Today OPC UA information models focused on the functional aspects of a dedicated device and the management of parameters in a device parameter set, are typically based on the OPC UA for Devices (DI) base information model (defined in [OPC 10000-100], referenced as OPC UA DI also in this document). In contradiction to this the I4.0 system modelling, including multiple aggregated devices and controllers, requires the representation of several different aspects of the system and therefore will lead to more sophisticated modelling approaches. Such a system model approach using four different independent partial models called “Facets”, linked together by typified references is shown in Figure 16. Here the Asset partial model contains an independent model related to orderable components (assets). The Physical Network partial model contains the independent model of the ethernet network structure. The PROFNET partial model contains all communication related aspects of the PN Controllers and Devices in the system. The Function partial model at least represents the application function aspect of the system. Objects out of the different partial models are connected to each other by typified references expressing semantic information about their relationship.
To be future proof and easily integrable to different base modelling approaches, this Companion Specification defines the PROFINET information model as an independent partial model using the OPC UA Interface and AddIn technology (See [OPC 10001-7]) . This gives the opportunity to connect the same unique PROFINET base information model to the OPC UA DI base model and to use the same PROFNET base model as partial model for the PROFINET communication aspect in the “Facet” modelling approach as shown in Figure 16.
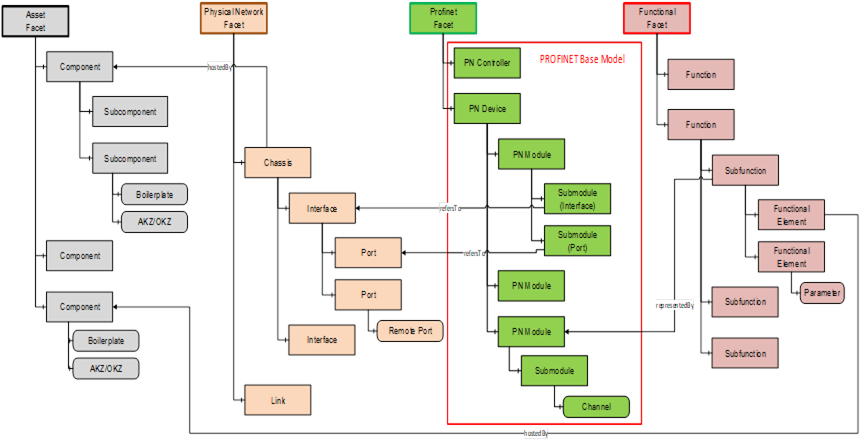
Figure 16 – “Facet” modelling approach for I4.0 System Modelling
The base information model in chapter 6.3 defines all common types of the PROFINET OPC UA information model.
The Annex B shows how to use the base information model together with OPC UA for Devices.
|
Method |
Meaning |
|
DCP |
The mentioned values or properties are read with the DCP Identify service |
|
GSDML |
The mentioned values or properties are read from a GSD file |
|
Read |
The mentioned values or properties are read with a CLRPC or RSI read record service |
The mentioned values are obtained by the blocks (optionally also subblocks) and fields given in the description. The following syntax is used: “Block | field”.
All variables are read-only unless stated otherwise explicitly.
The first 4 chapters of the base information model include the object types for the internal module/submodule structure of a PROFINET device and controller.
Figure 17 shows a simplified example for a module/submodule object structure. The container folders have been skipped in the figure.
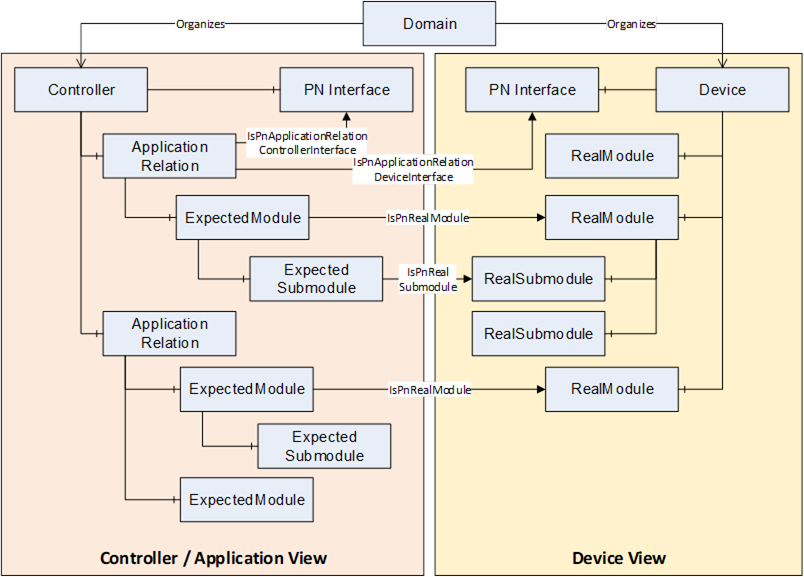
The Device View includes devices in the PROFINET network and their real existing modules and submodules.
The Controller / Application View includes the PROFINET connections (Application Relationships) and the expected modules and submodules which have been configured in the PROFINET controller.
Both views relate to each other by non-hierarchical references.
The chapter 6.3.1.7 includes the object types for the PROFINET network mapping.
The chapter 6.3.1.8 includes the 2 object types for the asset identification within a PROFINET device.
All object instances of the base information model represent the online view on the PROFINET network.
All PROFINET objects modeled in this specification are only created in the address space when the OPC UA Server detects their PROFINET counterpart. The objects are removed from the address space when the OPC UA Server detects their absence in the PROFINET network or PROFINET device.
The chapter 6.10 of [PN TAD] describes the possible ways of implementing the PROFINET device discovery. The chapter 11.3 of [PN TAD] describes the detection of the real modules and real submodules of a device and how to get their identification and asset data.
All these ContainerType objects only exist if objects are available in the container.
Table 23 – IPnDomainType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnDomainType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseInterfaceType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Nodes |
|
PnEquipmentContainerType |
Mandatory |
The Nodes object of the Domain includes all device and controller nodes which belong to the PROFINET domain.
