Errata exists for this version of the document.
The UserIdentityToken structure used in the Server Service Set allows Clients to specify the identity of the user they are acting on behalf of. The exact mechanism used to identify users depends on the system configuration. The different types of identity tokens are based on the most common mechanisms that are used in systems today. Table 180 defines the current set of user identity tokens. The ExtensibleParameter type is defined in 7.12.
Table 180 – UserIdentityToken parameterTypeIds
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
AnonymousIdentityToken |
No user information is available. |
|
UserNameIdentityToken |
A user identified by user name and password. |
|
X509IdentityToken |
A user identified by an X.509 v3 Certificate. |
|
IssuedIdentityToken |
A user identified by a token issued by an external Authorization Service. |
The Client shall always prove possession of a UserIdentityToken when it passes it to the Server. Some tokens include a secret such as a password which the Server will accept as proof. In order to protect these secrets the Token may be encrypted before it is passed to the Server. Other types of tokens allow the Client to create a signature with the secret associated with the Token. In these cases, the Client proves possession of a UserIdentityToken by creating a signature with the secret and passing it to the Server.
Each UserIdentityToken allowed by an Endpoint shall have a UserTokenPolicy specified in the EndpointDescription. The UserTokenPolicy specifies what SecurityPolicy to use when encrypting or signing. If this SecurityPolicy is omitted then the Client uses the SecurityPolicy in the EndpointDescription. If the matching SecurityPolicy is set to None then no encryption or signature is required. The possible SecurityPolicies are defined in OPC 10000-7.
It is recommended that applications never set the SecurityPolicy to None for UserIdentityTokens that include a secret because these secrets could be used by an attacker to gain access to the system.
The encrypted secret and Signature are embedded in a ByteString which is part of the UserIdentityToken. The format of this ByteString depends on the type of UserIdentityToken and the SecurityPolicy.
The legacy token secret format defined in 7.36.2.2 is not extensible and provides only encryption but the encrypted data is not signed. It is used together with the USERNAME_1 UserIdentityToken. The password secret exchanged with this format shall not exceed 64 bytes.
The EncryptedSecret format defined in 7.36.2.3 provides an extensible secret format together with the definition how the secret is signed and encrypted. It allows for the layout to be updated as new token types are defined or new SecurityPolicies are added.
The UserIdentityToken types and the token formats supported by the Endpoint are identified by the UserTokenPolicy defined in 7.37.
When encrypting a UserIdentityToken, the Client appends the last ServerNonce to the secret. The data is then encrypted with the public key from the Server’s Certificate.
If no encryption is applied, the structure is not used and only the secret without any Nonce is passed to the Server.
Table 181 describes how to serialize UserIdentityTokens before applying encryption.
Table 181 – Legacy UserIdentityToken Encrypted Token Secret Format
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Length |
Byte [4] |
The length of the data to be encrypted including the ServerNonce but excluding the length field. This field is a 4-byte unsigned integer encoded with the least significant bytes appearing first. |
|
tokenData |
Byte [*] |
The token data. |
|
serverNonce |
Byte [*] |
The last ServerNonce returned by the Server in the CreateSession or ActivateSession response. |
The EncryptedSecret uses an extensible format which has the TypeId of a DataType Node as a prefix as defined for the ExtensionObject encoding in OPC 10000-6. The general layout of the EncryptedSecret is shown in Figure 39.
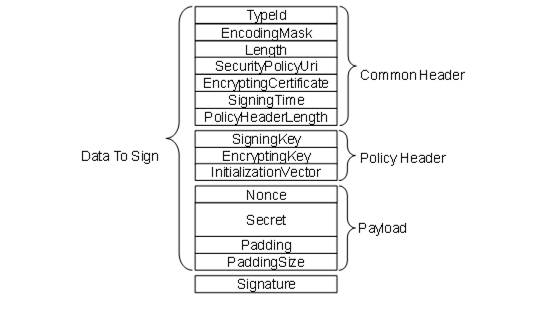
Figure 39 – EncryptedSecret Layout
The TypeId specifies how the EncryptedSecret is serialized and secured. For example, RsaEncryptedSecrets require that the policy header be encrypted with the public key associated with the EncryptingCertificate before it is serialized. Other TypeIds may or may not require the policy header to be encrypted.
The SecurityPolicyUri is used to determine what algorithms were used to encrypt and sign the data.
The payload is always encrypted using the symmetric encryption algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. The EncryptingKey and InitializationVector are used to initialize this algorithm. The mechanisms used to initialize the symmetric encryption algorithm depend on the TypeId. The lengths of the fields are specified by the SecurityPolicyUri.
The Signature using the symmetric signature algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. The SymmetricKey and InitializationVector are used to initialize this algorithm. The mechanisms used to initialize the symmetric signature algorithm depend on the TypeId. The length of the SymmetricKey is specified by the SecurityPolicyUri.
The EncryptedSecret is secured and serialized as follows:
- Serialize the common header;
- Serialize the policy header;
- Encrypt the policy header and append the result to the common header;
- Update the PolicyHeaderLength with the length of the encrypted header;
- Append the Nonce and the Secret to the encrypted policy header;
- Calculate padding required on the payload and append after the Secret;
- Encrypt the payload;
- Calculate a Signature on {common header | encrypted policy header | encrypted payload};
- Append the Signature.
Individual fields are serialized using the UA Binary encoding (see OPC 10000-6) for the DataType specified in Table 182. The Padding is used to ensure there is enough data to fill an integer multiple of encryption blocks. The size of the encryption block depends on the encryption algorithm. Two separate padding operations are needed because two different encryption algorithms may be used. The total length of the Padding, not including the PaddingSize, is encoded as a UInt16. The individual bytes of the Padding are set to the the least significant byte of the PaddingSize.
The EncryptedSecret is deserilized and validated as follows:
- Deserialize the common header;
- Decrypt the policy header using the private key associated with the EncryptingCertificate;
- Verify the padding in the policy header;
- Verify the Signature with the SigningKey;
- Decrypt the payload;
- Verify the padding on the payload;
- Extract the Secret;
If the TypeId does not require the policy header to be encrypted then the padding on the policy header is omitted and the PolicyHeaderLength specifies the length of the unencrypted data.
The fields in the EncryptedSecret are described in Table 182. The first three fields TypeId, EncodingMask and Length belong to the ExtensionObject encoding defined in OPC 10000-6.
Table 182 – EncryptedSecret Layout
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TypeId |
NodeId |
|
|
EncodingMask |
Byte |
This value is always 1. |
|
Length |
Int32 |
The length of the data that follows including the Signature. |
|
SecurityPolicyUri |
String |
The URI for the SecurityPolicy used to apply security. |
|
EncryptingCertificate |
ByteString |
The SHA1 thumbprint of the DER form of the encrypting Certificate. |
|
SigningTime |
DateTime |
When the Signature was created. |
|
PolicyHeaderLength |
UInt16 |
The length of the policy header that follows If the policy header is encrypted this is the length of the encrypted data; Otherwise, it is the length of the unencrypted data; |
|
SigningKey |
ByteString |
The key data used to create the Signature. The TypeId specifies how this data is used. |
|
EncryptingKey |
ByteString |
The key data used to encrypt the payload. The TypeId specifies how this data is used. |
|
InitializationVector |
ByteString |
The data used to initialize the algorithm used to encrypt the payload. The TypeId specifies how this data is used. |
|
Nonce |
ByteString |
This is the last serverNonce returned in the CreateSession or ActivateSession Response when a UserIdentityToken is passed with the ActivateSession Request. If used outside of an ActivateSession call, the source of the Nonce is defined by the context in which this EncryptedSecret is used. The length of the Nonce shall equal the SecureChannelNonceLength specified by the SecurityPolicy. |
|
Secret |
ByteString |
The tokenData that depends on the IssuedIdentityToken. If the tokenData is a String is it encoded using UTF-8 first. |
|
PayloadPadding |
Byte[*] |
Additional padding added to ensure the size of the encrypted payload is an integer multiple of the input block size for the symmetric encryption algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. The value of each byte is the least significant byte of the PayloadPaddingSize. |
|
PayloadPaddingSize |
UInt16 |
The size of the padding added to the payload. |
|
Signature |
Byte[*] |
The signature calculated using the symmetric signing algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. The length of the signature is specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. |
The currently available EncryptedSecret DataTypes are defined in Table 183.
Table 183 – EncryptedSecret DataTypes
|
Type Name |
When to Use |
|
RsaEncryptedSecret |
Used when the SecurityPolicy requires the use of RSA based asymmetric encryption. It is described in 7.36.2.4. |
The RsaEncryptedSecret uses RSA based asymmetric encryption to encrypt the policy header.
Additional semantics for the fields in the EncryptedSecret layout for the RsaEncryptedSecret Structure are described in Table 184.
Table 184 – RsaEncryptedSecret Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TypeId |
NodeId |
The NodeId of the RsaEncryptedSecret DataType Node. |
|
EncodingMask |
Byte |
See Table 182. |
|
Length |
UInt32 |
See Table 182. |
|
SecurityPolicyUri |
String |
See Table 182. |
|
EncryptingCertificate |
ByteString |
See Table 182. |
|
SigningTime |
DateTime |
See Table 182. |
|
PolicyHeaderLength |
UInt16 |
See Table 182. |
|
SigningKey |
ByteString |
The key used to compute the Signature. See Table 182 for additional details. |
|
EncryptingKey |
ByteString |
The key used to encrypt payload. See Table 182 for additional details. |
|
InitializationVector |
ByteString |
The initialization vector used with the EncryptingKey. See Table 182 for additional details. |
|
Nonce |
ByteString |
See Table 182. |
|
Secret |
ByteString |
See Table 182. |
|
PayloadPadding |
Byte[*] |
See Table 182. |
|
PayloadPaddingSize |
UInt16 |
See Table 182. |
|
Signature |
Byte[*] |
See Table 182. |
The AnonymousIdentityToken is used to indicate that the Client has no user credentials.
Table 185 defines the AnonymousIdentityToken parameter.
Table 185 – AnonymousIdentityToken
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
AnonymousIdentityToken |
Structure |
An anonymous user identity. |
|
policyId |
String |
An identifier for the UserTokenPolicy that the token conforms to. The UserTokenPolicy structure is defined in 7.37. |
The UserNameIdentityToken is used to pass simple username/password credentials to the Server.
This token shall be encrypted by the Client if required by the SecurityPolicy of the UserTokenPolicy. The Server should specify a SecurityPolicy for the UserTokenPolicy if the SecureChannel has a SecurityPolicy of None and no transport layer encryption is available. If None is specified for the UserTokenPolicy and SecurityPolicy is None then the password only contains the UTF-8 encoded password. The SecurityPolicy of the SecureChannel is used if no SecurityPolicy is specified in the UserTokenPolic y.
If the token is to be encrypted the password shall be converted to a UTF-8 ByteString, encrypted and then serialized as shown in Table 181.
The Server shall decrypt the password and verify the ServerNonce.
If the SecurityPolicy is None then the password only contains the UTF-8 encoded password. This configuration should not be used unless the network is encrypted in some other manner such as a VPN. The use of this configuration without network encryption would result in a serious security fault, in that it would cause the appearance of a secure user access, but it would make the password visible in clear text.
Table 186 defines the UserNameIdentityToken parameter.
Table 186 – UserNameIdentityToken
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
UserNameIdentityToken |
Structure |
UserName value. |
|
policyId |
String |
An identifier for the UserTokenPolicy that the token conforms to. The UserTokenPolicy structure is defined in 7.37. |
|
userName |
String |
A string that identifies the user. |
|
password |
ByteString |
The password for the user. The password can be an empty string. This parameter shall be encrypted with the Server’s public key using the algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicy. The format used for the encrypted data is described in 7.36.2.2. |
|
encryptionAlgorithm |
String |
A string containing the URI of the AsymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm. The URI string values are defined names that may be used as part of the security profiles specified in OPC 10000-7. This parameter is null if the password is not encrypted. |
Table 187 describes the dependencies for selecting the AsymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm for the UserNameIdentityToken. The SecureChannel SecurityPolicy URI is specified in the EndpointDescription and used in subsequent OpenSecureChannel requests. The UserTokenPolicy SecurityPolicy URI is specified in the EndpointDescription. The encryptionAlgorithm is specified in the UserNameIdentityToken or IssuedIdentityToken provided by the Client in the ActivateSession call. The SecurityPolicy Other in the table refers to any SecurityPolicy other than None. The selection of the EncryptionAlgorithm is based on the UserTokenPolicy. The SecureChannel SecurityPolicy is used if the UserTokenPolicy is null or empty.
Table 187 – EncryptionAlgorithm selection
|
SecureChannel SecurityPolicy |
UserTokenPolicy SecurityPolicy |
UserIdentityToken EncryptionAlgorithm |
|
Security Policy - None |
Null or empty |
No encryption |
|
Security Policy - None |
Security Policy - None |
No encryption |
|
Security Policy - None |
Security Policy - Other |
Asymmetric algorithm for "Other" |
|
Security Policy - Other |
Null or empty |
Asymmetric algorithm for "Other" |
|
Security Policy - Other |
Security Policy - Yet another |
Asymmetric algorithm for "Yet another" |
|
Security Policy - Other |
Security Policy - Other |
Asymmetric algorithm for "Other" |
|
Security Policy - Other |
Security Policy - None |
No encryption |
The X509IdentiyToken is used to pass an X.509 v3 Certificate which is issued by the user.
This token shall always be accompanied by a Signature in the userTokenSignature parameter of ActivateSession if required by the SecurityPolicy. The Server should specify a SecurityPolicy for the UserTokenPolicy if the SecureChannel has a SecurityPolicy of None.
Table 188 defines the X509IdentityToken parameter.
Table 188 – X.509 v3 Identity Token
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
X509IdentityToken |
structure |
X.509 v3 value. |
|
policyId |
String |
An identifier for the UserTokenPolicy that the token conforms to. The UserTokenPolicy structure is defined in 7.37. |
|
certificateData |
ByteString |
The X.509 v3 Certificate in DER format. |
The IssuedIdentityToken is used to pass SecurityTokens issued by an external Authorization Service to the Server. These tokens may be text or binary.
OAuth2 defines a standard for Authorization Services that produce JSON Web Tokens (JWT). These JWTs are passed as an Issued Token to an OPC UA Server which uses the signature contained in the JWT to validate the token. OPC 10000-6 describes OAuth2 and JWTs in more detail. If the token is encrypted, it shall use the EncryptedSecret format defined in 7.36.2.3.
This token shall be encrypted by the Client if required by the SecurityPolicy of the UserTokenPolicy. The Server should specify a SecurityPolicy for the UserTokenPolicy if the SecureChannel has a SecurityPolicy of None and no transport layer encryption is available. The SecurityPolicy of the SecureChannel is used If no SecurityPolicy is specified in the UserTokenPolic y.
If the SecurityPolicy is not None, the tokenData shall be encoded in UTF-8 (if it is not already binary), signed and encrypted according the rules specified for the tokenType of the associated UserTokenPolicy (see 7.37).
If the SecurityPolicy is None then the tokenData only contains the UTF-8 encoded tokenData. This configuration should not be used unless the network is encrypted in some other manner such as a VPN. The use of this configuration without network encryption would result in a serious security fault, in that it would cause the appearance of a secure user access, but it would make the token visible in clear text.
Table 189 defines the IssuedIdentityToken parameter.
Table 189 – IssuedIdentityToken
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
IssuedIdentityToken |
structure |
The token provided by an Authorization Service. |
|
policyId |
String |
An identifier for the UserTokenPolicy that the token conforms to. The UserTokenPolicy structure is defined in 7.37. |
|
tokenData |
ByteString |
The text or binary representation of the token. The format of the data depends on the associated UserTokenPolicy. |
|
encryptionAlgorithm |
String |
The URI of the AsymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm. The list of OPC UA-defined names that may be used is specified in OPC 10000-7. See Table 187 for details on picking the correct URI. This parameter is null if the tokenData is not encrypted or if the EncryptedSecret format is used. |