The JoiningSystemType provides the overview of the information exposed from a given joining system.
Note:
- An instance of the JoiningSystemType does not represent a specific asset. It is a container which represents an entry point for assets, results, etc. in the joining system.
- An instance of a JoiningSystemType can be associated with other joining systems using AssociatedWith or any other reference type. It can be useful when there is an aggregation of multiple joining systems.
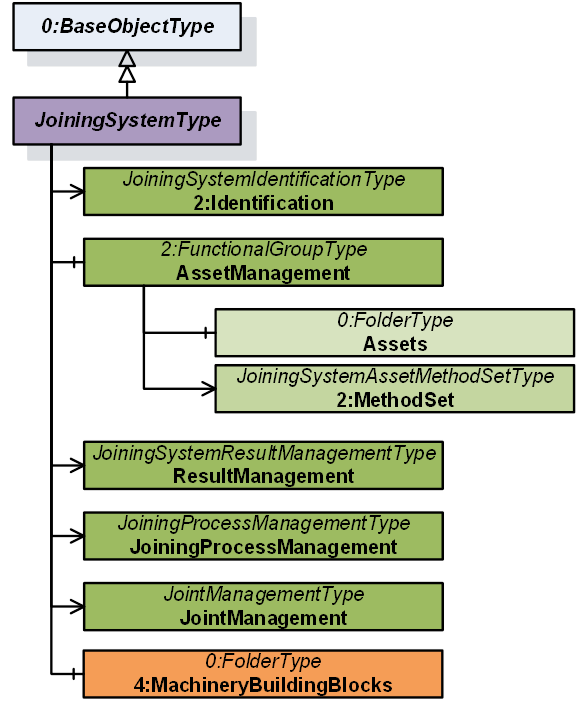
Figure 9 – Joining System Overview
It is formally defined in Table 15.
Table 15 – JoiningSystemType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JoiningSystemType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5, i.e., inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
2:Identification |
- |
JoiningSystemIdentificationType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
AssetManagement |
- |
2:FunctionalGroupType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
5:ResultManagement |
- |
JoiningSystemResultManagementType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
JoiningProcessManagement |
- |
JoiningProcessManagementType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
JointManagement |
- |
JointManagementType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
4:MachineryBuildingBlocks |
- |
0:FolderType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Joining System Base |
|||||
|
IJT Joining System Identification |
|||||
|
IJT Joining System Machinery Building Blocks |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management |
|||||
|
IJT Result Management |
|||||
|
IJT Joining Process Management |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Management |
|||||
The 2:Identification Object provides identification parameters of the joining system.
The AssetManagement Object is an instance of 2:FunctionalGroupType to group assets and related objects in the joining system.
The ResultManagement Object is an instance of JoiningSystemResultManagementType which provides mechanisms to access results generated by the joining system.
The JoiningProcessManagement Object is an instance of JoiningProcessManagementType which provides mechanisms to manage joining processes in the joining system.
The JointManagement Object is an instance of JointManagementType which provides mechanisms to manage joint and associated information.
4:MachineryBuildingBlocks contains building blocks from OPC UA for Machinery.
The components of the JoiningSystemType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 16.
Table 16 – JoiningSystemType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
AssetManagement |
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
2:MethodSet |
|
JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType |
O |
2:MethodSet Object is an instance of JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType which provides set of methods for various assets in a joining system.
The components of the JoiningSystemType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 17.
Table 17 – JoiningSystemType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Controllers |
|
0:FolderType |
M |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Tools |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Servos |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
MemoryDevices |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Sensors |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Cables |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Batteries |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
PowerSupplies |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Feeders |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Accessories |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
SubComponents |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
SoftwareComponents |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
VirtualStations |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
The components of the JoiningSystemType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 18.
Table 18 – JoiningSystemType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Controller> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
MP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Tool> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Servo> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<MemoryDevice> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Sensor> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Cable> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Battery> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Feeder> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<PowerSupply> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Accessory> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<SubComponent> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<Software> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
|||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<VirtualStation> |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
OP |
The components of the JoiningSystemType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 19.
Table 19 – JoiningSystemType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IControllerType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IToolType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IServoType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IMemoryDeviceType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
ISensorType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
ICableType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IBatteryType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IFeederType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IPowerSupplyType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IAccessoryType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
ISubComponentType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
ISoftwareType |
|
|
|
||||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IVirtualStationType |
|
|
|
The JoiningSystemIdentificationType provides the identification parameters of the joining system and is formally defined in Table 20.
Table 20 – JoiningSystemIdentificationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JoiningSystemIdentificationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 2:FunctionalGroupType defined in OPC 10000-100, i.e., inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
0:QualifiedName |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:ProductInstanceUri |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Name |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
IntegratorName |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Description |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
JoiningTechnology |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:Manufacturer |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:ManufacturerUri |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:Model |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
SystemId |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
4:Location |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Joining System Base |
|||||
|
|
|||||
The component Variables of the JoiningSystemIdentificationType have additional Attributes defined in Table 21.
Table 21 – JoiningSystemIdentificationType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
|
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
2:Identification |
The default BrowseName for instances of the type. |
2: ProductInstanceUri is a globally unique resource identifier provided by the manufacturer.
Name is the name of the joining system. It is allowed to set it as the string part of the standard browse name of the instance of JoiningSystemType.
IntegratorName is the name of the system integrator.
Description is the description of the system which could be written by the customer to identify the system. It could be the purpose of the system in the assembly line.
Note: Although there is a description attribute at the node level in OPC UA, the Description property was added at the same level as the 2:Identification node for consistency.
JoiningTechnology is a human-readable text to identify the joining technology of the joining system.
2:Manufacturer provides a human-readable, localized name of the joining system manufacturer.
2:ManufacturerUri provides a unique identifier for this company. This identifier should be a fully qualified domain name; however, it may be a GUID or similar construct that ensures global uniqueness.
2:Model provides the type of the joining system. Examples: Fixtured System, Handheld System, etc.
SystemId is the system integrator specific identifier for the system. It represents a reference to the manufacturer's ERP system.
4:Location is the location of the given system in the given plant or factory in text format.
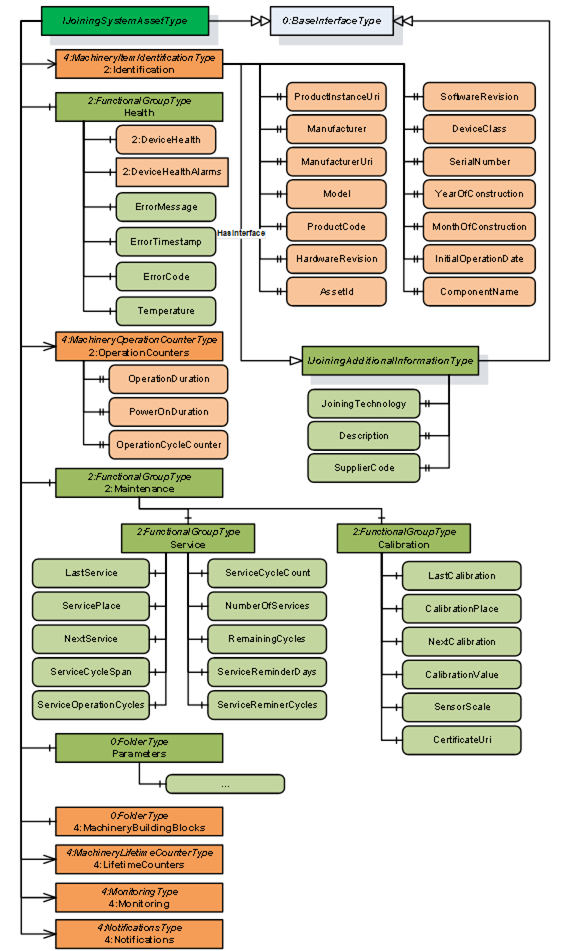
Figure 10 – Overview of Joining System Asset
This is a generic interface common for all assets in the Joining System. The purpose of this interface is to provide the common information (Example: Identification, Health, Maintenance, etc.) of all the assets in a standardized way.
