Space between glass panes, width depends on spacer. Filled with a gas or gas mixture to provide demanded thermal properties.
The gas filling refers to gas in the space between glass of an Insulating Glass Unit IGU. Typically, the gas used is Argon or Xenon, both gases which allow good thermal resistance.
Used to protect the second sealant of an Insulating Glass Unit. Typically, an aluminum tape is used to wrap the edge of the unit.
Applied to the spacer to prevent ingress of moisture and loss of gases between spacer and glass.
Note: See also Secondary Sealing
The minimum dimension from the spacer to the outer edge of the silicone secondary seal.
This dimension may also be referred to as the “bite” or “height” of the insulating glass sealant.
A Sealing applied to IGU after assembling.
Provides resistance against moisture and loss of gas. Provides additional structural strength. Possible materials: polyurethane, polysulfide, butyl, silicone, polyisobutylene
Note: See also Primary Sealing
Element which is used in IGU’s to physically separate the individual glass panes.
Spacer can be of different material such as for example:
- Metal spacers out of aluminum or stainless steel
- Carbon based spacers either rigid or flexible
- TPS (Thermoplastic spacer): a gel like liquid that is formed to spacer size when applied to the glass.
- Other (e.g. elastic spacer)
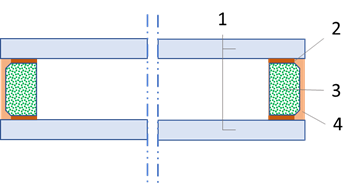
Unit of 2 or more panes of glass. Gas filling is used to set thermal transfer properties. Spacer defines the distance between the panes and also accounts for thermal properties. Sealants prevent loss of gas filling and entrance of humidity. Figure 1 shows a sectional drawing of an IGU with the different elements.
|
|
Key:
1 glass panes 2 primary sealing 3 spacers with desiccant 4 secondary sealing |
Production line for IGU´s.
Type of glass according to prEN12543-1:2020, e.g., glass that is made of two or more panes of glass joined together by a layer of plastic, or polyvinyl butyral (PVB).