The FunctionalStateMachineType is the top level StateMachine for the LADS ActiveProgram, FunctionalUnit or Function. The basic idea behind this architecture is that the instances of the FunctionalStateMachineType, the ActiveProgramStateMachineType, the FunctionalUnitStateMachineType and the FunctionStateMachineType use the same s tates, Transitions and Methods, but add their own Start Methods with different Method Signatures to trigger the StoppedToRunning Transition from a Client.
The FunctionalStateMachineType defines the available states in a LADS system.
The FunctionalStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 26. StateTypes and TransitionTypes only exist in the type system, thus they do not have a modelling rule.
The FunctionalStateMachine is depicted in Figure 16.
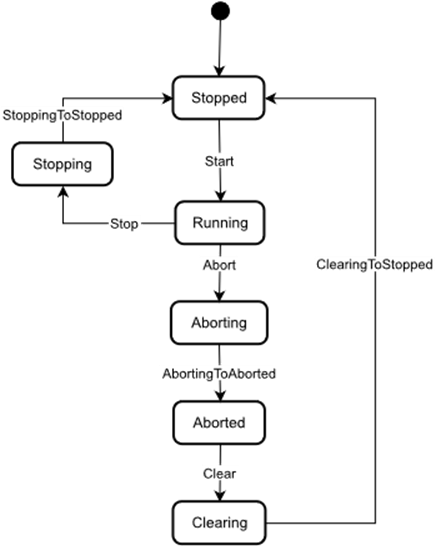
Figure 16 – FunctionalStateMachine
Table 26 – FunctionalStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
FunctionalStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
0:AvailableTransitions |
0:NodeId[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
0:AvailableStates |
0:NodeId[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Abort |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
AbortedToClearing |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Aborting |
|
StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
AbortingToAborted |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Clear |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Clearing |
|
StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ClearingToStopped |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Running |
|
StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
RunningStateMachine |
|
RunningStateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
RunningToAborting |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
RunningToStopping |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Stop |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Stopped |
|
InitialStateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
StoppedToRunning |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Stopping |
|
StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
StoppingToStopped |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
0:CurrentState |
0:LocalizedText |
FiniteStateVariableType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
LADS FunctionalStateMachineType |
|||||
|
|
|||||
The AvailableTransitions and AvailableStates Nodes are overwritten and made Mandatory in the FunctionalStateMachineType.
Abort is a Method to trigger a change of state to Aborting. This will affect all sub-states in a cleared state.
Aborted maintains unit/device status information relevant to the Abort condition. The unit/device can only exit the Aborted state after an explicit Clear command subsequent to manual intervention to correct and reset the detected unit/device faults.
Aborting represents a state that can be entered at any time in response to the Abort command or in the event of a unit/device fault. The aborting logic will bring the unit/device to a rapid safe stop. Operation of the emergency stop will cause the unit/device to be tripped by its safety system. It will also provide a signal to initiate the Aborting state.
Clear is a Method to trigger a change of state to Cleared.
Clearing is initiated by a state command to clear faults that may have occurred when Aborting that are present in the Aborted state.
Running is the state when the ActiveProgram, Function or FunctionalUnit is currently running/executing.
RunningStateMachine is a RunningStateMachineType that details the Running state.
Stop is a Method to trigger a change of state to Stopped. This will affect all sub-states in a Run state.
Stopped is the initial state for an ActiveProgram, FunctionalUnit or Function. It is an Idle state which means that the Function, FunctionalUnit or ActiveProgram is stopped and ready for activation. It can also be used to represent a non-running state, potentially caused by an error, where the Function, FunctionalUnit or ActiveProgram can invoke the Reset() Function before starting again.
Stopping indicates that the ActiveProgram, FunctionalUnit, or Function is in the process of stopping. This state usually occurs when the program execution is finished or stopped, either because it has ended or has been triggered by the Stop Method.
The Transitions of the FunctionalStateMachineType have additional References which are defined in Table 27. This StateMachine includes the transition from Unholding to Holding, Starting, Unsuspending, Suspended, and Suspending, all of which are extensions to the ISA-TR88.00.02-2015 specification.
Table 27 – FunctionalStateMachineType additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
AbortedToClearing |
0:FromState |
True |
Aborted |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Clearing |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
Clear |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
AbortingToAborted |
0:FromState |
True |
Aborting |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Aborted |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ClearingToStopped |
0:FromState |
True |
Clearing |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Stopped |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
RunningToAborting |
0:FromState |
True |
Running |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Aborting |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
Abort |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
RunningToStopping |
0:FromState |
True |
Running |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Stopping |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
Stop |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
StoppedToRunning |
0:FromState |
True |
Stopped |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Running |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
StoppingToStopped |
0:FromState |
True |
Stopping |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Stopped |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
Running |
0:HasSubStateMachine |
True |
RunningStateMachine |
The Component Variables of the FunctionalStateMachineType have additional Attributes, as defined in Table 28.
Table 28 – FunctionalStateMachineType Attribute Values for Child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
6 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
||
|
7 |
||
|
8 |
The Abort Method switches the state machine to the Aborting state. The current process will be aborted. The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 29 specifies its representation in the AddressSpace.
Signature
Abort ()
Table 29 – Abort Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Abort |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Clear Method allows an OPC UA Client to change the state of this state machine to the Cleared state. The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 30 specifies its representation in the AddressSpace.
Signature
Clear ()
Table 30 – Clear Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Clear |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Stop Method allows an OPC UA Client to change the state of this state machine to the Stopping state. The signature of this Method is specified below. Table 31 specifies the Arguments and AddressSpace representation.
Signature
Stop ()
Table 31 – Stop Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Stop |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|