This interface has a standard MachineryItemIdentificationType add-in which can be assigned with MachineIdentificationType or MachineryComponentIdentificationType for an asset based on the requirement of the system.
Note: In a Joining System, Controller and Tool instances are generally considered as Machines and other assets can be modelled as components.
To determine if an asset is classified as Machine or Component is flexible and that is achieved using base add-in from OPC UA for Machinery specification MachineryItemIdentificationType which can be specialized using MachineIdentificationType or MachineryComponentIdentificationType.
The 2:Identification Object includes parameters from MachineryItemIdentificationType (which can be specialized to MachineIdentificationType or MachineryComponentIdentificationType) defined in .OPC 40001-1 It also implements IJoiningAdditionalInformationType.
Table 22 – IJoiningSystemAssetType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IJoiningSystemAssetType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the BaseInterfaceType defined in OPC 10000-7. |
|||||
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
2:Identification |
|
4:MachineryItemIdentificationType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Health |
|
2:FunctionalGroupType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
2:OperationCounters |
|
4:MachineryOperationCounterType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
4:LifetimeCounters |
|
4:MachineryLifetimeCounterType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
2:Maintenance |
|
2:FunctionalGroupType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
4:MachineryBuildingBlocks |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
4:Monitoring |
|
4:MonitoringType |
O |
|
0:HasAddIn |
Object |
4:Notifications |
|
4:NotificationsType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
4:Machinery Machine Identification |
|||||
|
4:Machinery Component Identification |
|||||
|
4:Machinery Building Block Organization |
|||||
|
4:Machinery Monitoring |
|||||
|
4:Machinery Notifications |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Health |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Monitoring Health |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Operation Counters |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Service |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Calibration |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Machinery Building Blocks |
|||||
The components of the IJoiningSystemAssetType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 23.
Table 23 – IJoiningSystemAssetType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
||
|
2:Identification |
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IJoiningAdditionalInformationType |
|
|
|
||
|
2:Identification |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Description |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
2:Identification |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
JoiningTechnology |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
2:Identification |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
SupplierCode |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
2:OperationCounters |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:PowerOnDuration |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
2:OperationCounters |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:OperationDuration |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
2:OperationCounters |
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:OperationCycleCounter |
0:UInteger |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
||
|
4:LifetimeCounters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
<LifetimeVariable> |
0:Number |
2:LifetimeVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
2:IDeviceHealthType |
|
|
|
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
2:DeviceHealth |
2:DeviceHealthEnum |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
2:DeviceHealthAlarms |
|
0:FolderType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorMessage |
0:LocalizedText |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorTimestamp |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorCode |
0:Int64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Health |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Temperature |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
2:IDeviceHealthType |
|
|
|
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
2:DeviceHealth |
2:DeviceHealthEnum |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
2:DeviceHealthAlarms |
|
0:FolderType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorMessage |
0:LocalizedText |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorTimestamp |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ErrorCode |
0:Int64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Temperature |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastService |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServicePlace |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NextService |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServiceCycleSpan |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServiceCycleCount |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NumberOfServices |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServiceReminderDays |
0:Int16 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
RemainingCycles |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServiceReminderCycles |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ServiceOperationCycles |
0:UInt64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
CalibrationValue |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastCalibration |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
CalibrationPlace |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NextCalibration |
0:UtcTime |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
SensorScale |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
CertificateUri |
0:UriString |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Connected |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Enabled |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
||
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
IOSignals |
SignalDataType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
The 2:Identification Object, using the standardized name defined in OPC 10000-100, provides identification information about the asset. This is a mandatory place holder and any asset inheriting IJoiningSystemAssetType will replace it with MachineIdentificationType or MachineryComponentIdentificationType.
The 2:Identification Object implements IJoiningAdditionalInformationType interface with the following properties:
Description is the system specific description of the asset.
Note: Although there is a description attribute at the node level in OPC UA, the Description property was added at the same level as the 2:Identification node for consistency.
JoiningTechnology is a human readable text to identify the joining technology.
SupplierCode is the SAP or ERP Supplier Code of the asset.
The Health Object is an instance of 2:FunctionalGroupType to group health related parameters for all the assets in a Joining System. The parameters for Health Object are described below.
Note: The Health Object is obsolete and upgraded based on the Machinery Base Specification. The following parameters are recommended to be accessed using 4:Monitoring/Health object.
2: DeviceHealth indicates the status as defined by NAMUR Recommendation NE107. Clients can read or monitor this Variable to determine the device condition.
ErrorMessage is the user readable text of the error reported by the given asset.
ErrorTimestamp is the timestamp when the error occurred in the given asset.
ErrorCode is the system specific code for the error that occurred.
Temperature is the measured temperature of the asset.
The 2:OperationCounters Object is an instance of 4:MachineryOperationCounterType which provides information about the duration something is turned on and how long it performs an activity. The parameters for 2:OperationCounters Object are defined in OPC 40001-1.
Note: The data type of 2:OperationCycleCounter is 0:UInteger and it is recommended to use 0:UInt64 for instances of an asset in a joining system.
The 4:LifetimeCounters Object is an instance of 4:MachineryLifetimeCounterType which provides an entry point to various lifetime variables.
The <LifetimeVariable > can be used for any kind of lifetime variables.
The Maintenance Object is an instance of 2:FunctionalGroupType to group maintenance related parameters for the given asset in a Joining System. It has the following objects described below:
The Service Object provides a set of parameters related to the service operations performed on a given asset.
The Calibration Object provides a set of parameters related to the calibration operations performed on a given asset.
The parameters for the Service Object are described below.
LastService is the date when the last service was completed.
ServicePlace is the location where the last service was completed.
Note: LastService and ServicePlace should have the initial operation date and the place for new assets.
NextService is the date of the next planned service.
ServiceCycleSpan is the maximum allowed number of cycles between two services.
ServiceCycleCount is the total cycle counter since the last service.
NumberOfServices is the total number of services taken place.
ServiceReminderDays is the number of days before a service reminder should be sent.
RemainingCycles is the remaining cycles before the service or maintenance. It can go negative if a service is skipped to indicate overshoot cycles.
ServiceReminderCycles is the configured threshold for the number of remaining cycles before the service reminder is sent. This is calculated based on the RemainingCycles.
Example: If ServiceReminderCycles <= RemainingCycles, then a service reminder is sent.
ServiceOperationCycles is the value of the 2:OperationCycleCounter when the last service was performed.
The parameters for Calibration Object are described below.
CalibrationValue is the configured value of the calibration.
LastCalibration is the date when the last calibration was completed.
CalibrationPlace is the location where the last calibration was completed.
NextCalibration is the date of the next planned calibration.
SensorScale is the nominal scale of the sensor. It corresponds also with the measurement range of the sensor.