Table 24 – IPnEquipmentType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnEquipmentType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseInterfaceType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Interfaces |
|
PnInterfaceContainerType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Modules |
|
PnRealModuleContainerType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Assets |
|
PnAssetContainerType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
|
PnIdentificationType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Vendor |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
|
FolderType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
ShowLocation |
|
ShowLocationMethod |
Optional |
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
|
If the IM component is provided, it must contain the data of the representative submodule for the device in accordance with the I&M0FilterDataDevice block (See [PN TAD] – Identification & Maintenance).
The Assets and IM objects are optional. If the interface is used with the OPC UA facet model, the asset data can be part of another facet (See chapter 6 “PROFINET OPC UA Information Model” and Figure 16 – “Facet” modelling approach for I4.0 System Modelling).
The <Assets> objects are only assets which are directly related to this device. Assets related to the modules or submodules are components of these objects.
The server may provide diagnosis data with the Diagnosis variable or by sending PnDiagnosisAlarmType events. The diagnosis data at the device object includes the diagnosis information of the whole device including the one of all real modules and real submodules. An OPC UA Server might provide instances of the PnDiagnosisAlarmType as objects under the Alarms object.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
DCP |
DeviceVendorBlockRes | DeviceVendorValue |
|
|
Read |
DiagnosisData (0xF80C device specific) |
This optional method shall trigger a perceivable signal which allows the identification of the physical device represented by the device object the method is invoked on. This is usually accomplished with a blinking LED.
The method has no parameters (no [in] and no [out] parameters) and no return value.
Signature
ShowLocation (
);
Table 25 – PnEquipmentContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnEquipmentContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<PnEquipments> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <PnEquipments> shall have the references and components defined in Table 26 and Table 27.
Table 26 – PnEquipmentContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
||||
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 27 – PnEquipmentContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnEquipmentType |
|||||
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Interfaces |
PnInterfaceContainerType |
M |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Modules |
PnRealModuleContainerType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Assets |
PnAssetContainerType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
PnIdentificationType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Vendor |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[]BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
FolderType |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:HasComponent |
Method |
ShowLocation |
ShowLocationMethod |
O |
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
<PnEquipments> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
<PnEquipments> |
DCP |
List of IdentifyResBlock |
Table 28 – IPnDeviceType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnDeviceType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of IPnEquipmentType |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
State |
PnDeviceStateEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
The BrowseName of a device object instance shall be the content of the NameOfStation variable of the first interface sub module. If the NameOfStation variable is not set, the content of the MAC Address variable of the first interface sub module shall be used. The MAC address string should use the canonical format (separated with -, e.g. AC-FD-CE-EC-03-80).
If the GSDDescription property is provided, it must contain the InfoText with Device Id from the GSD (see mapping table below).
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
GSD |
DeviceIdentity | InfoText with Device Id |
|
|
Read |
ARData | NumberOfARs | ARPropertiesEmpty block if offline. Online if at least one ARProperties block with ARProperties.DeviceAccess != 1 can be found in the record data. |
Table 29 – IPnControllerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnControllerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of IPnEquipmentType |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ARs |
|
PnApplicationRelationContainerType |
Optional |
Table 30 – PnApplicationRelationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnApplicationRelationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Modules |
|
PnExpectedModuleContainerType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
State |
PnARStateEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Id |
Guid |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Type |
PnARTypeEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SendClockFactor |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ReductionRatio |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DataHoldFactor |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
The BrowseName of an application relationship object instance shall be the Id in standard GUID string format.
The Modules container object is the root of the configuration hierarchy consisting of the expected modules of the application relationship and their expected submodules (See chapter 6.3 - Base Information Model and Figure 17 – Object Structure).
The State variable has always the value CONNECTED on devices since the object only exists if an AR is established.
An IsPnApplicationRelationControllerInterface reference points to the interface object of the controller used for the AR. If the AR relates to the device an IsPnApplicationRelationDeviceInterface reference points to the interface object of the device. See sections 6.3.2.11 and 6.3.2.12 also.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ARData | ARUUID |
|
|
Read |
ARData | ARType |
|
|
Read |
available also on Device/Gateway since PROFINET V2.4 via ARData | SendClockFactor or PDSyncData | SendClockFactor |
|
|
Read |
available also on Device/Gateway since PROFINET V2.4 via ARData | ReductionRatio |
|
|
Read |
IOCRBlockReq | DataHoldFactor (not available on Device/Gateway) |
Table 31 – PnApplicationRelationContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnApplicationRelationContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnApplicationRelation |
Object |
<ARs> |
|
PnApplicationRelationType |
Optional Placeholder |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ARData | NumberOfARs entries | ARUUID |
Table 32 – IPnModuleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnModuleType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of BaseInterfaceType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Slot |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
The properties Slot and IdentNumber must contain the data as described in the mapping table provided for the subtypes IPnRealModuleType and IPnExpectedModuleType.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
GSDML |
ModuleList | ModuleItem | ModuleInfo | Name |
|
|
GSDML |
ModuleList | ModuleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText |
Table 33 – IPnRealModuleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnRealModuleType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of IPnModuleType |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Submodules |
|
PnRealSubmoduleContainerType |
Optional |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
|
PnIdentificationType |
Optional |
|
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
|
FolderType |
Optional |
|
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
|
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
|
|
The BrowseName of a module object instance shall be the content of the Slot variable in decimal number string format.
If the IM component is provided, it must contain the data of the representative submodule for the module in accordance with the I&M0FilterDataModule block (See [PN TAD] – Identification & Maintenance).
The server may provide diagnosis data with the Diagnosis variable or by sending PnDiagnosisAlarmType events. The diagnosis data at the real module object includes the diagnosis information of the whole module including the one of the real submodules of the module. An OPC UA Server may provide instances of the PnDiagnosisAlarmType as objects under the Alarms object.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | SlotNumber |
|
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | IdentNumber |
|
|
Read |
DiagnosisData (0xC00C slot specific) |
Table 34 – PnRealModuleContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnRealModuleContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnRealModule |
Object |
<Modules> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <Modules> shall have the references and components defined in Table 35 and Table 36.
