The AxisType describes an axis of a motion device. It is formally defined in Table 21.
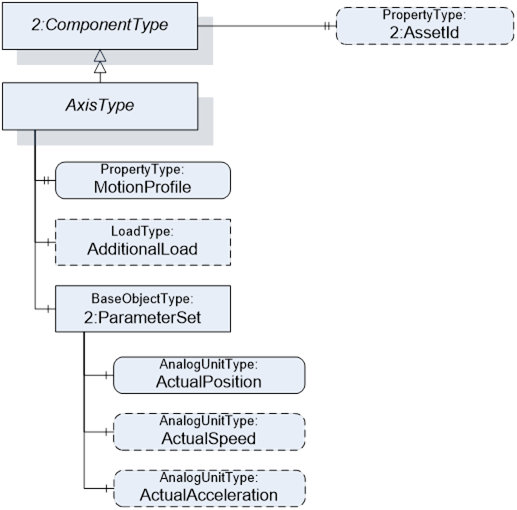
Table 21 – AxisType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||||||
|
BrowseName |
AxisType |
||||||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
||||
|
Subtype of the ComponentType defined in OPC Unified Architecture for Devices (DI) |
|||||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
MotionProfile |
AxisMotionProfileEnumeration |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
AdditionalLoad |
|
LoadType
|
Optional |
||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
2:ParameterSet |
|
BaseObjectType |
Mandatory |
||||
|
Requires |
Object |
<PowerTrainIdentifier> |
|
PowerTrainType |
OptionalPlaceholder |
||||
|
The following instance declarations are not defined by this type, but by the supertype ComponentType and repeated here for better readability |
|||||||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
2:AssetId |
String |
PropertyType |
Optional |
||||
The AssetId property is a user writable alphanumeric character sequence uniquely identifying a component. The ID is provided by the vendor, integrator or user of the device. It contains typically an identifier in a branch, use case or user specific naming scheme.
This could be for example a reference to an electric scheme. For electric schemes typically EN 81346-2 is used.
The AssetID of the AxisType provides a manufacturer-specific axis identifier within the control system.
This property is defined by ComponentType defined in OPC UA DI.
The MotionProfile property provides the kind of axis motion as defined by the AxisMotionProfileEnumeration.
Table 22 – AxisMotionProfileEnumeration
|
AxisMotionProfileEnumeration |
||
|
EnumString |
Value |
Description |
|
OTHER |
0 |
Any motion-profile which is not defined by the AxisMotionProfileEnumeration |
|
ROTARY |
1 |
Rotary motion is a rotation along a circular path with defined limits. Motion movement is not going always in the same direction. Control unit is mainly degree. |
|
ROTARY_ENDLESS |
2 |
Rotary motion is a rotation along a circular path with no limits. Motion movement is going endless in the same direction. Control unit is mainly degree. |
|
LINEAR |
3 |
Linear motion is a one dimensional motion along a straight line with defined limits. Motion movement is not going always in the same direction. Control unit is mainly mm. |
|
LINEAR_ENDLESS |
4 |
Linear motion is a one dimensional motion along a straight line with no limits. Motion movement is going endless in the same direction. Control unit is mainly mm. |
AdditionalLoad provides data for the load that is mounted on this axis, e.g., a transformer for welding.
Table 23 – ParameterSet of AxisType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AxisType |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
ActualPosition |
Double |
AnalogUnitType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
ActualSpeed |
Double |
AnalogUnitType |
Optional |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
ActualAcceleration |
Double |
AnalogUnitType |
Optional |
Description of ParameterSet of AxisType:
- Variable ActualPosition: The ActualPosition variable provides the current position of the axis and may have limits. If the axis has physical limits, the EURange property of the AnalogUnitType shall be provided.
- Variable ActualSpeed: The ActualSpeed variable provides the axis speed. Applicable speed limits of the axis shall be provided by the EURange property of the AnalogUnitType
- Variable ActualAcceleration: The ActualAcceleration variable provides the axis acceleration. Applicable acceleration limits of the axis shall be provided by the EURange property of the AnalogUnitType.
The Requires reference provides the relationship of axes to power trains. For complex kinematics this does not need to be a one to one relationship, because more than one power train might influence the motion of one axis. This reference connects all power trains to an axis that must be actively driven when only this axis should move and all other axes should stand still.
Virtual axes that are not actively driven by a power train do not have this reference. The InverseName is IsRequiredBy.