctionalGroups defined for the AnalyserDeviceType. Additional Parameters may be defined on subtypes of AnalyserDeviceType and associated with those FunctionalGroups.
All AnalyserDevice Parameters exist as components of ParameterSet Object defined on that AnalyserDevice through inheritance from DeviceType. Each Parameter defined for an AnalyserDevice shall be accessible through one or more FunctionalGroup defined on that AnalyserDevice. Note, that the same Parameter is not instantiated more than once. Both, ParameterSet and a specific FunctionalGroup maintain References to the same instance of the Parameter.
Table 3 shows Parameters that will be organized by the Configuration FunctionalGroup.
Table 3 – AnalyserDevice Configuration Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
ConfigData |
Optional representation of the AnalyserDevice configuration |
FileType
|
O |
|
|
|
|
|
ConfigData is an optional representation of the AnalyserDevice configuration. When it is present, it may be used to read and write the AnalyserDevice configuration in chunks. The main purpose of this element is to provide a way to read and write configuration that are larger than the maximum size of the OPC UA message. Reading and writing configuration through this object are subject to the same state machine constraints as GetConfiguration and SetConfiguration.
To maintain configuration consistency, the server must grant read and write access to one and only one user at any given time.
The steps to update the configuration through the ConfigData object are:
- When SetConfiguration is allowed based on the state machine states, a single user may cal “open” the ConfigData. If an “Open” is attempted when not permitted, the server shall return “Bad_InvalidState”.
- The user updates the configuration by calling repeatitively and in increasing order “write” method on ConfigData. If the “Write” are not sequential, the server shall return “Bad_InvalidArgument”.
- When the whole configuration has been written, the user calls “close” method on the ConfigData.
- The server is responsible to verify the configuration. If an error occurs during the verification, the server shall return “Bad_InvalidArgument” on the “Close”. In case of error, the previous configuration is restored.
- The server commits the new configuration. . If an error occurs during the commit, the server shall return “Bad_InvalidArgument” on the “Close”. In case of error, the previous configuration is restored.
Table 4 shows Parameters that will be organized by the Status FunctionalGroup. All Parameters organized by this FunctionalGroup shall be read-only.
Table 4 – AnalyserDevice Status Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
DiagnosticStatus |
General health status of the analyser |
DataItemType DataType=DeviceHealthEnumeration
|
M |
|
|
|
|
|
The DiagnosticStatus Parameter reflects the general health of analyser. It is defined as a Variable of DataItemType type and its possible values are defined by [OPC 10000-100] enumerationDeviceHealthEnumeration. Its value must be the same as DeviceType.DeviceHealth Property.
Table 5 shows Parameters that will be organized by the FactorySettings FunctionalGroup component of the AnalyserDeviceType.
Table 5 – AnalyserDevice FactorySettings Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
The SerialNumber, Manufacturer, Model, DeviceManual, DeviceRevision, SoftwareRevision and the HardwareRevision Properties are defined on DeviceType and as such available on AnalyserDeviceType. As a general rule, they are read-only properties. However, they can be updated to reflect changes made to the analyser configuration e.g. upgrading the firmware.
DeviceRevision Property will be used to indicate an overall change in the analyser. It is mandatory and shall be updated automatically or manually each time the analyser configuration is altered. It is the customer’s QA responsibility to determine if this particular change affects the validation of the analyser.
The RevisionCounter Property is an incremental counter indicating the number of times the semi-static data within the AnalyserDevice has been modified.
If the analytical device represented by an AnalyserDevice Object is unable to publish a value for a mandatory Parameter defined in Table 5, the Analyser Server should provide a way to manually enter that value.
All Methods defined for AnalyserDeviceType and its state machines are grouped under the MethodSet component inherited from DeviceType [OPC 10000-100].
AnalyserDeviceType defines a Method called GetConfiguration, which is used to read the complete configuration of the AnalyserDevice and all of its components (AnalyserChannel, Accessory, AccessorySlot etc.) from the Analyser Server. The configuration is a proprietary structure defined by the analyser vendor, and is represented as a ByteString.
AnalyserDeviceType defines a Method called SetConfiguration, which is used to write the complete configuration of the AnalyserDevice and all of its components to the Analyser Server. This Method can be executed only when all of the AnalyserChannels are in a Stopped state or in a Maintenance state (see 5.3.4.3). An attempt to call it while in any other state results in a failure of the Method call.
When the SetConfiguration Method is executed, it automatically causes a transition of all AnalyserChannels in a Stopped state to the Resetting state and the new configuration becomes active. The configuration is a structure provided by the analyser vendor, and represented as a ByteString.
Even if the ADI Client verifies the configuration before calling the SetConfiguration Method, the Analyser Server has the ultimate responsibility to verify the configuration (Parameter ranges, Parameter values relating to each other, Parameter values in regard to installed hardware) before applying the requested changes. If any Parameter value is invalid, the whole configuration shall be rejected.
If an error occurs during a method call, the analyser state should be returned the same as before the call or at least a stable state.
Table 6 – GetConfiguration Method
|
Method |
Description |
|||
|
GetConfiguration |
Read the complete configuration of the AnalyserDevice and all of its components to the Analyser Server. |
|||
|
|
InputArguments |
|||
|
|
Name |
DataType |
ValueRank / arrayDimension |
Description |
|
|
|
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
|
OutputArguments |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
ConfigData |
ByteString |
-1/[0] |
Configuration structure represented as a single dimensional array of Bytes. Length of an array is provided by the Server at runtime. If the size of ConfigData parameter is larger than a single OPC UA message, the AnalyserDevice.ConfigData object shall be used. |
Table 7 – SetConfiguration Method
|
Method |
Description |
|||
|
SetConfiguration |
Write the complete configuration of the AnalyserDevice and all of its components to the Analyser Server and make the new configuration active. |
|||
|
|
InputArguments |
|||
|
|
Name |
DataType |
ValueRank / arrayDimension |
Description |
|
|
ConfigData |
ByteString |
-1/[0] |
Configuration structure represented as a single dimensional array of Bytes. Length of an array is provided by the Client at runtime. If the size of ConfigData parameter is larger than a single OPC UA message, the AnalyserDevice.ConfigData object shall be used. |
|
|
OutputArguments |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
ConfigDataDigest |
String |
-1/[0] |
Vendor specific digest (like SHA1) of the ConfigData. It is calculated, by the Server, after ConfigData is received and before any change has been made. It is used as the reference to know if the configuration has been altered after the SetConfiguration call. This string is intended to be human readable for example the hexadecimal or Base64 representation of the SHA1. |
AnalyserDevice defines a Method called GetConfigDataDigest, which is used to read the digest (e.g. SHA1 hash) of the complete analyser configuration. The digest is returned in a Method argument called ConfigDataDigest. It represents the same data which is calculated by the Server, when SetConfiguration Method is called. The value returned in ConfigDataDigest will change when the configuration of the analyser is changed in a way that may alter the results it produces. Examples of analyser changes that may affect the value of ConfigDataDigest are:
- A configuration Parameter of the analyser or any of its components is modified. There are rare cases where a change of a Parameter does not affect the analyser results like setting an acquisition trigger. In these cases the ConfigDataDigest shall not be recomputed. The vendor shall clearly specify which Parameters do not affect ConfigDataDigest.
- A Method call which does not update Parameters but alters behaviour of the analyser (e.g. firmware update) is called. The vendor shall clearly specify which Methods affect the returned value from ConfigDataDigest
- An accessory is added or removed
- Analyser is configured locally via built-in panel.
By comparing the ConfigDataDigest output argument from the SetConfiguration Method with the current value returned in the ConfigDataDigest argument of the GetConfigDataDigest Method, a Client shall be able to determine if the analyser configuration has been modified in such a way that the results produced by the analyser may be different than expected.
Table 8 – GetConfigDataDigest Method
|
Method |
Description |
|||
|
GetConfigDataDigest |
Read the digest of the complete analyser configuration as computed by the Server. |
|||
|
|
InputArguments |
|||
|
|
Name |
DataType |
ValueRank / arrayDimension |
Description |
|
|
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
|
OutputArguments |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
ConfigDataDigest |
String |
-1/[0] |
Vendor specific digest (like SHA1) of the complete analyser configuration. It is used as the reference to know if the configuration has been altered after the last SetConfiguration call. This string is intended to be human readable for example the hexadecimal or Base64 representation of the SHA1. |
A Method called CompareConfigDataDigest can be used to ask the AnalyserDevice if the ConfigDataDigest held by the Client reflects the current configuration of the analyser. This approach relieves the client from the responsibility for comparing the configuration digests.
Table 9 – CompareConfigDataDigest Method
|
Method |
Description |
|||
|
CompareConfigDataDigest |
Compare the provided ConfigDataDigest with the actual one of the analyser. |
|||
|
|
InputArguments |
|||
|
|
Name |
DataType |
ValueRank / arrayDimension |
Description |
|
|
ConfigDataDigest |
String |
-1/[0] |
Vendor specific digest (like SHA1) of the complete analyser configuration as returned by SetConfiguration and GetConfigurationDataDigest. This string is intended to be human readable for example the hexadecimal or Base64 representation of the SHA1. |
|
|
OutputArguments |
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
IsEqual |
Boolean |
-1/[0] |
True if the input ConfigDataDigest is equal to the actual digest of the analyser configuration. |
AnalyserDeviceType defines several Methods used for simultaneous control of analyser channels. Those Methods are defined in the following tables.
Table 10 – ResetAllChannels Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
ResetAllChannels |
Reset all AnalyserChannels belonging to this AnalyserDevice. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 11 – StartAllChannels Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
StartAllChannels |
Start all AnalyserChannels belonging to this AnalyserDevice. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 12 – StopAllChannels Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
StopAllChannels |
Stop all AnalyserChannels belonging to this AnalyserDevice. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 13 – AbortAllChannels Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
AbortAllChannels |
Abort all AnalyserChannels belonging to this AnalyserDevice. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Methods described in Table 10, Table 11, Table 12, Table 13 operate on all AnalyserChannels that are in the Operating state and their Configuration.IsEnabled Parameter is set to True. These Methods are not guaranteed to be atomic and their effect on each AnalyserChannel is not necessarily simultaneous. For example, the following implementation is perfectly legal:
|
For each AnalyserChannel If AnalyserChannel.IsInOperatingState AND AnalyserChannel.Configuration.IsEnabled == TRUE AnalyserChannel.Reset ()
|
Table 14 - GotoOperating Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
GotoOperating |
Causes the AnalyserDeviceStateMachine to go to Operating state, forcing all AnalyserChannels to leave the SlaveMode state and go to the Operating state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 15 - GotoMaintenance Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
GotoMaintenance |
Causes the AnalyserDeviceStateMachine to go to Maintenance state, forcing all AnalyserChannels to SlaveMode state.. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 16 – Method result codes for AnalyserDeviceType methods
|
Result code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more argument re invalid. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
Method called when the analyser is not in the appropriate state. |
|
Bad_RequestTooLarge |
The request message size exceeds limits set by the server. |
|
Bad_ResponseTooLarge |
The response message size exceeds limits set by the client. |
|
Bad_ServiceUnsupported |
The analyser does not support the requested service. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
An unexpected error occurred. |
This ObjectType defines the structure of an AnalyserChannel Object. Figure 7 depicts the AnalyserChannelType hierarchy. Figure 8 and Figure 9 show the AnalyserChannelType components. It is formally defined in Table 17.
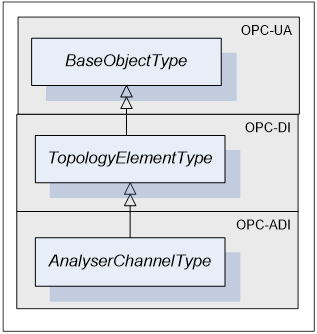
Figure 7 - AnalyserChannelType
AnalyserChannelType is a subtype of TopologyElementType.
An AnalyserChannel may have Parameters. If an AnalyserChannel has Parameters they appear in an Object called ParameterSet as a flat list of Parameters. ParameterSet is inherited from TopologyElementType [OPC 10000-100]. Parameters of an AnalyserChannel are identified by the <ParameterIdentifier> browse name.
TopologyElementType [OPC 10000-100] introduces a component called MethodSet, which shall be used to organize Methods exposed to the Client. AnalyserChannelType takes advantage of that inherited component and groups all of its Methods and the ones from its substate machines under MethodSet.
Parameters of an AnalyserChannel can be organized in FunctionalGroups identified as <GroupIdentifier> browse name.
AnalyserChannelType defines two mandatory FunctionalGroups (see clause 5.2.1.4 for details):
- Configuration - used to organize Parameters representing the high-level configuration items of the channel, which are expected to be modified by end users.
- Status - used to organize Parameters which describe the general health of the channel.
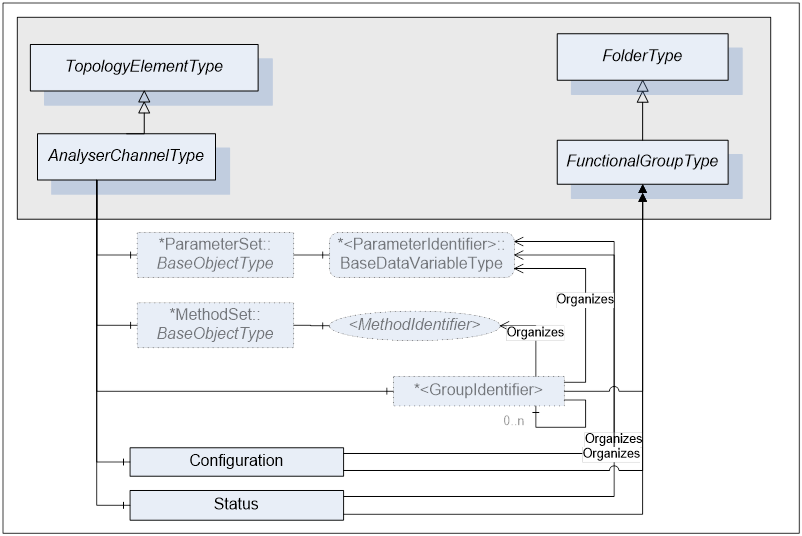
Figure 8 - AnalyserChannelType FunctionalGroups
AnalyserChannel Object has zero or more Objects of type AccessorySlotType and identified by <AccessorySlotIdentifier> browse name. AccessorySlotType is described in clause 5.2.3. AccessorySlot Objects represent physical locations on the physical channel where the analytical accessory can be mounted. Accessories currently mounted on the analyser channel as well as the supported accessories for the AccessorySlot are defined as components of the AccessorySlot Object. For details refer to clause 5.2.3.
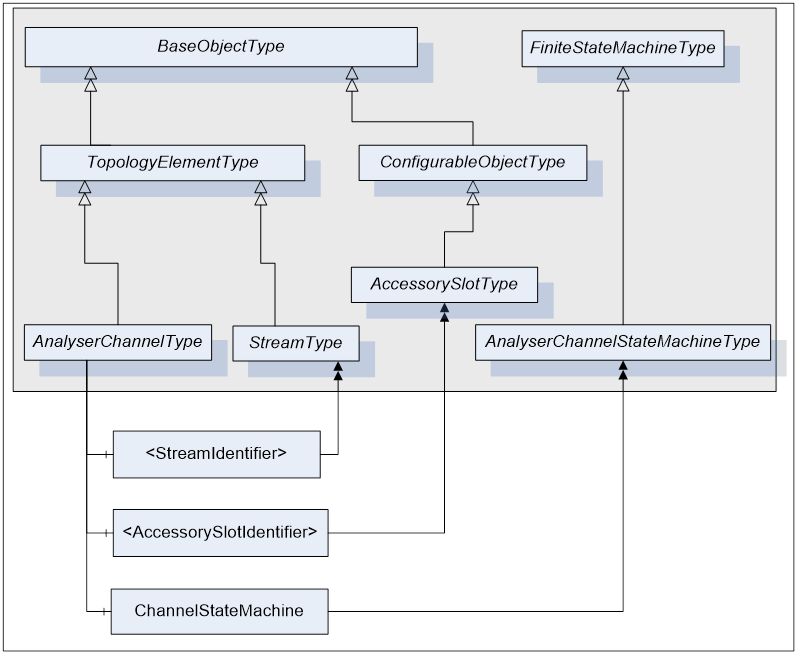
Figure 9 - AnalyserChannelType Components
AnalyserChannelType does not expose any mandatory Parameters to report or manipulate the state of an AnalyserChannel. Instead, AnalyserChannel states are exposed through the ChannelStateMachine Object of the type AnalyserChannelStateMachineType. For details on AnalyserChannelStateMachineType see clause 5.3.2.
Table 17 – AnalyserChannelType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the TopologyElementType defined in [OPC 10000-100]. |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ParameterSet |
|
BaseObjectType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<GroupIdentifier> |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Configuration |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Status |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<StreamIdentifier> |
|
StreamType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<AccessorySlotIdentifier> |
|
AccessorySlotType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ChannelStateMachine |
|
AnalyserChannelStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyserChannelType.MethodSet |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GotoOperating |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GotoMaintenance |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
StartSingleAcquisition |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Reset |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Stop |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Hold |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Unhold |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Suspend |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Unsuspend |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Abort |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Clear |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
The term AnalyserChannel refers to an instance of the AnalyserChannelType ObjectType as defined in Table 17.
All AnalyserChannels have Attributes and Properties inherited from the BaseObject.
Each AnalyserDevice Object has at least one AnalyserChannel Object as its component.
Parameters defined for the AnalyserChannelType are described in the following tables. The tables correspond to mandatory FunctionalGroups defined for the AnalyserChannelType. Additional Parameters may be defined for AnalyserChannel on subtypes of AnalyserDeviceType and associated with those FunctionalGroups.
All AnalyserChannel Parameters exist as components of the ParameterSet Object defined on that AnalyserChannel. Each Parameter defined for an AnalyserChannel shall be accessible through one and only one FunctionalGroup defined on that AnalyserChannel. Note, that the same Parameter is not instantiated more than once. Both, ParameterSet and a specific FunctionalGroup maintain References to the same instance of the Parameter.
Table 18 shows Parameters that will be organized by the Configuration FunctionalGroup.
Table 18 – AnalyserChannel Configuration Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
ChannelId |
Channel Id defined by user. On some analysers, the name of a channel may be configured using a maintenance tool, which leads to having two names to refer to the same channel for example: Channel1 and FirstChannel. In this case, one is for the BrowseName and the second is the ChannelId. |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
IsEnabled |
True if this AnalyserChannel maybe used to perform acquisition. Allow an AnalyserChannel to be marked as “not in use” so xxxAllChannels Methods of the AnalyserDevice may skip it. In the case of “software” AnalyserChannel like GC, this allows a chromatographic application to be disabled. |
DataItemType (DataType=Boolean) |
M |
Table 19 shows Parameters that will be organized by Status FunctionalGroup. All Parameters organized by this FunctionalGroup shall be read-only.
Table 19 – AnalyserChannel Status Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
DiagnosticStatus |
AnalyserChannel health status |
(DataType=DeviceHealthEnumeration) |
M |
|
ActiveStream |
Active stream for this AnalyserChannel. Its value is the BrowseName of the active stream. If no Stream is active, it shall be set to NULL. |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
M |
The DiagnosticStatus Parameter reflects the general health of the channel. It is defined as a Variable of DataItemType type and its value is defined by [OPC 10000-100] enumeration DeviceHealthEnumeration.
All Methods defined for AnalyserChannelType and its substate machines are grouped under the MethodSet component inherited from TopologyElementType [OPC 10000-100].
AnalyserChannel defines a Method called StartSingleAcquisition, which is used to start a single data acquisition, which uses current values of Parameters from the AcquisitionSettings FunctionalGroup of the Stream indicated by SelectedStream argument. The Method argument ExecutionCycle is used to indicate what it is that the acquisition is collecting e.g. sample, background, and dark noise.
If an error occurs during a method call, the analyser state should be the same as before the call.
Table 20 – StartSingleAcquisition Method
|
Method |
Description |
|||
|
StartSingleAcquisition |
Start collection of a single sample or reference data |
|||
|
|
InputArguments |
|||
|
|
Name |
DataType |
ValueRank / arrayDimension |
Description |
|
|
ExecutionCycle |
ExecutionCycleEnumeration |
-1/[0] |
Enumeration which specifies the type of the acquisition cycle (e.g. Calibration, Sampling ) |
|
|
ExecutionCycleSubcode |
UInteger |
-1/[0] |
Vendor defined code, which further describes the acquisition cycle. This code should correspond to one of the enumeration codes defined for ExecutionCycleSubcode Parameter in the AcquisitionStatus FunctionalGroup on a Stream. |
|
|
SelectedStream |
String |
-1/[0] |
Browse name of the target Stream for this acquisition |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|||
Table 21 - GotoOperating Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
GotoOperating |
Causes the AnalyserChannelStateMachine to go to Operating state.. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 22 - GotoMaintenance Method
|
Method |
Description |
|
GotoMaintenance |
Causes the AnalyserChannelStateMachine to go to Maintenance state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Reset |
Causes transition to the Resetting state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Start |
Causes transition to the Starting state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Stop |
Causes transition to the Stopping state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Hold |
Causes transition to the Holding state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Unhold |
Causes transition to the Unholding state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Suspend |
Causes transition to the Suspending state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Unsuspend |
Causes transition to the Unsuspending state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Abort |
Causes transition to the Aborting state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
|
Method |
Description |
|
Clear |
Causes transition to the Clearing state. |
|
|
InputArguments: NONE |
|
|
OutputArguments: NONE |
Table 32 - Method result codes for AnalyserChannelType methods
|
Result code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
One or more argument re invalid. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
Method called when the analyser is not in the appropriate state on one of its state machines. |
|
Bad_RequestTooLarge |
The request message size exceeds limits set by the analyser; the ConfigData is too big. |
|
Bad_ResponseTooLarge |
The response message size exceeds limits set by the client; the ConfigData is too big. |
|
Bad_ServiceUnsupported |
The analyser does not support the requested service. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
An unexpected error occurred. |
This ObjectType defines the structure of a Stream Object. Figure 10 depicts the StreamType hierarchy. It is formally defined in Table 33.
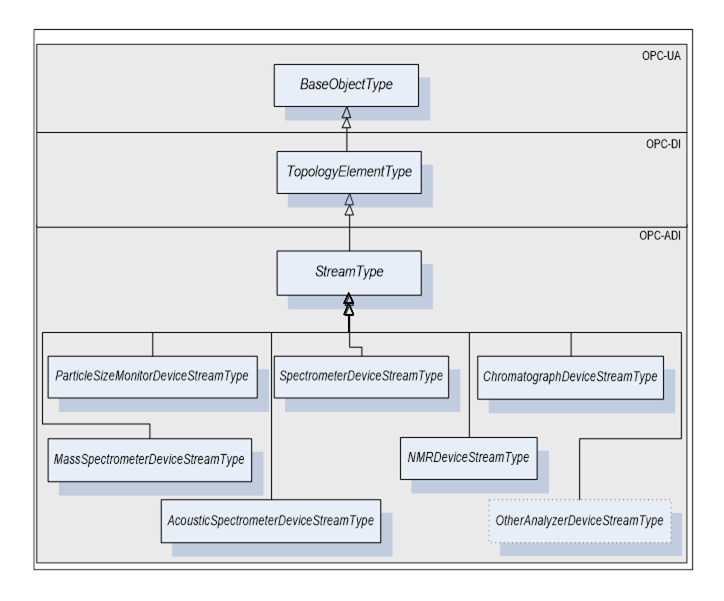
Figure 10 - StreamType Hierarchy
StreamType is a subtype of TopologyElementType.
A Stream may have Parameters. If a Stream has Parameters they appear in an Object called ParameterSet as a flat list of Parameters. Parameters of a Stream are identified by the <ParameterIdentifier> browse name. Parameters of a Stream can be organized in FunctionalGroups identified as <GroupIdentifier> browse name.
StreamType defines seven mandatory FunctionalGroups (see clause 5.2.1.4 for more details):
- Configuration - used to organize Parameters representing the high-level configuration items of the stream, which are expected to be modified by end users.
- Status - used to organize Parameters which describe the general health of the stream.
- AcquistionSettings - used to organize Parameters which describe the conditions of the following acquisition on a stream.
- AcquisitionStatus – used to organize Parameters which describe the status of an ongoing acquisition on a stream.
- AcquisitionData - used to organize all Parameters which represent data retrieved at the end of the data acquisition.
- ChemometricModelSettings - used to organize Parameters which describe/configure the chemometric models used during the data acquisition
- Context - used to organize all Parameters which provide the context for the data acquired through the Stream. Context Parameters are not generally used by the analyser but can be published to uniquely tie acquired data with the controlling process. Examples of context Parameters are: CampaignID, BatchID, LotID, MaterialID, and SampleId.
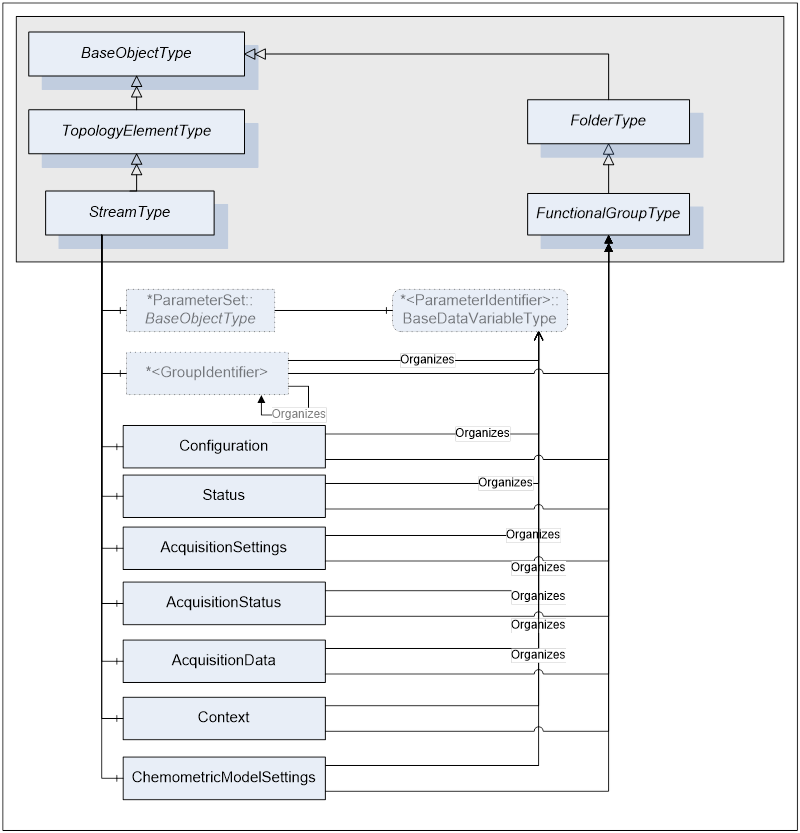
Figure 11 - Stream FunctionalGroups
Table 33 – StreamType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
StreamType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the TopologyElementType defined in [OPC 10000-100]. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ParameterSet |
|
BaseObjectType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<GroupIdentifier> |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Configuration |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Status |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AcquisitionSettings |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AcquisitionStatus |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AcquisitionData |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ChemometricModelSettings |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Context |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
Parameters defined for the StreamType are described in the following tables. The tables correspond to mandatory FunctionalGroups defined for the StreamType. Additional Parameters may be defined for Stream on subtypes of AnalyserDeviceType and associated with those FunctionalGroups.