Table 35 – PnRealModuleContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
|||||
|
<Modules> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 36 – PnRealModuleContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnRealModuleType |
|||||
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Slot |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Submodules |
PnRealSubmoduleContainerType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
PnIdentificationType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[]BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
FolderType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
<Modules> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | NumberOfSlots entries | SlotNumber |
Table 37 – IPnExpectedModuleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnExpectedModuleType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of IPnModuleType |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Submodules |
|
PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
State |
PnModuleStateEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
The BrowseName of a module object instance shall be the content of the Slot variable in decimal number string format.
An IsPnRealModule reference points to the real module which is the real realization of the expected module. See section 6.3.2.9 also.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | SlotNumber |
|
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | IdentNumber |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | ModuleState |
Table 38 – PnExpectedModuleContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnExpectedModuleContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnExpectedModule |
Object |
<Modules> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <Modules> shall have the references and subcomponents defined in Table 39 and Table 40.
Table 39 – PnExpectedModuleContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
|||||
|
<Modules> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 40 – PnExpectedModuleContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnExpectedModuleType |
|||||
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Slot |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
State |
PnModuleStateEnumeration BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
<Modules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Submodules |
PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType |
O |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | NumberOfSlots entries | SlotNumber |
Table 41 – IPnSubmoduleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnSubmoduleType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of BaseInterfaceType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
API |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Subslot |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
The properties GSDName and GSDDescription must contain the data from the GSD, as described in the mapping table provided for the subtypes IPnRealSubmoduleType and IPnExpectedSubmoduleType.
Table 42 – IPnRealSubmoduleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnRealSubmoduleType |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
Subtype of IPnSubmoduleType |
||||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
|
PnIdentificationType |
Optional |
|
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
|
FolderType |
Optional |
|
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
|
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
|
|
The BrowseName of a sub module object instance shall be the content of the Subslot variable in hexadecimal number string format (e.g. 0x8001).
If the IM component is provided, it must contain the data in accordance with the I&M0FilterDataSubmodule block (See [PN TAD] – Identification & Maintenance).
The server can provide diagnosis data with the Diagnosis variable or by sending PnDiagnosisAlarmType events. The diagnosis data at the real submodule object includes only the diagnosis information of the real submodule. An OPC UA Server might provide instances of the PnDiagnosisAlarmType as objects under the Alarms object.
An IsPnInterface reference exists if the submodule is an interface submodule. See section 6.3.2.13 also.
An IsPnPort reference exists if the submodule is a port submodule. It points to the PnPortType object. See section 6.3.2.14 also.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | API |
|
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | SubslotNumber |
|
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | SubmoduleIdentNumber |
|
|
GSDML |
SubmoduleList | SubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name orSubmoduleList | VirtualSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name orSubmoduleList | PortSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name |
|
|
GSDML |
SubmoduleList | SubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText orSubmoduleList | VirtualSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText orSubmoduleList | PortSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText |
|
|
Read |
DiagnosisData (0x800C subslot specific) |
Table 43 – PnRealSubmoduleContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnRealSubmoduleContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnRealSubmodule |
Object |
<Submodules> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <Submodules> shall have the references defined in Table 44 and Table 45.
Table 44 – PnRealSubmoduleContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
|||||
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 45 – PnRealSubmoduleContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnRealSubmoduleType |
|||||
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
API |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Subslot |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IM |
PnIdentificationType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Diagnosis |
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType[]BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Alarms |
FolderType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
|
|
|
<Submodules> |
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
RealIdentificationData | NumberOfSubslots entries | SubslotNumber |
Table 46 – IPnExpectedSubmoduleType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnExpectedSubmoduleType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of IPnSubmoduleType |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
State |
|
PnSubmoduleStateType |
Optional |
An IsPnRealSubmodule reference points to the real submodule which is the real realization of the expected submodule. See section 6.3.2.10 also.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | API |
|
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | SubslotNumber |
|
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | SubmoduleIdentNumber |
|
|
GSDML |
SubmoduleList | SubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name orSubmoduleList | VirtualSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name or SubmoduleList | PortSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | Name |
|
|
GSDML |
SubmoduleList | SubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText or SubmoduleList | VirtualSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText or SubmoduleList | PortSubmoduleItem | ModuleInfo | InfoText |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState |
Table 47 – PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnExpectedSubmodule |
Object |
<Submodules> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <Submodules> shall have the references and subcomponents defined in Table 48 and Table 49.
Table 48 – PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
|||||
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 49 – PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnExpectedSubmoduleType |
|||||
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
API |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Subslot |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
IdentNumber |
UInt32 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDName |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
GSDDescription |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Submodules> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
State |
PnSubmoduleStateType |
O |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ExpectedIdentificationData | NumberOfSubslots entries | SubslotNumber |
Table 50 – PnSubmoduleStateType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnSubmoduleStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
AddInfo |
PnSubmoduleAddInfoEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
QualifiedInfo |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Maintenance Required |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Maintenance Demanded |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
DiagInfo |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
ARInfo |
PnSubmoduleARInfoEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
IdentInfo |
PnSubmoduleIdentInfoEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.AddInfo If entry not found, use: None |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.Advice If entry not found, use: No Advice information available |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.MaintenanceRequired If entry not found, use: No MaintenanceRequired information available |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.MaintenanceDemanded If entry not found, use: No MaintenanceDemanded information available |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.Fault If entry not found, use: No Fault information available |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.ARInfo If entry not found, use: Own |
|
|
Read |
ModuleDiffBlock | SubmoduleState.IdentInfo If entry not found, use: OK |
This chapter includes all object types needed to represent the physical network topology of a PROFINET network.
Figure 18 shows an example which illustrates the relations between network objects of a single port PROFINET device and a 4 port Ethernet switch.
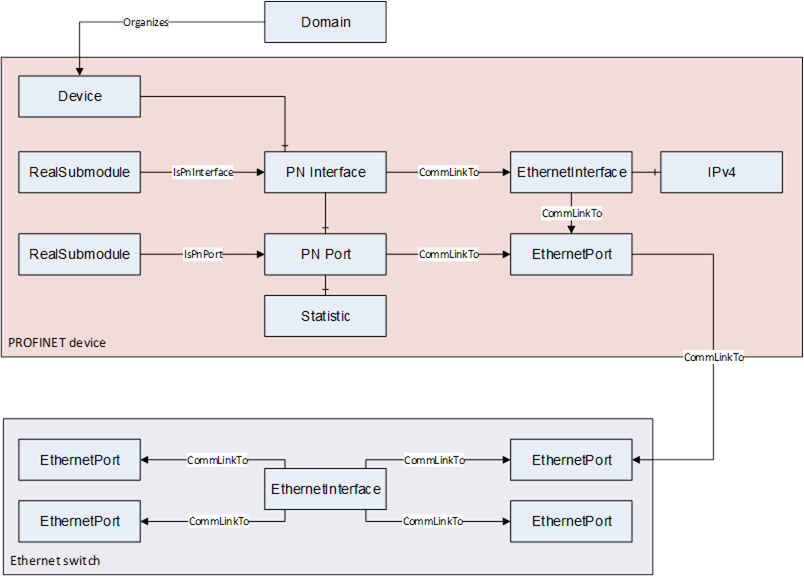
The Ethernet interface, ports and cables are represented by objects in the address space. This Ethernet objects relate to each other by CommLinkTo references. This enables the OPC UA Server to represent the physical network topology of the PROFINET network.
Table 51 – IPnInterfaceType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPnInterfaceType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseInterfaceType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Ports |
|
PnPortContainerType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
NameOfStation |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceRole |
PnDeviceRoleOptionSet |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceVendor |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
VendorId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceInstance |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OEMVendorId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OEMDeviceId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
CommLinkTo |
Object |
EthernetInterface |
|
EthernetInterfaceType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Statistic |
|
PnPortStatisticType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
SetNameOfStation |
|
SetNameOfStationMethod |
Optional |
The BrowseName of an interface object instance shall be the PROFINET interface id with the range 1..16 in decimal number string format.
The NameOfStation variable may be set with the SetNameOfStation method. Nevertheless, the variable itself shall always be read-only.
The CommLinkTo reference points to an EthernetInterfaceType object instance. An object of the IPv4FeatureType must be implemented in this EthernetInterfaceType object instance.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | NameOfStationValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DeviceRoleDetails |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DeviceVendorValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DeviceIDBlockRes | DeviceIDValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DeviceIDBlockRes | DeviceIDValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DeviceInstanceValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | OEMDeviceIDBlockRes | DeviceIDValue |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | OEMDeviceIDBlockRes | DeviceIDValue |
This optional method writes the NameOfStation remanent to the PROFINET device and sets the NameOfStation variable accordingly.
Signature
SetNameOfStation (
[in]String NameOfStation
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
NameOfStation |
String containing the new NameOfStation to be written remanent to the device. The maximum length shall be limited to 240 characters (See [PN Protocol] for details). |
Method Result Codes
|
ResultCode |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The Server is not able to apply the name. The name may be too long or may contain invalid characters. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
The Server is not able to apply the name because an unexpected error occurred. The device might be temporarily unavailable or unreachable due to network failure. |
Table 52 – PnInterfaceContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnInterfaceContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnInterface |
Object |
<Interfaces> |
|
BaseObjectType |
Optional Placeholder |
The <Interfaces> shall have the references defined in Table 53 and Table 54.
Table 53 – PnInterfaceContainerType Additional References
|
Source Path |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
Target Path |
||||
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasInterface |
True |
|
Table 54 – PnInterfaceContainerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Applied from IPnInterfaceType |
|||||
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Ports |
PnPortContainerType |
M |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
NameOfStation |
String PropertyType |
M |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceRole |
PnDeviceRoleOptionSet PropertyType |
M |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceVendor |
StringPropertyType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
VendorId |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceId |
UInt16 PropertyType |
M |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceInstance |
UInt16PropertyType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
OEMVendorId |
UInt16PropertyType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
OEMDeviceId |
UInt16PropertyType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
CommLinkTo |
Object |
EthernetInterface |
EthernetInterfaceType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Statistic |
PnPortStatisticType |
O |
|
<Interfaces> |
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetNameOfStation |
SetNameOfStationMethod |
O |
The PnPortType Object Type includes the port specific data of a port submodule.
A PnRealSubmoduleType instance representing a port submodule has an IsPnPort reference to a PnPortType object instance.
Table 55 – PnPortType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnPortType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Statistic |
|
PnPortStatisticType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
LinkState |
PnLinkStateEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
PortState |
PnPortStateEnumeration |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
MAUType |
UInt16 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
CableDelay |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
PowerBudget |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
IsWireless |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
CommLinkTo |
Object |
EthernetPort |
|
EthernetPortType |
Optional |
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnTopologyChangedEventType |
|
|
|
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
PDPortDataReal | MAUType |
|
|
Read |
PDPortDataReal | LineDelay |
|
|
Read |
PDPortFODataReal | FiberOpticDiagnosisInfo | FiberOpticPowerBudgetReal |
|
|
Read |
PDPortDataReal | MediaType |
Table 56 – PnPortContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnPortContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnPort |
Object |
<Ports> |
|
PnPortType |
Optional Placeholder |
Table 57 – PnPortStatisticType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnPortStatisticType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
InOctets |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
OutOctets |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
InDiscards |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
OutDiscards |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
InErrors |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
OutErrors |
UInt32 |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
The port statistic counters can be read from a PROFINET device with the Read PD Port Statistic PROFINET service.
The NetworkComponentType is the abstract base ObjectType for different types of network components.
Table 58 – NetworkComponentType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
NetworkComponentType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
<FeatureName> |
|
NetworkComponentFeatureType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Enabled |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
CommLinkTo |
Object |
<ComponentName> |
|
NetworkComponentType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
The Enabled variable indicates if the network component is activated (Enabled == True) or deactivated (Enabled == False).
The EthernetInterfaceType is used to represent Ethernet network interfaces.
Table 59 – EthernetInterfaceType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
EthernetInterfaceType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of NetworkComponentType. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
MacAddress |
Byte [6] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
CommLinkTo |
Object |
<PortName> |
|
EthernetPortType |
MandatoryPlaceholder |
The MacAddress Variable is read only and represents the unique Layer2 source MAC address of the related interface.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | MACAddressBlockRes | MACAddressValue |
The EthernetPortType is used to represent Ethernet ports.