CertificateUri contains the URI of a certificate of the calibration target in case the calibration target is certified and the information available. Otherwise, the Variable should be omitted. The String shall be a URI as defined by RFC 3986. Example: MCE test document.
The Parameters Object is an instance of 0:FolderType to group set of common parameters of an asset in a joining system. It has the following parameters described below:
Enabled indicates if a given asset is enabled or disabled. It can change by the EnableAsset method or by some other external interface.
Connected indicates if a given asset is connected or disconnected. It can change by DisconnectAsset method or by some other external interface.
IOSignals is an array of signals available for the asset.
Note: The Parameters Object is overridden for the specific assets and contains a set of additional parameters of the given asset.
The MachineryBuildingBlocks contains building blocks from OPC UA for Machinery.
The 4:Monitoring Object is an instance of 4:MonitoringType which provides a base structure for monitoring information of an asset. It provides some sub-structures for grouping different monitoring information. It contains the following sub-structures:
4:Status is the entry point for status information of the asset. If this Object is provided, and the MachineryItemState is provided, it shall be referenced. If this Object is provided and the MachineryOperationMode is provided, it shall be referenced.
4:Health is the entry point of health information of the asset.
Note: This is the commended entry point for health information of the asset.
4:Process is the entry point for process information of the asset.
4:Consumption is the entry point for consumption information of the asset.
The 4:Notifications Object is an instance of 4:NotificationsType which provides the entry point into notifications of an asset. It allows to provide such notifications as Events by becoming an EventNotifier or providing specific Objects for notifications. This specification does not define any specific EventTypes or other ObjectTypes for notifications but just the base infrastructure.
The IJoiningAdditionalInformationType provides additional parameters for 2:Identification of a given asset and is formally defined in Table 24.
Note: The descriptions of the following properties are given in section 7.3.2.
Table 24 – IJoiningAdditionalInformationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IJoiningAdditionalInformationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the BaseInterfaceType defined in OPC 10000-7. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Description |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
JoiningTechnology |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
SupplierCode |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Additional Information |
|||||
Table 25 – IControllerType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IControllerType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Controller |
|||||
The components of the IControllerType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 26.
Table 26 – IControllerType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:Byte |
0:MultiStateDiscreteType |
O, RO |
Type is the classification of a Controller. In Table 27, standardized values for EnumStrings are defined. Each instance of this type shall follow the defined sequence for the entries.
Note: Servers can add additional entries into the EnumStrings array and may provide translations of the texts in different locales.
Table 27 – IControllerType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
|||
|
OTHER SUPERVISORY_CONTROLLER PLC COMPUTER JOINING_PROCESS_CONTROLLER COMMUNICATION_CONTROLLER FEEDING_CONTROLLER |
The descriptions for EnumStrings values corresponding to Type are given below:
- OTHER
- SUPERVISORY_CONTROLLER is a controller which is not executing the process or moving actuators. It manages other controllers and may be a node or hub to other controllers.
- PLC is a Programmable Logic Controller which executes a sequence of operations. Examples would be part handling, providing fasteners, managing bit strokes.
- COMPUTER is an information processing unit such as a PC.
- JOINING_PROCESS_CONTROLLER is controller which is handling the joining process. It performs the joining and publishes its results.
- COMMUNICATION_CONTROLLER is a controller which is mainly in charge of handling communications.
- FEEDING_CONTROLLER is a controller which performs the fastener flow and provides the fastening elements.
It is a generic interface for any type of tool for various joining technologies. Examples: Tightening Tool, Gluing Applicator, etc.
Note: The respective joining technology specifications can define a sub-type of this interface for additional properties.
Table 28 – IToolType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IToolType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Tool |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Tool Operation Cycle Counter |
|||||
The components of the IToolType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 29.
Table 29 – IToolType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:Byte |
0:MultiStateDiscreteType |
M, RO |
Type is the classification of a Tool.
Note: Servers can add additional entries into the EnumStrings array and may provide translations of the texts in different locales.
Table 30 – IToolType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
|||
|
OTHER FIXTURED HANDHELD MANUAL |
Table 31 – IServoType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IServoType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Servo |
|||||
The components of the IServoType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 32.
Table 32 – IServoType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NodeNumber |
0:Int16 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
NodeNumber is the node identifier in multiple configurations. Examples: Cabinet with one controller and multiple servo/modules.
Table 33 – IMemoryDeviceType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IMemoryDeviceType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Memory Device |
|||||
The components of the IMemoryDeviceType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 34.
Table 34 – IMemoryDeviceType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
StorageCapacity |
0:UInt64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
UsedSpace |
0:UInt64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is the type of memory device. It may define the form factor, interface, or technology. Examples: Flash, CFAST, USB, etc.
Note: Memory or storage devices can be classified based on various factors. Hence an open string is provided to make it generic.
StorageCapacity is the static information on the size of the storage in Bytes.
UsedSpace is the static information on the size of the used space in Bytes.
Table 35 – ISensorType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ISensorType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Sensor |
|||||
The components of the ISensorType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 36.
Table 36 – ISensorType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:Byte |
0:MultiStateDiscreteType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
OverloadCount |
0:Int64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
MeasuredValue |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is the classification of a Sensor. In Table 37, standardized values for the EnumStrings are defined. Each instance of this type shall follow the defined sequence for the entries.
Note: Servers can add additional entries into the EnumStrings array and may provide translations of the texts in different locales.
Table 37 – ISensorType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
|||
|
OTHER TIME TORQUE ANGLE IMPULSE DISTANCE AREA VOLUME FORCE PRESSURE VOLTAGE CURRENT RESISTANCE POWER ENERGY MASS TEMPERATURE FREQUENCY JOLT VIBRATION NUMBER LINEAR_SPEED ANGULAR_SPEED LINEAR_ACCELERATION ANGULAR_ACCELERATION TORQUE_SPEED TORQUE_ACCELERATION |
OverloadCount is the number of overloads of the sensor, where the permissible load of the sensor was exceeded.
MeasuredValue is the actual measured value reported from a sensor.
Note: An instance of Sensor can be referenced to a respective Calibration Target which was used to calibrate the sensor. The standard models for Calibration Targets are defined in OPC 10000-200.
Table 38 – ICableType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ICableType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Cable |
|||||
|
|
|||||
The components of the ICableType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 39.
Table 39 – ICableType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:Byte |
0:MultiStateDiscreteType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
CableLength |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is the classification of the cable.
In Table 40, standardized values for the EnumStrings are defined. Each instance of this type shall follow the defined sequence for the entries.
Note: Servers can add additional entries into the EnumStrings array and may provide translations of the texts in different locales.
Table 40 – ICableType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
|||
|
OTHER TOOL_CABLE SENSOR_CABLE COMMUNICATION_CABLE POWER_CABLE IO_CABLE BUS_CABLE |
CableLength is the length of the cable.
Table 41 – IBatteryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IBatteryType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Battery |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Battery Operation Cycle Counter |
|||||
The components of the IBatteryType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 42.
Table 42 – IBatteryType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NominalVoltage |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
M, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Capacity |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
M, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ChargeCycleCount |
0:Int64 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
StateOfCharge |
0:Byte |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
StateOfHealth |
0:Byte |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
NominalVoltage is the nominal DC voltage of the battery.
Capacity is the nominal capacity of the battery.
ChargeCycleCount is the number of times the battery has been charged since the initial operation date.
StateOfCharge is the state of charge (SOC) indicator functions as a sort of fuel gauge that displays the usable amount of energy. This helps determine optimal charging and discharging. It is given in percentage.