All Stream Parameters exist as components of the ParameterSet Object defined on that Stream. Each Parameter defined for a Stream shall be accessible through one and only one FunctionalGroup defined on that Stream. Note, that the same Parameter is not instantiated more than once. Both, ParameterSet and a specific FunctionalGroup maintain References to the same instance of the Parameter.
Table 34 describes the Parameters that are organized by the Configuration FunctionalGroup of a Stream.
Table 34 –Stream Configuration Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
IsEnabled |
True if this stream maybe used to perform acquisition. This Parameter is mainly used for maintenance. |
DataItemType (DataType=Boolean) |
M |
|
IsForced |
True if this Stream is forced, which means that is the only Stream on this AnalyserChannel that can be used to perform acquisitions. This Parameter is mainly used for maintenance. |
DataItemType (DataType=Boolean) |
O |
Table 35 describes the Parameters that are organized by the Status FunctionalGroup of a Stream. All Parameters organized by this FunctionalGroup shall be read-only.
Table 35 –Stream Status Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
DiagnosticStatus |
Stream health status |
(DataType=DeviceHealthEnumeration) |
M |
|
LastCalibrationTime |
Time at which the last successful calibration was run. This is the SourceTimestamp of the main acquisition data of the first acquisition for this calibration. If unknown, it shall be set to DateTime.MinValue. |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
O |
|
LastValidationTime |
Time at which the last successful validation was run. This is the SourceTimestamp of the main acquisition data of the first acquisition for this validation. If unknown, it shall be set to DateTime.MinValue. |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
O |
|
LastSampleTime |
Time at which the last sample was acquired. This is the SourceTimestamp of the main acquisition data for this sample acquisition. If unknown, it shall be set to DateTime.MinValue. |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
Table 36 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionSettings FunctionalGroup of a Stream.
Table 36 - Stream AcquisitionSettings Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
TimeBetweenSamples |
Number of milliseconds between two consecutive starts of acquisition. Value 0 means “as fast as possible” |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Duration) |
O |
Table 37 describes the Parameters that are organized by theAcquisitionStatus FunctionalGroup of a Stream. All Parameters organized by this FunctionalGroup shall be read-only.
Table 37 –Stream AcquisitionStatus Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
IsActive |
True if this stream is actually running, acquiring data. Only one Stream may be marked as IsActive on a given AnalyserChannel at any given time. |
DataItemType (DataType=Boolean) |
M |
|
ExecutionCycle |
Indicates which acquisition cycle is in progress |
DataItemType (ExecutionCycleEnumeration) |
M |
|
ExecutionCycleSubcode |
Indicates a vendor defined code, which further describes the acquisition cycle. |
MultiStateDiscreteType |
M |
|
Progress |
Indicates the progress of an acquisition (e.g. percentage of completion) |
DataItemType (DataType=Float) |
M |
ExecutionCycle indicates the type of acquisition in progress and it is set in the SelectExecutionCycle state of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine..
Progress is a float number from 0 to 100 defining the completion of the ongoing acquisition cycle. The granularity of the Progress update is vendor specific. It is set to 0 in the SelectExecutionCycle of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine.
Table 38 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup of a Stream.
Table 38 –Stream AcquisitionData Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
AcquisitionCounter |
Simple counter incremented after each Sampling acquisition performed on this Stream; The counter is not incremented for acquisition cycles other than Sampling. It is used to support detection of missing acquisition. Wrap to 0 when it reaches 2147483647. The starting value at power up is vendor specific |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Counter) |
M |
|
AcquisitionResultStatus |
Quality of the acquisition |
DataItemType (AcquisitionResultStatusEnumeration) |
M |
|
<ProcessVariableIdentifier> |
Most commonly, it is a reference to process data produced as a result of applying the chemometric model to ScaledData.. There can be multiple Parameters representing process data and uniquely identified by the <ProcessVariableIdentifier> BrowseName. |
ProcessVariableType |
O |
|
Offset |
The Offset Parameter holds the difference in milliseconds between the start of sample extraction and the start of the analysis. |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Duration) |
O |
|
RawData |
Raw data produced as a result of data acquisition on the Stream (see definition of raw data) |
DataItemType (DataType is defined on a subtype of AnalyserDeviceType) |
O |
|
ScaledData* |
Scaled data produced as a result of data acquisition on the Stream and applying the analyser model. The data type used is analyser dependent. (see definition of scaled data) |
DataItemType (DataType is defined on a subtype of AnalyserDeviceType) |
M |
|
AcquisitionEndTime |
The end time of the AnalyseSample or AnalyseCalibrationSample or AnalyseValidationSample state of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine state machine. This time should not be used for critical data synchronization but rather for correlation with other external events in the diagnostic context. If unknown, AcquisitionEndTime shall be set to DateTime.MinValue |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
M |
*Definition of the ScaledData Parameter here is only to indicate that this Parameter must be defined for a Stream on a subtype of an AnalyserDeviceType. Since different analyser classes will produce scaled data of different type as their output, it is impossible to fully define this Parameter at this level. See ScaledData Parameter definition for specific class of analyser. If more than one ScaledData is required, Parameters representing those additional ScaledData shall be called ScaledData1, ScaledData2... ScaledData<n>.
The Offset Parameter holds the difference in milliseconds between the start of sample extraction and the start of the analysis which is the time in millisconds between the WaitForXXXTrigger to ExtractXXXSample transition and the PrepareXXXSample to AnalyseXXXSample transition.
As a general rule, a single Parameter shall not be used to represent different data elements. For example, ScaledData shall be used for the Sample acquisition and another Parameter shall be used to publish the output of the Calibration acquisition. However, in the case where the Validation cycle consists only of acquisition of normal samples, the ScaledData Parameter may be used. A consumer of data from an Analyser Server must be able to correlate values collected from different Parameters. Specifically, it must be possible to associate scaled data with raw data, process data and context data collected during the same acquisition cycle. The data correlation is based on time-stamps used during data collection. SourceTimestamp shall be the time when the sampling system starts extracting the sample, defined by the start of the ExtractSample or ExtractCalibrationSample or ExtractValidationSample state of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine. The difference between the SourceTimestamp and the time when the sample is analysed, is reflected in the Offset Parameter defines in AcquisitionData.
To simplify integration with historians, Parameters in the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup shall be updated once per acquisition cycle.
Time-stamp management rules:
- The time-stamp of the analyser main data (RawData, ScaledData) shall be the start time of the ExtractSample or ExtractCalibrationSample or ExtractValidationSample state of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine.
- All values derived from acquired data shall have the same SourceTimestamp as the acquired data. For example RawData, ScaledData, AcquisitionEndTime shall have the same SourceTimestamp.
- If a derived value combines acquired data from different data sources, the time-stamp of the “main” data shall be used. Which data source is the main data, is vendor specific, but shall be consistent and documented.
- If a derived value combines acquired data from different AnalyserChannels, the time-stamp of the “main” AnalyserChannel shall be used. Which AnalyserChannel is the main AnalyserChannel, is vendor specific, but shall be consistent and documented.
- The last item updated after the end of acquisition (PublishResults state) is AcquisitionResultStatus which is set to GOOD_1, BAD_2, UNKNOWN_3 or PARITAL_4. This implies that all items that are part of this acquisition shall have been updated; this includes items from AcquisitionData and Context FunctionalGroup.
- The OPC UA SourceTimestamp is always in UTC time.
For details on SourceTimestamp elements of a DataValue see [OPC 10000-4].
When the analyser is working in a standalone mode i.e. it is not driven by a DCS or other external control system, the analyser should publish the Context Parameters using data provided by user or other system entry system like a barcode reader.
Table 39 describes the Parameters that are organized by the Context FunctionalGroup of a Stream.
Table 39 –Stream Context Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
CampaignId |
Defines the current campaign |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
BatchId |
Defines the current batch |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
SubBatchId |
Defines the current sub-batch |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
LotId |
Defines the current lot |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
MaterialId |
Defines the current material |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
Process |
Current Process name |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
Unit |
Current Unit name |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
Operation |
Current Operation name |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
Phase |
Current Phase name |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
UserId |
Login name of the user who is logged on at the device console. If no Operator logon, “System” shall be assigned to UserId. |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
|
SampleId |
Identifier for the sample |
DataItemType (DataType=String) |
O |
Table 40 shows Parameters that will be organized by the ChemometricModelSettings FunctionalGroup.
Table 40 – Stream ChemometricModelSettings Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
<ChemometricModelId> |
Chemometric Model used to convert scaled data into process data |
ChemometricModelType (DataType=Byte) |
O |
AccessorySlotType defines the general structure of an AccessorySlot Object. Figure 12 shows the detailed composition of AccessorySlotType. It is formally defined in Table 41.
The SupportedTypes folder is used to maintain the set of (sub-types of) AccessoryTypes supported by that accessory slot.
AccessorySlotType states are exposed through the AccessorySlotStateMachine Object of type AccessorySlotStateMachineType. For details on AccessorySlotStateMachineType see clause 5.3.5.
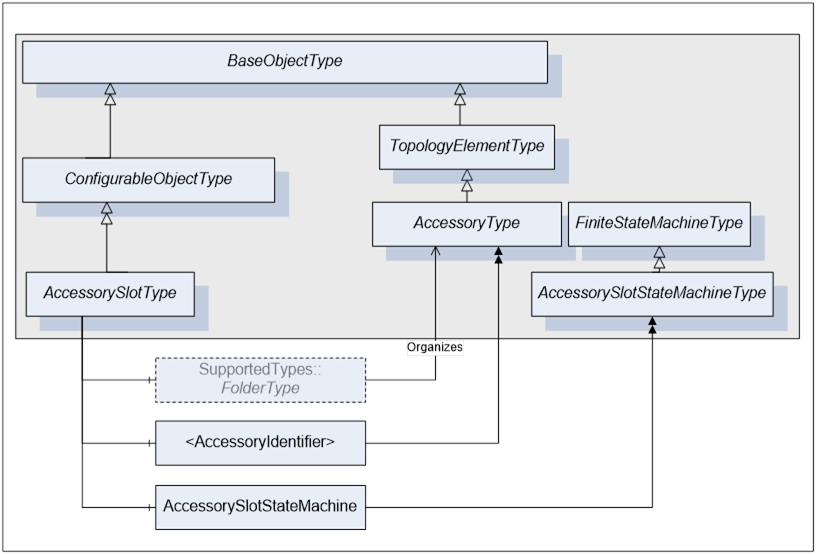
Figure 12 - AccessorySlotType Components
Table 41 – AccessorySlotType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
AccessorySlotType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the ConfigurableObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-100] |
||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IsHotSwappable |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IsEnabled |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AccessorySlotStateMachine |
|
AccessorySlotStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<AccessoryIdentifier> |
|
AccessoryType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
AccessorySlotType inherits from the ConfigurableObjectType. SupportedTypes contain References to supported AccessoryTypes. .
IsHotSwappable Property is True if an accessory can be inserted in the accessory slot while it is powered.
IsEnabled Property is True if this accessory slot is capable of accepting an accessory in it.
AccessorySlotStateMachine describes internal states of the accessory slot.
<AccessoryIdentifier> represents the accessory currently installed in the accessory slot.
The term AccessorySlot refers to an instance of AccessorySlotType ObjectType as defined in Table 41.
AccessorySlotType can be instantiated as components of an AnalyserDevice Object or any of its subtypes.
Optionally AccessorySlotAccessorySlotType can be instantiated as components of the AnalyserChannel Objects.
This ObjectType defines the structure of an Accessory Object. Figure 13 shows the AccessoryType components. It is formally defined in Table 42.
AccessoryType is a subtype of TopologyElementType.
An Accessory may have Parameters. If an Accessory has Parameters they appear in an Object called ParameterSet as a flat list of Parameters. Parameters of an Accessory are identified by <ParameterIdentifier> Parameters of an Accessory can be organized in FunctionalGroups identified as <GroupIdentifier>. An Accessory has at least three FunctionalGroups that expose its Parameters in an organized fashion. The three mandatory FunctionalGroups are:
- Configuration - used to organize Parameters representing the high-level configuration items of the accessory, which are expected to be modified by end users.
- Status - used to organize Parameters which describe the general health of the a ccessory.
- FactorySettings - used to organize Parameters which describe the factory settings of the accessory and are not expected to be modified by end users.
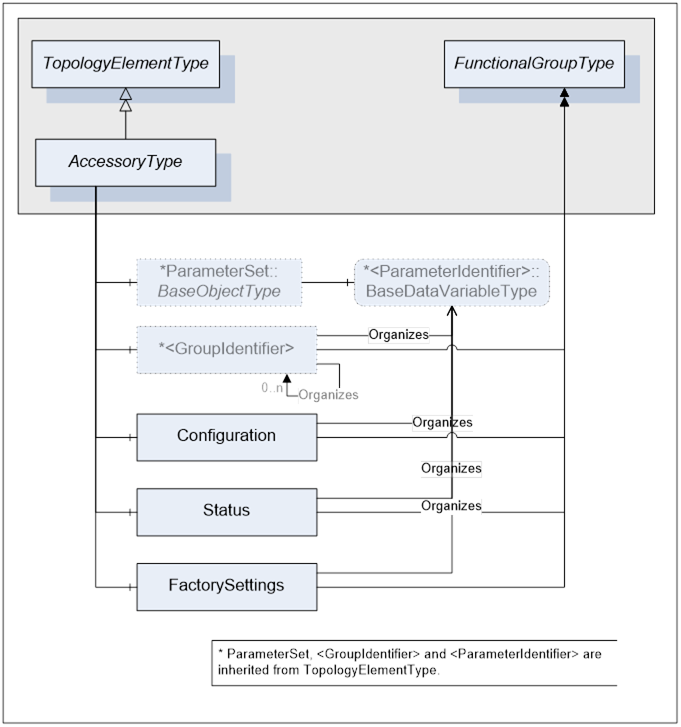
Table 42 – AccessoryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
AccessoryType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the TopologyElementTypee defined in [OPC 10000-100] |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Configuration |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Status |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
FactorySettings |
|
FunctionalGroupType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
IsHotSwappable |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
IsReady |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
IsHotSwappable Property is True if this accessory can be inserted in an accessory slot while it is powered. Its value may only be True when it is in Installed state. It shall be False in all other states.
