The SoftwareUpdateType defines an AddIn which can be used to extend Objects with software update features. All software update options are exposed as references of this AddIn. This way a Client can check for the references of the AddIn to determine which options are provided by a Server. If an option is available, it shall be used as specified.
The SoftwareUpdateType is illustrated in Figure 42 and formally described in Table 76.
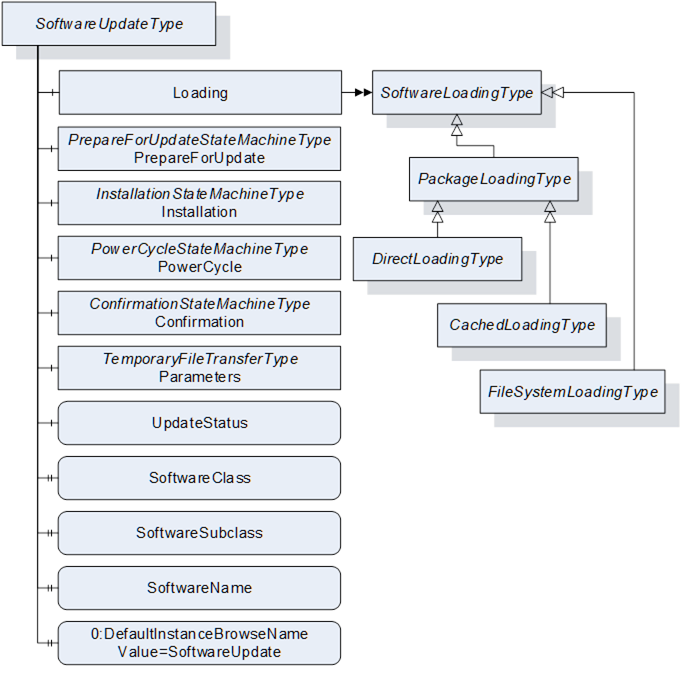
Figure 42 – SoftwareUpdateType
Table 76 – SoftwareUpdateType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:SoftwareUpdateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Loading |
|
1:SoftwareLoadingType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PrepareForUpdate |
|
1:PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Installation |
|
1:InstallationStateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PowerCycle |
|
1:PowerCycleStateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Confirmation |
|
1:ConfirmationStateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Parameters |
|
0:TemporaryFileTransferType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:UpdateStatus |
0:LocalizedText |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:SoftwareClass |
SoftwareClass |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:SoftwareSubclass |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:SoftwareName |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:UnsignedPackageAllowed |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:VendorErrorCode |
0:Int32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
0:QualifiedName |
0:PropertyType |
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
The optional Loading Object is of type SoftwareLoadingType, which is abstract. The Object can be one of the concrete sub-types DirectLoadingType (8.4.4), CachedLoadingType (8.4.5) or FileSystemLoadingType (8.4.6). SoftwareLoadingType is formally defined in 8.4.2.
The Loading Object is required for all variations of software installation, it is not required for read or restore of device parameters using the Parameters Object.
The optional PrepareForUpdate Object is of type PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType which is formally defined in 8.4.7.9.
This optional Installation Object is of type InstallationStateMachineType which is formally defined in 8.4.9.
This optional PowerCycle Object is of type PowerCycleStateMachineType which is formally defined in 8.4.10.
This optional Confirmation Object is of type ConfirmationStateMachineType which is formally defined in 8.4.11.
This optional Parameters Object is of type TemporaryFileTransferType (OPC 10000-5). It can be supported by devices that cannot retain parameters during update. If supported by the SoftwareUpdate AddIn a Client can read the parameters before the update and restore them after the update. This is not a general-purpose backup and restore function. It is intended to be used in the context of software update.
The GenerateFileForRead and GenerateFileForWrite Methods accept an unspecified generateOptions Parameter. This argument is not used, and Clients shall always pass null. Future versions of this specification can define concrete DataTypes.
If the restore of parameters succeeds but the software cannot run properly this should not be treated as an error of the restore. Instead, this should be indicated using the IDeviceHealthType Interface of the device / component.
This optional localized string provides status and error information for the update. This can be used whenever a long running update activity can provide detailed information to the user or when a state machine wants to provide error information to the user.
A Server can provide any text it wants to show to the operator of the software update. Important texts are the error messages in case anything went wrong, and the installation or preparation could not complete. These messages should explain what happened and how the operator could resolve the issue (e.g. “try again with a different version”). During preparation and installation, it is good practice to inform the operators about the current action to keep them patient and waiting for the completion. Also, if the installation gets stuck this text would help to find out the reason.
The UpdateStatus can be used together with the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType (8.4.7.9), the InstallationStateMachineType (8.4.9) and for CachedLoadingType (8.4.5), DirectLoadingType (8.4.4) and FileSystemLoadingType (8.4.6) it can be used during the transfer of the Software Package.
The optional SoftwareClass Property is used to distinguish device firmware from executable applications and from supporting configuration. A Software Update Client can use this information together with the SoftwareSubclass and the SoftwareName to identify the associated component (See 8.3.2).
