An OPC UA companion specification for an industry specific vertical market describes an information model by defining ObjectTypes, VariableTypes, DataTypes and ReferenceTypes that represent the concepts used in the vertical market. Table 1 contains an example of an ObjectType definition.
Table 1 – Example ObjectType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
WidgetType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the BaseObjectType from OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Color |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Flavor |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Rank |
Int32 |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
The BrowseName is a non-localized name for an ObjectType.
IsAbstract is a flag indicating whether instances of the ObjectType can be created.
The bottom of the table lists the child nodes for the type. The Reference is the type of reference between the Object instance and the child Node. The NodeClass is the class of Node. The BrowseName is the non-localized name for the child. The DataType is the structure of the Value accessible via the Node (only used for Variable NodeClass Nodes) and the TypeDefinition is the ObjectType or VariableType for the child.
The ModellingRule indicates whether a child is Mandatory or Optional. It can also indicate cardinality. Note that the BrowseName is not defined if the cardinality is greater than 1. Figure 12 visually depicts the ObjectType defined in Table 1 along with two instances of the ObjectType.
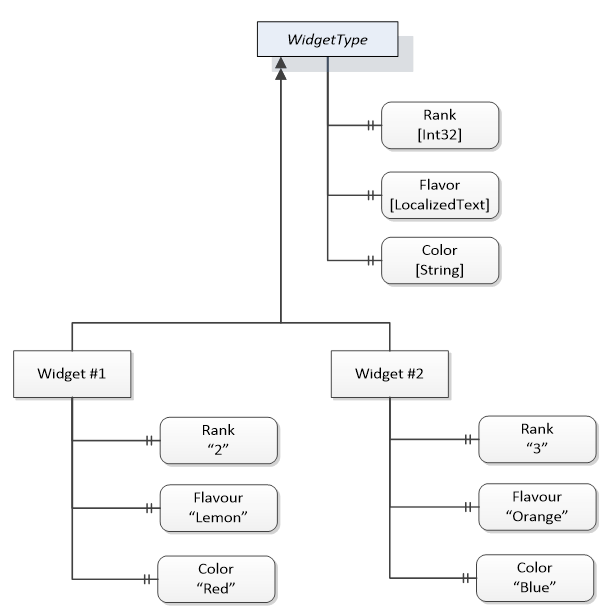
Figure 12 – A Visual Representation of the Sample ObjectType