StateOfHealth is the State of Health is a measurement that reflects the general condition of a battery and its ability to deliver the specified performance compared with a fresh battery. It considers such factors as charge acceptance, internal resistance, voltage, and self-discharge. It is given in percentage.
Type is a user readable text to determine the type of battery such as pack type, technology, chemical composition, battery standard, etc.
Table 43 – IPowerSupplyType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IPowerSupplyType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Power Supply |
|||||
The components of the IPowerSupplyType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 44.
Table 44 – IPowerSupplyType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
InputSpecification |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
OutputSpecification |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NominalPower |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ActualPower |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
InputSpecification is the input specification of the power supply. Example: 230 V, 50/60 Hz, 10 A.
OutputSpecification is the output specification of the power supply.
NominalPower is the maximum output power of the power supply.
ActualPower is the actual load consumption of the power supply.
Note: This value may not be exposed to the highest possible sample rate. This value is for information only and should not be used for real time processing.
Table 45 – IFeederType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IFeederType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Feeder |
|||||
The components of the IFeederType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 46.
Table 46 – IFeederType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:Byte |
0:MultiStateDiscreteType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Material |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
FillLevel |
0:Byte |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
FeedingSpeed |
0:Double |
JoiningDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is the classification of a Feeder. In Table 47, standardized values for the EnumStrings are defined. Each instance of this type shall follow the defined sequence for the entries.
Note: Servers can add additional entries into the EnumStrings array and may provide translations of the texts in different locales.
Table 47 – IFeederType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
|||
|
OTHER BOWL BUNKER CONVEYOR DRUM LINEAR SWORD TAPE MAGAZINE |
Material is the type or name of the part which is supplied by the feeder.
FillLevel is the fill level in the feeder in percentage [%]. (0%=empty, 100% = full).
FeedingSpeed indicates the output in parts per time. Example: fasteners / second.
Table 48 – IAccessoryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IAccessoryType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Accessory |
|||||
The components of the IAccessoryType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 49.
Table 49 – IAccessoryType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is a user readable open string to describe the type of accessory such as socket selector, operator panel, etc.
Table 50 – ISubComponentType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ISubComponentType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Parameters |
-- |
0:FolderType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management SubComponent |
|||||
The components of the ISubComponentType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 51.
Table 51 – ISubComponentType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Parameters |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Type |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
Type is a user readable open string to describe the type of subcomponent such as network module, etc.
Table 52 – ISoftwareType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ISoftwareType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Software |
|||||
Note: The instance of a Software most likely contains only the following parameters from IJoiningSystemAssetType, other parameters may not be applicable.
- Identification / ProductInstanceUri
- Identification / Manufacturer
- Identification / ManufacturerUri
- Identification / Model
- Identification / SoftwareRevision
- Identification / ComponentName
- Identification / ProductCode
- Identification / SerialNumber
- Identification / JoiningTechnology
Table 53 – IVirtualStationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IVirtualStationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the IJoiningSystemAssetType, inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Asset Management Virtual Station |
|||||
Note: The instance of a Virtual Station most likely contains only the following parameters from IJoiningSystemAssetType, other parameters may not be applicable.
- Identification / ProductInstanceUri
- Identification / Manufacturer
- Identification / ManufacturerUri
- Identification / ComponentName
- Identification / JoiningTechnology
- Identification / SerialNumber
- Note: SerialNumber is Mandatory from the MachineryItemIdentificationType and may not be applicable for a Virtual Station. Hence, it can be set to an empty value.
The Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service) are defined in Table 54. It shows the possible values for the Method call result codes.
Table 54 – Possible Method Result Codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The Method execution was successful, and the Status parameter indicates the successful operation. |
|
Uncertain |
The Method execution was successful, and the Status parameter indicates an error. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The user does not have the right to execute the Method. The client shall not evaluate the Status parameter. |
|
Bad_UnexpectedError |
The server is not able to execute the function because an unexpected error occurred. The Server might be temporarily unavailable or unreachable due to network failure. The client shall not evaluate the Status parameter. |
Table 55 shows the possible values for the Status parameter.
Note: The client shall not evaluate the Status parameter if the Method Result Code is Bad.
Table 55 – Possible Status Parameter Values
|
Status |
Description |
|
< 0 |
Shall be used for application-specific errors. |
|
> 0 |
Reserved for errors defined by this and future standards. |
|
0 |
OK/Success. |
|
1 |
NOT_OK – Generic Error. |
|
2 |
ProductInstanceUri not found. |
|
3 |
ProductInstanceUri not applicable. |
|
4 |
Input identifier/entity not found. |
|
5 |
Invalid input. |
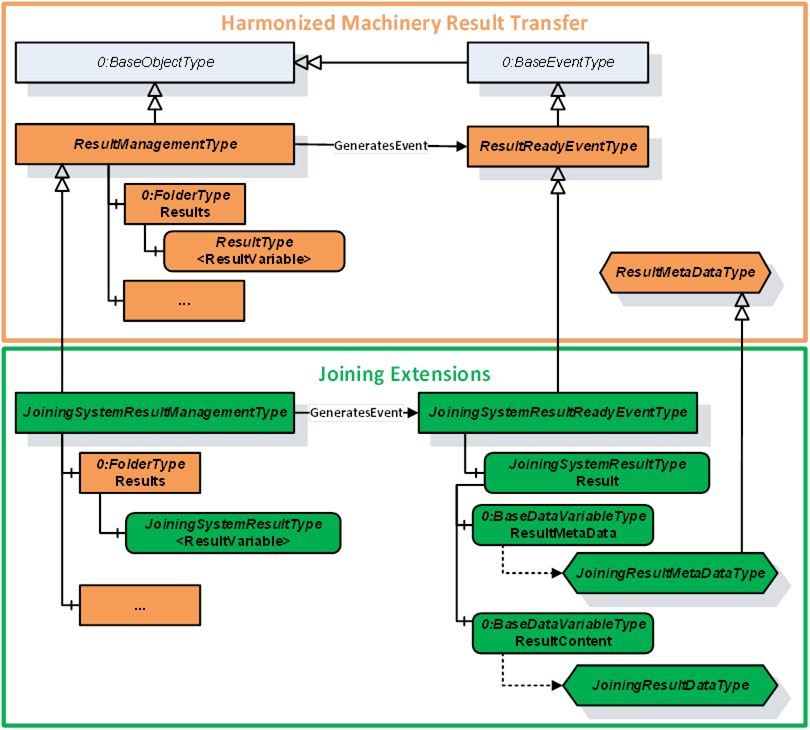
Figure 11 – Overview of Result Information Model
The JoiningSystemResultManagementType is a subtype of ResultManagementType and provides mechanism to access results generated by the underlying joining system. It is formally defined in Table 56.
Table 56 – JoiningSystemResultManagementType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JoiningSystemResultManagementType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 5:ResultManagementType defined in OPC 40001-101, which means it inherits the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
5:Results |
|
0:FolderType |
O |
|
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
JoiningSystemResultReadyEventType |
|
|
|
|
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
RequestedResultEventType |
|
|
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
RequestResults |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
RequestUnacknowledgedResults |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Get Latest Result |
|||||
|
IJT Get Result by Id |
|||||
|
IJT Get Result with Filter Criteria |
|||||
|
IJT Result Variable Access |
|||||
|
IJT Result Event Access |
|||||
|
IJT Acknowledge Results |
|||||
|
IJT Requested Result Variable Access |
|||||
|
IJT Requested Result Event Access |
|||||
|
IJT Request Results |
|||||
|
IJT Request Unacknowledged Results |
|||||
|
IJT Self Contained Consolidated Result |
|||||
|
IJT Consolidated Result with References |
|||||
|
IJT Partial Consolidated Result |
|||||
Note:
- 5:ResultTransfer Object is not used in the Joining System.
- The definition of the methods is available in OPC 40001-101.
The components of the JoiningSystemResultManagementType have additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 57.
Table 57 – JoiningSystemResultManagementType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
5:Results |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
<ResultVariable> |
5:ResultDataType |
JoiningSystemResultType |
OP |
|
5:Results |
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
<RequestedResultVariable> |
5:ResultDataType |
JoiningSystemResultType |
OP |
Each <ResultVariable> represents a result.
Note: It is recommended to use the BrowseName of the <ResultVariable> as “Result” if only one instance of the variable is exposed in the address space. The implementation of ResultVariable is application specific.
Each <RequestedResultVariable> represents a result returned by calling the RequestResults method or the RequestUnacknowledgedResults method.
Note: It is recommended to use the BrowseName of the <ResultVariable> as “RequestedResult” if only one instance of the variable is exposed in the address space. The implementation of RequestedResultVariable is application specific.
The Method RequestResults is used to receive stored results from the Server. A joining system can send live results or stored results.
The successful execution of this method will generate instances of RequestedResultEventType and update RequestedResultVariable.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 58 and Table 59 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
RequestResults (
[in]0:UInt64fromSequenceNumber,
[in]0:UInt64toSequenceNumber,
[in]0:UtcTimefromTime,
[in]0:UtcTimetoTime,
[in]0:DurationrequestedMinimumDurationBetweenResults,
[out]0:DurationrevisedMinimumDurationBetweenResults,
[out]0:Int64status,
[out]0:LocalizedTextstatusMessage)
Table 58 – RequestResults Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
fromSequenceNumber |
The starting sequence number for the Requested Results.
It is a required argument if results are requested based on the input sequence number range.
It shall be a valid value > 0. If 0, then fromTime and toTime are used. |
|
toSequenceNumber |
The ending sequence number of the Requested Results.
It is a required argument if results are requested based on the input sequence number range.
It shall be a valid value > 0 and shall be >= fromSequenceNumber. If 0, then fromTime and toTime are used. |
|
fromTime |
It is the start time for the Requested Results.
This argument is considered only when fromSequenceNumber and toSequenceNumber are set as 0. |
|
toTime |
It is the end time for the Requested Results.
This argument is considered only when fromSequenceNumber and toSequenceNumber are set as 0. |
|
requestedMinimumDurationBetweenResults |
The client can use this argument to configure a time interval between each Result to optimize the number of Results sent from the Server.
The Server can return the revised interval if the requested interval is not supported.
Note: It is only a requested minimum time interval by the client and the server could take additional time for processing. |
|
revisedMinimumDurationBetweenResults |
It is the minimum revised interval supported by the server. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 59 – RequestResults Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
RequestResults |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method RequestUnacknowledgedResults is used to receive unacknowledged results available in the joining system.
The successful execution of this method will generate instances of RequestedResultEventType and update RequestedResultVariable.
Note: It is recommended that this Method is used only by the Client that is responsible for exclusively storing the results.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 58 and Table 59 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
RequestUnacknowledgedResults (
[in]0:UInt32maxResults,
[in]0:DurationrequestedMinimumDurationBetweenResults,
[out]0:DurationrevisedMinimumDurationBetweenResults,
[out]0:UInt32unacknowledgedResultCount,
[out]0:Int64status,
[out]0:LocalizedTextstatusMessage)
Table 60 – RequestUnacknowledgedResults Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
maxResults |
It is the maximum results requested by the Client.
If 0, then the Server shall send all the unacknowledged results. |
|
requestedMinimumDurationBetweenResults |
The client can use this argument to configure a time interval between each Result to optimize the number of Results sent from the Server.
The Server can return the revised interval if the requested interval is not supported.
Note: It is only a requested minimum time interval by the client and the server could take additional time for processing. |
|
revisedMinimumDurationBetweenResults |
It is the minimum revised interval supported by the server. |
|
unacknowledgedResultCount |
It is the total count of unacknowledged results in the server. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 61 – RequestUnacknowledgedResults Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
RequestUnacknowledgedResults |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType provides a set of methods for various assets in a joining system and is formally defined in Table 62.
Table 62 – JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5, i.e., inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
0:QualifiedName |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetCalibration |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
EnableAsset |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DisconnectAsset |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
RebootAsset |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendFeedback |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetFeedbackFileList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetTime |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetOfflineTimer |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetIOSignals |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetIOSignals |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendIdentifiers |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendTextIdentifiers |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetIdentifiers |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
ResetIdentifiers |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetErrorInformation |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
ExecuteOperation |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Method Input Argument |
|||||
|
IJT Disconnect Asset |
|||||
|
IJT Enable Tool |
|||||
|
IJT Send Identifiers |
|||||
|
IJT Get Identifiers |
|||||
|
IJT Reset Identifiers |
|||||
|
IJT Set Calibration |
|||||
|
IJT Reboot Asset |
|||||
|
IJT Feedback Methods |
|||||
|
IJT IO Signals Methods |
|||||
|
IJT Get Error Information |
|||||
|
IJT Execute Operation |
|||||
|
IJT Set Time |
|||||
|
IJT Set Offline Timer |
|||||
The component Variables of the JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType have additional Attributes defined in Table 63.
Table 63 – JoiningSystemAssetMethodSetType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
|
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
2:MethodSet |
The default BrowseName for instances of the type. |
The Method SetCalibration is used to set the calibration information of a given asset.
It is intended to set the basic calibration information and does not cover the certification process.
Note:
- In a Joining System, calibration data is applicable primarily to a Sensor (if available), else it can be set for the Tool when the Sensor asset is not available.
- The Server shall update the respective Calibration information of the asset after execution of this method.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 64 and Table 65 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetCalibration (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]CalibrationDataTypecalibrationData,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 64 – SetCalibration Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
calibrationData |
It is the input calibration data which needs to be configured for the asset. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 65 – SetCalibration Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetCalibration |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method EnableAsset is used to Enable or Disable a given asset. It is mostly applicable for Tool.
The Asset.Parameters.Enabled variable shall be updated with the enable status and generate an event of JoiningSystemEventType with ConditionClass = SystemConditionClassType and ConditionSubClass = AssetEnabledConditionClassType or AssetDisabledConditionClassType..
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 66 and Table 67 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
EnableAsset (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Boolean enable,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 66 – EnableAsset Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
enable |
If true, it will enable the asset, else it will disable the asset. The default value is false. Note: If the asset is performing the joining operation when the method is executed, then it shall disable the asset after the current operation. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 67 – EnableAsset Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
EnableAsset |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DisconnectAsset is used to disconnect or connect the asset.
Note: It is intended to be used for physical assets connected with physical cables where an asset can be disconnected using the method before removing the cable connection.
Examples: Cable Tool connected to a Controller or a gateway, Robot docking.
The Asset.Parameters.Connected variable shall be updated with the connection status and generate an event of JoiningSystemEventType with ConditionClass = SystemConditionClassType and ConditionSubClass = AssetConnectedConditionClassType or AssetDisconnectedConditionClassType..
