It is assumed that basic concepts of OPC UA information modelling, “OPC UA for Machinery”, “OPC UA for ISA-95 – Part 4: Job Control” and “OPC UA for Machinery – Part 3: Job Management” are understood in this document. This document will use these concepts to describe the glass technology Information Model. For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in OPC 10000-1, OPC 10000-3, OPC 10000-4, OPC 10000-5, OPC 10000-7, OPC 10000-100, as well as the following apply.
Note that OPC UA terms and terms defined in this document are italicized in the document.
Layer structure usually applied onto the glass surface by a CVD or PVD process to influence the spectral properties of the component such as transmission and reflection. Such coating is essential for energy conserving glazing where IR radiation may be controlled by this layer. There are several coating classes which are distinguished as follows:
- Hard Coated (HC): This describes a type of coating or covering a glass surface in a way that the resulting surface is rather resistant against damage, at least at a similar level as compared to standard Floatglass. In a composite, the surface may be exposed to the environment.
- Soft Coated (SC): This describes a type of coating covering a glass surface resulting in a surface that is more vulnerable by environmental conditions such as moist, dirt etc. Soft coated glass panes require more care in processing.
- Coated with foil protection (FC): This describes glass panes where the coating (typically a soft coating) is protected against environmental influence by a foil that might have to be removed when the glass is to be processed.
Large format glass panes as produced from float tanks at flat glass production plant. The size is typically 6000*3210 mm.
The term “Significant Side” is used if there is a necessity to distinguish which side of a glass pane is “up” or “down” or “front” or “back” while processing the glass pane. Typical examples are:
- When producing flat glass, one side is floating on the tin bath, the other is exposed to the gas fire heating the chamber.
- If the glass is coated (a thin metallic layer is applied), it is essential to know which side is coated
- Glass having patterns or other surface treatments
A User Profile contains the meta data of a logged in user.
Space between glass panes, width depends on spacer. Filled with a gas or gas mixture to provide demanded thermal properties.
The gas filling refers to gas in the space between glass of an Insulating Glass Unit IGU. Typically, the gas used is Argon or Xenon, both gases which allow good thermal resistance.
Used to protect the second sealant of an Insulating Glass Unit. Typically, an aluminum tape is used to wrap the edge of the unit.
Applied to the spacer to prevent ingress of moisture and loss of gases between spacer and glass.
Note: See also Secondary Sealing
The minimum dimension from the spacer to the outer edge of the silicone secondary seal.
This dimension may also be referred to as the “bite” or “height” of the insulating glass sealant.
A Sealing applied to IGU after assembling.
Provides resistance against moisture and loss of gas. Provides additional structural strength. Possible materials: polyurethane, polysulfide, butyl, silicone, polyisobutylene
Note: See also Primary Sealing
Element which is used in IGU’s to physically separate the individual glass panes.
Spacer can be of different material such as for example:
- Metal spacers out of aluminum or stainless steel
- Carbon based spacers either rigid or flexible
- TPS (Thermoplastic spacer): a gel like liquid that is formed to spacer size when applied to the glass.
- Other (e.g. elastic spacer)
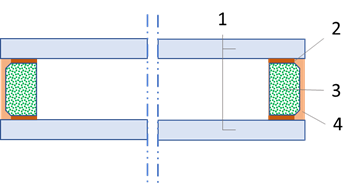
Unit of 2 or more panes of glass. Gas filling is used to set thermal transfer properties. Spacer defines the distance between the panes and also accounts for thermal properties. Sealants prevent loss of gas filling and entrance of humidity. Figure 1 shows a sectional drawing of an IGU with the different elements.
|
|
Key:
1 glass panes 2 primary sealing 3 spacers with desiccant 4 secondary sealing |
Production line for IGU´s.
Type of glass according to prEN12543-1:2020, e.g., glass that is made of two or more panes of glass joined together by a layer of plastic, or polyvinyl butyral (PVB).
