The following section details the generic MDISValveObjectType structure and defines the properties associated with it. This is in general a vendor and operator independent description, but all users of this MDISValveObjectType can add vendor specific data. The vendor specific data should be defined as part of a subtype of the MDISValveObjectType defined in this document. It is required that the subsea system is the Server and host of the valve Object. The DCS based system is the Client in the system. It is required that all interaction with the valve Object is initiated by the Client and is directed to the Server.
The valve Object is a basic component of any subsea control system. Subsea and surface trees have a large variety of valve configurations and combinations of manual and / or actuated (hydraulic or pneumatic) valves. Implementation shall ensure adherence to Mandatory [M] aspects in order to comply with the MDIS interface standardisation. Optional [O] may or may not be implemented within a project. Figure 16 provides an overview of the MDISValveObjectType as defined by MDIS. The figure includes all items inherited from the MDISBaseObjectType. It illustrates that an interlock might have one or more Interlock variables associated with it, or that they might not have an actual interlock associated.
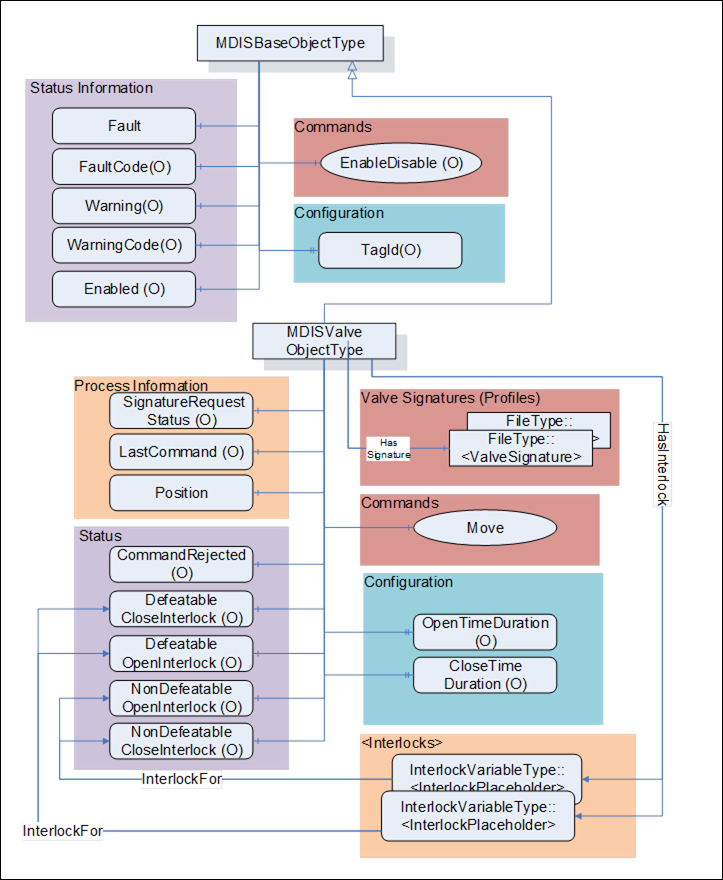
Figure 16 – Valve Object Overview
Table 51 details the generic properties for the MDISValveObjectType. Any vendor specified properties that have been implemented within a project should be documented within a similar format and supplied to the DCS vendor. The addition of vendor specific properties will result in a subtype of the MDISValveObjectType. When an MDISValveObjectType Instance is disabled the MDISBaseObjectType defaults are followed and only the OpenTimeDuration and CloseTimeDuration values will be available.
Table 51 – MDISValveObjectType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
MDISValveObjectType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the MDISBaseObjectType |
|
||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
Position |
ValvePositionEnum |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M, R |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
CommandRejected |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
SignatureRequestStatus |
SignatureStatusEnum |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastCommand |
CommandEnum |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NonDefeatableOpenInterlock |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
DefeatableOpenInterlock |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
NonDefeatableCloseInterlock |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
DefeatableCloseInterlock |
0:Boolean |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Move |
See 6.8.4 |
M |
|
|
HasInterlock |
Variable |
<InterlockPlaceholder> |
0:Boolean |
InterlockVariableType |
OP, RO |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
OpenTimeDuration |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
CloseTimeDuration |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
|
HasSignature |
Object |
<ValveSignature> |
|
FileType |
OP |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
MDIS Valve Base |
|||||
The following items describe status information from the valve:
- SignatureRequestStatus – The collection of data required for a valve signature may take some time after the completion of a Move command. The SignatureRequestStatus Variable indicates the status of the current signature request (see 8.1.4 for a description of the possible enumerations).
