This specification defines an Information Model for IO-Link Masters and Devices. An example of a system architecture, providing different deploy options for OPC UA applications, is shown in Figure 5. The OPC UA Server can directly be deployed on an IO-Link Master or a PLC connected to the IO-Link Master or another platform like a PC. The OPC UA Client can directly be connected to the OPC UA Server running on the IO-Link Master, it can be connected to the PLC running the OPC UA Server, or the PLC can forward the traffic from an OPC UA Client on top of the PLC to the OPC UA Server running on the IO-Link Master beneath the PLC. More deploy options are possible and not limited by this specification.
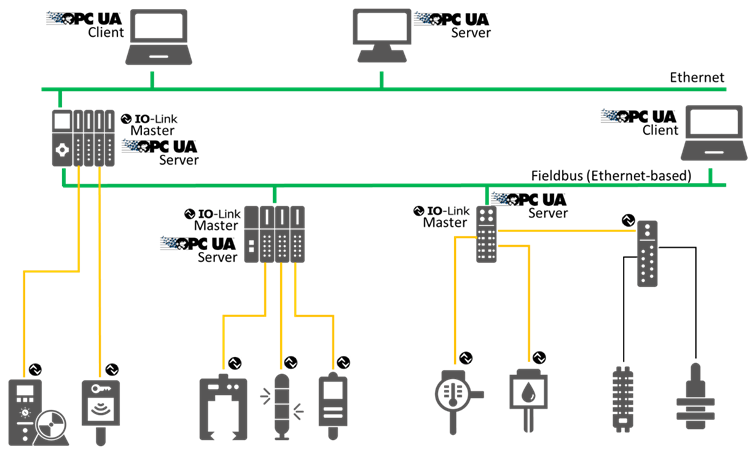
Figure 5 – System Architecture of IO-Link and OPC UA (Example)
The use cases that shall be fulfilled by this specification were defined by the IO-Link / OPC UA Integration Requirements Version 1.0.0 document. This section summarizes the use cases in scope.
Preparing the IO-Link Master for the respective application by adjusting its parameters. This use case is of relevance, if the IO-Link Master is not connected to a fieldbus and a PLC.
The user would like to know which IO-Link Masters are used in the plant/machine. He would like to find IO-Link Masters of all types and vendors in the same way using his SW-Tool. No vendor-specific implementation shall be needed.
To be able to parameterize the connected IO-Link Devices it must be possible to request the IO-Link Master to give the information about connected devices to each of its ports.
The user wants to parameterize the IO-Link Device for its application.
Add metadata to identify the role and position of a device in the machine or process. If the IO-Link Device does not support the IO-Link Common Profile with Application Specific Tag, Function Tag and Location Tag, these parameters shall be virtually provided in the OPC UA Server.
Setup data subscriptions to master or device variables and events to be able to:
- Calculate operation KPIs (e.g. OEE)
- Generate SPC (statistical process control) charts
- Measure process data for process optimization
The user (OPC UA Client) gets informed that a certain subscription is not available anymore, i.e. due to a disconnected IO-Link Device, to identify reasons for gaps in logs.
The user of an OPC UA Client can uniquely identify all connected IO-Link Masters by their serial number information and devices by vendor and device ID to recognize the status of the devices and facilitate the exchange. For each IO-Link Device and the IO-Link Master, the following data are provided for reading only:
- IO-Link DeviceType Version (mandatory)
- IO-Link Protocol Version (mandatory)
- Vendor Name (mandatory)
- Product Name (mandatory)
- Product ID (mandatory)
- Serial Number (mandatory)
- Hardware Revision (optional)
- Software Revision (optional)
- Vendor Text (optional)
- Product Text (optional)
- Application Specific Tag (mandatory – see UC.005)
- Function Tag (optional)
- Location Tag (optional)
- Implicit topology information (address of IO-Link Master and port number, where the IO-Link Device is connected to)
User shall have access to logged diagnosis events. General and specific access to diagnostic data after authorization. OPC UA Client may collect event information sent to him in a logging buffer. If the IO-Link Master provides event logging, this information should be accessible via OPC UA.
The maintenance staff would like to use the productivity of used devices to determine the characteristics of the device during the period of use and the number of failures to obtain a statement about plant availability.
The maintenance staffs receive data on the operating time and the failure times of the connected devices.
The data are generated in the IO-Link Master and updated on the OPC UA Server.
The IO-Link Master records for each connected IO-Link Device
- the duration the device is connected
- the duration the device has communicated without error
- the duration the device was not communicable
- how often the device has been plugged in
- how often the device has been changed
- how often the device was not accessible
The master cyclically updates the data on the OPC UA Server and stores it persistently.
- The data has a resolution in seconds.
- The duration refers to the time of the last reset (usually during commissioning).
The maintenance staff can reset the operating and failure statistics.
A machine in production needs to be optimized. This can be done by changing parameters of IO-Link Devices (e.g. limit values).
The operator staff would like to get immediately informed by the machine regarding process productivity and plant availability. In case of degradation, the possible location or source of problem shall also be reported.
Every plant subsystem with OPC UA Server connectivity sends an event if a critical condition has been detected or a configured threshold has been reached. The subsystem can also contain IO-Link Master and Devices, where IO-Link Events are translated into OPC UA events. The reported events from these subsystems shall consist of:
- the origin identity of the event
- the unambiguous identity of the event
- the absolute time of occurrence according to the subsystems time base
- if the occurrence is temporal, the duration of the erroneous condition
- if possible, the identity of the processed item
On the application level, the following is derived on this raw data:
- an availability signal in traffic light encoding
- notification towards the operator staff
The user would like to replace an IO-Link Master or IO-Link Device with transfer of the previous configuration to the new device.
Update device firmware individually and in groups of identical devices for IO-Link Masters and IO-Link Devices.
Note: Due to ongoing work in the OPC UA for Devices working group to standardize the firmware update, this version of the specification intentionally does not address the firmware update.
Manage all the assets in an automation network.
Maintenance staff is called to adjust one or more settings.
For Industry 4.0 application, an OPC UA Server will be the virtual interface between the cloud and the sensors in the field.
Therefore, the OPC UA Server has to apply the following functions:
- Find all IO-Link Masters
- Find IO-Link Devices
- Download IODD of connected devices
- Build up information model
- Record all replacement of connected devices and update information model
- Capture the status of connected devices
- Read cyclic IO data
- Read ISDU parameter sets
The Edge Gateway must find IO-Link Masters of all types and vendors in the same way. No vendor-specific implementation shall be necessary.