IsReady Property is True if this accessory is ready to be used. Its value may only be True when it is in Installed state, It shall be False in all other states.
The term Accessory refers to an instance of AccessoryType ObjectType as defined in Table 42.
Accessory Objects can be instantiated as components of an AccessorySlot Object.
This specification defines three sub-types of AccesoryType: DetectorType, SmartSamplingSystemType and SourceType.
Table 43 describes a detector Accessory which is capable of producing raw data for an analyser.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
DetectorType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AccessoryType defined in 5.2.5. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 44 describes an intelligent sampling system Accessory used to extract samples from the process monitored by an analyser. It may also be used for non-intrusive device like ATR. It is “smart” in the sense that it provides interaction through configuration and/or status compared to passive sampling systems that provide no status or control capabilities.
Table 44 - SmartSamplingSystemType
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
SmartSamplingSystemType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AccessoryType defined in 5.2.5. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 45 describes an Accessory used by spectrometers (infrared, visible, UV etc.) with internal source that illuminate the sample.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
SourceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AccessoryType defined in 5.2.5. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 46 - SpectrometerDeviceType
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
SpectrometerDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
The term SpectrometerDevice refers to an instance of SpectrometerDeviceType ObjectType as defined in Table 46
All SpectrometerDevice Objects have Attributes and Properties that they inherit from the AnalyserDeviceType.
Table 47 describes the Parameters that are organized by the FactorySettings FunctionalGroup of a SpectrometerDeviceType.
Table 47 – SpectrometerDeviceType FactorySettings Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
SpectralRange |
All spectral ranges that can be covered by this analyser. Vendors are expected to use a subtype of DataItemType to provide engineering units through the standard Property EngineeringUnits of type EUInformation. Typical units will be cm-1 and µm. |
DataItemType (DataType=Range[] ) |
O |
In general, a spectrometer covers one spectral range, but some spectrometers may cover more than one. In case of spectrometers based on a filter wheel, each entry in the array is the band of one of the filters. This is why an array of Range is used as the data type for this Parameter.
SpectrometerDeviceStreamType defines seven mandatory FunctionalGroups described in5.2.3.1: Configuration, Status, AcquistionSettings, AcquisitionStatus, AcquisitionData, ChemometricModelSettings, and Context.
Table 48 describes the Parameters that are organized by the Configuration FunctionalGroup of a SpectrometerDeviceStreamType.
Table 48 – SpectrometerDeviceStreamType Configuration Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
ActiveBackground |
Background spectrum used for the evaluation of the absorbance. In the case of spectrometer like diode array that requires black and white background, this is the white background. |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float)
|
M |
|
ActiveBackground1 |
Background spectrum used for the evaluation of the absorbance. In the case of spectrometer like diode array that requires black and white background, this is the black background and the Parameter is mandatory. |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float)
|
O |
If more then one background spectrum is required, Parameters representing those additional background spectra shall be called ActiveBackground1, ActiveBackground2,...,ActiveBackground<n> and the same ModellingRules as for ActiveBackground Parameter shall apply.
Table 49 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionSettings FunctionalGroup of a SpectrometerDeviceStreamType.
Table 49 – SpectrometerDeviceStreamType AcquisitionSettings Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
SpectralRange |
Spectral range of this acquisition. Vendors are expected to use a subtype of DataItemType to provide engineering units through the standard Property EngineeringUnits of type EUInformation. Typical units will be cm-1 and µm. |
O |
|
|
Resolution |
Acquisition resolution May be an enum or Float |
DataItemType
|
O |
|
RequestedNumberOfScans |
Number of scans to be averaged This Parameter is often referred to as ObservationTime |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Int32) |
O |
|
Gain |
Detector gain May be an enum or Float |
DataItemType
|
O |
|
TransmittanceCutoff |
Transmittance clipping limits |
DataItemType (DataType=Range) |
O |
|
AbsorbanceCutoff |
Absorbance clipping limits |
DataItemType (DataType=Range) |
O |
Many of the Parameters in the AcquisitionSettings FunctionalGroup are used for sample acquisition. Calibration and validation may or may not use the same value. It is up to the vendor to select his approach: share Parameters or use different ones. Nested FunctionalGroup may also be used to organize different set of Parameters.
Table 50 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionStatus FunctionalGroup of a SpectrometerDeviceStreamType. All Parameters organized by this FunctionalGroup shall be read-only.
Table 50 – SpectrometerDeviceStreamType AcquisitionStatus Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
RW |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
NumberOfScansDone |
Actual number of scans completed |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Int32) |
RO |
O |
Table 51 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup of a SpectrometerDeviceStreamType.
Table 51 – SpectrometerDeviceStreamType AcquisitionData Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
RW |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
RawData |
Raw spectrum in arbitrary units |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
RO |
O |
|
ScaledData* |
Absorbance |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
RO |
M |
|
TotalNumberOfScansDone |
Total number of scans done at the end of acquisition. |
AnalogItemType (DataType=Int32) |
RO |
M |
|
BackgroundAcquisitionTime |
Time stamp of the background used for this acquisition. If more then one background spectrum is required, the time of ActiveBackground shall be used. Background is acquired during calibration acquisition cycle. |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
RO |
M |
|
PendingBackground |
Last acquired Background spectrum. This Background is not automatically used for evaluation of ScaledData (Absorbance) - see ActiveBackground Parameter. In the case of spectrometer like diode array that requires black and white background, this is the white background. |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float)
|
RO |
M |
|
PendingBackground1 |
Last acquired Background spectrum. This Background is not automatically used for evaluation of ScaledData (Absorbance) - see ActiveBackground Parameter. In the case of spectrometer like diode array that requires black and white background, this is the black background and the Parameter is mandatory |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float)
|
RO |
O |
If more then one background spectrum is required, Parameters representing those additional background spectra shall be called PendingBackground1, PendingBackground2,...,PendingBackground<n> and the same ModellingRules as for PendingBackground Parameter shall apply.
* ScaledData Parameter at this level represents the same Parameter that was defined on StreamType. Since different types of analysers may represent ScaledData differently, it was impossible to declare the VariableType of this Parameter at the StreamType level. It is possible here because the scope of the definition is limited to SpectrometerDeviceType. Devices of this type use YArrayItemType to represent ScaledData.
Table 52 - MassSpectrometerDeviceType
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
MassSpectrometerDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The term MassSpectrometerDevice refers to an instance of MassSpectrometerDeviceType ObjectType as defined in Table 52.
There is no specific Parameter in MassSpectrometerDeviceStreamType.
Particle size can be determined by light scattering (e.g. Focus Beam Reflectance Measurement, Laser Diffraction) or other Methods. This type of analyser can be used to implement particle monitoring technique for in-line real-time measurement of particle size. A wide range of industrial process control applications are therefore possible such as the online control of crystallizers.
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType defines the general structure of a ParticleSizeMonitorDevice Object.
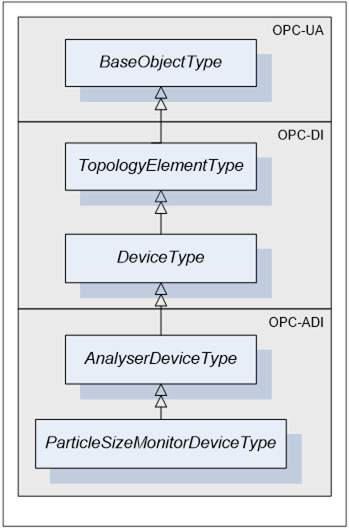
Figure 14 - ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType is a subtype of AnalyserDeviceType.
Table 53 - ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The term ParticleSizeMonitorDevice refers to an instance of ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceType ObjectType as defined in Table 53.
All ParticleSizeMonitorDevice have Attributes and Properties that they inherit from the AnalyserDeviceType.
ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceStreamType defines seven mandatory FunctionalGroups described in5.2.3.1: Configuration, Status, AcquistionSettings, AcquisitionStatus, AcquisitionData, ChemometricModelSettings, Context. Parameters exposed by an Stream of a ParticleSizeMonitorDevice should be organized by those FunctionalGroups based on their meaning.
Table 54 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup of a ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceStreamType.
Table 54 – ParticleSizeMonitorDeviceStreamType AcquisitionData Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
Background |
Array describing the measured background on detector(s.) |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
O |
|
RawData |
Array describing the measured raw data on detector(s) in arbitrary units. |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
O |
|
ScaledData |
Array describing the corrected measured data detector(s), for example after background subtraction |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
M |
|
SizeDistribution |
Returns the Particle Size Distribution |
YArrayItemType (DataType=Float) |
M |
|
BackgroundAcquisitionTime |
Time stamp of the background used for this acquisition |
DataItemType (DataType=DateTime) |
M |
Table 55 - AcousticSpectrometerDeviceType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||||
|
BrowseName |
AcousticSpectrometerDeviceType |
||||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
||
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
The term AcousticSpectrometerDevice refers to an instance of AcousticSpectrometerDeviceType ObjectType as defined in Table 55.
There is no specific Parameter in AcousticSpectrometerDeviceStreamType.
Chromatograph retrieves the concentration of chemical components by using a set of separation columns that separate each molecule based on the time it takes to go through a given column path.
ChromatographrDeviceType defines the general structure of a ChromatographDevice Object
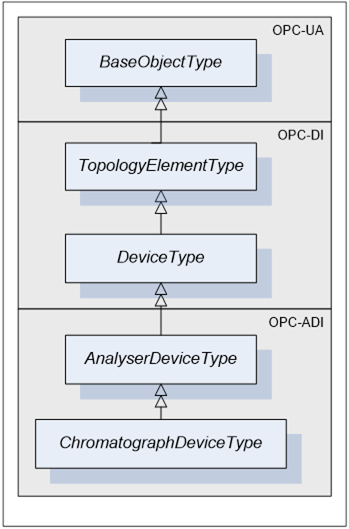
Figure 15 - ChromatographDeviceType
ChromatographDeviceType is a subtype of AnalyserDeviceType
Table 56 - ChromatographDeviceType
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
ChromatographDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The term ChromatographDevice refers to an instance of ChromatographType ObjectType as defined in Table 56.
All ChromatographDevices have Attributes and Properties that they inherit from the AnalyserDeviceType.
StreamType defines seven mandatory FunctionalGroups described in5.2.3.1: Configuration, Status, AcquistionSettings, AcquisitionStatus, AcquisitionData, ChemometricModelSettings, and Context. The following tables describe Parameters defined on the Stream of a ChromatographDevice.
Table 40 describes the Parameters that are organized by the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup of a ChromatographDeviceStreamType.
Table 57 – ChromatographDeviceStreamType AcquisitionData Parameters
|
BrowseName |
Description |
VariableType |
Optional/ Mandatory |
|
ScaledData* |
Chromatogram |
YArrayItemType [] (DataType=Float) |
M |
|
ComponentX |
Component analysed by a chromatograph |
EngineeringValueType (DataType=Float) |
M |
* ScaledData Parameter at this level represents the same Parameter that was defined on StreamType. Since different types of analysers may represent ScaledData differently, it was impossible to declare the VariableType of this Parameter at the StreamType level. It is possible here because the scope of the definition is limited to ChromatographDeviceType. Devices of this type use array of YArrayItemType to represent ScaledData.
The YArrayItem describing the chromatogram has the following behaviors:
- Because the Chromatograph may collect many chromatograms simultaneously, ScaledData is an array of YArrayItem.
- X axis is the time in seconds since the injection time, which is the start of the ExtractSample or ExtractCalibrationSample or ExtractValidationSample state of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine.
- Y axis unit is vendor specific, usually volts at the detector output.
- To reduce data bandwidth, the X axis may not be continuous i.e. when there is no peak, no data is produced. This implies that the xAxisDefinition.axisSteps shall be provided.
- The xAxisDefinition.axisSteps of each chromatogram may be different because the peak positions are different from column to column.
The Chromatograph Component values are mapped using EngineeringValueType and they are placed under the appropriate Stream in the AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup. Annex B provides an example of its sub-elements.
Table 58 describes a gas chromatograph oven Accessory which maintains its set of valves, columns and detectors at the temperature defined by the chromatographic application.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
GCOvenType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AccessoryType defined in 5.2.5. |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
NMRDeviceType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AnalyserDeviceType defined in 5.2.1.1 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The term NMRDevice refers to an instance of NMRDeviceType ObjectType as defined in Table 59.
There is no specific Parameter in NMRStreamType.
The following diagram shows the state and command model for the subclasses of the AnalyserDeviceType, AnalyserChannelType and AccessorySlotType. An AnalyserDeviceType contains a state machine of type AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType. AnalyserChannelType contains a state machine of type AnalyserChannelStateMachineType. AccessorySlotType contains a state machine of type AccessorySlotStateMachineType. (See [OPC 10000-5] for a description of state machines.)
For all state machines defined in this specification, for each self-Transition (where the from-state and to-state are the same) that is used to indicate the progress within a state, the self-Transition shall occur only if the time required to pass through this state exceeds 5 seconds and shall reoccur at 5 (±1) second intervals. The Transition event should include information on the remaining time to complete this state when available
All state machines defined in this specification are mandatory unless explicitly stated otherwise. However, some states may be implemented as transient (do-nothing) states depending on the unique characteristics of an analyser.
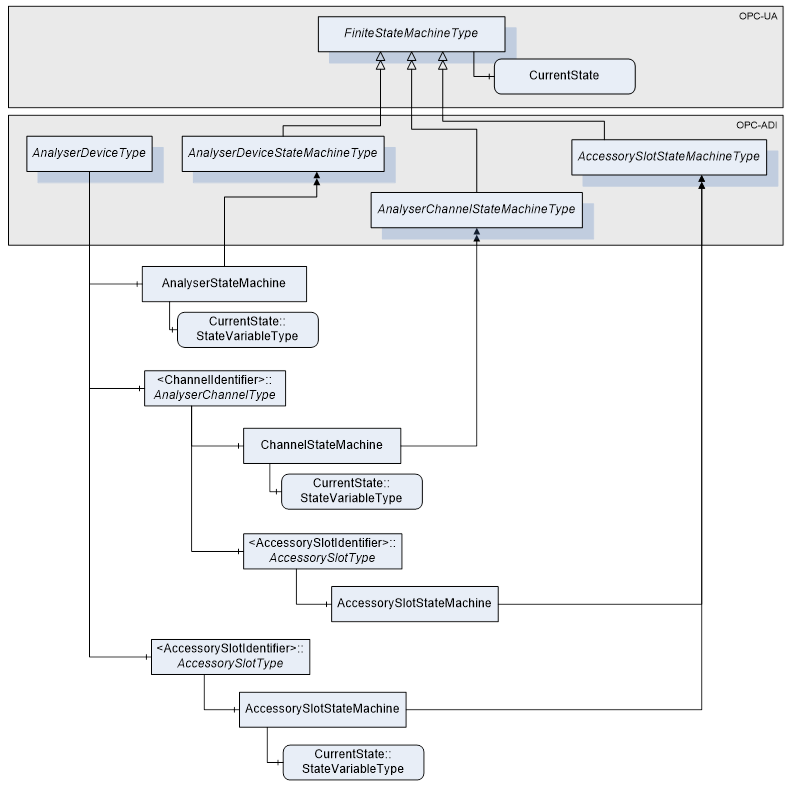
Figure 16 - ADI State Machines
AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType is a subtype of FiniteStateMachineType. The states are derived from the ANSI/ISA TR 88.02-2008 Machine and Unit States Technical Report [ISA-88 TR], which in turn were derived from the OMAC PackML tag definition set and the ANSI/ISA 88 Part 1 standard [ISA-88].
AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType contains a nested state model that defines the top level states Operating, Local and Maintenance (called Modes in [ISA-88 TR] and OMAC) of a device.
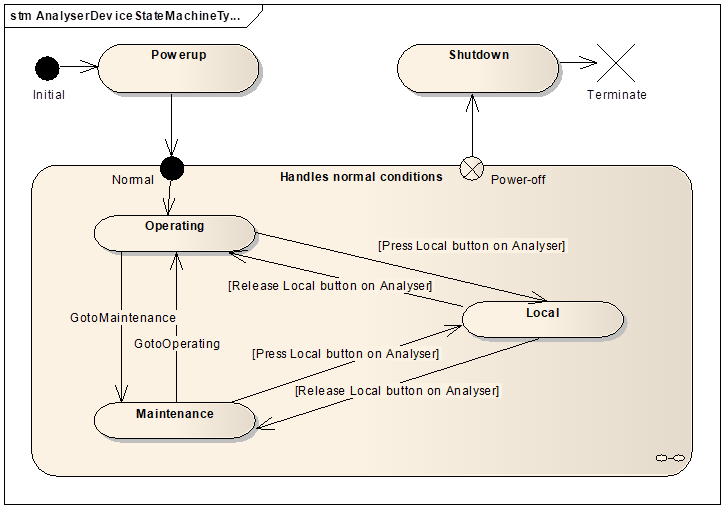
Figure 17 - AnalyserDeviceStateMachine
The Powerup state is where the AnalyserDevice waits for the completion of the power-up setup. Its sub-states are out of scope of the ADI specification.
The Shutdown state is where the AnalyserDevice waits for the completion of the power down sequence. Its sub-states are out of scope of the ADI specification.
AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType.is formally defined in Table 60 .
Table 60 – AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Powerup |
|
InitialStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Operating |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Local |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PowerupToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 61 specifies the AnalyserStateMachine’s State Objects. These State Objects are instances of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. Each State is assigned a unique StateNumber value. Subtypes of the AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType can add References from any state to a subordinate or nested StateMachine Object to extend the FiniteStateMachine.
See Table 62 for a description of the states.
Table 61 – AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType States
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
States |
|||||
|
Powerup |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
100 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PowerupToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
200 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PowerupToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Local |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
300 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
400 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
500 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
A standard set of states are defined for analyser devices. These states represent the operational condition of the device. All devices that contain an AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType must support this base set. A device may or may not require a Client action to cause the state to change, as defined in the state descriptions below.
Table 62 – AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType State Description
|
StateName |
Description |
|
Powerup |
The AnalyserDevice is in its power-up sequence and cannot perform any other task. |
|
Operating |
The AnalyserDevice is in the Operating mode. The ADI Client uses this mode for normal operation: configuration, control and data collection. In this mode, each child AnalyserChannels are free to accept commands from the ADI Client and the Parameter values published in the address space values are expected to be valid. When entering this state, all AnalyserChannels of this AnalyserDevice automatically leave the SlaveMode state and enter their Operating state. |
|
Local |
The AnalyserDevice is in the Local mode. This mode is normally used to perform local physical maintenance on the analyser. To enter the Local mode, the operator shall push a button, on the analyser itself. This may be a physical button or a graphical control on the local console screen. To quit the Local mode, the operator shall press the same or another button on the analyser itself. When the analyser is in Local mode, all child AnalyserChannels sit in the SlaveMode state of the AnalyserChannelStateMachine. In this mode, no commands are accepted from the ADI interface and no guarantee is given on the values in the address space. |
|
Maintenance |
The AnalyserDevice is in the Maintenance mode. This mode is used to perform remote maintenance on the analyser like firmware upgrade. To enter in Maintenance mode, the operator shall call the GotoMaintenance Method from the ADI Client. To return to the Operating mode, the operator shall call the GotoOperating Method from the ADI Client. When the analyser is in the Maintenance mode, all child AnalyserChannels sit in the SlaveMode state of the AnalyserChannelStateMachine. In this mode, no commands are accepted from the ADI interface for the AnalyserChannels and no guarantee is given on the values in the address space. |
|
Shutdown |
The AnalyserDevice is in its power-down sequence and cannot perform any other task. |
The set of states defined to describe an AnalyserDevice can be expanded. Sub-states can be defined for the base states to provide more resolution to the process and to describe the cause and effects of additional stimuli and transitions.
The Operating state of the AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType has no required sub-states.
The Local state of the AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType has no required sub-states.
The Local state provides suitably authorized personnel the ability to operate individual subordinate equipment controls (such as accessory logic) within the device under manual control (often pushbutton or embedded HMI). Such controls in this state may be on a "hold-to-run" basis such that removal of the run signal will cause a device to be stopped. The ability to perform specific functions will be dependent upon mechanical constraints and interlocks. Local state may be of particular use for setting up the machine to work.
The Maintenance state of the AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType has no required sub-states.
The Maintenance state allows suitably authorized personnel the ability to run an individual device independent of other devices that may be in the same production line or lab cell. This would typically be used for faultfinding, device trials or testing operational improvements.
Transitions are instances of Objects of the TransitionType defined in [OPC 10000-5] which also includes the definitions of the ToState, FromState, HasCause, and HasEffect References used. Table 63 specifies the Transitions defined for the AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType. Each Transition is assigned a unique TransitionNumber.
Table 63 – AnalyserDeviceStateMachineType Transitions
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
PowerupToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Powerup |
|
InitialStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Analyser is powering-up |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToLocalTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Local |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Pressing Local button on analyser |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
GotoMaintenance |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Releasing Local button on analyser |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Releasing Local button on analyser |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
GotoOperating |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Local |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Pressing Local button on analyser |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Analyser is powering-down |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Analyser is powering-down |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Analyser is powering-down |
|
|
External cause |
AnalyserChannelStateMachineType is a subtype of FiniteStateMachineType. The states are derived from the ANSI/ISA TR 88.02-2008 Machine and Unit States Technical Report [ISA-88 TR], which in turn were derived from the OMAC PackML tag definition set and the ANSI/ISA 88 Part 1 standard [ISA-88].
AnalyserChannelStateMachineType contains a nested state model that defines the top level states Operating, Local and Maintenance (called Modes in [ISA-88 TR] and OMAC) and the Operating sub-states of a device.
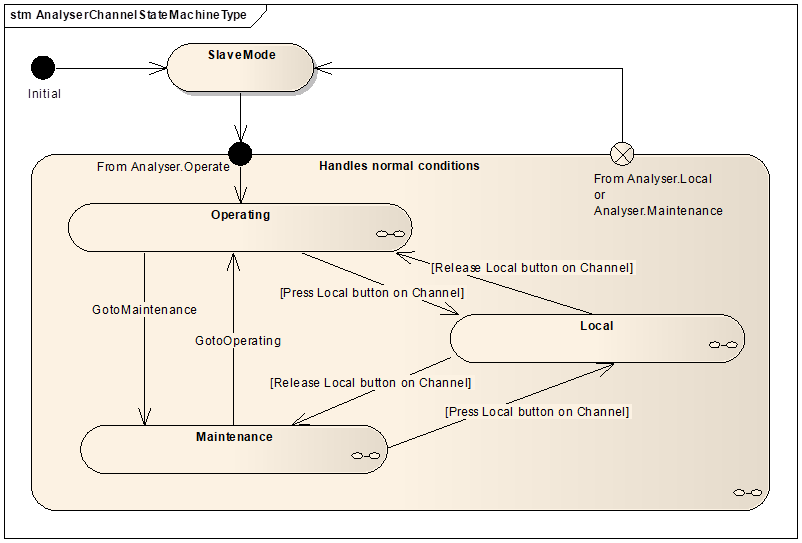
Figure 18 - AnalyserChannelStateMachine
The SlaveMode state is where the AnalyserChannel stays when its parent AnalyserDevice is in Local or Maintenance mode. In this context, the AnalyserDevice has the absolute control over all of its AnalyserChannels.
The Local button refers to a Local button on a given analyser channel for symmetry with the analyser device.
AnalyserChannelStateMachineType.is formally defined in Table 64.
Table 64 – AnalyserChannelStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SlaveMode |
|
InitialStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SlaveModeToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OperatingSubStateMachine |
|
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
LocalSubStateMachine |
|
FiniteStateMachineType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
MaintenanceSubStateMachine |
|
FiniteStateMachineType |
Optional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GotoOperating Method transitions the AnalyserChannel to Operating mode.
GotoMaintenance Method transitions the AnalyserChannel to Maintenance mode.
Table 65 – AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
OperatingSubStateMachine |
|
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
Table 66 – AnalyserChannelLocalStateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModelingRule |
|
Subtype of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
LocalSubStateMachine |
|
FiniteStateMachineType |
Optional |
Table 67 – AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
MaintenanceSubStateMachine |
|
FiniteStateMachineType |
Optional |
Table 69 specifies the AnalyserChannelStateMachine’s State Objects. These State Objects are instances of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. Each State is assigned a unique StateNumber value. Subtypes of the AnalyserChannelStateMachineType can add References from any state to a subordinate or nested StateMachine Object to extend the FiniteStateMachine.
A standard set of states are defined for analyser channels. These states represent the operational condition of the channel. All devices that contain an AnalyserChannelStateMachineType shall support this base set. A channel may or may not require a client action to cause the state to change. See Table 68 for a description of the states.
Table 68 – AnalyserChannelStateMachineType State Description
|
StateName |
Description |
|
SlaveMode |
The AnalyserDevice is in Local or Maintenance mode and all AnalyserChannels are in SlaveMode |
|
Operating |
The AnalyserChannel is in the Operating mode. The ADI Client uses this mode for normal operation: configuration, control and data collection. In this mode, AnalyserChannel can accept commands from the ADI Client and the Parameters published in the address space values are expected to be valid. |
|
Local |
The AnalyserChannel is in the Local mode. This mode is normally used to perform local physical maintenance on the AnalyserChannel. To enter the Local mode, the operator shall push a button, on the AnalyserChannel itself. This may be a physical button or a graphical control on the local console screen. To quit the Local mode, the operator shall press the same or another button on the AnalyserChannel itself. When the AnalyserChannel is in the Local mode, the parent AnalyserDevice has no control over it. In this mode, no commands are accepted from the ADI interface and no guarantee is given on the values in the address space of the AnalyserChannel. |
|
Maintenance |
The AnalyserChannel is in the Maintenance mode. This mode is used to perform remote maintenance on the AnalyserChannel. To enter the Maintenance mode, the operator shall call the GotoMaintenance Method from the ADI Client. To return to the Operating mode, the operator shall call the GotoOperating Method from the ADI Client. When the AnalyserChannel is in the Maintenance mode, the parent AnalyserDevice has no control over it. In this mode, there is no guarantee given on the values in the address space. |
Table 69 – AnalyserChannelStateMachineType States
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
States |
|||||
|
SlaveMode |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
100 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SlaveModeToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
200 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SlaveModeToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OperatingToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Local |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
300 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
LocalToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
400 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
MaintenanceToSlaveModeTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
The set of states defined to describe an AnalyserChannel can be expanded. Sub-states can be defined for the base states to provide more resolution to the process and to describe the cause and effects of additional stimuli and transitions.
Transitions are instances of Objects of the TransitionType defined in [OPC 10000-5] which also includes the definitions of the FromState, ToState, HasCause, and HasEffect References used. Table 70 specifies the Transitions defined for the AnalyserChannelStateMachineType. Each Transition is assigned a unique TransitionNumber.
Table 70 – AnalyserChannelStateMachineType Transitions
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
SlaveModeToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SlaveMode |
|
InitialStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
|
|
|
The AnalyserDevice moves from Local or Maintenance state to Operating state |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToLocalTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Press Local button on channel |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToMaintenanceTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
GotoMaintenance |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Release Local button on channel |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToMaintenanceTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Release Local button on channel |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToOperatingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
GotoOperating |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToLocalTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Press Local button on channel |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OperatingToSlaveModeTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Operating |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
SlaveMode |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
AnalyserDevice moves from Operating to Local or Maintenance state. |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LocalToSlaveModeTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Local |
|
AnalyserChannelLocalStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
SlaveMode |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
AnalyserDevice moves from Operating to Local or Maintenance state. |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaintenanceToSlaveModeTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Maintenance |
|
AnalyserChannelMaintenanceStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
SlaveMode |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
AnalyserDevice moves from Operating to Local or Maintenance state. |
|
|
External cause |
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType is a subtype of FiniteStateMachineType. The states are derived from the ANSI/ISA TR 88.02-2008 Machine and Unit States Technical Report [ISA-88 TR], which in turn were derived from the OMAC PackML tag definition set and the ANSI/ISA 88 Part 1 standard.
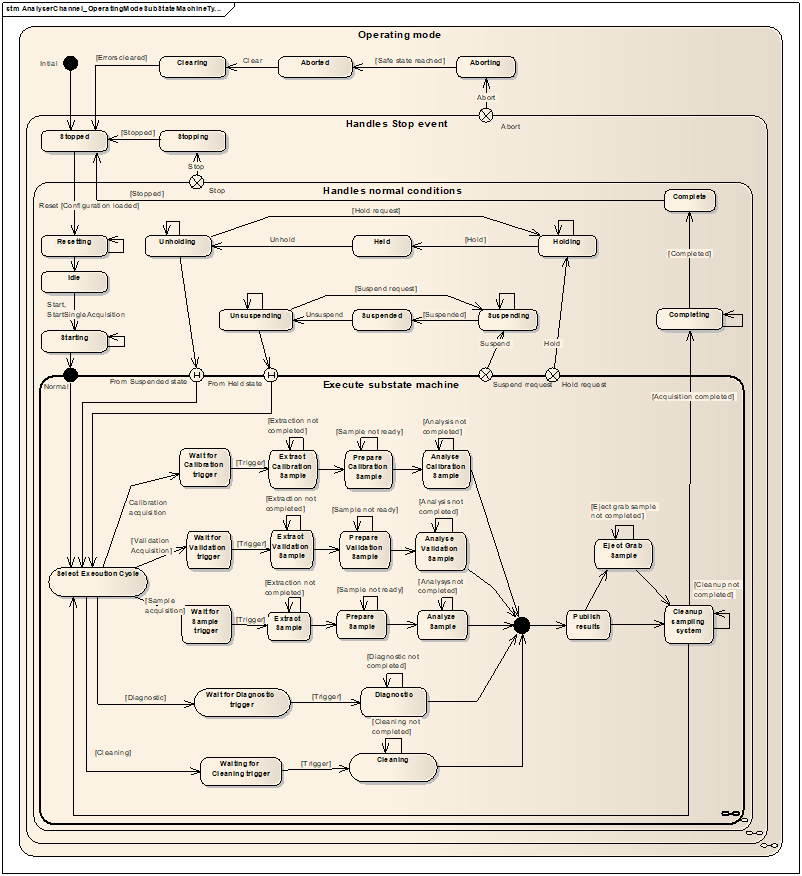
Figure 19 - AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType
When the AnalyserChannel is suspended or held:
- The normal Execute state is interrupted
- The actual Execute sub-state information shall be kept
When returning from Suspended or Held state:
- The restart point in Execute state shall be the junction point driven by the SelectExecutionCycle
- All sub-states shall be executed, but the vendor may use the information stored at the interruption point to optimize the execution of some sub-states.
The AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 71.
Table 71 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
Target Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Stopped |
|
InitialStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Idle |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Starting |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Execute |
|
AnalyserChannelOperatingModeExecuteStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Completing |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Complete |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Holding |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Held |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Clearing |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StoppedToResettingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ResettingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ResettingToIdleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToStartingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StartingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StartingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteToCompletingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompletingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompletingToCompleteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompleteToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteToHoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HoldingToHeldTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HeldToUnholdingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnholdingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnholdingToHoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnholdingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteToSuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendingToSuspendedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToUnsuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnsuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnsuspendingToSuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnsuspendingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StoppingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AbortingToAbortedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AbortedToClearingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ClearingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ResettingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StartingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompletingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompleteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnsuspendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HoldingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HeldToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnholdingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StoppedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ResettingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StartingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompletingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CompleteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnsuspendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HoldingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
HeldToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
UnholdingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
StoppingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExecuteSubStateMachine |
|
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
Table 72 – AnalyserChannelOperatingModeExecuteStateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannelOperatingModeExecuteStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
ExecuteSubStateMachine |
|
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType |
Mandatory |
Table 74 specifies the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType’s State Objects. These State Objects are instances of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. Each State is assigned a unique StateNumber value. Subtypes of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType can add References from any state to a subordinate or nested StateMachine Object to extend the FiniteStateMachine.
A standard set of states are defined for the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType. These states represent the operational condition of the AnalyserChannel in Operating mode. All AnalyserChannels that contain an AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType must support this base set. A device may or may not require a Client action to cause the state to change. See Table 73 for the description of the states.
Table 73 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType State Descriptions
|
State No. |
StateName |
Description |
|
1 |
Clearing |
Initiated by Clear Method call, this state clears faults that may have occurred when Aborting and are present in the Aborted state before proceeding to a Stopped state. This state guarantees that the Client will see fault signals before going back to Stopped state. |
|
2 |
Stopped |
This is the initial state after AnalyserDeviceStateMachine state Powerup. At this point:
|
|
3 |
Starting |
The analyser has received the Start or StartSingleAcquisition Method call and it is preparing to enter in Execute state. At this point: The analyser system shall be ready to start. Prepare the system for continuous acquisition. When completed, the state machine automatically goes in Execute state. |
|
4 |
Idle |
At the beginning of this state:
|
|
5 |
Suspended |
The analyser or channel may be running but no results are being generated while the analyser or channel is waiting for external process conditions to return to normal. When the offending process conditions return to normal, the Suspended state will transition to Unsuspending and hence continue towards the normal Execute state. At this state, no acquisition cycle is performed. Note: The Suspended state can be reached as a result of abnormal external process conditions and differs from Held in that Held is typically a result of an operator request or an automatically detected analyser or channel fault condition that should be corrected before an operator request to transition to the Unholding state will be processed.
|
|
6 |
Execute
|
All repetitive acquisition cycles are done in this state:
See AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine for more details. |
|
7 |
Stopping |
Initiated by a Stop Method call, this state:
Transitions automatically to Aborted state. |
|
8 |
Aborting |
The Aborting state can be entered at any time in response to the Abort command or on the occurrence of a machine fault. The aborting logic will bring the device to a rapid safe stop. Operation of an Emergency Stop may cause the machine to be tripped by its safety system and may provide a signal to initiate the Aborting State.This state may include:
All error conditions are saved and exposed in the AnalyserDevice/Channel.Status FunctionalGroup. Transitions automatically to Aborted state. |
|
9 |
Aborted |
This state maintains machine status information relevant to the Abort condition. The analyser is in safe state and:
The analyser can only exit the Aborted state after an explicit Clear Method call, often after manual intervention to correct and reset the detected device fault.
|
|
10 |
Holding
|
When the analyser or channel is in the Execute state, the Hold command can be used to start Holding logic which brings the analyser or channel to a controlled stop or to a state which represents Held for the particular unit control mode. An analyser or channel can go into this state either when an internal equipment fault is automatically detected or by an operator command. The Hold command offers the operator a safe way to intervene manually in the process (such as replacing solvent container) and restarting execution when conditions are safe. |
|
11 |
Held
|
The Held state holds the analyser or channel's operation. At this state, no acquisition cycle is performed.
|
|
12 |
Unholding
|
The Unholding state is a response to an operator command to resume the Execute state. Issuing the Unhold Method call will prepare the analyser or channel to re-enter the normal Execute state. The actions of this state may include:
Note that an operator Unhold command is always required and Unholding can never be initiated automatically. |
|
13 |
Suspending |
This state is a result of a change in monitored conditions due to process conditions or factors. The trigger event will cause a temporary suspension of the Execute state. Suspending is typically the result of starvation of the process to analyse or or issues with the sampling system that prevents the analyser or channel from continued Execution. During the controlled sequence of Suspending the analyser or channel will transition to a Suspended state. The Suspending state might be forced by the operator using the Suspend Method call. |
|
14 |
Unsuspending
|
This state is a result of a device request from Suspended state to transition back to the Execute state by calling the Unsuspend Method. The actions of this state may include:
This state is entered prior to the Execute state, and prepares the analyser or channel for the Execute state. |
|
15 |
Resetting
|
This state is the result of a Reset or SetConfiguration Method call from the Stopped state. The Parameters are committed at this state. The actions of this state may include:
When completed, the state machine goes automatically to the Idle state. |
|
16 |
Completing
|
This state is an automatic or commanded exit from the Execute state. Normal operation has run to completion, i.e. the requested number of samples has been analysed. At this point, the pre-configured acquisition cycle(s) are completed. The actions of this state may include:
When done, it automatically transitions to the Complete state. |
|
17 |
Complete |
At this point, the Completing state is done and it transitions automatically to Stopped state to wait. From an analyser point of view, this is almost a transient state. |
Table 74 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType States
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
States |
|||||
|
Stopped |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
CompleteToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
StoppingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
ClearingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StoppedToResettingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StoppedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resetting |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
15 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
StoppedToResettingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ResettingToIdleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ResettingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ResettingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ResettingToIdleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
IdleToStartingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
idleToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
IdleToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Starting |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
IdleToStartingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StartingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StartingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StartingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Execute |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
StartingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ExecuteToCompletingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ExecuteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ExecuteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Completing |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
16 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExecuteToCompletingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompletingToCompleteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompletingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompletingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Complete |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
17 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
CompletingToCompleteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompleteToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompleteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
CompleteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suspending |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
13 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExecuteToSuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendingToSuspendedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Suspended |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendingToSuspendedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendedToUnsuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendedToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
SuspendiedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unsuspending |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
14 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendedToUnsuppendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnsuppendingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnsuppendingToSuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnsuppendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnsuppendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Holding |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExecuteToHoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HoldingToHeldTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HoldingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HoldingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Held |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
11 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
HoldingToHeldTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HeldToUnholdingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HeldToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
HeldToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Unholding |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
12 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
HeldToUnholdingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnholdingToExecuteTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnholdingToHoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnholdingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
UnholdingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stopping |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ResettingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
IdleToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
StartingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
ExecuteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
CompletingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
CompleteToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendedToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
UnsuspendingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
HoldingToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
HeldToStoppingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StoppingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
StoppingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aborting |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
StoppingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
StoppedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
ResettingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
IdleToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
StartingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
ExecuteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
CompletingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
CompleteToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
SuspendedToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
UnsuspendingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
HoldingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
HelpToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
FromTransition |
UnholdingToAbortingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
AbortingToAbortedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aborted |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
AbortingToAbortedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
AbortedToClearingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clearing |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
AbortedToClearingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
|
|
ToTransition |
ClearingToStoppedTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Method |
The set of states defined to describe in AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType can be expanded. Sub-states can be defined for the base states to provide more resolution to the process and to describe the cause and effects of additional stimuli and transitions. For example, the “Stopped” state can include the sub states “Preparing” and “Done” to indicate if the function is still preparing the device or if it has completed preparation
Transitions are instances of Objects of the TransitionType defined in [OPC 10000-5] which also includes the definitions of the ToState, FromState, HasCause, and HasEffect References used. Table 75 specifies the Transitions defined for the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachineType. Each Transition is assigned a unique TransitionNumber.
Table 75 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachine Transitions
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
StoppedToResettingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Stopped |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Reset |
|
Method |
|
|
|
HasCause |
SetConfiguration |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ResettingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ResettingToIdleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Idle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IdleToStartingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Idle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Start |
|
Method |
|
|
|
HasCause |
StartSingleAcquisition |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StartingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StartingToExecuteTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExecuteToCompletingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompletingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompletingToCompleteTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Complete |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompleteToStoppedTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Complete |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopped |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExecuteToHoldingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
11 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Hold |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HoldingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
12 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HoldingToHeldTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
13 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Held |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HeldToUnholdingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
14 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Held |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Unhold |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnholdingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
15 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnholdingToHoldingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
16 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Hold |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnholdingToExecuteTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
17 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExecuteToSuspendingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
18 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Suspend |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
19 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendingToSuspendedTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
20 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendedToUnsuspendingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
21 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Unsuspend |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnsuspendingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
22 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnsuspendingToSuspendingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
23 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Suspend |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnsuspendingToExecuteTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
24 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StoppingToStoppedTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
25 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopped |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AbortingToAbortedTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
26 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AbortedToClearingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
27 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Clearing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Clear |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ClearingToStoppedTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
28 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Clearing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopped |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ResettingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
29 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IdleToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
30 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Idle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StartingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
31 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExecuteToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
32 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompletingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
33 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompleteToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
34 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Complete |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
35 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendedToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
36 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnsuspendingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
37 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HoldingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
38 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HeldToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
39 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Held |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnholdingToStoppingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
40 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Stop |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StoppedToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
41 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Stopped |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ResettingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
42 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Resetting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IdleToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
43 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Idle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StartingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
44 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Starting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExecuteToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
45 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Execute |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompletingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
46 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Completing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CompleteToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
47 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Complete |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
48 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendedToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
49 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnsuspendingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
50 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unsuspending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HoldingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
51 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Holding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HeldToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
52 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Held |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
UnholdingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
53 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Unholding |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
StoppingToAbortingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
54 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Abort |
|
Method |
|
The Reset transition specifies the Transition from the Complete or Stopped to the Resetting State. It may be caused by the Reset Method or by the SetConfiguration Method.
The Start transition specifies the Transition from the Idle to the Starting State. It may be caused by the Start Method.
The Stop transition specifies the Transition from the Stopping, Idle, Resetting, Unholding, Starting, Unsuspending, Held, Execute, Suspend, Holding, Completing, Suspending, or Complete to the Stopping State. It may be caused by the Stop Method.