The optional SoftwareSubclass Property can be used to further specialize the type of software (See 8.3.2).
If there can be more than one instance of a software, the optional SoftwareName Property can be used distinguish the individual instances (see 8.3.2).
This Property indicates whether the server accepts Software Packages that are not signed.
The optional VendorErrorCode Property provides a machine-readable error code in case anything went wrong during the transfer, the installation, or the preparation. Comparable to an error message in UpdateStatus this Variable can provide additional information about the issue. The VendorErrorCode is an additional information for a Client. It is not required for normal operation and error handling.
The value 0 shall be interpreted as no error.
The VendorErrorCode can be used together with the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType (8.4.7.9) for prepare and resume, in the InstallationStateMachineType (8.4.9) during the installation. For CachedLoadingType (8.4.5), DirectLoadingType (8.4.4) and FileSystemLoadingType (8.4.6) it can be used during the transfer of the Software Package.
The DefaultInstanceBrowseName Property – defined in OPC 10000-3 – is required for the AddIn model as specified in 8.3.11. It is used to specify the BrowseName of the instance of the SoftwareUpdateType. It always has the value “SoftwareUpdate”.
Table 77 – SoftwareUpdateType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
Source Path |
Value |
|
0:DefaultInstanceBrowseName |
SoftwareUpdate |
The SoftwareLoadingType is the abstract base for all different kinds of loading. The concrete information and behavior is modeled in its sub-types.
The SoftwareLoadingType is formally defined in Table 78.
Table 78 – SoftwareLoadingType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:SoftwareLoadingType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|||||
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
1:PackageLoadingType |
|
|
|
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
1:FileSystemLoadingType |
|
|
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:UpdateKey |
0:String |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
The optional write-only UpdateKey Object can be used if the underlying system requires some key to unlock the update feature. The format and where to get the key is vendor-specific and not described in this specification. If UpdateKey is supported, the Client shall set the key before the installation. If the PrepareForUpdateStateMachine is used, the UpdateKey shall be set before the Prepare Method is called. The Server shall not keep the value for more than one update.
The PackageLoadingType provides information about the Current Version and allows transfer of a Software Package to and from the Server.
The PackageLoadingType is illustrated in Figure 43 and formally defined in Table 79.
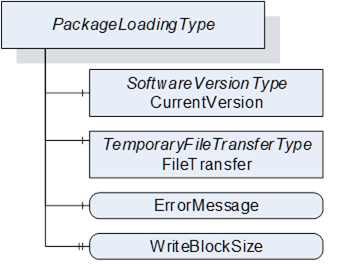
Figure 43 – PackageLoadingType
Table 79 – PackageLoadingType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:PackageLoadingType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the SoftwareLoadingType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:CurrentVersion |
|
1:SoftwareVersionType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:FileTransfer |
|
0:TemporaryFileTransferType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:ErrorMessage |
0:LocalizedText |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:WriteBlockSize |
0:UInt32 |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
1:DirectLoadingType |
|
|
|
|
0:HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
1:CachedLoadingType |
|
|
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
To identify the Current Version, the CurrentVersion Object provides ManufacturerUri, SoftwareRevision and PatchIdentifiers along with other information that allows the user to identify the currently used software. With this information the Client can determine a suitable update.
Note: This version information is about the installed software. The Manufacturer is not necessarily the same as the Manufacturer of the physical device that executes the software.
The FileTransfer Object is of type TemporaryFileTransferType as defined in OPC 10000-5. It is used to create temporary files for download and upload of the Software Package. See 8.7 for the definition of a standard packaging format.
In the TemporaryFileTransferType type the GenerateFileForRead and GenerateFileForWrite Methods take an unspecified generateOptions Parameter. For the FileTransfer Object an Enumeration of type SoftwareVersionFileType is used for this Parameter. It is used to select the file to upload or download. All allowed values are defined in Table 112. Additional Result Codes of the GenerateFileForRead and GenerateFileForWrite Methods are specified in Table 80.
Table 80 – TemporaryFileTransferType Result Codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
This result code is only used with DirectLoading.f the PrepareForUpdate is available, the UpdateBehavior requires preparation and the PrepareForUpdate state machine is not in the state PreparedForUpdate. |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If there is no file to read from the device. |
|
Bad_NotSupported |
If the device does not support to upload / download of the Software Package. |
For all errors that occur during the file transfer the ErrorMessage Variable should provide an error message for the user.
It is implementation dependent which version (see SoftwareVersionFileType in 8.5.1) is readable and which one is writable. Additional restrictions are defined in the concrete sub-types of PackageLoadingType.
The software is transferred as a single package. File type and content are device specific. If WriteBlockSize is supported, the Client shall write the file in chunks of this size.
The software should be validated during the transfer process. Errors shall be indicated either in the Write Method, the CloseAndCommit Method or an asynchronous completion of the file transfer. If the validation is performed synchronous, the Method returns Bad_InvalidArgument; if the validation is performed asynchronous, the error is indicated by the Error state of the FileTransferStateMachineType. If the ErrorMessage Variable is provided, it shall contain an error message representing the validation error.
