Errata exists for this version of the document.
This Service Set defines Services for an application layer connection establishment in the context of a Session.
This Service is used by an OPC UA Client to create a Session and the Server returns two values which uniquely identify the Session. The first value is the sessionId which is used to identify the Session in the audit logs and in the Server’s AddressSpace. The second is the authenticationToken which is used to associate an incoming request with a Session.
Before calling this Service, the Client shall create a SecureChannel with the OpenSecureChannel Service to ensure the Integrity of all Messages exchanged during a Session. This SecureChannel has a unique identifier which the Server shall associate with the authenticationToken. The Server may accept requests with the authenticationToken only if they are associated with the same SecureChannel that was used to create the Session. The Client may associate a new SecureChannel with the Session by calling the ActivateSession method.
The SecureChannel is always managed by the Communication Stack which means it shall provide APIs which the Server can use to find out information about the SecureChannel used for any given request. The Communication Stack shall, at a minimum, provide the SecurityPolicy and SecurityMode used by the SecureChannel. It shall also provide a SecureChannelId which uniquely identifies the SecureChannel or the Client Certificate used to establish the SecureChannel. The Server uses one of these to identify the SecureChannel used to send a request. Clause 7.31 describes how to create the authenticationToken for different types of Communication Stack.
Depending upon on the SecurityPolicy and the SecurityMode of the SecureChannel, the exchange of ApplicationInstanceCertificates and Nonces may be optional and the signatures may be empty. See OPC 10000-7 for the definition of SecurityPolicies and the handling of these parameters.
The Server returns its EndpointDescriptions in the response. Clients use this information to determine whether the list of EndpointDescriptions returned from the DiscoveryEndpoint matches the Endpoints that the Server has. If there is a difference then the Client shall close the Session and report an error. The Server returns all EndpointDescriptions for the serverUri specified by the Client in the request. The Client only verifies EndpointDescriptions with a transportProfileUri that matches the profileUri specified in the original GetEndpoints request. A Client may skip this check if the EndpointDescriptions were provided by a trusted source such as the Administrator.
The Session created with this Service shall not be used until the Client calls the ActivateSession Service and provides its SoftwareCertificates and proves possession of its Application Instance Certificate and any user identity token that it provided.
A Server application should limit the number of Sessions. To protect against misbehaving Clients and denial of service attacks, the Server shall close the oldest Session that is not activated before reaching the maximum number of supported Sessions.
The SoftwareCertificates parameter in the Server response is deprecated to reduce the message size for OPC UA Applications with limited resources. The SoftwareCertificates are provided in the Server’s AddressSpace as defined in OPC 10000-5. A SoftwareCertificate identifies the capabilities of the Server and also contains the list of OPC UA Profiles supported by the Server. OPC UA Profiles are defined in OPC 10000-7.
Additional Certificates issued by other organisations may be included to identify additional Server capabilities. Examples of these Profiles include support for specific information models and support for access to specific types of devices.
When a Session is created, the Server adds an entry for the Client in its SessionDiagnosticsArray Variable. See OPC 10000-5 for a description of this Variable.
Sessions are created to be independent of the underlying communications connection. Therefore, if a communications connection fails, the Session is not immediately affected. The exact mechanism to recover from an underlying communication connection error depends on the SecureChannel mapping as described in OPC 10000-6.
Sessions are terminated by the Server automatically if the Client fails to issue a Service request on the Session within the timeout period negotiated by the Server in the CreateSession Service response. This protects the Server against Client failures and against situations where a failed underlying connection cannot be re-established. Clients shall be prepared to submit requests in a timely manner to prevent the Session from closing automatically. Clients may explicitly terminate Sessions using the CloseSession Service.
When a Session is terminated, all outstanding requests on the Session are aborted and Bad_SessionClosed StatusCodes are returned to the Client. In addition, the Server deletes the entry for the Client from its SessionDiagnosticsArray Variable and notifies any other Clients who were subscribed to this entry.
