CreateSession and ActivateSession are used to establish Sessions based on the UserIdentity.
CreateSession and ActivateSession can be supported by the following TrustAnchor capabilities:
- Computation of asymmetric cryptographic operations using private keys. Long-term private keys, i.e., private keys corresponding to an application certificate, can effectively be protected by TrustAnchor capabilities. CreateSession and ActivateSession use these keys to authenticate the identity of the client resp. server identity.
- Protecting the UserIdentityToken (RSA only)
Note that authentication of the actual user using X.509 credentials is not in scope of this document. X.509 user credentials are supposed to be user specific and will typically not be persisted on the device.
The interactions between Client and GTA API in the sequence shown in Figure 22 for CreateSession and ActivateSession are similar to the process to establish a secure channel shown in Figure 17. The two trust anchor functions used are gta_verify_data_detached() to validate the integrity seal on the TrustList and gta_authenticate_data_detached() to compute the authentication proof of the client.
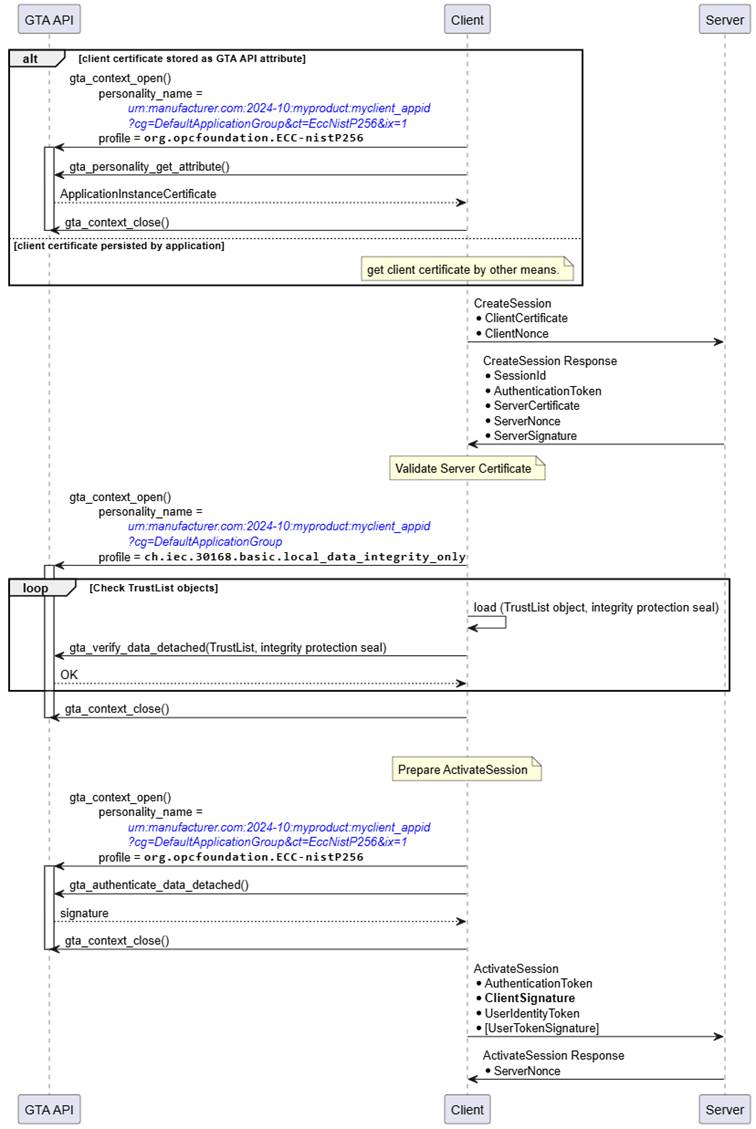
Figure 22 – CreateSession, ActivateSession (ECC, Client View)
Likewise, the interactions between Server and GTA API in the sequence shown in Figure 23 for CreateSession and ActivateSession are similar to the process to establish a secure channel shown in Figure 18. The two trust anchor functions used are gta_verify_data_detached() to validate the integrity seal on the TrustList and gta_authenticate_data_detached() to compute the authentication proof of the server.
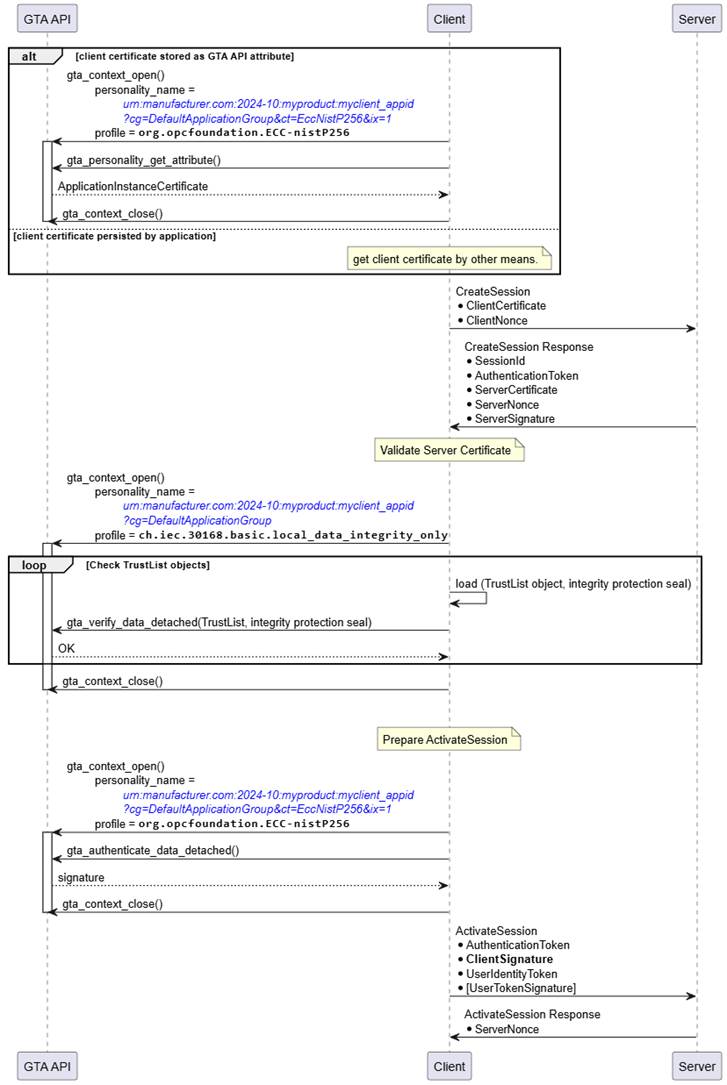
Figure 23 – CreateSession, ActivateSession (ECC, Server View)
Note that for ECC SecurityPolicies the protection of the UserIdentityToken is achieved using symmetric encryption with keys derived from the ECCDH handshake. Thus, the protection of the UserIdentityToken is done in software and does not require functionality provided by the trust anchor.
The interactions between Client and GTA API in the sequence shown in Figure 24 for CreateSession and ActivateSession are similar to the process to establish a SecureChannel shown in Figure 20. The two trust anchor functions used are gta_verify_data_detached() to validate the integrity seal on the TrustList and gta_authenticate_data_detached() to compute the authentication proof of the client.
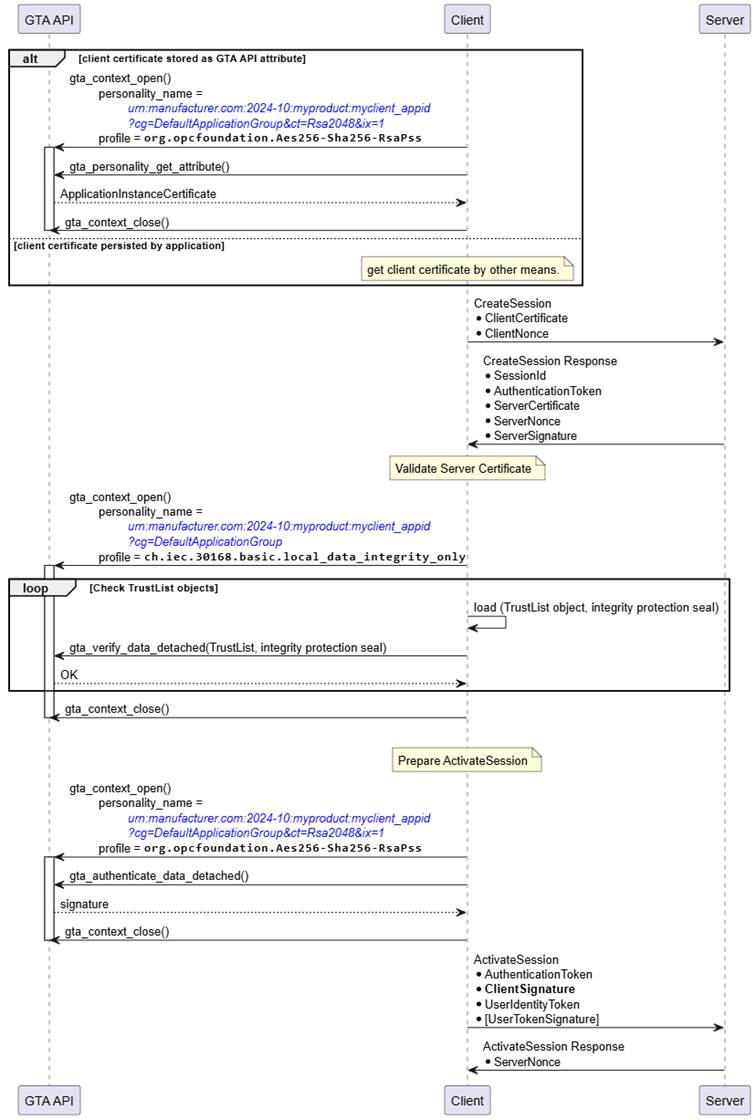
Figure 24 – CreateSession, ActivateSession (RSA, Client View)
Likewise, the interactions between Server and GTA API in the sequence shown in Figure 25 for CreateSession and ActivateSession are similar to the process to establish a secure channel shown in Figure 21. The three trust anchor functions used are gta_verify_data_detached() to validate the integrity seal on the TrustList, gta_authenticate_data_detached() to compute the authentication proof of the server, and (conditionally) gta_unseal_data() to decrypt the UserIdentityToken provided by the Client. The protection of the UserIdentityToken only applies for UserNameIdentityToken and IssuedIdentityToken.
In contrary to the ECC SecurityPolicy described in 5.6.1, with RSA SecurityPolicies, the client used the servers public RSA key to encrypt the UserIdentityToken. Therefore, the server needs to use its private key to decrypt the UserIdentityToken. The private key is protected by the trust anchor.
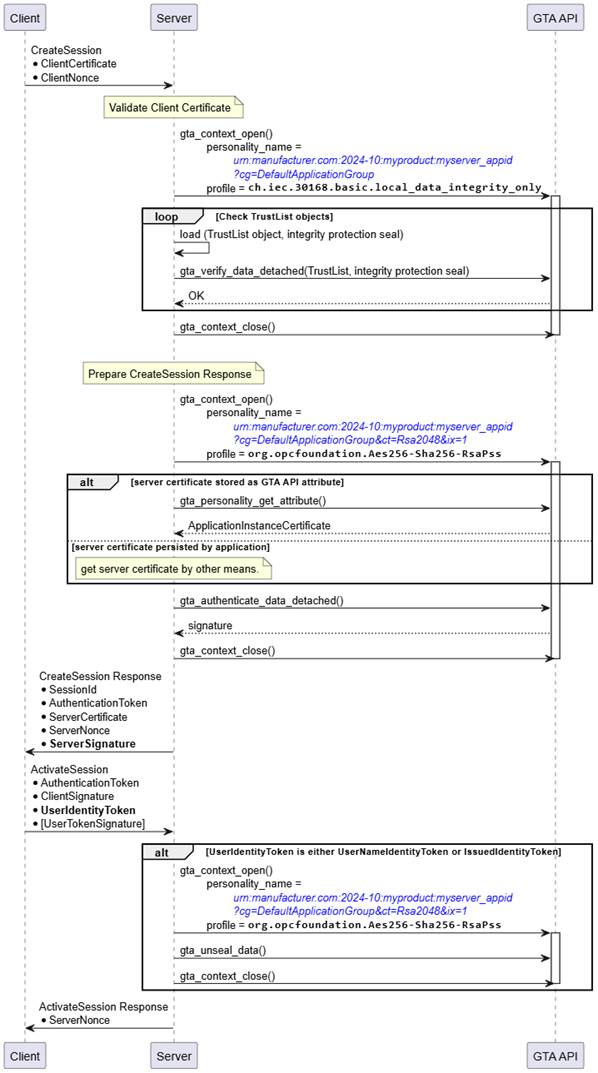
Figure 25 – CreateSession, ActivateSession (RSA, Server View)