Table 60 – EthernetPortType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
EthernetPortType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of NetworkComponentType. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
PhysAddress |
Byte [6] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Optional |
|
CommLinkTo |
Object |
<EthernetPort> |
|
EthernetPortType |
Optional |
The PhysAddress Variable is read only and contains a MAC address representing the Port.
The NetworkComponentFeatureType is the abstract base ObjectType for different types of network components.
Table 61 – NetworkComponentFeatureType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
NetworkComponentFeatureType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
The IPv4FeatureType is used to represent IPv4 settings of a network interface.
Table 62 – IPv4FeatureType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPv4FeatureType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of NetworkComponentFeatureType. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
IpAddress |
Byte[4] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
SubnetMask |
Byte[4] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
DefaultGateway |
Byte[4] |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
DhcpEnabled |
Boolean |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | IPParameterBlockRes | IPParameterValue | IPAddress |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | IPParameterBlockRes | IPParameterValue | Subnetmask |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | IPParameterBlockRes | IPParameterValue | StandardGateway |
|
|
DCP |
DCP-Identify-ResPDU | DHCPParameterBlockRes | DHCPParameter | DHCPParameterLength |
The IpAddress Variable describes the IPv4 address on the interface.
The SubnetMask Variable describes the IPv4 Subnet mask on the interface.
The DefaultGateway Variable describes the IPv4 address of the default gateway.
The DhcpEnabled Variable specifies whether the DHCPv4 Client functionality for this interface is enabled.
Table 63 – PnIdentificationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnIdentificationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
VendorId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OrderId |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SerialNumber |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SoftwareRevision |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
HardwareRevision |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ProfileId |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ProfileSpecificType |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Version |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
RevisionCounter |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IMSupported |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
TagFunction |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
TagLocation |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Date |
DateTime |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Descriptor |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Signature |
ByteString |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
IM5 |
PnIM5DataType[] |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
SetTags |
|
SetTagsMethod |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
SetDate |
|
SetDateMethod |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
SetDescriptor |
|
SetDescriptorMethod |
Optional |
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
I&M0 | VendorID |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | OrderID |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Serial_Number |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Software_Revision |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Hardware_Revision |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Profile_ID |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Profile_Specific_Type |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Version |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Revision_Counter |
|
|
Read |
I&M0 | IM_Supported |
|
|
Read |
I&M1 | IM_Tag_Function |
|
|
Read |
I&M1 | IM_Tag_Location |
|
|
Read |
I&M2 | IM_Date |
|
|
Read |
I&M3 | IM_Descriptor |
|
|
Read |
I&M4 | IM_Signature |
|
|
Read |
I&M5 | I&M5Data, see chapter 6.3.3.1.2 for details Array size: I&M5 | NumberOfEntries |
This optional method writes the I&M1 fields IM_TagFunction and IM_Tag_Location remanent to the PROFINET device and sets the TagFunction and TagLocation variables accordingly.
Signature
SetTags (
[in] IMTagSelectorEnumeration Tag_Selector,
[in] String Tag_Function,
[in] String Tag_Location
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Tag_Selector |
If FUNCTION, Tag_Function shall be written, If LOCATION, Tag_Location shall be written, if BOTH both. |
|
Tag_Function |
String containing the new I&M1 | IM_Tag_Function to be written remanent to the device. |
|
Tag_Location |
String containing the new I&M1 | IM_Tag_Location to be written remanent to the device. |
Method Result Codes
|
ResultCode |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The Server is not able to apply an argument. The argument may be too long or may contain invalid characters. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
The Server is not able to apply the name because an unexpected error occurred. The device might be temporarily unavailable or unreachable due to network failure. |
This optional method writes the I&M2 field IM_Date remanent to the PROFINET device and sets the Date variable accordingly.
Signature
SetDate (
[in] DateTime IM_Date
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
IM_Date |
New I&M2 | IM_Date to be written remanent to the device. |
Method Result Codes
|
ResultCode |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The Server is not able to apply an argument. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
The Server is not able to apply the name because an unexpected error occurred. The device might be temporarily unavailable or unreachable due to network failure. |
This optional method writes the I&M3 field IM_Descriptor remanent to the PROFINET device and sets the Descriptor variable accordingly.
Signature
SetDescriptor (
[in] String Descriptor
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Descriptor |
New I&M3 | IM_Descriptor to be written remanent to the device. |
Method Result Codes
|
ResultCode |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The Server is not able to apply an argument. The argument may be too long or may contain invalid characters. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
The Server is not able to apply the name because an unexpected error occurred. The device might be temporarily unavailable or unreachable due to network failure. |
Table 64 – PnAssetType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnAssetType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
UniqueIdentifier |
Guid |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Location |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Annotation |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OrderId |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SoftwareRevision |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
HardwareRevision |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SerialNumber |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
TypeIdentification |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Organization |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
VendorId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
DeviceSubId |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
|
|
|
The BrowseName of an asset object instance shall be the content of the UniqueIdentifier variable in standard GUID string format.
Mapping to PROFINET properties:
|
BrowseName |
Method |
Source |
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_UniqueIdentifier |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_Location |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_Annotation |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_OrderID |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_Software_Revision or AM_SoftwareRevision |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_Hardware_Revision or AM_HardwareRevision |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | IM_Serial_Number |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_TypeIdentification |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_DeviceIdentification.Organization |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_DeviceIdentification.VendorID |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_DeviceIdentification.DeviceID |
|
|
Read |
AssetManagementData | AM_DeviceIdentification.DeviceSubID |
If the AM_Location field is coded using the level tree format, each used level shall be encoded in the Location string with a ‘.’ followed by the value of the level bits encoded as decimal number string. According to [PN TAD] – Figure 38, the HART sensor has the Location string ”.0.4.1.1”.
If the AM_Location field is coded using the slot- and subslotnumber format, the Location string shall be encoded as ‘BeginSlotNumber/BeginSubslotNumber-EndSlotNumber/EndSubslotNumber’. BeginSlotNumber and EndSlotNumber shall be encoded as decimal number strings. BeginSubslotNumber and EndSubslotNumber shall be encoded as hexadecimal number strings (0x…) According to [PN TAD] – Figure 38, the IO-MC 1 asset has the Location string ”2/0x1-4/0x1”.