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 68 and Table 69 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DisconnectAsset (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Boolean disconnect,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 68 – DisconnectAsset Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
disconnect |
If true, it will prepare the asset for disconnect. The default value is false. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 69 – DisconnectAsset Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DisconnectAsset |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method RebootAsset is used to reboot an asset.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 70 and Table 71 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
RebootAsset (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 70 – RebootAsset Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 71 – RebootAsset Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
RebootAsset |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SendFeedback is used to send any type of feedback to a given asset. The feedback can be a text input or other types of feedback supported by the asset.
Note: The types of feedback files supported is application specific. Refer to the application documentation or configuration for the details of the feedback files.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 72 and
Table 73 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendFeedback (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Int16 feedbackType,
[in]0:String feedbackText,
[in]0:String feedbackFile,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 72 – SendFeedback Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
feedbackType |
It is the type of feedback and has the following pre-defined values: 0 – UNDEFINED 1 – OTHER 2 – TEXT 3 – VISUAL 4 – AUDIO 5 – VIBRATE |
|
feedbackText |
It is the text feedback if the feedbackType is TEXT. It is empty for any other feedback type. |
|
feedbackFile |
It is the file available in the asset which needs to be run for different types of feedback such as AUDIO, VIBRATE, etc. This can be retrieved using the GetFeedbackFileList method. It is optional and not applicable for text feedback. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 73 – SendFeedback Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendFeedback |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetFeedbackFileList is used to get the list of feedback files from the asset.
Note: The types of feedback files supported is application specific. Refer to the application documentation or configuration for the details of the feedback files.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 74 and Table 75 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetFeedbackFileList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]0:String[] feedbackFileList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 74 – GetFeedbackFileList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
feedbackFileList |
It is the list of feedback files available in the system. It contains the feedback filenames or the file paths which can be used as an input in SendFeedback method. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 75 – GetFeedbackFileList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetFeedbackFileList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetTime is used to set the time of the asset manually. It is recommended to be used only when an asset does not have automated time synchronization.
The joining system can report a respective event when the time is configured manually using this method.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 76 and Table 77 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetTime (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:UtcTime inputTime,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 76 – SetTime Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
inputTime |
It is the input time to be configured in the asset. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 77 – SetTime Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetTime |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetOfflineTimer is used to set the offline timer for the asset to determine how long the asset can perform the joining operations in an offline mode.
Note: If an asset performs the joining operation in offline mode after setting the offline timer, the corresponding results generated shall have the IsGeneratedOffline flag set to TRUE.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 78 and Table 79 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetOfflineTimer (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Duration offlineTimer,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 78 – SetOfflineTimer Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
offlineTimer |
It is the offlineTimer to be set. The behaviour of the asset when the timer is elapsed is application specific. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 79 – SetOfflineTimer Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetOfflineTimer |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetIOSignals is used to set a list of IO signals of the asset. The type of operations mapped to each signal is application specific.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 80 and Table 81 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetIOSignals (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]SignalDataType[] signalList,
[out]0:Int32[] signalStatusList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 80 – SetIOSignals Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
signalList |
It is the list of signals which needs to be set in the asset. |
|
signalStatusList |
It is the list of status for each signal. 0 – OK Values > 0 are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards. Values < 0 shall be used for application-specific errors. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 81 – SetIOSignals Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetIOSignals |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetIOSignals is used to get the list of available signals from the asset.
Note: Client can also subscribe to IOSignals variable in the address space to get the list of signals.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 82 and Table 83 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetIOSignals (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString[] signalIdList,
[out]SignalDataType[] signalList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 82 – GetIOSignals Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
signalIdList |
It is the list of signal identifiers requested. If it is empty, then all the available signals are returned from the asset. |
|
signalList |
It is the list of signals which are available in the asset based on the input signalIdList. If the signalIdList is empty, then all the available signals are sent from the asset. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 83 – GetIOSignals Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetIOSignals |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SendIdentifiers is used to send one or more identifiers to the joining system.
These identifiers can be used for selection of a joining process, etc.
These identifiers can often be part of the generated result.
The input argument to this method is an array of EntityDataType structure where every entity in the joining system can be associated to a specific type for filtering.
SendTextIdentifiers method can be used if identifiers cannot be sent as an array of EntityDataType.
Note: The decision on which set of identifiers are used for the selection of a joining process and which set of identifiers should be part of the generated result is application specific.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 84 and Table 85 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendIdentifiers (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]EntityDataType[] entityList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 84 – SendIdentifiers Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
entityList |
It is the list of identifiers sent to the joining system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 85 – SendIdentifiers Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendIdentifiers |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SendTextIdentifiers is used to send one or more identifiers to a joining system.
These identifiers can be used for selection of a joining process, etc.
These identifiers can often be part of the generated result.
Note: The decision on which set of identifiers are used for the selection of a joining process and which set of identifiers should be part of the generated result is application specific.
This method can be used only to send the values of the identifiers but it is recommended that SendIdentifiers is used instead of this method.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 86 and Table 87 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendTextIdentifiers (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString[] identifierList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 86 – SendTextIdentifiers Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
identifierList |
It is the list of identifiers sent to the joining system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 87 – SendTextIdentifiers Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendTextIdentifiers |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetIdentifiers is used to get the list of identifiers available in the system which were managed by external systems. The list of identifiers reported includes the identifiers sent by a Client or any other external interface.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 88 and Table 89 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetIdentifiers (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString[] identifierNames,
[out]EntityDataType[] entityList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 88 – GetIdentifiers Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
identifierNames |
The list of names of the identifiers which are requested. If it is empty, then all available identifiers are returned. |
|
entityList |
It is the list of identifiers available in the joining system based on the input criteria. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 89 – GetIdentifiers Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetIdentifiers |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method ResetIdentifiers is used to reset the specified identifiers.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 90 and Table 91 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
ResetIdentifiers (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString[] identifierList,
[in]0:Boolean resetAll,
[in]0:Boolean resetLatest,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 90 – ResetIdentifiers Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
identifierList |
It is the list of names of the identifiers which are requested to be reset. If it is NOT empty, then resetAll and resetLatest flags are ignored. If it is empty, then the resetAll or resetLatest flag is used. |
|
resetAll |
If True, it will reset all the identifiers available in the joining system and resetLatest flag is ignored. If False and identifierList is empty then the resetLatest flag is used. |
|
resetLatest |
If True, it will reset the latest identifier available in the system. Note: This is provided for supporting legacy systems. The criteria to determine which identifier is latest is application specific. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 91 – ResetIdentifiers Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ResetIdentifiers |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetErrorInformation is used to get the error information based on the input identifier. The details returned from the joining system is application specific.
Examples: Log file, Detailed Error Information or Event Logs, or an actual file or reference to some other entity in the system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 92 and Table 93 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetErrorInformation (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString errorId,
[out]0:BaseDataType errorContent,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 92 – GetErrorInformation Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
errorId |
It is the identifier of the error. It could be available as part of the JoiningResult. It is a mandatory input argument. |
|
errorContent |
It is the detailed error information. Examples: Log file, Detailed Error Information or Event Logs, etc. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 93 – GetErrorInformation Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetErrorInformation |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method ExecuteOperation is an application specific interface to execute any generic operations supported by a joining system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 94 and Table 95 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
ExecuteOperation (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Int32 operationType,
[in]0:String operationText,
[in]0:String vendorName,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 94 – ExecuteOperation Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
operationType |
It is the type of operation. The list of integer values corresponding to a specific operation is provided by the documentation or the joining system via some interface. |
|
operationText |
It is the optional text to provide information on the type of operation. |
|
vendorName |
It is the optional vendor’s name provided to identify the type of operations supported. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 95 – ExecuteOperation Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ExecuteOperation |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The JoiningProcessManagementType provides access to various joining processes in a joining system and is formally defined in Table 96.