AC Alarm and Condition
CSV Character-separated values
CVD Chemical vapor deposition
DCS Distributed Control Systems
DI Device integration
ERP Enterprise resource planning
FC Foil coated
HC Hard coated
HLS Higher level system
ID Identifier
IG Insulating glass
IGU Insulating glass unit
M Mandatory
MES Manufacturing execution system
O Optional
OPC Open platform communications
PVB Polyvinyl butyral
PVD Physical vapor deposition
RAMI 4.0Reference architecture model industry 4.0
SC Soft coated
SI International system of units
TPS Thermoplastic spacer
UA Unified architecture
UD User defined
URI Uniform Resource Identifier
URL Uniform resource locator
UTC Coordinated universal time
Node definitions are specified using tables (see Table 2).
Attributes are defined by providing the Attribute name and a value, or a description of the value.
References are defined by providing the ReferenceType name, the BrowseName of the TargetNode and its NodeClass.
- If the TargetNode is a component of the Node being defined in the table the Attributes of the composed Node are defined in the same row of the table.
- The DataType is only specified for Variables; “[<number>]” indicates a single-dimensional array, for multi-dimensional arrays the expression is repeated for each dimension (e.g. [2][3] for a two-dimensional array). For all arrays the ArrayDimensions is set as identified by <number> values. If no <number> is set, the corresponding dimension is set to 0, indicating an unknown size. If no number is provided at all the ArrayDimensions can be omitted. If no brackets are provided, it identifies a scalar DataType and the ValueRank is set to the corresponding value (see OPC 10000-3). In addition, ArrayDimensions is set to null or is omitted. If it can be Any or ScalarOrOneDimension, the value is put into “{<value>}”, so either “{Any}” or “{ScalarOrOneDimension}” and the ValueRank is set to the corresponding value (see OPC 10000-3) and the ArrayDimensions is set to null or is omitted. Examples are given in Table 1.
Table 1 – Examples of DataTypes
|
Notation |
DataType |
ValueRank |
ArrayDimensions |
Description |
|
0:Int32 |
0:Int32 |
-1 |
omitted or null |
A scalar Int32. |
|
0:Int32[] |
0:Int32 |
1 |
omitted or {0} |
Single-dimensional array of Int32 with an unknown size. |
|
0:Int32[][] |
0:Int32 |
2 |
omitted or {0,0} |
Two-dimensional array of Int32 with unknown sizes for both dimensions. |
|
0:Int32[3][] |
0:Int32 |
2 |
{3,0} |
Two-dimensional array of Int32 with a size of 3 for the first dimension and an unknown size for the second dimension. |
|
0:Int32[5][3] |
0:Int32 |
2 |
{5,3} |
Two-dimensional array of Int32 with a size of 5 for the first dimension and a size of 3 for the second dimension. |
|
0:Int32{Any} |
0:Int32 |
-2 |
omitted or null |
An Int32 where it is unknown if it is scalar or array with any number of dimensions. |
|
0:Int32{ScalarOrOneDimension} |
0:Int32 |
-3 |
omitted or null |
An Int32 where it is either a single-dimensional array or a scalar. |
- The TypeDefinition is specified for Objects and Variables.
- The TypeDefinition column specifies a symbolic name for a NodeId, i.e. the specified Node points with a HasTypeDefinition Reference to the corresponding Node.
- The ModellingRule of the referenced component is provided by specifying the symbolic name of the rule in the ModellingRule column. In the AddressSpace, the Node shall use a HasModellingRule Reference to point to the corresponding ModellingRule Object.
If the NodeId of a DataType is provided, the symbolic name of the Node representing the DataType shall be used.
Note that if a symbolic name of a different namespace is used, it is prefixed by the NamespaceIndex (see 3.5.2.2).
Nodes of all other NodeClasses cannot be defined in the same table; therefore only the used ReferenceType, their NodeClass and their BrowseName are specified. A reference to another part of this document points to their definition. Table 2 illustrates the table. If no components are provided, the DataType, TypeDefinition and ModellingRule columns may be omitted and only a Comment column is introduced to point to the Node definition.
Each Type Node or well-known Instance Node defined shall have one or more ConformanceUnits defined in 9.2 that require the Node to be in the AddressSpace.