Table 65 – PnAssetContainerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnAssetContainerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseObjectType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasPnAsset |
Object |
<Assets> |
|
PnAssetType |
Optional Placeholder |
Table 66 – HasPnApplicationRelation Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnApplicationRelation |
|
InverseName |
IsPnApplicationRelationOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnApplicationRelation reference is used to append nodes to the PnApplicationRelationContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnApplicationRelationType.
Table 67 – HasPnRealModule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnRealModule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnRealModuleOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnRealModule reference type is used to append nodes to the PnRealModuleContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealModuleType interface.
Table 68 – HasPnRealSubmodule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnRealSubmodule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnRealSubmoduleOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnRealSubmodule reference type is used to append nodes to the PnRealSubmoduleContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealSubmoduleType interface.
Table 69 – HasPnExpectedModule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnExpectedModule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnExpectedModuleOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnExpectedModule reference type is used to append nodes to the PnExpectedModuleContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnExpectedModuleType interface.
Table 70 – HasPnExpectedSubmodule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnExpectedSubmodule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnExpectedSubmoduleOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnExpectedSubmodule reference type is used to append nodes to the PnExpectedSubmoduleContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnExpectedSubmoduleType interface.
Table 71 – HasPnAsset Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnAsset |
|
InverseName |
IsPnAssetOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnAsset reference type is used to append nodes to the PnAssetContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnAssetType.
Table 72 – HasPnInterface Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnInterface |
|
InverseName |
IsPnInterfaceOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnInterface reference type is used to append nodes to the PnInterfaceContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnInterfaceType interface.
Table 73 – HasPnPort Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
HasPnPort |
|
InverseName |
IsPnPortOf |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the HasComponent from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The HasPnPort reference type is used to append nodes to the PnPortContainerType node.
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnPortType.
Table 74 – IsPnRealModule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnRealModule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnExpectedModule |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnRealModule reference type is used to link ExpectedModule objects to their RealModule counterparts (See Figure 17 – Object Structure).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealModuleType interface.
The source of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnExpectedModuleType interface.
Table 75 – IsPnRealSubmodule Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnRealSubmodule |
|
InverseName |
IsPnExpectedSubmodule |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnRealSubmodule reference type is used to link ExpectedSubmodule objects to their RealSubmodule counterparts (See Figure 17 – Object Structure).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealSubmoduleType interface.
The source of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnExpectedSubmoduleType interface.
Table 76 – IsPnApplicationRelationDeviceInterface Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnApplicationRelationDeviceInterface |
|
InverseName |
UsedByPnApplicationRelation |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnApplicationRelationDeviceInterface is used to link PnApplicationRelationType objects to the PN Interface object of the Device object (objects implementing IDeviceType) the application relation connects to (See Figure 17 – Object Structure).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnInterfaceType interface.
The source of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnApplicationRelationType and shall not use the reference type more than once.
Table 77 – IsPnApplicationRelationControllerInterface Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnApplicationRelationControllerInterface |
|
InverseName |
UsedByPnApplicationRelation |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnApplicationRelationControllerInterface is used to link PnApplicationRelationType objects to the PN Interface object of the controller object (objects implementing IControllerType) the application relation belongs to (See Figure 17 – Object Structure).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnInterfaceType interface.
The source of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnApplicationRelationType and shall not use the reference more than once.
Table 78 – IsPnInterface Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnInterface |
|
InverseName |
RealizedByPnSubmodule |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnInterface reference type is used to link RealSubmodule objects to PN Interface objects (See Figure 18 – Network Topology).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnInterfaceType interface.
The source of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealSubmoduleType interface.
Table 79 – IsPnPort Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
IsPnPort |
|
InverseName |
RealizedByPnSubmodule |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The IsPnPort reference type is used to link RealSubmodule objects to PN Port objects (Figure 18 – Network Topology).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
The destination of the reference shall be an object of the ObjectType PnPortType.
The source of the reference shall be an object implementing the IPnRealSubmoduleType interface.
Table 80 – CommLinkTo Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
BrowseName |
CommLinkTo |
|
InverseName |
CommLinkFrom |
|
Symmetric |
False |
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|
Subtype of the Organizes from [OPC 10000-5]. |
|
The CommLinkTo reference type is used between object instances representing network entities like Ethernet interfaces and Ethernet ports to describe their communication as well as their topology dependencies. (See Figure 18 – Network Topology).
This reference should always be bidirectional.
Table 81 – PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
PnDeviceDiagnosisDataType |
Structure |
|
|
API |
UInt32 |
|
|
Slot |
UInt16 |
|
|
Subslot |
UInt16 |
|
|
ChannelNumber |
UInt16 |
|
|
Type |
PnChannelTypeEnumeration |
|
|
Accumulative |
PnChannelAccumulativeEnumeration |
|
|
Maintenance |
PnChannelMaintenanceEnumeration |
|
|
Specifier |
PnChannelSpecifierEnumeration |
|
|
Direction |
PnChannelDirectionEnumeration |
|
|
UserStructureIdentifier |
UInt16 |
|
|
ChannelErrorType |
UInt16 |
|
|
ExtChannelErrorType |
UInt16 |
|
|
ExtChannelAddValue |
UInt32 |
|
|
QualifiedChannelQualifier |
UInt32 |
|
|
ManufacturerData |
ByteString |
Manufacturer specific diagnosis data |
|
Message |
LocalizedText |
Diagnosis message read from the GSDML |
|
HelpText |
LocalizedText |
Help text read from the GSDML |
If the field UserStructureIdentifier indicates manufacturer specific diagnosis information, the ByteString ManufacturerData contains the manufacturer specific diagnosis data.
The Message and the HelpText variables are retrieved from the GSDML file. If the Message includes a dynamic format string, this is replaced by the ExtChannelAddValue.
Table 82 – PnIM5DataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
PnIM5DataType |
Structure |
Contains the fields of the APDU element I&M5 | I&M5Data |
|
Annotation |
String |
I&M5Data | IM_Annotation |
|
OrderId |
String |
I&M5Data | IM_OrderID |
|
VendorId |
UInt16 |
I&M5Data | VendorID |
|
SerialNumber |
String |
I&M5Data | IM_Serial_Number |
|
HardwareRevision |
String |
I&M5Data | IM_Hardware_Revision |
|
SoftwareRevision |
String |
I&M5Data | IM_Software_Revision |
Table 83 – PnDeviceRoleOptionSet
|
Value |
Bit No. |
Description |
|
IO_DEVICE |
0 |
The device contains an IO device interface. |
|
IO_CONTROLLER |
1 |
The device contains an IO controller interface. |
|
IO_MULTIDEVICE |
2 |
The device contains multiple IO device interfaces. |
|
IO_SUPERVISOR |
3 |
The device contains an IO supervisor interface. |
|
IO_CIM |
4 |
The device contains a CIM device interface. |
The PnDeviceRole OptionSet representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 84.
Table 84 – PnDeviceRoleOptionSet Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
PnDeviceRoleOptionSet |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the OptionSet type defined in [OPC 10000-5] |
||||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OptionSetValues |
0:LocalizedText [] |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
See: [PN Protocol], Table – DeviceRoleDetails
Table 85 – PnDeviceStateEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
OFFLINE_0 |
The device is not online, or no information is available. The device is offline if no ARs other than possible Device Access AR’s exist. |
|
OFFLINE_DOCKING_1 |
The device is a docking device and currently not online. |
|
ONLINE_2 |
The device is online. This is the case if at least one AR other than possible Device Access AR’s exists. |
|
ONLINE_DOCKING_3 |
The device is a docking device and currently online. |
Table 86 – PnARStateEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
CONNECTED_0 |
The AR connection to the device is established |
|
UNCONNECTED_1 |
The AR connection to the device is not established |
|
UNCONNECTED_ERR_DEVICE_NOT_FOUND_2 |
The AR connection to the device is not established because the device is not available in the network |
|
UNCONNECTED_ERR_DUPLICATE_IP_3 |
The AR connection to the device is not established because the IP address of the device exists multiple times |
|
UNCONNECTED_ERR_DUPLICATE_NOS_4 |
The AR connection to the device is not established because the Name of Station of the device exists multiple times |
Table 87 – PnARTypeEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
IOCARSingle_0 |
- |
|
IOSAR_6 |
The supervisor AR is a special form of the IOCARSingle allowing takeover of the ownership of a submodule |
|
IOCARSingleUsingRT_CLASS_3_16 |
This is a special form of the IOCARSingle indicating RT_CLASS_3 communication |
|
IOCARSR_32 |
The SR AR is a special form of the IOCARSingle indicating system redundancy or dynamic reconfiguration usage |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 508 – ARType
Table 88 – PnModuleStateEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_MODULE_0 |
For example module not plugged |
|
WRONG_MODULE_1 |
For example ModuleIdentNumber wrong |
|
PROPER_MODULE_2 |
Module is okay but at least one submodule is locked, wrong or missing |
|
SUBSTITUTE_3 |
Module is not the same as requested – but the IO device was able to adapt by its own knowledge |
|
OK_4 |
Default state |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 586 – ModuleState
Table 89 – PnSubmoduleAddInfoEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
NO_ADD_INFO_0 |
- |
|
TAKEOVER_NOT_ALLOWED_1 |
This Submodule is not available for takeover by IOSAR. |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 587 – SubmoduleState.AddInfo
Table 90 – PnSubmoduleARInfoEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
OWN_0 |
This AR is owner of the submodule |
|
APPLICATION_READY_PENDING_128 |
This AR is owner of the submodule but it is blocked. For example parameter checking pending |
|
SUPERORDINATED_LOCKED_256 |
This AR is not owner of the submodule. It is blocked by superordinated means |
|
LOCKED_BY_IO_CONTROLLER_384 |
This AR is not owner of the submodule. It is owned by another IOAR |
|
LOCKED_BY_IO_SUPERVISOR_512 |
This AR is not owner of the submodule. It is owned by another IOSAR |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 592 – SubmoduleState.ARInfo
Table 91 – PnSubmoduleIdentInfoEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
OK_0 |
OK |
|
SUBSTITUTE_2048 |
Substitute (SU) |
|
WRONG_4096 |
Wrong (WR) |
|
NO_SUBMODULE_6144 |
NoSubmodule (NO) |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 593 – SubmoduleState.IdentInfo
Table 92 – PnChannelTypeEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
UNSPECIFIC_0 |
Shall be used if the field ChannelNumber contains the value 0x8000 (submodule)Furthermore, it shall be used if none of the below defined types are appropriate. |
|
1BIT_1 |
The data length of this channel is 1 Bit. |
|
2BIT_2 |
The data length of this channel is 2 Bit. |
|
4BIT_3 |
The data length of this channel is 4 Bit. |
|
8BIT_4 |
The data length of this channel is 8 Bit. |
|
16BIT_5 |
The data length of this channel is 16 Bit. |
|
32BIT_6 |
The data length of this channel is 32 Bit. |
|
64BIT_7 |
The data length of this channel is 64 Bit. |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 651 – ChannelProperties.Type
Table 93 – PnChannelAccumulativeEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
SINGLE_0 |
Single channel Diagnosis only for the reported channel |
|
ACCUMULATIVE_256 |
Multiple channel Accumulative diagnosis from more than one channel |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 652 – ChannelProperties.Accumulative
Table 94 – PnChannelMaintenanceEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
FAULT_0 |
Fault |
|
MAINTENANCE_REQUIRED_512 |
Maintenance required |
|
MAINTENANCE_DEMANDED_1024 |
Maintenance demanded |
|
USE_QUALIFIED_CHANNEL_QUALIFIER_1536 |
Use QualifiedChannelQualifier variable |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 653 – ChannelProperties.Maintenance
Table 95 – PnChannelSpecifierEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
ALL_DISAPPEARS_0 |
The Diagnosis ASE contains no longer any entries (of any severity) for this channel |
|
APPEARS_2048 |
An event appears and/or exists further The Diagnosis ASE contains this and possible other entries for this channel. |
|
DISAPPEARS_4096 |
An event disappears and/or exists no longer The Diagnosis ASE contains no longer any entries of the same severity for this channel |
|
DISAPPEARS_OTHER_REMAIN_6144 |
An event disappears The Diagnosis ASE still contains other entries of the same severity for this channel |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 656 – ChannelProperties.Specifier
