A power train typically consists of one motor and gear to provide the required torque. Often there is a one-to-one relation between axes and power trains, but it is also possible to have axis coupling and thus one power train can move multiple axes and one axis can be moved by multiple power trains. One power train can have multiple drives, motors, and gears when these components move logically the same axes, for example in a master/slave setup. Examples are described in Annex B. The PowerTrainType represents instances of power trains of a motion device and is formally defined in
Table 17.
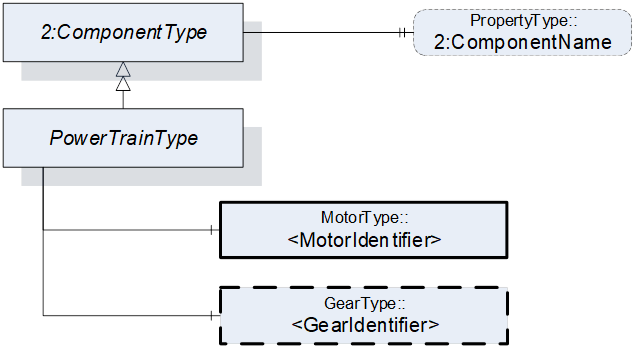
Figure 15 – Overview PowerTrainType
Table 17 – PowerTrainType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
PowerTrainType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the ComponentType defined in OPC Unified Architecture for Devices (DI), inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<MotorIdentifier> |
|
MotorType |
MP |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<GearIdentifier> |
|
GearType |
OP |
|
Moves |
Object |
<AxisIdentifier> |
|
AxisType |
OP |
|
HasSlave |
Object |
<PowerTrainIdentifier> |
|
PowerTrainType |
OP |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:ComponentName |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Rob MotionDeviceSystem Base |
|||||
|
Rob PowerTrain AM Extended |
|||||
The ComponentName property provides a user writable name provided by the vendor, integrator, or user of the device. The ComponentName may be a default name given by the vendor.
The ComponentName of the PowerTrainType provides a manufacturer-specific power train identifier within the control system.
This property is defined by ComponentType defined in OPC 10000-100.
<MotorIdentifier> indicates that a power train contains one or more motors represented by MotorType instances.
The IsConnectedTo ReferenceType defined in 8.6 is intended to provide the relationship between a motor and a gear of a power train.
<GearIdentifier> indicates that a power train may contain one or more gears represented by GearType instances.
The IsConnectedTo ReferenceType defined in 8.6 is intended to provide the relationship between a motor and a gear of a power train.
Moves is a reference to provide the relationship of power trains to axes. For complex kinematics this does not need to be a one-to-one relationship, because a power train might influence the motion of more than one axis. This reference connects all axis to a power train that that move when only this power train moves and all other powertrains stand still. The InverseName is IsMovedBy.
HasSlave is a reference to provide the master-slave relationship of power trains which provide torque for a common axis. The InverseName is IsSlaveOf.