- LastCommand – The enumeration reflects the last command sent to the equipment by the SPCS (see 8.1.5 for a description of the possible enumerations).
- Enabled – This Boolean reflects if the valve is available for control. The behaviour follows the MDISBaseObjectType.
- Position – This enumeration provides information about the current position of the valve (see section 8.1.7 for additional details).
- CommandRejected – A flag that, if set to True, indicates that the valve has rejected the last command issued to it. The command could be rejected for a number of reasons. Possible reasons for rejecting a command include:
- Loss of subsea communication reported by the SPCS.
- An active interlock.
- The valve is in the disabled state.
For any of the following Variables, if they are true, there shall be at least one instance of an InterlockVariableType that describes the active interlock.
- NonDefeatableOpenInterlock – The open valve command is interlocked and cannot be overridden.
- DefeatableOpenInterlock – The open valve command is interlocked and can be overridden.
- NonDefeatableCloseInterlock – The close valve command is interlocked and cannot be overridden.
- DefeatableCloseInterlock – The close valve command is interlocked and can be overridden.
The following items are related to valve control: These items allow information to flow from the DCS to the SPCS. All commands from the DCS to SPCS may require access controls to ensure that only appropriate personnel initiate them.
<InterlockPlaceholder> – The number of interlock Variables will change based on the project and even valve instance. The Variables shall be of InterlockVariableType or a subtype of it. The interlock contains an InterlockFor Reference to one of the previously described flags. Clients can use this information to categorise the interlocks appropriately. Figure 17 provides an example of how this interlock Variable is used and could be deployed.
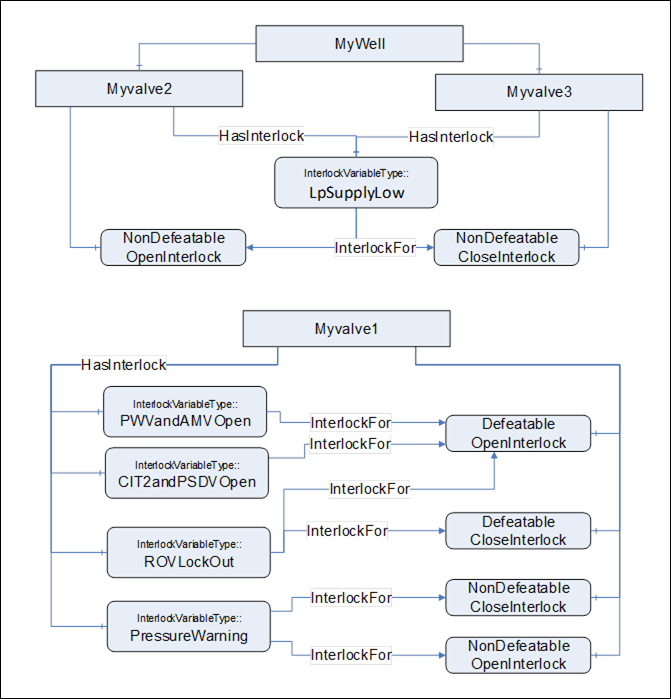
Note: in OPC UA it is allowed to have a Node which is the target of multiple 0:HasComponent References, this allows a single interlock to be shared between multiple Objects; such as a low pressure interlock that maybe shared by all of the valves and chokes in a system.
The following items describe configuration related items:
- OpenTimeDuration – Estimated max time to travel to open position, used for DCS systems to indicate a move fail condition if time is exceeded. Time is provided in milliseconds. The OpenTimeDuration can be used for any kind of valve (hydraulic, electric, etc.). [Note: this time is an estimate and Clients may need to allow for additional delays in transmitting and receiving any move commands].
- CloseTimeDuration - Estimated max time to travel to close position, used for DCS systems to indicate a move fail condition if time is exceeded. Time is provided in milliseconds. The CloseTimeDuration can be used for any kind of valve (hydraulic, electric, etc.) [Note: this time is an estimate and Clients may need to allow for additional delays in transmitting and receiving any Move commands].
