Objects and Variables described in the following subclauses can be extended by additional Properties or References to other Nodes, except where it is stated in the text that it is restricted.
To promote interoperability of clients and Servers, the OPC UA AddressSpace is structured as a hierarchy, with the top levels standardised for all Servers. Figure 1 illustrates the structure of the AddressSpace. All Objects in this figure are organised using Organizes References and have the ObjectType FolderType as type definition.
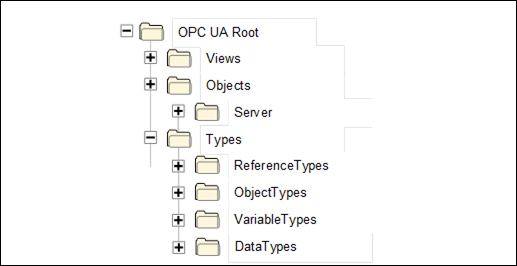
Figure 1 – Standard AddressSpace structure
The remainder of this provides descriptions of these standard Nodes and the organization of Nodes beneath them. Servers typically implement a subset of these standard Nodes, depending on their capabilities.
This standard Object is the browse entry point for the AddressSpace. It contains a set of Organizes References that point to the other standard Objects. The "Root" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses. It is formally defined in Table 100.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Root |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
Views |
Defined in 8.2.3 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
Objects |
Defined in 8.2.4 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
Types |
Defined in 8.2.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
||||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for Views. Only Organizes References are used to relate View Nodes to the "Views" standard Object. All View Nodes in the AddressSpace shall be referenced by this Node, either directly or indirectly. That is, the "Views" Object may reference other Objects using Organizes References. Those Objects may reference additional Views. Figure 2 illustrates the Views organization. The "Views" standard Object directly references the Views "View1" and "View2" and indirectly "View3" by referencing another Object called "Engineering".
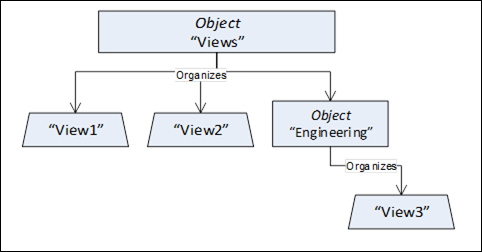
The "Views" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses. The "Views" Object is formally defined in Table 101.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||
|
BrowseName |
Views |
||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
Conformance Units |
|||
|
Base Info Core Views Folder |
|||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for Object Nodes. Figure 3 illustrates the structure beneath this Node. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects to the "Objects" standard Object. A View Node can be used as entry point into a subset of the AddressSpace containing Objects and Variables and thus the "Objects" Object can also reference View Nodes using Organizes References. The intent of the "Objects" Object is that all Objects and Variables that are not used for type definitions or other organizational purposes (e.g. organizing the Views) are accessible through hierarchical References starting from this Node. However, this is not a requirement, because not all Servers may be able to support this. This Object references the standard Server Object defined in 8.3.2.
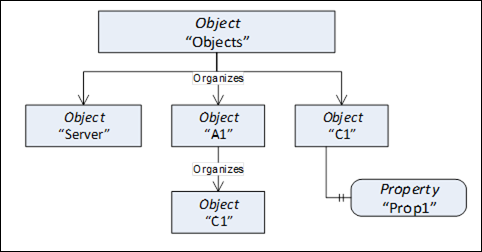
Figure 3 – Objects organization
The "Objects" Object is formally defined in Table 102.
Table 102 – Objects definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Objects |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
Server |
Defined in 8.3.2 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
Locations |
Defined in 8.2.12. |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
||||
This standard Object Node is the browse entry point for type Nodes. Figure 1 illustrates the structure beneath this Node. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects to the "Types" standard Object. The "Types" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses. It is formally defined in Table 103.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Types |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
ObjectTypes |
Defined in 8.2.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
VariableTypes |
Defined in 8.2.7 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
ReferenceTypes |
Defined in 8.2.8 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
DataTypes |
Defined in 8.2.9 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
EventTypes |
Defined in 8.2.10 |
|
|
Organizes |
Object |
InterfaceTypes |
Defined in 8.2.11 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Types Folders |
||||
This standard Object Node is the browse entry point for ObjectType Nodes. Figure 4 illustrates the structure beneath this Node showing some of the standard ObjectTypes defined in Clause 6. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects and ObjectTypes to the "ObjectTypes" standard Object. The "ObjectTypes" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses.