The relations between Nodes and ConformanceUnits are defined at the end of the tables defining Nodes, one row per ConformanceUnit. The ConformanceUnits are reflected in the Category element for the Node definition in the UANodeSet (see OPC 10000-6).
The list of ConformanceUnits in the UANodeSet allows Servers to optimize resource consumption by using a list of supported ConformanceUnits to select a subset of the Nodes in an Information Model.
When a Node is selected in this way, all dependencies implied by the References are also selected.
Dependencies exist if the Node is the source of HasTypeDefinition, HasInterface, HasAddIn or any HierarchicalReference. Dependencies also exist if the Node is the target of a HasSubtype Reference. For Variables and VariableTypes, the value of the DataType Attribute is a dependency. For DataType Nodes, any DataTypes referenced in the DataTypeDefinition Attribute are also dependencies.
For additional details see OPC 10000-5.
Table 2 – Type Definition Table
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
Attribute name |
Attribute value. If it is an optional Attribute that is not set “--“ will be used. |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
ReferenceType name |
BrowseName of the target Node. |
DataType of the referenced Node, only applicable for Variables. |
TypeDefinition of the referenced Node, only applicable for Variables and Objects. |
Additional characteristics of the TargetNode such as the ModellingRule or AccessLevel. |
|
|
NOTE Notes referencing footnotes of the table content. |
|||||
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Name of ConformanceUnit, one row per ConformanceUnit |
|||||
Components of Nodes can be complex that is containing components by themselves. The TypeDefinition, NodeClass and DataType can be derived from the type definitions, and the symbolic name can be created as defined in 3.5.3.1. Therefore, those containing components are not explicitly specified; they are implicitly specified by the type definitions.
The Other column defines additional characteristics of the Node. Examples of characteristics that can appear in this column are show in Table 3.
Table 3 – Examples of Other Characteristics
|
Name |
Short Name |
Description |
|
0:Mandatory |
M |
The Node has the Mandatory ModellingRule. |
|
0:Optional |
O |
The Node has the Optional ModellingRule. |
|
0:MandatoryPlaceholder |
MP |
The Node has the MandatoryPlaceholder ModellingRule. |
|
0:OptionalPlaceholder |
OP |
The Node has the OptionalPlaceholder ModellingRule. |
|
ReadOnly |
RO |
The Node AccessLevel has the CurrentRead bit set but not the CurrentWrite bit. |
|
ReadWrite |
RW |
The Node AccessLevel has the CurrentRead and CurrentWrite bits set. |
|
WriteOnly |
WO |
The Node AccessLevel has the CurrentWrite bit set but not the CurrentRead bit. |
If multiple characteristics are defined they are separated by commas. The name or the short name may be used.
To provide information about additional References, the format as shown in Table 4 is used.
Table 4 – <some> Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
SourceBrowsePath is always relative to the TypeDefinition. Multiple elements are defined as separate rows of a nested table. |
ReferenceType name |
True = forward Reference |
TargetBrowsePath points to another Node, which can be a well-known instance or a TypeDefinition. You can use BrowsePaths here as well, which is either relative to the TypeDefinition or absolute. If absolute, the first entry needs to refer to a type or well-known instance, uniquely identified within a namespace by the BrowseName. |
References can be to any other Node.
To provide information about sub-components, the format as shown in Table 5 is used.
Table 5 – <some>Type Additional Subcomponents
|
BrowsePath |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
BrowsePath is always relative to the TypeDefinition. Multiple elements are defined as separate rows of a nested table |
NOTE Same as for Table 2 |
|||||
The type definition table provides columns to specify the values for required Node Attributes for InstanceDeclarations. To provide information about additional Attributes, the format as shown in Table 6 is used.
Table 6 – <some>Type Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
<Attribute name> Attribute |
|
BrowsePath is always relative to the TypeDefinition. Multiple elements are defined as separate rows of a nested table |
The values of attributes are converted to text by adapting the reversible JSON encoding rules defined in OPC 10000-6. If the JSON encoding of a value is a JSON string or a JSON number then that value is entered in the value field. Double quotes are not included. If the DataType includes a NamespaceIndex (QualifiedNames, NodeIds or ExpandedNodeIds) then the notation used for BrowseNames is used. If the value is an Enumeration the name of the enumeration value is entered. If the value is a Structure then a sequence of name and value pairs is entered. Each pair is followed by a newline. The name is followed by a colon. The names are the names of the fields in the DataTypeDefinition. If the value is an array of non-structures then a sequence of values is entered where each value is followed by a newline. If the value is an array of Structures or a Structure with fields that are arrays or with nested Structures then the complete JSON array or JSON object is entered. |
There can be multiple columns to define more than one Attribute.