The Hold transition specifies the Transition from the Unholding or Execute to the Holding State. It may be caused by the Hold Method.
The Unhold transition specifies the Transition from the Held to the Unholding State. It may be caused by the Unhold Method.
The Suspend transition specifies the Transition from the Unsuspending or Execute to the Suspending State. It may be caused by the Suspend Method.
The Abort transition specifies the Transition from the Stopping, Idle, Resetting, Unholding, Starting, Unsuspending, Held, Execute, Suspend, Holding, Completing, Suspending, Complete, Clearing, Stopped, or Stopping to the Aborting State. It may be caused by the Abort Method.
The Clear transition specifies the Transition from the Aborted to the Clearing State. It may be caused by the Clear Method.
The Complete transition specifies the Transition from the Execute to the Completing State.
The AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType describes the sub-states of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeStateMachine state Execute. Figure 20 illustrates components of AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType.
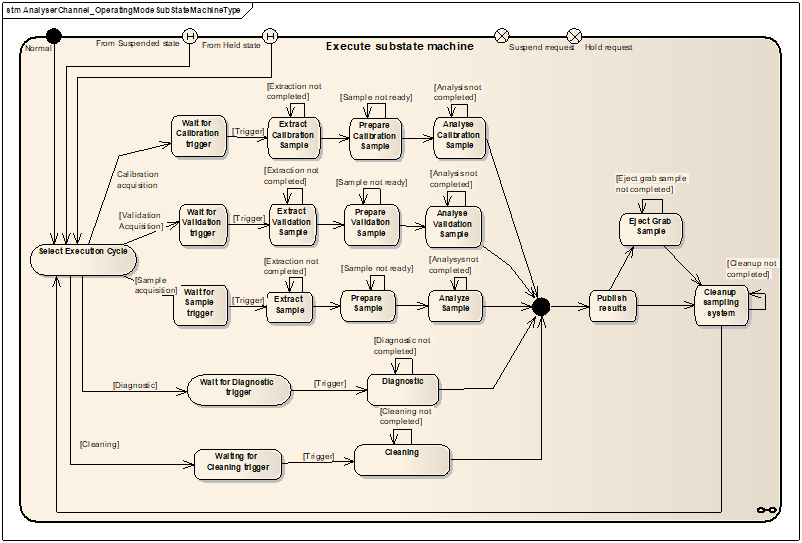
Figure 20 - AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 76.
Table 76 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSub StateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSub StateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
Type Definition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
InitialStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForCalibrationTrigger |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForValidationTrigger |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractValidationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareValidationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseValidationSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForSampleTrigger |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForDiagnosticTrigger |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Diagnostic |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForCleaningTrigger |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Cleaning |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
EjectGrabSample |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCalibrationTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForCalibrationTriggerToExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractCalibrationSampleToPrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareCalibrationSampleToAnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseCalibrationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForTriggerValidationTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForValidationTriggerToExtractValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractValidationSampleToPrepareValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareValidationSampleToAnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseValidationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForSampleTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForSampleTriggerToExtractSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ExtractSampleToPrepareSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PrepareSampleToAnalyseSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AnalyseSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForDiagnosticTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForDiagnosticTriggerToDiagnosticTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
DiagnosticTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
DiagnosticToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCleaningTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
WaitForCleaningTriggerToCleaningTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CleaningTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CleaningToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PublishResultsToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PublishResultsToEjectGrabSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
EjectGrabSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
EjectGrabSampleToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
CleanupSamplingSystemToSelectExecutionCycleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
Table 78 specifies the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine’s State Objects. These State Objects are instances of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. Each State is assigned a unique StateNumber value. Subtypes of the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType can add References from any state to a subordinate or nested StateMachine Object to extend the FiniteStateMachine.
A standard set of sub-states are defined for AnalyseChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType. These sub-states represent the operational condition of the AnalyseChannel_OperatingModeSubStateMachine Execute state. All the sub-states must be supported, though they can be transient states.
Table 77 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSub StateMachineType State Descriptions
|
StateName |
Description |
|
SelectExecutionCycle |
This pseudo-state is used to decide which acquisition path shall be taken. This decision is made using a Parameter ExecutionCycle that can be:
The state machine waits at this state until the underlying system is ready to take a given acquisition path. |
|
WaitForCalibrationTrigger |
Wait until the analyser channel is ready to perform the Calibration acquisition cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
ExtractCalibrationSample |
Collect / setup the sampling system to perform the acquisition cycle of a Calibration cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
PrepareCalibrationSample |
Prepare the Calibration sample for the AnalyseCalibrationSample state ,for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
Perform the analysis of the Calibration Sample, for example:
|
|
WaitForValidationTrigger |
Wait until the analyser channel is ready to perform the Validation acquisition cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
ExtractValidationSample |
Collect / setup the sampling system to perform the acquisition cycle of a Validation cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
PrepareValidationSample |
Prepare the Validation sample for the AnalyseValidationSample state ,for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
AnalyseValidationSample |
Perform the analysis of the Validation Sample, for example:
|
|
WaitForSampleTrigger |
Wait until the analyser channel is ready to perform the Sample acquisition cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
ExtractSample |
Collect the Sample from the process, for example:
Some analyser probes do not need to extract the Sample from the process, for example a NIR reflectance probe. In this case, this state is a pass-through. |
|
PrepareSample |
Prepare the Sample for the AnalyseSample state, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
AnalyseSample |
Perform the analysis of the Sample, for example:
|
|
WaitForDiagnosticTrigger |
Wait until the analyser channel is ready to perform the Diagnostic cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
Diagnostic |
Perform the Diagnostic cycle. This cycle is a placeholder allowing the analyser vendor to extend this state to represent vendor specific analyser diagnostic cycles. |
|
WaitForCleaningTrigger |
Wait until the analyser channel is ready to perform the cleaning acquisition cycle, for example:
For analysers that do not need the step, the state is transient. |
|
Cleaning |
Perform the cleaning cycle. |
|
PublishResults |
Publish the results of the previous acquisition cycle. When the transition from PublishResults to CleanupSamplingSystem occurs, all results must be available. |
|
EjectGrabSample |
The Sample that was just analysed is ejected from the system to allow the operator or another system to grab it and send it to a control lab for example. |
|
CleanupSamplingSystem |
Cleanup the sampling sub-system to be ready for the next acquisition, for example:
For in-process probes, this state is transient. |
The set of states defined to describe an AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachine can be expanded. Sub-states can be defined for the base states to provide more resolution to the process and to describe the cause and effects of additional stimuli and transitions. See Table 77 for a description of the states.
ExecutionCycle, ExecutionCycleSubcode and ActiveStream Parameters are set during the SelectExecutionCycle state. From the end of SelectExecutionCycle to the end of CleanupSamplingSystem, these two Parameters shall not change.
ExecutionCycle, ExecutionCycleSubcode, ActiveStream and IsActive Parameters are set during the SelectExecutionCycle state. From the end of SelectExecutionCycle to the end of CleanupSamplingSystem, these two Parameters shall not change.
WaitForxxxTrigger states represent waiting for situation like:
•External input i/o visible or not in the address space
•Internal timer (visible or not in the address space)
Table 78 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSub StateMachineType States
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
|
|
States |
|||||
|
SelectExecutionCycle |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
100 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
CleanupSamplingSystemToSelectExecutionCycleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCalibrationTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForValidationTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForSampleTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForDiagnosticTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCleaningTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToHoldingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToSuspendingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForCalibrationTrigger |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
200 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCalibrationTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
WaitForCalibrationTriggerTo ExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractCalibrationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
300 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
WaitForCalibrationTriggerToExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
ExtractCalibrationSampleToPrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareCalibrationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
400 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExtractCalibrationSampleToPrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PrepareCalibrationSampleToAnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
500 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PrepareCalibrationSampleToAnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
AnalyseCalibrationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForValidationTrigger |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
600 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForValidationTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
WaitForValidationTriggerToExtractValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractValidationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
700 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
WaitForValidationTriggerToExtractValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
ExtractValidationSampleToPrepareValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareValidationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
800 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExtractValidationSampleToPrepareValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PrepareValidationSampleToAnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseValidationSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
900 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PrepareValidationSampleToAnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
AnalyseValidationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForSampleTrigger |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1000 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForSampleTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
WaitForSampleTriggerToExtractSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1100 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
WaitForSampleTriggerToExtractSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
ExtractSampleToPrepareSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1200 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ExtractSampleToPrepareSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PrepareSampleToAnalyseSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1300 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PrepareSampleToAnalyseSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
AnalyseSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForDiagnosticTrigger |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1400 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForDiagnosticTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
WaitForDiagnosticTriggerToDiagnosticTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1500 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
WaitForDiagnosticTriggerToDiagnosticTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
DiagnosticToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForCleaningTrigger |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1600 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCleaningTriggerTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
WaitForCleaningTriggerToCleaningTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cleaning |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1700 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
WaitForCleaningTriggerToCleaningTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
CleaningToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PublishResults |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1800 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
AnalyseCalibrationToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
AnalyseValidationToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
AnalyseSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
DiagnosticToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
CleaningToPublishResultsTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PublishResultsToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PublishResultsToEjectGrabSampleSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EjectGrabSample |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
1900 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PublishResultsToEjectGrabSampleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
EjectGrabSampleToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CleanupSamplingSystem |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
2000 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PublishResultsToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
EjectGrabSampleToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
CleanupSamplingSystemToSelectExecutionCycleTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
Transitions are instances of Objects of the TransitionType defined in [OPC 10000-5] which also includes the definitions of the ToState, FromState, HasCause, and HasEffect References used. Table 79 specifies the Transitions defined for the AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType. Each Transition is assigned a unique TransitionNumber.
Table 79 – AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSub StateMachine Transitions
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCalibrationTriggerTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
WaitForCalibrationTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForCalibrationTriggerToExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
WaitForCalibrationTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Trigger received |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractCalibrationSampleToPrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareCalibrationSampleToAnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseCalibrationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseCalibrationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseCalibrationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForValidationTriggerTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
WaitForValidationTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForValidationTriggerToExtractValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
WaitForValidationTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Trigger received |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
11 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractValidationSampleToPrepareValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
12 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
13 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareValidationSampleToAnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
14 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseValidationSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
15 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseValidationSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
16 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseValidationSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitFoSampleTriggerTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
17 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
WaitFoSampleTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForSampleTriggerToExtractSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
18 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
WaitForSampleTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Trigger received |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
19 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
ExtractSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ExtractSampleToPrepareSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
20 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
ExtractSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
21 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PrepareSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PrepareSampleToAnalyseSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
22 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PrepareSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
23 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
AnalyseSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AnalyseSampleToPublishResultsTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
24 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
AnalyseSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForDiagnostic TriggerTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
25 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
WaitForDiagnostic Trigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForDiagnosticTriggerToDiagnosticTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
26 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
WaitForDiagnosticTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Diagnostic |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Trigger received |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DiagnosticTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
27 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Diagnostic |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Diagnostic |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DiagnosticToPublishResultsTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
28 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Diagnostic |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SelectExecutionCycleToWaitForCleaningTriggerTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
29 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
WaitForCleaningTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WaitForCleaningTriggerToCleaningTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
30 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
WaitForCleaningTrigger |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Cleaning |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Trigger received |
|
|
External cause |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CleaningTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
31 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Cleaning |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Cleaning |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CleaningToPublishResultsTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
32 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Cleaning |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PublishResultsToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
33 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PublishResultsToEjectGrabSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
34 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
PublishResults |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
EjectGrabSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EjectGrabSampleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
35 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
EjectGrabSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
EjectGrabSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EjectGrabSampleToCleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
36 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
EjectGrabSample |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CleanupSamplingSystemTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
37 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CleanupSamplingSystemToSelectExecutionCycleTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
38 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
CleanupSamplingSystem |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
SelectExecutionCycle |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Configured acquisition is not completed |
|
|
External cause |
There are no Methods defined for AnalyserChannel_OperatingModeExecuteSubStateMachineType.
This specification does not define any sub-states for the AnalyserChannel_LocalModeSubStateMachineType.
This specification does not define any sub-states for the AnalyserChannel_MaintenanceModeSubStateMachineType.
The AccessorySlotStateMachine describes the behaviour of an AccessorySlot when a physical accessory is inserted or removed.
Figure 21 illustrates components of the AccessorySlotStateMachineType.
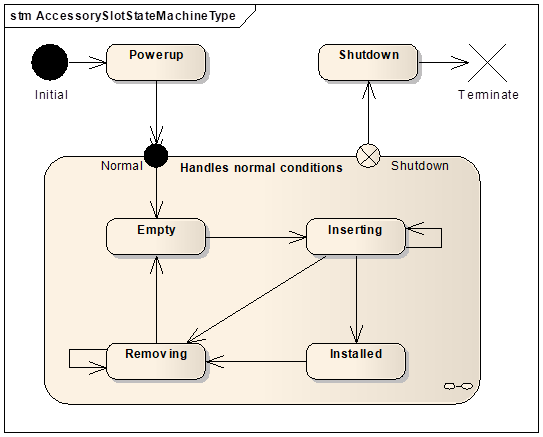
Figure 21 – AccessorySlotStateMachineTypeMachineType
If the accessory is not hot swappable or the accessory is already installed when the AnalyserDevice is powered-on the Inserting state becomes transient but remains present.
AccessorySlotStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 80.