If a Client invokes the CloseSession Service then all Subscriptions associated with the Session are also deleted if the deleteSubscriptions flag is set to TRUE. If a Server terminates a Session for any other reason, Subscriptions associated with the Session, are not deleted. Each Subscription has its own lifetime to protect against data loss in the case of a Session termination. In these cases, the Subscription can be reassigned to another Client before its lifetime expires.
Some Servers, such as aggregating Servers, also act as Clients to other Servers. These Servers typically support more than one system user, acting as their agent to the Servers that they represent. Security for these Servers is supported at two levels.
First, each OPC UA Service request contains a string parameter that is used to carry an audit record id. A Client, or any Server operating as a Client, such as an aggregating Server, can create a local audit log entry for a request that it submits. This parameter allows the Client to pass the identifier for this entry with the request. If the Server also maintains an audit log, then it can include this id in the audit log entry that it writes. When the log is examined and the entry is found, the examiner will be able to relate it directly to the audit log entry created by the Client. This capability allows for traceability across audit logs within a system. See OPC 10000-2 for additional information on auditing. A Server that maintains an audit log shall provide the information in the audit log entries via event Messages defined in this standard. The Server may choose to only provide the Audit information via event Messages. The Audit EventType is defined in OPC 10000-3.
Second, these aggregating Servers may open independent Sessions to the underlying Servers for each Client that accesses data from them. Figure 14 illustrates this concept.
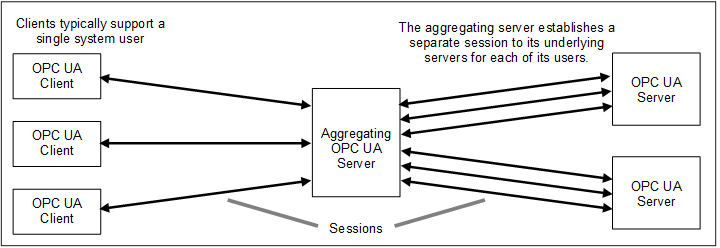
Figure 14 – Multiplexing Users on a Session
Table 15 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 15 – CreateSession Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters. The authenticationToken is always null. The type RequestHeader is defined in 7.28. |
|
clientDescription |
Application Description |
Information that describes the Client application. The type ApplicationDescription is defined in 7.1. |
|
serverUri |
String |
This value is only specified if the EndpointDescription has a gatewayServerUri. This value is the applicationUri from the EndpointDescription which is the applicationUri for the underlying Server. The type EndpointDescription is defined in 7.10. |
|
endpointUrl |
String |
The network address that the Client used to access the Session Endpoint. The HostName portion of the URL should be one of the HostNames for the application that are specified in the Server’s ApplicationInstanceCertificate (see 7.2). The Server shall raise an AuditUrlMismatchEventType event if the URL does not match the Server’s HostNames. AuditUrlMismatchEventType event type is defined in OPC 10000-5. The Server uses this information for diagnostics and to determine the set of EndpointDescriptions to return in the response. |
|
sessionName |
String |
Human readable string that identifies the Session. The Server makes this name and the sessionId visible in its AddressSpace for diagnostic purposes. The Client should provide a name that is unique for the instance of the Client. If this parameter is not specified the Server shall assign a value. |
|
clientNonce |
ByteString |
A random number that should never be used in any other request. This number shall have a minimum length of 32 bytes. Profiles may increase the required length. The Server shall use this value to prove possession of its Application Instance Certificate in the response. |
|
clientCertificate |
ApplicationInstance Certificate |
The Application Instance Certificate issued to the Client. The ApplicationInstanceCertificate type is defined in 7.2. If the securityPolicyUri is None, the Server shall ignore the ApplicationInstanceCertificate. |
|
Requested SessionTimeout |
Duration |
Requested maximum number of milliseconds that a Session should remain open without activity. If the Client fails to issue a Service request within this interval, then the Server shall automatically terminate the Client Session. |
|
maxResponse MessageSize |
UInt32 |
The maximum size, in bytes, for the body of any response message. The Server should return a Bad_ResponseTooLarge service fault if a response message exceeds this limit. The value zero indicates that this parameter is not used. The transport protocols defined in OPC 10000-6 may imply minimum message sizes. More information on the use of this parameter is provided in 5.3. |
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
ResponseHeader |
Common response parameters (see 7.29 for ResponseHeader type). |
|
sessionId |
NodeId |
A unique NodeId assigned by the Server to the Session. This identifier is used to access the diagnostics information for the Session in the Server AddressSpace. It is also used in the audit logs and any events that report information related to the Session. The Session diagnostic information is described in OPC 10000-5. Audit logs and their related events are described in 6.5. |
|
authentication Token |
Session AuthenticationToken |
A unique identifier assigned by the Server to the Session. This identifier shall be passed in the RequestHeader of each request and is used with the SecureChannelId to determine whether a Client has access to the Session. This identifier shall not be reused in a way that the Client or the Server has a chance of confusing them with a previous or existing Session. The SessionAuthenticationToken type is described in 7.31. |
|
revisedSessionTimeout |
Duration |
Actual maximum number of milliseconds that a Session shall remain open without activity. The Server should attempt to honour the Client request for this parameter, but may negotiate this value up or down to meet its own constraints. |
|
serverNonce |
ByteString |
A random number that should never be used in any other request. This number shall have a minimum length of 32 bytes. The Client shall use this value to prove possession of its Application Instance Certificate in the ActivateSession request. This value may also be used to prove possession of the userIdentityToken it specified in the ActivateSession request. |
|
serverCertificate |
ApplicationInstance Certificate |
The Application Instance Certificate issued to the Server. A Server shall prove possession by using the private key to sign the Nonce provided by the Client in the request. The Client shall verify that this Certificate is the same as the one it used to create the SecureChannel. The ApplicationInstanceCertificate type is defined in 7.2. If the securityPolicyUri is NONE and none of the UserTokenPolicies requires encryption, the Client shall ignore the ApplicationInstanceCertificate. |
|
serverEndpoints [] |
EndpointDescription |
List of Endpoints that the Server supports. The Server shall return a set of EndpointDescriptions available for the serverUri specified in the request. The EndpointDescription type is defined in 7.10. The Client shall verify this list with the list from a DiscoveryEndpoint if it used a DiscoveryEndpoint to fetch the EndpointDescriptions. It is recommended that Servers only include the server.applicationUri, endpointUrl, securityMode, securityPolicyUri, userIdentityTokens, transportProfileUri and securityLevel with all other parameters set to null. Only the recommended parameters shall be verified by the client. |
|
serverSoftware Certificates [] |
SignedSoftware Certificate |
This parameter is deprecated and the array shall be empty. The SoftwareCertificates are provided in the Server AddressSpace as defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|
serverSignature |
SignatureData |
This is a signature generated with the private key associated with the serverCertificate. This parameter is calculated by appending the clientNonce to the clientCertificate and signing the resulting sequence of bytes. If the clientCertificate contains a chain, the signature calculation shall be done only with the leaf Certificate. For backward compatibility a Client shall check the signature with the full chain if the check with the leaf Certificate fails. The SignatureAlgorithm shall be the AsymmetricSignatureAlgorithm specified in the SecurityPolicy for the Endpoint. The SignatureData type is defined in 7.32. |
|
maxRequest MessageSize |
UInt32 |
The maximum size, in bytes, for the body of any request message. The Client Communication Stack should return a Bad_RequestTooLarge error to the application if a request message exceeds this limit. The value zero indicates that this parameter is not used. See OPC 10000-6 for protocol specific minimum or default values. 5.3 provides more information on the use of this parameter. |
Table 16 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 177.
Table 16 – CreateSession Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_SecureChannelIdInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_NonceInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. A Server shall check the minimum length of the Client nonce and return this status if the length is below 32 bytes. A check for a duplicated nonce is optional and requires access to the nonce used to create the secure channel. |
|
Bad_SecurityChecksFailed |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateTimeInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateIssuerTimeInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateHostNameInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateUriInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateUseNotAllowed |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateIssuerUseNotAllowed |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateUntrusted |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateRevocationUnknown |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateIssuerRevocationUnknown |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateRevoked |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_CertificateIssuerRevoked |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManySessions |
|
|
Bad_ServerUriInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
This Service is used by the Client to specify the identity of the user associated with the Session. This Service request shall be issued by the Client before it issues any Service request other than CloseSession after CreateSession. Failure to do so shall cause the Server to close the Session.
Whenever the Client calls this Service the Client shall prove that it is the same application that called the CreateSession Service. The Client does this by creating a signature with the private key associated with the clientCertificate specified in the CreateSession request. This signature is created by appending the last serverNonce provided by the Server to the serverCertificate and calculating the signature of the resulting sequence of bytes.
Once used, a serverNonce cannot be used again. For that reason, the Server returns a new serverNonce each time the ActivateSession Service is called.
When the ActivateSession Service is called for the first time then the Server shall reject the request if the SecureChannel is not same as the one associated with the CreateSession request. Subsequent calls to ActivateSession may be associated with different SecureChannels. If this is the case then the Server shall verify that the Certificate the Client used to create the new SecureChannel is the same as the Certificate used to create the original SecureChannel. In addition, the Server shall verify that the Client supplied a UserIdentityToken that is identical to the token currently associated with the Session. Once the Server accepts the new SecureChannel it shall reject requests sent via the old SecureChannel.
The ActivateSession Service is used to associate a user identity with a Session. When a Client provides a user identity then it shall provide proof that it is authorized to use that user identity. The exact mechanism used to provide this proof depends on the type of the UserIdentityToken. If the token is a UserNameIdentityToken then the proof is the password that is included in the token. If the token is an X509IdentityToken then the proof is a signature generated with private key associated with the Certificate. The data to sign is created by appending the last serverNonce to the serverCertificate specified in the CreateSession response. If a token includes a secret then it should be encrypted using the public key from the serverCertificate.
Servers shall take proper measures to protect against attacks on user identity tokens. Such an attack is assumed if repeated connection attempts with invalid user identity tokens happen. One option is to lock out an OPC UA Client for a period of time if the user identity token validation fails several times. The OPC UA Client is either detected by IP address for unsecured connections or by the ApplicationInstanceUri for secured connections. Another option is delaying the Service response when the validation of a user identity fails. This delay time could be increased with repeated failures. Sporadic failures shall not delay connections with valid tokens.
Clients can change the identity of a user associated with a Session by calling the ActivateSession Service. The Server validates the signatures provided with the request and then validates the new user identity. If no errors occur the Server replaces the user identity for the Session. Changing the user identity for a Session may cause discontinuities in active Subscriptions because the Server may have to tear down connections to an underlying system and re-establish them using the new credentials.
When a Client supplies a list of locale ids in the request, each locale id is required to contain the language component. It may optionally contain the <country/region> component. When the Server returns a LocalizedText in the context of the Session, it also may return both the language and the country/region or just the language as its default locale id.
When a Server returns a string to the Client, it first determines if there are available translations for it. If there are, then the Server returns the string whose locale id exactly matches the locale id with the highest priority in the Client-supplied list.
If there are no exact matches, then the Server ignores the <country/region> component of the locale id, and returns the string whose <language> component matches the <language> component of the locale id with the highest priority in the Client supplied list.
If there still are no matches, then the Server returns the string that it has along with the locale id.
A Gateway Server is expected to impersonate the user provided by the Client when it connects to the underlying Server. This means it shall re-calculate the signatures on the UserIdentityToken using the nonce provided by the underlying Server. The Gateway Server will have to use its own user credentials if the UserIdentityToken provided by the Client does not support impersonation.
Table 17 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 17 – ActivateSession Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters. The type RequestHeader is defined in 7.28. |
|
clientSignature |
SignatureData |
This is a signature generated with the private key associated with the clientCertificate. This parameter is calculated by appending the serverNonce to the serverCertificate and signing the resulting sequence of bytes. If the serverCertificate contains a chain, the signature calculation shall be done only with the leaf Certificate. For backward compatibility a Server shall check the signature with the full chain if the check with the leaf Certificate fails. The SignatureAlgorithm shall be the AsymmetricSignatureAlgorithm specified in the SecurityPolicy for the Endpoint. The SignatureData type is defined in 7.32. |
|
clientSoftwareCertificates [] |
SignedSoftwareCertificate |
Reserved for future use. The SignedSoftwareCertificate type is defined in 7.33. |
|
localeIds [] |
LocaleId |
List of locale ids in priority order for localized strings. The first LocaleId in the list has the highest priority. If the Server returns a localized string to the Client, the Server shall return the translation with the highest priority that it can. If it does not have a translation for any of the locales identified in this list, then it shall return the string value that it has and include the locale id with the string. See OPC 10000-3 for more detail on locale ids. If the Client fails to specify at least one locale id, the Server shall use any that it has. This parameter only needs to be specified during the first call to ActivateSession during a single application Session. If it is not specified the Server shall keep using the current localeIds for the Session. |
|
userIdentityToken |
Extensible Parameter UserIdentityToken |
The credentials of the user associated with the Client application. The Server uses these credentials to determine whether the Client should be allowed to activate a Session and what resources the Client has access to during this Session. The UserIdentityToken is an extensible parameter type defined in 7.36. The EndpointDescription specifies what UserIdentityTokens the Server shall accept. Null or empty user token shall always be interpreted as anonymous. |
|
userTokenSignature |
SignatureData |
If the Client specified a user identity token that supports digital signatures, then it shall create a signature and pass it as this parameter. Otherwise the parameter is null. The SignatureAlgorithm depends on the identity token type. The SignatureData type is defined in 7.32. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
ResponseHeader |
Common response parameters (see 7.29 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
serverNonce |
ByteString |
A random number that should never be used in any other request. This number shall have a minimum length of 32 bytes. The Client shall use this value to prove possession of its Application Instance Certificate in the next call to ActivateSession request. |
|
results [] |
StatusCode |
List of validation results for the SoftwareCertificates (see 7.34 for StatusCode definition). |
|
diagnosticInfos [] |
DiagnosticInfo |
List of diagnostic information associated with SoftwareCertificate validation errors (see 7.8 for DiagnosticInfo definition). This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 18 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 177.
Table 18 – ActivateSession Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_IdentityTokenInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_IdentityTokenRejected |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_ApplicationSignatureInvalid |
The signature provided by the Client application is missing or invalid. |
|
Bad_UserSignatureInvalid |
The user token signature is missing or invalid. |
|
Bad_NoValidCertificates |
The Client did not provide at least one Software Certificate that is valid and meets the profile requirements for the Server. |
|
Bad_IdentityChangeNotSupported |
The Server does not support changing the user identity assigned to the session. |
This Service is used to terminate a Session. The Server takes the following actions when it receives a CloseSession request:
- It stops accepting requests for the Session. All subsequent requests received for the Session are discarded.
- It returns negative responses with the StatusCode Bad_SessionClosed to all requests that are currently outstanding to provide for the timely return of the CloseSession response. Clients are urged to wait for all outstanding requests to complete before submitting the CloseSession request.
- It removes the entry for the Client in its SessionDiagnosticsArray Variable.
When the CloseSession Service is called before the Session is successfully activated, the Server shall reject the request if the SecureChannel is not the same as the one associated with the CreateSession request.
Table 19 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 19 – CloseSession Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.28 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
deleteSubscriptions |
Boolean |
If the value is TRUE, the Server deletes all Subscriptions associated with the Session. If the value is FALSE, the Server keeps the Subscriptions associated with the Session until they timeout based on their own lifetime. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
ResponseHeader |
Common response parameters (see 7.29 for ResponseHeader definition). |
Table 20 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 177.
Table 20 – CloseSession Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_SessionIdInvalid |
See Table 177 for the description of this result code. |
This Service is used to cancel outstanding Service requests. Successfully cancelled service requests shall respond with Bad_RequestCancelledByClient.
Table 21 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 21 – Cancel Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.28 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
requestHandle |
IntegerId |
The requestHandle assigned to one or more requests that should be cancelled. All outstanding requests with the matching requestHandle shall be cancelled. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
ResponseHeader |
Common response parameters (see 7.29 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
cancelCount |
UInt32 |
Number of cancelled requests. |
Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 177.