Table 96 – JoiningProcessManagementType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JoiningProcessManagementType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5, i.e., inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
0:QualifiedName |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJoiningProcessList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJoiningProcessRevisionList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetJoiningProcessMapping |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SelectJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DeselectJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
IncrementJoiningProcessCounter |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DecrementJoiningProcessCounter |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetJoiningProcessCounter |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SetJoiningProcessSize |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
ResetJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
AbortJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
StartJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
StartSelectedJoining |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DeleteJoiningProcess |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetSelectedJoiningProgram |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Method Input Argument |
|||||
|
IJT Joining Process Management |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joining Process List |
|||||
|
IJT Abort Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Start Selected Joining |
|||||
|
IJT Select Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Deselect Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Reset Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Increment Joining Process Counter |
|||||
|
IJT Decrement Joining Process Counter |
|||||
|
IJT Set Joining Process Size |
|||||
|
IJT Start Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Delete Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Get Selected Joining Program |
|||||
|
IJT Send Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joining Process |
|||||
|
IJT Set Joining Process Counter |
|||||
|
IJT Set Joining Process Mapping |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joining Process Revision List |
|||||
The component Variables of the JoiningProcessManagementType have additional Attributes defined in Table 97.
Table 97 – JoiningProcessManagementType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
|
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
JoiningProcessManagement |
The default BrowseName for instances of the type. |
The Method SendJoiningProcess is used to send a joining process to the joining system. It can be used to insert a joining program or joining batch or joining job or any other process applicable to a joining system. It shall overwrite the joining process if it already exists in the joining system.
Note: The Server includes the business logic to validate the received joining process.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 98 and Table 99 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessDataTypejoiningProcess,
[in]0:TrimmedString selectionName,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 98 – SendJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcess |
With this argument the Client can provide the content of the joining process. |
|
selectionName |
With this argument the Client can provide the required selection name for the given joining process. It is optional and can be empty. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 99 – SendJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJoiningProcessList is used to get the list of joining process meta data available in the system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 100 and Table 101 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJoiningProcessList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]JoiningProcessMetaDataType[]joiningProcessList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 100 – GetJoiningProcessList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessList |
It is the list of joining process meta data available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 101 – GetJoiningProcessList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJoiningProcessList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJoiningProcessRevisionList is used to get the list available revisions of a specific joining process based on the joiningProcessOriginId.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 102 and Table 103 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJoiningProcessRevisionList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString joiningProcessOriginId,
[out]JoiningProcessMetaDataType[]joiningProcessList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 102 – GetJoiningProcessRevisionList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessOriginId |
It is the origin identifier of the joining process which is used to manage the revisions of a given joining process. |
|
joiningProcessList |
It is the list of joining process meta data available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 103 – GetJoiningProcessRevisionList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJoiningProcessRevisionList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJoiningProcess is used to get the joining process based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 104 and Table 105 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString joiningProcessId,
[out]JoiningProcessDataType joiningProcess,
[out]0:TrimmedString selectionName,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 104 – GetJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessId |
It is the identifier of the joining process. |
|
joiningProcess |
It is the joining process available in the system. |
|
selectionName |
It is the selection name of the joining process configured in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 105 – GetJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetJoiningProcessMapping is used to set the mapping of the joining process in a joining system. It can be used to map a joining process to a selection name.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 106 and Table 107 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetJoiningProcessMapping (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 106 – SetJoiningProcessMapping Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to map the respective joiningProcessId with selectionName and joiningProcessOriginId.
It shall at least contain the joiningProcessId and selectionName. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 107 – SetJoiningProcessMapping Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetJoiningProcessMapping |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SelectJoiningProcess is used to select the joining process based on the input arguments.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 108 and Table 109 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SelectJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 108 – SelectJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 109 – SelectJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SelectJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DeselectJoiningProcess is used to deselect any selected joining process.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 110 and Table 111 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DeselectJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 110 – DeselectJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 111 – DeselectJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DeselectJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method StartJoiningProcess is used to start the input joining process.
Note: It is not intended to be used in a hard real-time use case.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 112 and Table 113 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
StartJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in] EntityDataType[] associatedEntities,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 112 – StartJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
associatedEntities |
It is the list of identifiers used for performing the joining operation. It is optional and can be empty. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 113 – StartJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
StartJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method StartSelectedJoining is used to start the selected joining. The joining operation can be selected using SelectJoiningProcess or SelectJoint.
Note: It is not intended to be used in a hard real-time use case.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 114 and Table 115 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
StartSelectedJoining (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:Boolean deselectAfterJoining,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 114 – StartSelectedJoining Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
deselectAfterJoining |
If True, it will deselect the existing joining process after the joining operation is completed. The default value is False. Note: If deselection is not possible or fails, but the joining operation starts successfully, the status will be returned as successful. However, the statusMessage can include additional information. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 115 – StartSelectedJoining Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
StartSelectedJoining |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetJoiningProcessSize is used to set the size of the batch joining process.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 116 and Table 117 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetJoiningProcessSize (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in]0:UInt32 maxCounterSize,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 116 – SetJoiningProcessSize Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
maxCounterSize |
It is the maximum counter size for the joining process. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 117 – SetJoiningProcessSize Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetJoiningProcessSize |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method IncrementJoiningProcessCounter is used to increment the counter of the sequential joining processes such as Job, etc.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 118 and Table 119 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
IncrementJoiningProcessCounter (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in]0:UInt32 incrementCount,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 118 – IncrementJoiningProcessCounter Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
incrementCount |
It is the number of increments to be done for the joining process counter. The default value is 1 if it is not provided. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 119 – IncrementJoiningProcessCounter Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IncrementJoiningProcessCounter |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DecrementJoiningProcessCounter used to decrement the counter of the sequential joining processes such as Job, etc .
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 120 and Table 121 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DecrementJoiningProcessCounter (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in]0:UInt32 decrementCount,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 120 – DecrementJoiningProcessCounter Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
decrementCount |
It is the number of decrements to be done for the joining process counter. The default value is 1 if it is not provided. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 121 – DecrementJoiningProcessCounter Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DecrementJoiningProcessCounter |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SetJoiningProcessCounter is used to set the counter of a sequential joining processes (such as Job, etc.) to the given input value.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 122 and Table 123 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SetJoiningProcessCounter (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in]0:UInt32 counterValue,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 122 – SetJoiningProcessCounter Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
counterValue |
It is the new counter value for the joining process. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 123 – SetJoiningProcessCounter Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SetJoiningProcessCounter |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method ResetJoiningProcess is used to reset/restart the sequential joining processes such as Job, etc.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 124 and Table 125 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
ResetJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 124 – ResetJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 125 – ResetJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ResetJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method AbortJoiningProcess is used to abort the input joining process if it is under execution.
Note: It is not intended to be used in a hard real-time use case.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 126 and Table 127 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
AbortJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[in]0:LocalizedText abortMessage,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 126 – AbortJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
abortMessage |
It is an optional message sent from the Client to the joining system to indicate the reason for aborting the joining operation. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 127 – AbortJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AbortJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DeleteJoiningProcess is used to delete the input joining process.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 126 and Table 127 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DeleteJoiningProcess (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JoiningProcessIdentificationDataType
joiningProcessIdentification,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 128 – DeleteJoiningProcess Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joiningProcessIdentification |
It is the identification information of the joining process which can be used to select the joiningProcess.