Table 80 – AccessorySlotStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all Attributes specified for the FiniteStateMachineType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AccessorySlotStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Powerup |
|
InitialStateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Empty |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Installed |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Removing |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
PowerupToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
EmptyToInsertingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InsertingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InsertingToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InsertingToInstalledTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InsttalledToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
RemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
RemovingToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
EmptyToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InsertingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
InstalledToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
RemovingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
Mandatory |
This specification does not define any Methods, which cause transitions in the AccessorySlotStateMachineType. Transitions occur as a result of two external causes:
- Accessory insertion
- Accessory removal
Table 82 specifies the AccessorySlotStateMachine’s State Objects. These State Objects are instances of the StateType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. Each State is assigned a unique StateNumber value. Subtypes of the AccessorySlotStateMachineType can add References from any state to a subordinate or nested StateMachine Object to extend the FiniteStateMachine.
A standard set of states are defined for AccessorySlots. These states represent the operational condition of the AccessorySlot. All AccessorySlots must support this base set. See Table 81 for the descriptions of the states.
Table 81 – AccessorySlotStateMachineType State Descriptions
|
StateName |
Description |
|
Powerup |
The AccessorySlot is in its power-up sequence and cannot perform any other task. |
|
Empty |
This represents an AccessorySlot where no Accessory is installed. |
|
Inserting |
This represents an AccessorySlot when an Accessory is being inserted and initializing. |
|
Installed |
This represents an AccessorySlot where an Accessory is installed and ready to use |
|
Empty |
This represents an AccessorySlot where no Accessory is installed. |
|
Shutdown |
The AccessorySlot is in its power-down sequence and cannot perform any other task. |
The set of states defined to describe an AccessorySlot can be expanded. Sub-states can be defined for the base states to provide more resolution to the process and to describe the cause and effects of additional stimuli and transitions. See Table 82 for the definitions of the states.
Table 82 – AccessorySlotStateMachineType States
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target TypeDefinition |
Notes |
|
States |
|||||
|
Powerup |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
100 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
PowerupToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Empty |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
200 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
PowerupToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
RemovingToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
EmptyToInsertingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
EmptyToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inserting |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
300 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
EmptyToInsertingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
InsertingToInstalledTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
InsertingToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
InsertingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Installed |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
400 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
InsertingToInstalledTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
InstalledToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
InstalledToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Removing |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
500 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
InsertingToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
InstalledToRemovingTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
RemovingToEmptyTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
RemovingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shutdown |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
600 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
EmptyToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
InsertingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
InstalledToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
RemovingToShutdownTransition |
|
TransitionType |
|
Table 83 specifies the Transitions defined for the AccessorySlotStateMachineType. Each Transition is assigned a unique TransitionNumber.
Table 83 – AccessorySlotStateMachineType Transitions
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target Type Definition |
Notes |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
PowerupToEmptyTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
1 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Powerup |
|
InitialStateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Empty |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EmptyToInsertingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
2 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Empty |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InsertingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
3 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InsertingToRemovingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
4 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InsertingToInstalledTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Installed |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InstalledToRemovingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Installed |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RemovingTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RemovingToEmptyTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Empty |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
EmptyToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Empty |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InsertingToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Inserting |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
InstalledToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
11 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Installed |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RemovingToShutdownTransition |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
12 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Removing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Shutdown |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[OPC 10000-8] defines a DataItem as a link to arbitrary, live automation data, i.e. data that represents currently valid information. Examples of such data are: device data (such as temperature sensors), calculated data, status information (open/closed, moving), dynamically-changing system data (such as stock quotes), and diagnostic data.
AnalogItems are DataItems that represent continuously-variable physical quantities. Typical examples are the values provided by temperature sensors or pressure sensors. OPC UA defines AnalogItemType VariableType to identify an AnalogItem.
The ADI Information Model extends the Variable model defined in OPC UA specification [OPC 10000-3], [OPC 10000-5] and [OPC 10000-8], It introduces VariableTypes, which are specifically utilized for the process analytical domain.
Parameters which hold simple data like a single numerical value, string value or a time-stamp value are represented by BaseDataVariableType defined in [OPC 10000-5] or one of its subtypes.
For more details see paragraph C.1.
Parameters which hold array data that may be acquired during normal analyser operation or used as inputs (e.g. background, calibration) are represented by VariableTypes, which are direct subtypes of DataItemType and described in [OPC 10000-8].
For more details on DataItemType and its relationship with ADI Parameters see paragraph C.2
The EngineeringValue Variables are used to expose key results of an analyser and the associated values that qualified it. This type helps the Client quickly identify important values. For example, the concentration of a given chemical and the associated confidence factors like the F-Ratio from the PLS model. EngineeringValueType is formally defined in Table 84
Table 84 – EngineeringValueType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
EngineeringValueType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the DataItemType defined in [OPC 10000-8] |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
<Identifier> |
|
DataItemType |
OptionalPlaceHolder |
|
The Value Attribute of the EngineeringValue is the main value, for example, the concentration. Its HasComponent elements are there to qualify or describe this value. For example the associated confidence factors like F-Ratio from the PLS model.
The ChemometricModel Variables are used to hold the descriptions of a mathematical process and associated information to convert scaled data into one or more process values. ChemometricModelType is formally defined in Table 85.
All ChemometricModel Variables are located in the ChemometricModelSettings FunctionalGroup on a Stream.
Table 85 – ChemometricModelType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||||
|
BrowseName |
ChemometricModelType |
||||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
||
|
Subtype of the BaseDataVariableType defined in [[OPC 10000-3] |
|||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Name |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
CreationDate |
DateTime |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ModelDescription |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
HasInput |
Variable |
<User defined Input#> |
|
BaseVariableType |
MandatoryPlaceholder |
||
|
HasOutput |
Variable |
<User defined Output#> |
|
BaseVariableType |
MandatoryPlaceHolder |
||
Name is a descriptive name of the chemometric model itself e.g. XYZ_Moisture_V1.0.
CreationDate is the creation date of the chemometric model.
ModelDescription is a localized string describing the chemometric model itself e.g. Predict the moisture in powder XYZ.
HasInput is a subtype of HasOrderedComponent Reference which points to a Variable, defined in the Analyser Server address space, which is used as input for the chemometric model prediction. As a general rule, the target of HasInput is not instantiated at the ChemometricModel instantiation because it already exists elsewhere in the address space.
HasOutput is a subtype of HasOrderedComponent Reference which points to a Variable that is updated when the chemometric model is executed. As a general rule, the target of HasOutput is instantiated at the model instantiation because it is generated by the model itself. Often, the target of this HasOuput Reference is also the target of “Source” Reference of ProcessVariable.
Table 86 summarizes constraints on Variable Attributes and Properties for ChemometricModelType. For a complete set of Attributes see [OPC 10000-3], section 5.6.2.
Table 86 - Setting OPC UA Variable Attributes and Properties for ChemometricModelType
|
Attributes/Properties |
Description |
|
Value |
Binary blob containing all elements of the chemometric model |
|
DataType |
ByteString |
|
ValueRank |
Always set to -1 (Scalar) |
|
ArrayDimensions |
Not applicable |
The ProcessVariables are used to provide a stable address space view from the user point of view even if the Analyser Server address space changes, after the new configuration is loaded. This is important to simplify integration with systems like DCS or LIMS that often require a stable mapping.
All ProcessVariable Variables are most of the time located in the Stream AcquisitionData FunctionalGroup. The location of the ProcessVariable can be found with these prioritized rules:
1) The location of a ProcessVariable shall remain constant between configurations. For example, if the number of Streams changes from one configuration to the other, the ProcessVariables shall be pushed one level up to the AnalyserChannel.
2) ProcessVariable should be located in the same FunctionalGroup as its Source.
The following bullets describe how the above rules should be applied to common scenarios:
- A typical lab analyser has one AnalyserChannel and one sample holder, which translates to a single Stream. In this case, ProcessVariables shall be located at the Stream level.
- A process analyser attached to a multi-port vessel with a fixed hardware setting, in this case also, ProcessVariables shall be located at the Stream level.
- A process analyser is installed on a dolly and can be attached to different vessels for diagnostic purposes. In this case, the number of Streams is likely to change from configuration to configuration. ProcessVariables shall be pushed to least AnalyserChannel level.
- An analyser publishes only a few values through ProcessVariables to mimic a legacy system. In this case, it may make sense to place ProcessVariables at the AnalyserDevice level.
- In gas chromatographs, new Chromatographic Applications (software AnalyserChannels) may be added over the time and similarly new Streams may be added or removed. Because these operations usually require hardware addition and they do not happen very often, it is strongly recommended to apply rule 2) to ensure the consistent way in which the control system views the gas chromatograph.
When a ProcessVariable is linked with another Variable through the Source Reference, it is the Server’s responsibility to copy and maintain in sync the following Attributes and Properties from the Source target:
- Attributes: Value, DataType, ValueRank, ArrayDimensions, AccessLevel, UserAccessLevel, MinimumSamplingInterval
- Standard Properties: TimeZone, DayLightSavingTime, DictionaryFragment, AllowNulls if they are present.
Knowing that the ProcessVariables are used to exchange values with control system, it is a good practice to keep the DataType, ValueRank and ArrayDimensions consistent between configurations.
Also, when the Server responds to read or Subscription Services, the returned DataValue shall be the same for both the ProcessVariable and the Variable pointed by the Source Reference, especially the StatusCode, value and SourceTimestamp.
ProcessVariableType is formally defined in Table 87.
Table 87 – ProcessVariableType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
ProcessVariableType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the DataItemType defined in [[OPC 10000-8] |
||||||
|
HasDataSource |
Variable |
<Source> |
|
DataItemType (DataType defined by Source Variable) |
Mandatory |
|
Source is a Reference that usually points to an output Variable of a model but it is allowed to point to another Variable. The DataType of the ProcessVariable shall be the same as the one pointed by Source Reference.
The following paragraphs define the data types introduced by the ADI Information Model.
Enumeration is used to represent a Parameter value that has a limited set of possible numeric values, each of which has a descriptive name. All Parameters of this kind are instances of DataItemType VariableType. The following definitions describe the values of the EnumString Property for those Parameters for the English locale (LocaleId=en).
ExecutionCycleEnumeration describes the type of acquisition cycle performed on a stream, in progress or completed.
Table 88 – ExecutionCycleEnumeration states
|
Seq. number |
EnumString |
Description |
|
0 |
IDLE_0 |
No acquisition cycle in progress |
|
1 |
DIAGNOSTIC_1 |
Diagnostic cycle |
|
2 |
CLEANING_2 |
Cleaning cycle |
|
3 |
CALIBRATION_4 |
Calibration cycle |
|
4 |
VALIDATION_8 |
Validation cycle |
|
5 |
SAMPLING_16 |
Normal Sample acquisition cycle |
|
6 |
DIAGNOSTIC_WITH_GRAB_SAMPLE_32769 |
Diagnostic cycle with grab sample operation |
|
7 |
CLEANING_WITH_GRAB_SAMPLE_32770 |
Cleaning cycle with grab sample operation |
|
8 |
CALIBRATION_WITH_GRAB_SAMPLE_32772 |
Calibration cycle with grab sample operation |
|
9 |
VALIDATION_WITH_GRAB_SAMPLE_32776 |
Validation cycle with grab sample operation |
|
10 |
SAMPLING_WITH_GRAB_SAMPLE_32784 |
Normal Sample acquisition cycle with grab sample operation |
When an ExecutionCycle with sequence number 6 through 10 (GRAB_SAMPLE) is selected, the operator or a system can grab a sample and send it to a control lab for analysis.
AcquisitionResultStatusEnumeration describes acquisition result status on the Stream (general quality of the acquired data).
Table 89 – AcquisitionResultStatusEnumeration states
|
Seq. number |
EnumString |
Description |
|
0 |
NOT_USED_0 |
No longer used. |
|
1 |
GOOD_1 |
The acquisition has been completed as requested without any error. |
|
2 |
BAD_2 |
The acquisition has been completed as requested with error. |
|
3 |
UNKNOWN_3 |
The acquisition has been completed but nothing can be said about the quality of the result. |
|
4 |
PARTIAL_4 |
The acquisition has been partially completed as requested without any error. For example, an averaging of 30 spectra as been requested, but the user terminates the acquisition after averaging 20 spectra. |
The HasDataSource ReferenceType is a concrete ReferenceType that can be used directly. It is a subtype of the HasOrderedComponent ReferenceType.
The semantic is a part-of relationship. The TargetNode of a Reference of the HasDataSource ReferenceType is providing the value for the SourceNode
Like all other ReferenceTypes, this ReferenceType does not specify anything about the ownership of the parts, although it represents a part-of relationship semantic. That is, it is not specified if the TargetNode of a Reference of the HasDataSource ReferenceType is deleted when the SourceNode is deleted.
The source of the HasDataSource ReferenceType shall be of type ProcessVariableType.
There are no additional constraints defined for this ReferenceType.
The HasInput ReferenceType is a concrete ReferenceType that can be used directly. It is a subtype of the HasOrderedComponent ReferenceType.
The semantic is a part-of relationship. The TargetNode of a Reference of the HasInput ReferenceType is providing an input value for a ChemometricModelType instance.
Like all other ReferenceTypes, this ReferenceType does not specify anything about the ownership of the parts, although it represents a part-of relationship semantic. That is, it is not specified if the TargetNode of a Reference of the HasInput ReferenceType is deleted when the SourceNode is deleted.
The source of the HasInput ReferenceType shall be of type ChemometricModelType.
There are no additional constraints defined for this ReferenceType.
The HasOutput ReferenceType is a concrete ReferenceType that can be used directly. It is a subtype of the HasOrderedComponent ReferenceType.
The semantic is a part-of relationship. The TargetNode of a Reference of the HasOutput ReferenceType is exposing an output value of a ChemometricModelType instance.
Like all other ReferenceTypes, this ReferenceType does not specify anything about the ownership of the parts, although it represents a part-of relationship semantic. That is, it is not specified if the TargetNode of a Reference of the HasOutput ReferenceType is deleted when the SourceNode is deleted.
The source of the HasOutput ReferenceType shall be of type ChemometricModelType.
As a general rule, the target of HasOutput ReferenceType is a DataVariable generated by the ChemometricModel source.
There are no additional constraints defined for this ReferenceType.