Ethernet POWERLINK is a communication profile for Real-Time Ethernet (RTE). It extends Ethernet according to the IEEE 802.3 standard with mechanisms to transfer data with predictable timing and precise synchronisation. The communication profile meets timing demands typical for high-performance automation and motion applications. It does not change basic principles of the Fast Ethernet Standard IEEE 802.3 but extends it towards RTE. Thus, it is possible to leverage and continue to use any standard Ethernet silicon, infrastructure component or test and measurement equipment like a network analyser.
POWERLINK provides mechanisms to achieve the following:
- Transmit time-critical data in precise isochronous cycles. Data exchange is based on a publish/subscribe relationship. Isochronous data communication can be used for exchanging position data of motion applications of the automation industry.
- Synchronise networked POWERLINK Devices with high accuracy.
- Transmit less time-critical data asynchronously on request. Asynchronous POWERLINK Data communication can be used to transfer IP-based protocols like TCP or UDP and higher layer protocols such as HTTP, FTP, etc.
POWERLINK manages the network traffic in a way that there are dedicated time-slots for Isochronous and Asynchronous POWERLINK Data. It takes care that always only one networked device gains access to the network media. Thus, transmission of Isochronous POWERLINK Data and Asynchronous POWERLINK Data will never interfere and precise communication timing is guaranteed. The mechanism is called Slot Communication Network Management (SCNM). SCNM is managed by one particular networked device – the POWERLINK Managing Node (MN) – which includes the MN functionality. All other nodes are called POWERLINK Controlled Nodes (CN).
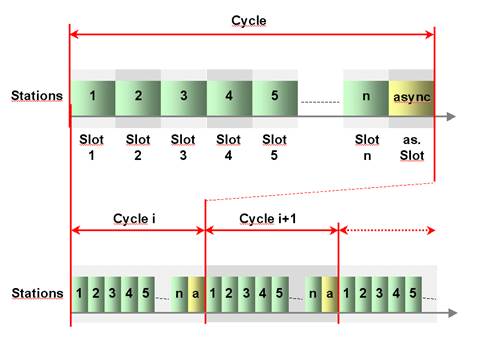
Figure 1 – Slot Communication Network Management (SCNM)