The metal forming principles are one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in the world. During the forming process of the incoming metal sheets, bars, plates, tubes or powder, the material is plastically deformed by a force to obtain the required size and shape, as well as the physical properties of the desired product. Figure 1 shows the main principles of metal forming covered in this specification. These principles are classified into three main categories: bulk forming, sheet forming, and powder forming. The selection of the metal forming process depends on the application, material properties, and desired shape and properties of the final product.
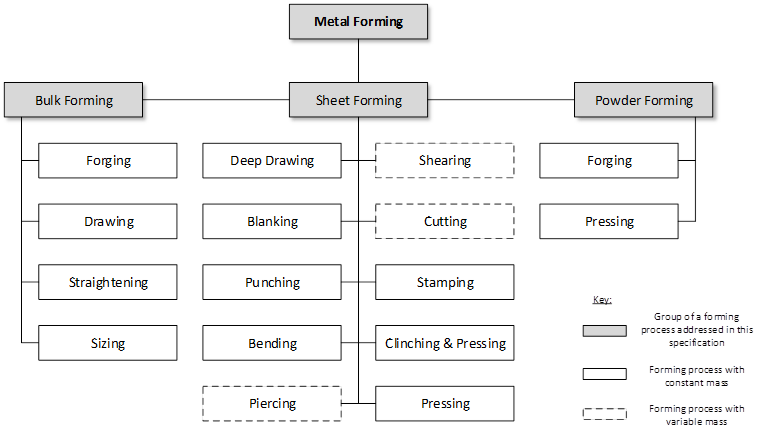
Figure 1 – Overview metal forming processes
There are different types of metal forming machines, which can be divided into several categories based on their specific applications and processes. The basic definitions for the DeviceClass Variable are used in the MachineIdentificationType as defined by OPC 10000-100. Next to the already defined technologies which are also commonly used in metal forming, like bending machine, forming machine, forging machine, punching machine and press, last mentioned can be extended and subdivided into hydraulic press, mechanic press and servo-electric press as they describe the widely distributed kinds of press machines.
There are several types of tools used in metal forming processes to shape and manipulate metal. Figure 2 shows a sheet metal forming press of a multi-stage press line in action. Between the upper and lower tool, which forms relevant shapes, the transfer moves the blank sheets from one stage to the next. Especially in the environment of press machines, the designation of a metal forming tool differs from tools in e.g. CNC machining context. Moreover, a tool is a combination of two or more individual parts, like upper tool, lower tool, blank holders or a kind of matrix in between.
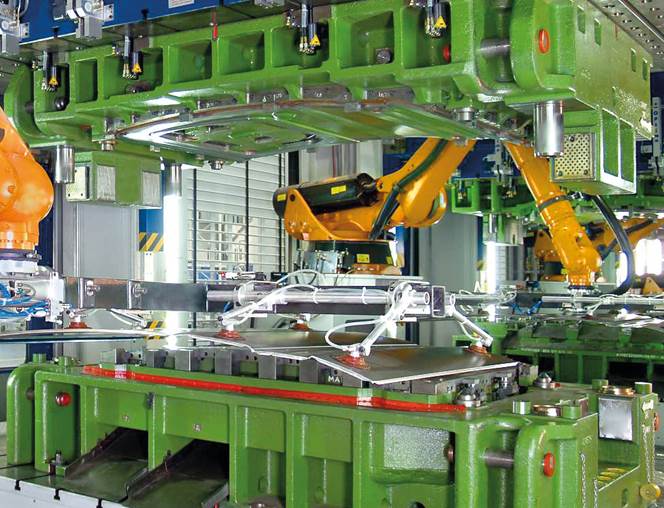

Figure 2 – Sheet Metal Forming Press with die and punch (Schuler Group GmbH)