The TaskControlStateMachineType represents the behaviour of a task control and can be used for monitoring or for remote control.
To provide information about the condition of a program loaded inside a task control and the possibility to reset the loaded program the Ready State can be extended by the ReadySubstateMachineType.
The Task Control Monitor ConformanceUnit supports monitoring of the activities done by the operator or system internally. The Task Control Operation ConformanceUnit supports additional operations by Methods.
The overview of the state machine with all transitions is shown in
When the state machine changes from Executing State to Ready State caused by internal behaviour of the task control (e.g. because program is ended) it is expected that the task control can be started immediately again e.g. by the Start() method. So, the application may set the loaded program to its entry point (like the ResetToProgramStart() Method) while transition ExecutingToReady or when the Start() Method is called, that no additional reset of the program is needed.
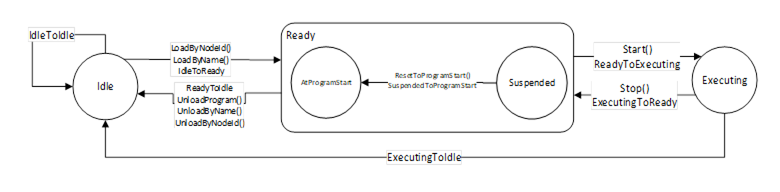
Figure 29 – TaskControl State Machine with ReadySubstateMachine in Ready State
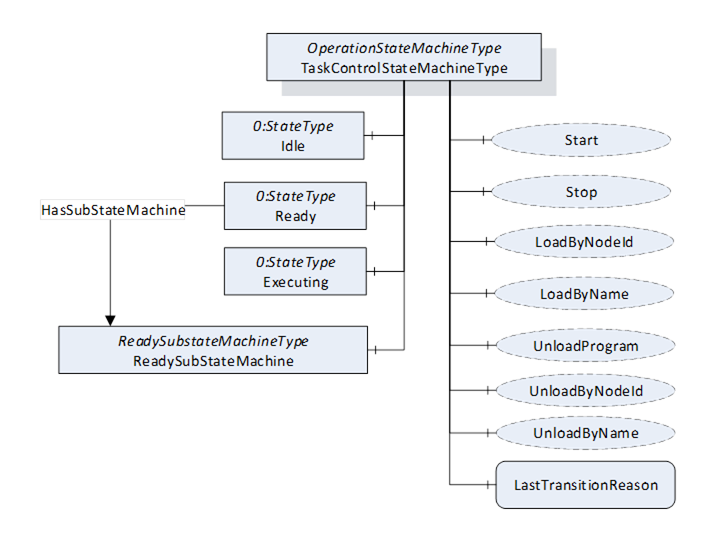
Figure 30 – TaskControlStateMachineType with the ReadySubstateMachine
The TaskControlStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 65.
Table 65 – TaskControlStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
TaskControlStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtype of the OperationStateMachineType |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadySubstateMachine |
|
ReadySubstateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
LoadByNodeId |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
LoadByName |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
UnloadProgram |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
UnloadByNodeId |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
UnloadByName |
|
|
O |
|
Inherited from OperationStateMachineType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransitionReason |
0:Int16 |
0:MultiStateValueDiscreteType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
PossibleStopModes |
0:EnumValueType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ConfiguredDefaultStopMode |
0:Int16 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Idle |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Ready |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Executing |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToExecuting |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Stop |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransition |
0:LocalizedText |
0:FiniteTransitionVariableType |
M |
|
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
TransitionEventType |
|
|
O |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Monitor |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control ReadySubstate |
|||||
|
Rob System Events |
|||||
The Ready State of TaskControlStateMachineType has additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 66.
Table 66 – TaskControlStateMachineType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Ready |
0:HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
ReadySubstateMachine |
|
ReadySubstateMachineType |
O |
The states of the TaskControlStateMachineType are described in Table 67.
Table 67 – TaskControlStateMachineType State Descriptions
|
StateName |
Description |
|
Idle |
The task control is not loaded with a program. |
|
Ready |
The task control is loaded with a program and is not executing the program. |
|
Executing |
The task control is loaded with a program and is executing the program. If the task control automatically starts the program at the beginning, after reaching the end, it shall stay in Executing state (continuously executing). |
The transitions are described in the table below.
Table 68 – TaskControlStateMachineType Transition Descriptions
|
TransitionName |
Description |
|
IdleToIdle |
Occurs if the program could not be loaded correctly. |
|
IdleToReady |
Occurs in response to LoadProgram() or internal events, when loading a program to the task control. |
|
ReadyToIdle |
Occurs in response to UnloadProgram() or internal events, when unloading a program from the task control. |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
Occurs in response to Start() or internal events, when starting a loaded program in the task control. |
|
ExecutingToReady |
Occurs in response to Stop() or internal events, when stopping a loaded program in the task control. |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
Occurs in response to internal events, when stopping a loaded program in the task control and unloading the task control. |
The components of the TaskControlStateMachineType have additional references which are defined in Table 69.
Table 69 – TaskControlStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
IdleToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
IdleToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
0:HasCause |
True |
LoadByNodeId |
0:HasCause |
True |
LoadByName |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasCause |
True |
UnloadProgram |
0:HasCause |
True |
UnloadByNodeId |
0:HasCause |
True |
UnloadByName |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
0:ToState |
True |
Executing |
0:HasCause |
True |
Start |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
0:HasCause |
True |
Stop |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
The component Variables of the TaskControlStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 70.
Table 70 – TaskControlStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
LoadByNodeId (
[in]0:ExpandedNodeId Id
[out]0:Int32 Status
);
Table 71 specifies the Arguments.
Table 71 – LoadByNodeId Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Id |
ExpandedNodeId pointing to an instance of FileType representing a task control program or module |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The LoadByNodeId Method is called by a Client to load a program or a module into a task control.
For the storage of programs, the Server may support the Programs folder defined within the ControllerType. (see 7.18). This method can be used to load the program or module into the Task Control if the program or module itself is available in the address space (e.g. within the Programs folder). The Id input argument shall be used to identify the program in the address space. This method can be a synchronous or an asynchronous method. In case it is a synchronous method, the return output arguments may contain more information about the Success or Failure of the method call. If the system is in the Idle state when the method is called, and something goes wrong internally then instead of the IdleToReady transition, the IdleToIdle transition shall be observed by the client. If the system is already in the Ready state and the LoadByNodeId is called and fails, it is system dependent, whether the system goes back to the Idle state or remains in the Ready state. Calling LoadByNodeId in the Executing state will fail in normal circumstances.
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 72. Some of these StatusCodes correspond to the ProgramId input argument.
Clients may inspect the Status output argument to determine if the program was successfully loaded or if it failed.
Table 72 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
|
Bad_NodeIdUnknown |
|
|
Bad_NodeIdInvalid |
The syntax of the NodeId is not valid. |
The LoadByNodeId Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 73.
Table 73 – LoadByNodeId Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
LoadByNodeId |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
LoadByName (
[in]0:StringName
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The table below specifies the Arguments.
Table 74 – LoadByName Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Name |
Name to identify a task control program or module |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The LoadByName Method is called by a Client to load a program or module to a task control. The controller uses the Name input argument to identify the program or module to load into the task control. The behaviour of this method is identical to the LoadByNodeId (see 7.16.2).
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in the table below. Some of these StatusCodes correspond to the Name input argument.
Clients may inspect the Status output argument to determine if the program was successfully loaded or if it failed.
Table 75 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The LoadByName Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in the table below.
Table 76 – LoadByName Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
LoadByName |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
UnloadProgram (
[out]0:Int32 Status
);
The table below specifies the Arguments.
Table 77 – UnloadProgram Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The UnloadProgram Method is called by a Client to unload the program from a task control.
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in the table below.
Table 78 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The UnloadProgram Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in the table below.
Table 79 – UnloadProgram Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
UnloadProgram |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
UnloadByNodeId (
[in] 0:ExpandedNodeId Id
[out]0:Int32 Status
);
Table 80 specifies the Arguments.
Table 80 – UnloadByNodeId Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Id |
Expanded NodeId of the module to be unloaded |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The UnloadByNodeId Method is called by a Client to unload a task module from a task control. This only works if the task modules are expressed in the address space (7.22).
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in the table below.
Table 81 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The UnloadByNodeId Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 82. This method might not always result in a state change from Ready to Idle.
Table 82 – UnloadByNodeId Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
UnloadByNodeId |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
UnloadByName (
[in] 0:String Name
[out]0:Int32 Status
);
Table 83 specifies the Arguments.
Table 83 – UnloadByName Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Name |
Name of the module to be unloaded |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The UnloadByName Method is called by a Client to unload a module from a task control. This can be used to unload the task modules if they are not expressed in the address space and internal logic is used to find the module to be unloaded based on the Name input argument.
This method might not always result in a state change from Ready to Idle.
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in the table below.
Table 84 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The UnloadByName Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in the table below.
Table 85 – UnloadByName Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
UnloadByName |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Start (
[out]0:Int32Status
);
Table 86 specifies the Arguments.
Table 86 – Start Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The Start method can only be successfully called when the task control is in the Ready state. Depending on the program pointer, the system shall attempt to start executing from the beginning of the program or continue executing from where it was suspended (see Substate machine description of this state in 7.17).
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 87.
Table 87 - Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The Start Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 88.
Table 88 – Start Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Start |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Stop (
[in]0:Int64 StopMode
[out]0:Int32Status
);
Table 89 specifies the Arguments.
Table 89 – StopMethod Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
StopMode |
must either be 0 or one of those listed in the PossibleStopModes Variable (see Table 31) |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The Stop Method allows an authorized Client to command the task control to stop executing and leave the Executing state and go to the Ready state. If the ReadySubstateMachine (see 7.17) is present, the task control shall be in the Suspended state of the Substate machine.
The input argument StopMode must be either 0 or one of those listed in the PossibleStopModes Variable (see Section). If not, then a Bad_InvalidArgument Result Code is returned.
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in the table below.
Table 90 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The task control operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The task control operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The Stop Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 91.
Table 91 – Stop Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Stop |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob Task Control Operation |
|||||