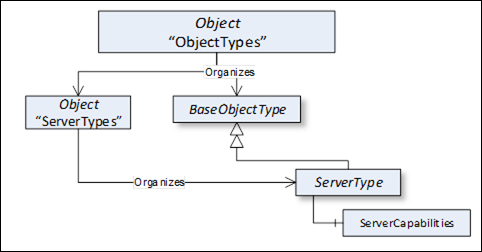
Figure 4 – ObjectTypes organization
The intention of the "ObjectTypes" Object is that all ObjectTypes of the Server are either directly or indirectly accessible browsing HierarchicalReferences starting from this Node. However, this is not required and Servers might not provide some of their ObjectTypes because they may be well-known in the industry, such as the ServerType defined in 6.3.1.
This Object also indirectly references the BaseEventType defined in 6.4.2, which is the base type of all EventTypes. Thereby it is the entry point for all EventTypes provided by the Server. It is required that the Server expose all its EventTypes, so a client can usefully subscribe to Events.
The "ObjectTypes" Object is formally defined in Table 104.
Table 104 – ObjectTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
ObjectTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
ObjectType |
BaseObjectType |
Defined in 6.2 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Types Folders |
||||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for VariableType Nodes. Figure 5 illustrates the structure beneath this Node. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects and VariableTypes to the "VariableTypes" standard Object. The "VariableTypes" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses.
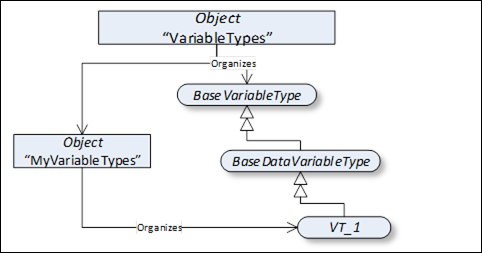
Figure 5 – VariableTypes organization
The intent of the "VariableTypes" Object is that all VariableTypes of the Server are either directly or indirectly accessible browsing HierarchicalReferences starting from this Node. However, this is not required and Servers might not provide some of their VariableTypes, because they may be well-known in the industry, such as the "BaseVariableType" defined in 7.2.
The "VariableTypes" Object is formally defined in Table 105.
Table 105 – VariableTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
VariableTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
VariableType |
BaseVariableType |
Defined in 7.2 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Types Folders |
||||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for ReferenceType Nodes. Figure 6 illustrates the organization of ReferenceTypes. Organizes References are used to define ReferenceTypes and Objects referenced by the "ReferenceTypes" Object. The "ReferenceTypes" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses. See Clause 11 for a discussion of the standard ReferenceTypes that appear beneath the "ReferenceTypes" Object.
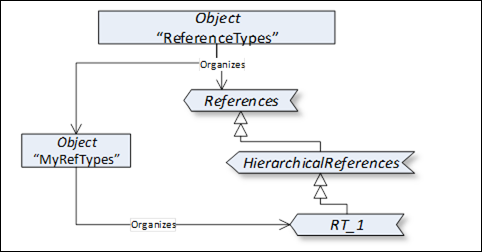
Figure 6 – ReferenceType definitions
Since ReferenceTypes will be used as filters in the browse Service and in queries, the Server shall provide all its ReferenceTypes, directly or indirectly following hierarchical References starting from the "ReferenceTypes" Object. This means that, whenever the client follows a Reference, the Server shall expose the type of this Reference in the ReferenceType hierarchy. It shall provide all ReferenceTypes so that the client would be able, following the inverse subtype of References, to come to the base References ReferenceType. It does not mean that the Server shall expose the ReferenceTypes that the client has not used any Reference of.
The "ReferenceTypes" Object is formally defined in Table 106.
Table 106 – ReferenceTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
ReferenceTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
ReferenceType |
References |
Defined in 11.1 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Types Folders |
||||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for DataTypes that the Server wishes to expose in the AddressSpace.
DataType Nodes should be made available using Organizes References pointing either directly from the "DataTypes" Object to the DataType Nodes or using additional Folder Objects for grouping purposes. The intent is that all DataTypes of the Server exposed in the AddressSpace are accessible following hierarchical References starting from the "DataTypes" Object. However, this is not required.
The "DataTypes" Object is formally defined in Table 107.
Table 107 – DataTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
DataTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
DataType |
BaseDataType |
Defined in 12.2 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Core Types Folders |
||||
This standard Object Node is the browse entry point for EventType Nodes. Figure 7 illustrates the structure beneath this Node showing some of the standard EventTypes defined in Clause 6. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects and ObjectTypes to the "EventTypes" standard Object. The "EventTypes" Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses.
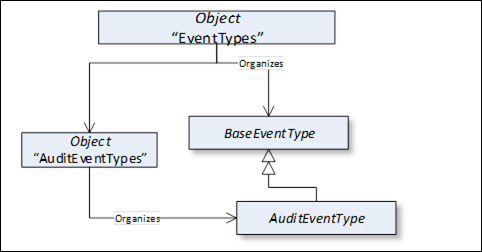
Figure 7 – EventTypes organization
The intention of the "EventTypes" Object is that all EventTypes of the Server are either directly or indirectly accessible browsing HierarchicalReferences starting from this Node. It is required that the Server expose all its EventTypes, so a client can usefully subscribe to Events.
The "EventTypes" Object is formally defined in Table 108.
Table 108 – EventTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
EventTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
ObjectType |
BaseEventType |
Defined in 6.4.2 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Address Space Events 2 |
||||
This standard Object Node is the browse entry point for ObjectType Nodes that represent Interfaces. Figure 8 illustrates the structure beneath this Node showing some of the standard ObjectTypes defined in clause 6. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects and Interfaces to the “InterfaceTypes” standard Object. The “InterfaceTypes” Object shall not reference any other NodeClasses.
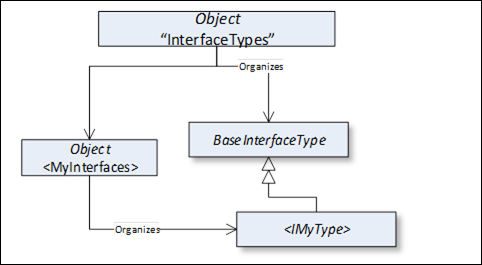
Figure 8 – InterfaceTypes Organization
The intention of the “InterfaceTypes” Object is that all Interfaces of the Server are either directly or indirectly accessible browsing HierarchicalReferences starting from this Node. However, this is not required and Servers might not provide some of their Interfaces because they may be well-known in the industry.
The “InterfaceTypes” Object is formally defined in Table 109.
Table 109 – InterfaceTypes definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
InterfaceTypes |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Organizes |
ObjectType |
BaseInterfaceType |
Defined in 6.9 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Address Space Interfaces |
||||
This standard Object is the browse entry point for Object Nodes which represent different types of locations. Figure 9 illustrates the structure beneath this Node. Only Organizes References are used to relate Objects.
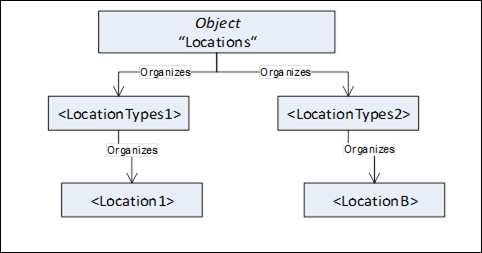
Figure 9 – Locations organization
The intent of the "Locations" Object is an entry point for different types of locations. The types of locations organize locations.
The "Locations" Object is formally defined in Table 110.
Table 110 – Locations definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Locations |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
FolderType |
Defined in 6.6 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Locations Object |
||||
The Server Object and its containing Objects and Variables are built in a way that the information can be gained in several ways, suitable for different kinds of clients having different requirements. Annex A gives an overview of the design decisions made in providing the information in that way and discusses the pros and cons of the different approaches. Figure 10 gives an overview of the containing Objects and Variables of the diagnostic information of the Server Object and where the information can be found.
The SessionsDiagnosticsSummary Object contains one Object per session and a Variable with an array with one entry per session. This array is of a complex DataType holding the diagnostic information about the session. Each Object representing a session references a complex Variable containing the information about the session using the same DataType as the array containing information about all sessions. Such a Variable also exposes all its information as Variables with simple DataTypes containing the same information as in the complex DataType. Not shown in Figure 10 is the security-related information per session, which follows the same rules.
The Server provides an array with an entry per subscription containing diagnostic information about this subscription. Each entry of this array is also exposed as a complex Variable with Variables for each individual value. Each Object representing a session also provides such an array, but provides the subscriptions of that session.
The arrays containing information about the sessions or the subscriptions may be of different length for different connections with different user credentials since not all users may see all entries of the array. That also implies that the length of the array may change if the user is impersonated. Therefore, clients that subscribe to a specific index range may get unexpected results.
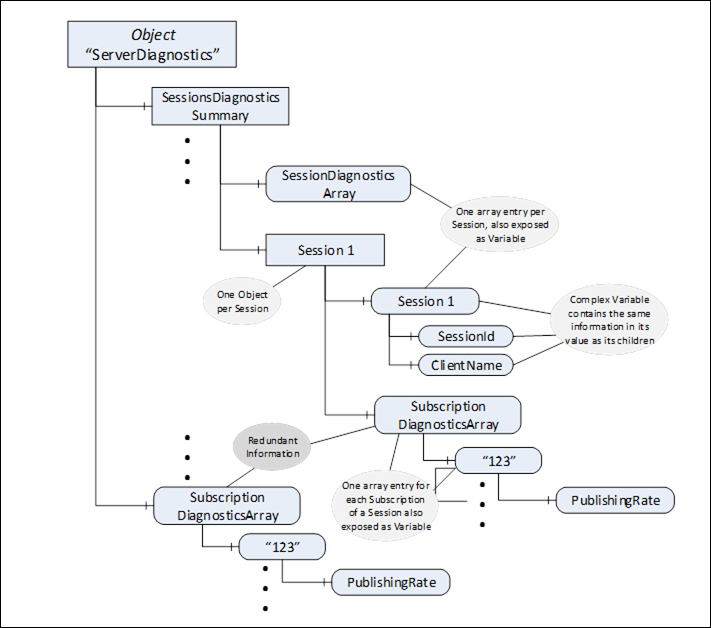
Figure 10 – Excerpt of diagnostic information of the Server
This Object is used as the browse entry point for information about the Server. The content of this Object is already defined by its type definition in 6.3.1. It is formally defined in Table 111. The Server Object serves as root notifier, that is, its EventNotifier Attribute shall be set providing Events. All Events of the Server shall be accessible subscribing to the Events of the Server Object.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
Server |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ServerType |
Defined in 6.3.1 |
|||
|
Conformance Units |
||||||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
||||||
|
Address Space Events 2 |
||||||
The additional definition for the conformance units of the Server Object are defined in Table 112.
Table 112 – Server Additional Conformance Units
|
BrowsePath |
Conformance Units |
|||
|
ServerArray |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
NamespaceArray |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
ServerStatus |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
ServiceLevel |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Auditing |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
VendorServerInfo |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
ServerRedundancy |
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Core Structure 2 |
|||
|
ServerCapabilities |
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities 2 |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
Base Info Server Capabilities Subscriptions |
|||
|
ServerDiagnostics |
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Diagnostics |
|||
|
Base Info Fixed SamplingInterval |
|||
|
Base Info Security Role Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info Events Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info Events Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info Method Capabilities |
|||
|
GetMonitoredItems |
Base Info GetMonitoredItems Method |
|||
|
ResendData |
Base Info ResendData Method |
|||
|
SetSubscriptionDurable |
Subscription Durable |
|||
|
EstimatedReturnTime |
Base Info Estimated Return Time |
|||
|
UrisVersion |
Session Sessionless Invocation |
|||
|
RequestServerStateChange |
Base Info RequestServerStateChange Method |
|||
|
LocalTime |
Base Info LocalTime |
|||
|
Base Info History Read Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info History ReadData Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info History ReadEvents Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info History UpdateEvents Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info History UpdateData Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info Node Management Capabilities |
|||
|
Base Info Query Capabilities |
The ModellingRule ExposesItsArray is defined in OPC 10000-3. Its representation in the AddressSpace, the "ExposesItsArray" Object, is formally defined in Table 113.
Table 113 – ExposesItsArray definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
ExposesItsArray |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ModellingRuleType |
Defined in 6.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Base Types |
||||
The ModellingRule Mandatory is defined in OPC 10000-3. Its representation in the AddressSpace, the "Mandatory" Object, is formally defined in Table 114.
Table 114 – Mandatory definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Mandatory |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ModellingRuleType |
Defined in 6.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Base Types |
||||
The ModellingRule Optional is defined in OPC 10000-3. Its representation in the AddressSpace, the "Optional" Object, is formally defined in Table 115.
Table 115 – Optional definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
Optional |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ModellingRuleType |
Defined in 6.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Base Types |
||||
The ModellingRule OptionalPlaceholder is defined in OPC 10000-3. Its representation in the AddressSpace, the "OptionalPlaceholder" Object, is formally defined in Table 116.
Table 116 – OptionalPlaceholder definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
OptionalPlaceholder |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ModellingRuleType |
Defined in 6.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Base Types |
||||
The ModellingRule MandatoryPlaceholder is defined in OPC 10000-3. Its representation in the AddressSpace, the "MandatoryPlaceholder" Object, is formally defined in Table 117.
Table 117 – MandatoryPlaceholder definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||
|
BrowseName |
MandatoryPlaceholder |
|||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Comment |
|
|
HasTypeDefinition |
ObjectType |
ModellingRuleType |
Defined in 6.5 |
|
|
Conformance Units |
||||
|
Base Info Base Types |
||||