The NodeIds of all Nodes described in this standard are only symbolic names. Annex A defines the actual NodeIds.
The symbolic name of each Node defined in this document is its BrowseName, or, when it is part of another Node, the BrowseName of the other Node, a “.”, and the BrowseName of itself. In this case “part of” means that the whole has a HasProperty or HasComponent Reference to its part. Since all Nodes not being part of another Node have a unique name in this document, the symbolic name is unique.
The NamespaceUri for all NodeIds defined in this document is defined in Annex A. The NamespaceIndex for this NamespaceUri is vendor-specific and depends on the position of the NamespaceUri in the server namespace table.
Note that this document not only defines concrete Nodes, but also requires that some Nodes shall be generated, for example one for each Session running on the Server. The NodeIds of those Nodes are Server-specific, including the namespace. But the NamespaceIndex of those Nodes cannot be the NamespaceIndex used for the Nodes defined in this document, because they are not defined by this document but generated by the Server.
The text part of the BrowseNames for all Nodes defined in this document is specified in the tables defining the Nodes. The NamespaceUri for all BrowseNames defined in this document is defined in Annex A.
For InstanceDeclarations of NodeClass Object and Variable that are placeholders (OptionalPlaceholder and MandatoryPlaceholder ModellingRule), the BrowseName and the DisplayName are enclosed in angle brackets (<>) as recommended in OPC 10000-3.
If the BrowseName is not defined by this document, a namespace index prefix is added to the BrowseName (e.g., prefix '0' leading to ‘0:EngineeringUnits’ or prefix '2' leading to ‘2:DeviceRevision’). This is typically necessary if a Property of another specification is overwritten or used in the OPC UA types defined in this document. Table 45 provides a list of namespaces and their indexes as used in this document.
The Attributes of Nodes, their DataTypes and descriptions are defined in OPC 10000-3. Attributes not marked as optional are mandatory and shall be provided by a Server. The following tables define if the Attribute value is defined by this specification or if it is server-specific.
For all Nodes specified in this specification, the Attributes named in Table 7 shall be set as specified in the table.
Table 7 – Common Node Attributes
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
DisplayName |
The DisplayName is a LocalizedText. Each server shall provide the DisplayName identical to the BrowseName of the Node for the LocaleId “en”. Whether the server provides translated names for other LocaleIds is server-specific. |
|
Description |
Optionally a server-specific description is provided. |
|
NodeClass |
|
|
NodeId |
The NodeId is described by BrowseNames as defined in 3.5.2.1. |
|
WriteMask |
Optionally the WriteMask Attribute can be provided. If the WriteMask Attribute is provided, it shall set all non-server-specific Attributes to not writable. For example, the Description Attribute may be set to writable since a Server may provide a server-specific description for the Node. The NodeId shall not be writable, because it is defined for each Node in this specification. |
|
UserWriteMask |
Optionally the UserWriteMask Attribute can be provided. The same rules as for the WriteMask Attribute apply. |
|
RolePermissions |
Optionally server-specific role permissions can be provided. |
|
UserRolePermissions |
Optionally the role permissions of the current Session can be provided. The value is server-specifc and depend on the RolePermissions Attribute (if provided) and the current Session. |
|
AccessRestrictions |
Optionally server-specific access restrictions can be provided. |
For all Objects specified in this specification, the Attributes named in Table 8 shall be set as specified in the table. The definitions for the Attributes can be found in OPC 10000-3.
Table 8 – Common Object Attributes
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
EventNotifier |
Whether the Node can be used to subscribe to Events or not is server-specific. |
For all Variables specified in this specification, the Attributes named in Table 9 shall be set as specified in the table. The definitions for the Attributes can be found in OPC 10000-3.
Table 9 – Common Variable Attributes
|
Attribute |
Value |
|
MinimumSamplingInterval |
Optionally, a server-specific minimum sampling interval is provided. |
|
AccessLevel |
The access level for Variables used for type definitions is server-specific, for all other Variables defined in this specification, the access level shall allow reading; other settings are server-specific. |
|
UserAccessLevel |
The value for the UserAccessLevel Attribute is server-specific. It is assumed that all Variables can be accessed by at least one user. |
|
Value |
For Variables used as InstanceDeclarations, the value is server-specific; otherwise it shall represent the value described in the text. |
|
ArrayDimensions |
If the ValueRank does not identify an array of a specific dimension (i.e. ValueRank <= 0) the ArrayDimensions can either be set to null or the Attribute is missing. This behaviour is server-specific. If the ValueRank specifies an array of a specific dimension (i.e. ValueRank > 0) then the ArrayDimensions Attribute shall be specified in the table defining the Variable. |
|
Historizing |
The value for the Historizing Attribute is server-specific. |
|
AccessLevelEx |
If the AccessLevelEx Attribute is provided, it shall have the bits 8, 9, and 10 set to 0, meaning that read and write operations on an individual Variable are atomic, and arrays can be partly written. |
For all VariableTypes specified in this specification, the Attributes named in Table 10 shall be set as specified in the table. The definitions for the Attributes can be found in OPC 10000-3.
Table 10 – Common VariableType Attributes
|
Attributes |
Value |
|
Value |
Optionally a server-specific default value can be provided. |
|
ArrayDimensions |
If the ValueRank does not identify an array of a specific dimension (i.e. ValueRank <= 0) the ArrayDimensions can either be set to null or the Attribute is missing. This behaviour is server-specific. If the ValueRank specifies an array of a specific dimension (i.e. ValueRank > 0) then the ArrayDimensions Attribute shall be specified in the table defining the VariableType. |
For all Methods specified in this specification, the Attributes named in Table 11 shall be set as specified in the table. The definitions for the Attributes can be found in OPC 10000-3.
Table 11 – Common Method Attributes
|
Attributes |
Value |
|
Executable |
All Methods defined in this specification shall be executable (Executable Attribute set to “True”), unless it is defined differently in the Method definition. |
|
UserExecutable |
The value of the UserExecutable Attribute is server-specific. It is assumed that all Methods can be executed by at least one user. |
OPC 10000-3 differentiates between different kinds of Structures. The following conventions explain, how these Structures shall be defined.
The first kind are Structures without optional fields where none of the fields allows subtype (except fields with abstract DataTypes). Its definition is in Table 12.
Table 12 – Structures without optional fields where none of the fields allow subtypes
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
<someStructure> |
structure |
Subtype of <someParentStructure> defined in … |
|
SP1 |
0:Byte[] |
Setpoint 1 |
|
SP2 |
0:Byte[] |
Setpoint 2 |
The second kind are Structures with optional fields where none of the fields allows subtypes (except fields with abstract DataTypes). Its definition is in Table 13.
Structures with fields that are optional have an “Optional” column. Fields that are optional have True set, otherwise False.
Table 13 – Structures with optional fields
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
Optional |
|
<someStructure> |
structure |
Subtype of <someParentStructure> defined in … |
|
|
SP1 |
0:Byte[] |
Setpoint 1 |
False |
|
SP2 |
0:Byte[] |
Setpoint 2 |
True |
The third kind are Structures without optional fields where one or more of the fields allow subtypes. Its definition is in Table 14.
Structures with fields that allow subtypes have an “Allow Subtypes” column. Fields that allow subtypes have True set, otherwise False. Fields with abstract DataTypes can always be subtyped.
Table 14 – Structures where one or more of the fields allow subtypes
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
Allow SubTypes |
|
<someStructure> |
structure |
Subtype of <someParentStructure> defined in … |
|
|
SP1 |
0:Byte[] |
Setpoint 1 |
False |
|
Allow Subtypes |
0:ByteString |
Some Bytestring |
True |