- <ValveSignature> - The reference shall point to an instance of FileType, where the file contains valve signature information. The name of this object is project or vendor specific, but it should be related to the name of the instance of the MDISValveObjectType. The name shall include a timestamp. The FileType ObjectType (defined in OPC 10000-5 (older version), OPC 10000-20 (newer versions)) includes two properties (illustrated below), for all MDIS instances both of these properties shall have the value False. For additional detail see 6.14.3.
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:Writable |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:UserWritable |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
Mandatory |
Vendor specific subtypes of this ObjectType are allowed. They may add additional vendor specific information or may change some Optional items to Mandatory. A standard file content is defined in Annex E.
The MDISValveObjectType is a subtype of MDISBaseObjectType and inherit the FaultCode Variable. The MDISValveObjectType defines the standard FaultCodes (for bits 0-15 as defined in 6.2.2) in Table 52. All subtypes of this the MDISValveObjectType will inherit all FaultCodes defined in this table. Subtypes may define additional FaultCodes in their own table.
Table 52 – MDISValveObjectType FaultCode Values
|
Value |
Bit no. |
Description |
|
CommunicationFault |
1 |
Not possible to operate the valve. |
|
FailedToOpen |
2 |
Device failed to move open |
|
FailedToClose |
3 |
Device failed to move close |
|
PressureFeedbackFailure |
4 |
Pressure check feedback verification failed |
|
FlowFeedbackFailure |
5 |
Flow check feedback verification failed |
The MDISValveObjectType defines the standard WarningCodes (for bits 0-15 as defined in 6.2.2) in Table 53. All subtypes of this the MDISValveObjectType will inherit all WarningCodes defined in this table. Subtypes may define additional WarningCodes in their own table.
Table 53 – MDISValveObjectType WarningCode Values
|
Value |
Bit no. |
Description |
|
SideAProblem |
0 |
There is an issue with the A side of the valve |
|
SideBProblem |
1 |
There is an issue with the B side of the valve. |
|
PositionDiscrepancy |
2 |
The valve position has a discrepancy (Side A and Side B are different and neither is broken) |
|
UncommandedChange |
3 |
Position of valve changed without an authorized move |
|
CalibrationRequired |
4 |
The valve requires calibration |
Move Method is used to open or close a valve.
Signature
Move (
[in] CommandEnum Direction,
[in] 0:Boolean OverrideInterlock,
[in] SEMEnum SEM,
[in] 0:Boolean Signature,
[in] 0:Boolean ShutdownRequest);
Table 54 – Move Arguments (Valve)
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Direction |
The enumeration indicates whether the command is to open the valve or to close the valve |
|
OverrideInterlock |
Boolean indicating if the open or close command should override any defeatable interlocks |
|
SEM |
The enumeration indicates which SEM to send the command to. |
|
Signature |
Boolean indicating if a profile /signature should be generated by this move command request. If the optional Variable SignatureRequestStatus is not provided on the Object, this parameter is ignored by the Server. |
|
ShutdownRequest |
Boolean indicates that this command is part of a shutdown sequence. It should be noted that the responsibility for the shutdown is on the DCS and operator side. All non defeatable interlocks of the subsea system will be overridden which can cause damage to the subsea system. |
Method result codes are defined as part of the Call Service (see OPC 10000-4). They are described in Table 124 for ease of reference.
Comments:
The Move Method initiates a move operation. Parameters include opening or closing of the valve, overriding of any interlocks, the SEM selection to use for the command, if a profile / signature is being requested for this move operation or if a shutdown is being requested. The Method will complete when the command has been accepted. If the command has not been accepted by the Server, then the Method returns an error indicating the operation could not be performed. In the case when the Move command is accepted by the Server, the move operation may or may not be complete at the time the Method returns to the Client. Therefore, the Client must monitor the Position of the valve to determine when the Move command actually finishes.
The OverrideInterlocks, SEM, Signature and Shutdown are optional parameters, but OPC UA Methods do not allow for optional parameters. These parameters must always be provided. On a Server basis the parameter may be configured to not be utilised. If a Server is configured to not utilise a parameter, this is because the functionality is not required.
Table 55 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the Move Method.
Table 55 – Move Method AddressSpace Definition (Valve)
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Move |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
MDIS Valve Base |
|||||