If it includes joiningProcessId then it is used for the selection and other arguments are ignored.
If it does not include joiningProcessId, then the system checks for joiningProcessOriginId which will be used for the selection.
If joiningProcessId and joiningProcessOriginId are not available, then the system uses the selectionName for the selection of the joining process. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 129 – DeleteJoiningProcess Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DeleteJoiningProcess |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetSelectedJoiningProgram is used to get the selected joining program for a given asset.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 130 and Table 131 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetSelectedJoiningProgram (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]JoiningProcessMetaDataTypeselectedJoiningProgram,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 130 – GetSelectedJoiningProgram Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
selectedJoiningProgram |
It is the selected joining program for the input asset. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 131 – GetSelectedJoiningProgram Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetSelectedJoiningProgram |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The JointManagementType provides access to the Joint and associated information and is formally defined in Table 132.
Table 132 – JointManagementType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
JointManagementType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5, i.e., inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
0:QualifiedName |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendJoint |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendJointDesign |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SendJointComponent |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
SelectJoint |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointRevisionList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointDesignList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointComponentList |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJoint |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointDesign |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetJointComponent |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DeleteJoint |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DeleteJointDesign |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
DeleteJointComponent |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
IJT Method Input Argument |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Management |
|||||
|
IJT Send Joint |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint List |
|||||
|
IJT Select Joint |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Data |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint |
|||||
|
IJT Send Joint Design |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint Design List |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint Design |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Design Data |
|||||
|
IJT Send Joint Component |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint Component List |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint Component |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Component Data |
|||||
|
IJT Joint Management |
|||||
|
IJT Delete Joint |
|||||
|
IJT Delete Joint Design |
|||||
|
IJT Delete Joint Component |
|||||
|
IJT Get Joint Revision List |
|||||
The component Variables of the JointManagementType have additional Attributes defined in Table 133.
Table 133 – JointManagementType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
|
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
JointManagement |
The default BrowseName for instances of the type. |
The Method SendJoint is used to send a joint to a joining system. If the input joint already exists in the system, it shall be overwritten.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 134 and Table 135 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendJoint (
[in]0:StringproductInstanceUri,
[in]JointDataTypejoint,
[out]0:Int64status,
[out]0:LocalizedTextstatusMessage)
Table 134 – SendJoint Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
joint |
With this argument the Client can provide the content of the joint. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 135 – SendJoint Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendJoint |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SendJointDesign is used to send a joint design to a joining system. If the input joint design already exists in the system, it shall be overwritten.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 136 and Table 137 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendJointDesign (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JointDesignDataTypejointDesign,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 136 – SendJointDesign Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointDesign |
With this argument the Client can provide the content of the joint design. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 137 – SendJointDesign Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendJointDesign |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SendJointComponent is used to send a joint component to a joining system. If the input joint component already exists in the system, it shall be overwritten.
Examples: Threaded fastener, rivet, etc.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 138 and Table 139 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SendJointComponent (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]JointComponentDataTypejointComponent,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 138 – SendJointComponent Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointComponent |
With this argument the Client can provide the joint component. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 139 – SendJointComponent Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SendJointComponent |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method SelectJoint is used to select the joint and the associated joining process.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 140 and Table 141 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
SelectJoint (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointId,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointOriginId,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 140 – SelectJoint Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointId |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the joint which should be selected for performing the next joining operation. |
|
jointOriginId |
With this argument the Client can provide the common identifier of the joint which should be selected for performing the next joining operation.
It is optional and can be empty if the underlying system does not manage revisions of a joint. If jointId is provided, then this argument shall be ignored. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 141 – SelectJoint Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SelectJoint |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointList is used to get the list of available joints in the system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 142 and Table 143 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]JointDataType[] jointList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 142 – GetJointList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointList |
It is the list of joints available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 143 – GetJointList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointRevisionList is used to get the list available revisions of a specific joint based on the jointOriginId.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 144 and Table 145 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointRevisionList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointOriginId,
[out]JointDataType[] jointList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 144 – GetJointRevisionList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointOriginId |
It is the origin identifier of the joint which is used to manage the revisions of a given joint. |
|
jointList |
It is the list of joints available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 145 – GetJointRevisionList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointRevisionList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointDesignList is used to get the list of available joint designs in the system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 146 and
Table 147 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointDesignList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]JointDesignDataType[]jointDesignList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 146 – GetJointDesignList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointDesignList |
It is the list of joint designs available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 147 – GetJointDesignList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointDesignList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointComponentList is used to get the list of available joint components in the system.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 148 and Table 149 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointComponentList (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[out]JointComponentDataType[]jointComponentList,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 148 – GetJointComponentList Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointComponentList |
It is the list of joint components available in the system. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 149 – GetJointComponentList Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointComponentList |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJoint is used to get the joint based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 150 and Table 151 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJoint (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointId,
[out]JointDataType joint,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 150 – GetJoint Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointId |
It is the identifier of the joint. |
|
joint |
It is the joint based on the input identifier. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 151 – GetJoint Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJoint |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointDesign is used to get the joint design based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 152 and Table 153 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointDesign (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointDesignId,
[out]JointDesignDataTypejointDesign,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 152 – GetJointDesign Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointDesignId |
It is the identifier of the joint design |
|
jointDesign |
It is the joint design based on the input identifier. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 153 – GetJointDesign Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointDesign |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method GetJointComponent is used to get the joint component based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 154 and Table 155 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
GetJointComponent (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointComponentId,
[out]JointComponentDataTypejointComponent,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 154 – GetJointComponent Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointComponentId |
It is the identifier of the joint component. |
|
jointComponent |
It is the joint component based on the input identifier. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 155 – GetJointComponent Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetJointComponent |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DeleteJoint is used to delete the joint based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 150 and Table 151 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DeleteJoint (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointId,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointOriginId,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 156 – DeleteJoint Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointId |
It is the identifier of the joint. |
|
jointOriginId |
With this argument the Client can provide the common identifier of the joint which should be selected for performing the next joining operation.
It is optional and can be empty if the underlying system does not manage revisions of a joint. If jointId is provided, then this argument shall be ignored. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 157 – DeleteJoint Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DeleteJoint |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DeleteJointDesign is used to delete the joint design based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 150 and Table 151 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DeleteJointDesign (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointDesignId,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 158 – DeleteJointDesign Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointDesignId |
It is the identifier of the joint design. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 159 – DeleteJointDesign Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DeleteJointDesign |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The Method DeleteJointComponent is used to delete the joint component based on the input identifier.
The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 150 and Table 151 specify the Arguments and AddressSpace representation, respectively.
Signature
DeleteJointComponent (
[in]0:String productInstanceUri,
[in]0:TrimmedString jointComponentId,
[out]0:Int64 status,
[out]0:LocalizedText statusMessage)
Table 160 – DeleteJointComponent Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
productInstanceUri |
With this argument the Client can provide the identifier of the asset on which this method is applicable. It can be empty if the method is modelled directly under the required asset. If it is empty, the system can consider the identifier of the asset where the Server is running. |
|
jointComponentId |
It is the identifier of the joint component. |
|
status |
It provides the status of the Method execution. Refer 7.4 for details. |
|
statusMessage |
It provides the high-level status information in a user-friendly text. |
Table 161 – DeleteJointComponent Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DeleteJointComponent |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |