This section defines the ReferenceTypes that are inherent to the present companion specification. Figure 25 describes informally the hierarchy of these Reference Types. OPC UA Reference Types are defined in OPC 10000-3.
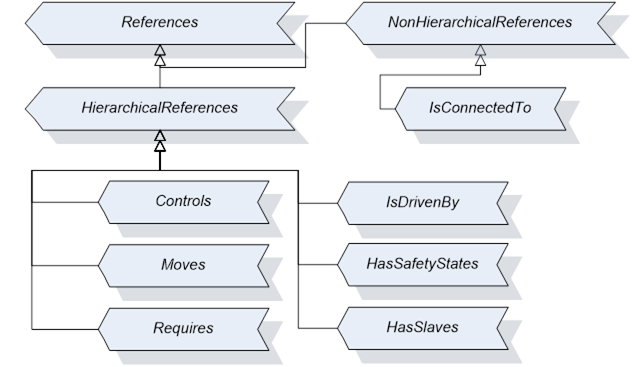
Figure 25 – Reference Type Hierarchy
The OPC UA ReferenceType Controls is used to describe dependencies between objects which have a controlling character. The BrowseName Controls and the InverseName IsControlledBy describe semantically the hierarchical dependency e.g. a controlling device Controls a controlled machine module.
Example for usage in this companion specification: If one controller Controls several motion devices, each motion device IsControlledBy the same controller.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 50 – Controls Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Controls |
||||
|
InverseName |
IsControlledBy |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType Moves is used to describe the coupling between a power train and the axes from the power train point of view. A power train has a Moves reference to all axis that are moving when only this powertrain moves.
For examples see Annex B.1.8.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 51 – Controls Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Moves |
||||
|
InverseName |
IsMovedBy |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType Requires is used to describe the coupling between a power train and axes from the axis point of view. An axis has a Requires reference to all powertrains that need to move such that only this single axis moves.
For examples see Annex B.1.8.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 52 – Controls Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Requires |
||||
|
InverseName |
IsRequiredBy |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType IsDrivenBy is used to describe dependencies between objects which have a driving or powering character. The BrowseName IsDrivenBy and the InverseName Drives describe semantically the hierarchical dependency.
Example for usage in this companion specification: an electrical motor IsDrivenBy an servo amplifier (drive) and an internal drive of a motion device or a drive as a component of a controller Drives a motor.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 53 – Drives Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IsDrivenBy |
||||
|
InverseName |
Drives |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType IsConnectedTo is used to describe dependencies between objects which are mounted or mechanically linked or connected to each other. The IsConnectedTo reference is symmetric and has no InverseName.
Example for usage in this companion specification: a motor IsConnectedTo to a gear and vice versa.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 54 – IsConnectedTo Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IsConnectedTo |
||||
|
InverseName |
|
||||
|
Symmetric |
True |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the NonHierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType HasSafetyStates is used to describe dependencies between objects to show which (controller) object is responsible for the execution of the safety-functionality. The BrowseName HasSafetyStates and the InverseName SafetyStatesOf describe semantically the hierarchical dependency.
Example for usage in this companion specification: a controller HasSafetyStates and the reference shows to an instance of SafetyStatesType. It is possible that there are two controller in one motion device system.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 55 – HasSafetyStates Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
HasSafetyStates |
||||
|
InverseName |
SafetyStatesOf |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
The OPC UA ReferenceType HasSlave is a reference to provide the master-slave relationship of power trains which provide torque for a common axis. The InverseName is IsSlaveOf.
The SourceNode of this type shall be an ObjectType or Object and the TargetNode shall be an Object.
Table 56 – HasSlave Reference Definition
|
Attributes |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
HasSlave |
||||
|
InverseName |
IsSlaveOf |
||||
|
Symmetric |
False |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Subtype of the HierarchicalReferences defined in OPC Unified Architecture Part 5 |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |