The implicit use case means the Client’s Application Certificate and any UserIdentityToken associated with the Session is used to determine whether an AccessToken is permitted and what claims are available. This use case is illustrated in Figure 30.
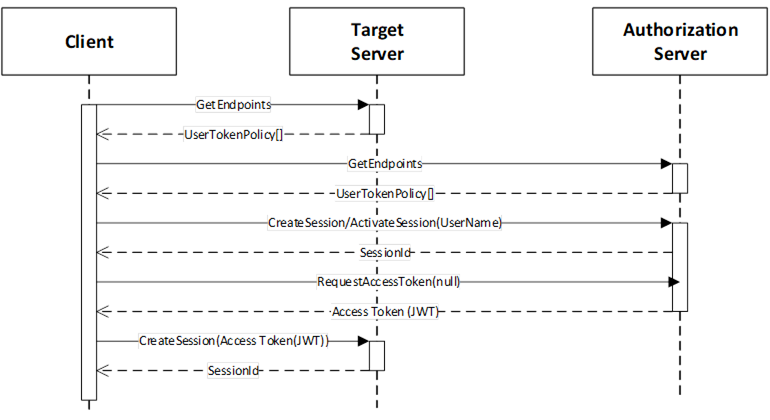
Figure 30 – Implicit Authorization
The Target Server is the Server that the Client wishes to access. It publishes a UserTokenPolicy that indicates that it accepts AccessTokens from an Authorization Server. The parameters needed to connect to the Authorization Server are stored in the IssuerEndpointUrl field of the UserTokenPolicy and are defined in OPC 10000-6. Note these parameters are specified as a JSON object rather than a URL as implied by the field name. The ua:tokenEndpoint field specifies the NodeId of the AuthorizationService Object encoded using the URI qualified syntax defined in OPC 10000-6. It is then is used to request the AccessToken.
The Client shall be trusted by the Authorization Server and this could require the Client to present user credentials. These credentials can be provided to the Client out-of-band (e.g. an administrator specified them in the Client configuration file). The user credentials used can be any type of user credential including X.509 and JWT.
The Session with the Authorization Server may be created explicitly with a call to CreateSession or it can be implicit via a Session-less Method Call. The DiscoveryUrl for the Server containing the AuthorizationService is a parameter in the UserTokenPolicy.
With this use case, the Client uses the EndpointDescriptions provided by the Authorization Server to determine what credentials to provide when creating a Session. The NodeId of the UserTokenPolicies Property is the ua:authorizationEndpoint field in the UserTokenPolicy provided by the Server (see OPC 10000-6). If this NodeId is null Implicit authorization is required.
After creating the Session, the Client calls the RequestAccessToken Method on the AuthorizationService Object. The NodeId of the AuthorizationService Object is the ua:tokenEndpoint in the UserTokenPolicy. The Authorization Server determines if the Client is permitted to receive an AccessToken and populates it with any claims granted to the Client. This claim may include Roles granted to the Session by applying the mapping rules for the Roles (see OPC 10000-3).
Once the Client has the AccessToken, it passes the AccessToken to the Target Server which validates the AccessToken, as described in OPC 10000-4. The Target Server is configured out-of-band with the Certificate used to validate the AccessTokens issued by the Authorization Server.