Table 96 – PnChannelDirectionEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
MANUFACTURER_SPECIFIC_0 |
Manufacturer specific |
|
INPUT_CHANNEL_8192 |
Input |
|
OUTPUT_CHANNEL_16384 |
Output |
|
BIDIRECTIONAL_CHANNEL_24576 |
Input/Output |
See: [PN Protocol], Table 585 – ChannelProperties.Direction
Table 97 – PnAssetTypeEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
DEVICE_0 |
Device |
|
MODULE_1 |
Real Module |
|
SUBMODULE_2 |
Real Submodule |
|
ASSET_3 |
Asset |
Table 98 – PnAssetChangeEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
INSERTED_0 |
Asset has been added |
|
REMOVED_1 |
Asset has been removed |
|
CHANGED_2 |
Asset has been changed |
Table 99 – PnLinkStateEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
UP_1 |
Ready to pass packets |
|
DOWN_2 |
No packets are passed |
|
TESTING_3 |
In some test mode |
|
UNKNOWN_4 |
Status cannot be determined |
|
DORMANT_5 |
In pending state waiting for some external event |
|
NOT_PRESENT_6 |
Port not present |
|
LOWER_LAYER_DOWN_7 |
Down due to lower layer |
Table 100 – PnPortStateEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
UNKNOWN_0 |
Status cannot be determined |
|
DISABLED_DISCARDING_1 |
The port is administratively disabled and discarding frames |
|
BLOCKING_2 |
The port blocks incoming frames |
|
LISTENING_3 |
The port is listening to and sending BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units). |
|
LEARNING_4 |
The port is listening for and processing BPDUs and starts learning MAC’s |
|
FORWARDING_5 |
The port is processing BPDUs and forwarding frames |
|
BROKEN_6 |
The port blocks incoming frames since a configuration error is detected |
Table 101 – IMTagSelectorEnumeration
|
Name |
Description |
|
FUNCTION_0 |
The Tag_Function argument shall be written. |
|
LOCATION_1 |
The Tag_Location argument shall be written. |
|
BOTH_2 |
Both arguments, Tag_Function and Tag_Location, shall be written. |
This event type is used for PROFINET diagnosis events.
Table 102 – PnDiagnosisAlarmType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnDiagnosisAlarmType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of AlarmConditionType defined in [OPC 10000-9]. |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
API |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Slot |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Subslot |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ChannelNumber |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Type |
PnChannelTypeEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Accumulative |
PnChannelAccumulativeEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Maintenance |
PnChannelMaintenanceEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Specifier |
PnChannelSpecifierEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Direction |
PnChannelDirectionEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
UserStructureIdentifier |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ChannelErrorType |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ExtChannelErrorType |
UInt16 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ExtChannelAddValue |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
QualifiedChannelQualifier |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ManufacturerData |
ByteString |
PropertyType |
Optional |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
HelpText |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
Optional |
If the variable UserStructureIdentifier indicates manufacturer specific diagnosis information, the variable ManufacturerData contains the manufacturer specific diagnosis data.
The Message variable of the Event and the HelpText variable are retrieved from the GSDML file. If the message includes a dynamic format string, this is replaced by the ExtChannelAddValue.
For an active alarm the Severity variable of the Event must be dependent on the Maintenance and the QualifiedChannelQualifier variables.
The Severity is divided into the 4 categories shown in the following table:
|
Category |
Severity Range |
|
Fault |
750 – 1000 |
|
Maintenance demanded |
500 – 749 |
|
Maintenance required |
250 – 499 |
|
Advise |
2 – 249 |
If the Maintenance variable is provided, the following mapping is used for the Severity value:
|
Maintenance |
Severity |
|
FAULT |
1000 |
|
MAINTENANCE_DEMANDED |
612 |
|
MAINTENANCE_REQUIRED |
362 |
If the QualifiedChannelQualifier is provided, the Severity value depends on the bit set in the UInt32 value of the QualifiedChannelQualifier. The bits 0 – 2 are not used.
The following mapping is used for the Severity value:
|
Bit |
Severity |
|
31 |
1000 |
|
30 |
937 |
|
29 |
875 |
|
28 |
812 |
|
27 |
750 |
|
26 |
725 |
|
25 |
700 |
|
24 |
675 |
|
23 |
650 |
|
22 |
625 |
|
21 |
600 |
|
20 |
575 |
|
19 |
550 |
|
18 |
525 |
|
17 |
500 |
|
16 |
475 |
|
15 |
450 |
|
14 |
425 |
|
13 |
400 |
|
12 |
375 |
|
11 |
350 |
|
10 |
325 |
|
9 |
300 |
|
8 |
275 |
|
7 |
250 |
|
6 |
200 |
|
5 |
150 |
|
4 |
100 |
|
3 |
50 |
This event is fired when a new asset (controller, device, real module, real submodule or asset) is detected, an asset was removed, or the data of an asset changed. The event is fired on the object with the change.
An asset change for a device, real module or real submodule means that its I&M data (PnIdentificationType) has changed. See section 5.3.2.6 “Asset change detection” for details.
Table 103 – PnAssetChangedEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnAssetChangedEventType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseEventType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
AssetType |
PnAssetTypeEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
AssetChange |
PnAssetChangeEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The SourceNode variable of the event includes the NodeId of the asset object.
The Severity variable shall be set according to the following table.
|
Severity |
Cause |
|
10 |
Minor important asset detected |
|
20 |
Normal important asset detected |
|
30 |
Asset of vital importance detected |
|
110 |
Minor important asset changed |
|
120 |
Normal important asset changed |
|
130 |
Asset of vital importance changed |
|
1100 |
Minor important asset removed |
|
1200 |
Normal important asset removed |
|
1300 |
Asset of vital importance removed |
This event is fired when the CommLinkTo reference between two EthernetPortType objects is created, removed or changed. The event is fired by the PnPortType object.
This means that the physical network topology has changed.
The Severity variable (inherited from BaseEventType) shall be set to 1.
Table 104 – PnTopologyChangedEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PnTopologyChangedEventType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of BaseEventType defined in [OPC 10000-5]. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The SourceNode variable of the event includes the NodeId of the PnPortType object.