The FileTransfer Object can optionally support the transfer of a Software Package from the device to the Client.
If this transfer is not supported, the Server shall return the Result Code Bad_NotSupported. If it is supported but there is currently no data, the Result Code Bad_NotFound shall be used instead.
This is a textual information about errors that can occur with the file transfer. Whenever a method of the TemporaryFileTransferType returns an error, the ErrorMessage Variable should provide a localized error message for the user. For every new file transfer the value should be reset to an empty string.
Optional size of the Blocks (number of bytes) that a Client shall write to the file. The client shall write the Software Package in chunks of this size to the FileType object (the last Block can be smaller).
The DirectLoadingType provides information about the Current Version and allows transfer of a Software Package to and from the Server. Transfer of the Software Package to the Server also includes the installation. The Direct-Loading option is described in 8.3.4.3.
The DirectLoadingType is illustrated in Figure 44 and formally defined in Table 81.
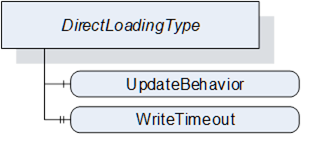
Table 81 – DirectLoadingType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:DirectLoadingType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 1:PackageLoadingType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:UpdateBehavior |
1:UpdateBehavior |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:WriteTimeout |
0:Duration |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU DirectLoading |
|||||
The FileTransfer Object is inherited from the PackageLoadingType. In this sub-type the Current version shall be writable (see SoftwareVersionFileType in 8.5.1). Writing to this file also includes the actual installation.
The UpdateBehavior OptionSet informs the update Client about the specific behavior of the component during update via Direct-Loading.
Optional Property that informs the Client about the maximum duration of the call to the Write Method of FileType (maximum time the write of a block of data can take). If the write operation takes longer the Client can assume that the Server has an issue.
The CachedLoadingType provides information about the Current Version, the Pending Version and the Fallback Version (if supported). Additionally, it allows upload and download of different versions of the software. The Cached-Loading option is described in 8.3.4.4.
The CachedLoadingType is illustrated in Figure 45 and formally defined in Table 82.
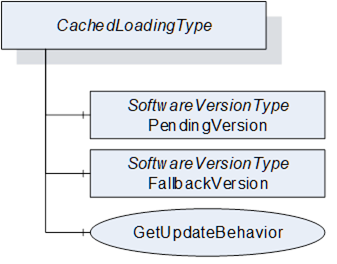
Table 82 – CachedLoadingType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:CachedLoadingType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 1:PackageLoadingType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PendingVersion |
|
1:SoftwareVersionType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:FallbackVersion |
|
1:SoftwareVersionType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:GetUpdateBehavior |
|
|
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU CachedLoading |
|||||
The FileTransfer Object is inherited from the PackageLoadingType. In this sub-type the Current version shall not be writable and the Pending version shall be writable (see SoftwareVersionFileType in 8.5.1).
The PendingVersion Object describes an already transferred new Software Package that is ready to be installed.
If there is no Software Package available, the values should be empty.
The optional FallbackVersion Object describes an alternate version on the device. This could be a factory default version or the version before the last update. Installing the Fallback Version can be used to revert to a reliable version of the software.
If a Fallback Version is supported by the device the object shall be available. If there is currently no Fallback Version on the device, the values should be empty.
With this Method the Client can check the specific update behavior for a specified software version. To identify the version the GetUpdateBehavior Method requires the ManufacturerUri, SoftwareRevision and PatchIdentifiers Properties of the SoftwareVersionType.
Signature
GetUpdateBehavior(
[in]0:String ManufacturerUri,
[in]0:String SoftwareRevision,
[in]0:String[] PatchIdentifiers,
[out]UpdateBehaviorUpdateBehavior);
Table 83 – GetUpdateBehavior Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
ManufacturerUri |
ManufacturerUri Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed. |
|
SoftwareRevision |
SoftwareRevision Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed. |
|
PatchIdentifiers |
PatchIdentifiers Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed. (or empty array if not supported by the SoftwareVersionType instance) |
|
UpdateBehavior |
Update behavior option set for the specified SoftwareVersionType instance |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If the Software Package, identified by the parameters, does not exist. |
Table 84 – GetUpdateBehavior Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:GetUpdateBehavior |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU CachedLoading |
|||||
The FileSystemLoadingType enables software update based on an open file system. This enables the FileSystem based Loading option of 8.3.4.5.
It is illustrated in Figure 46 and formally defined in Table 85.
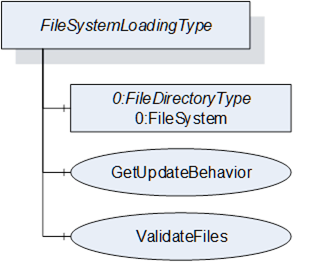
Figure 46 – FileSystemLoadingType
Table 85 – FileSystemLoadingType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:FileSystemLoadingType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the SoftwareLoadingType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
0:FileSystem |
|
0:FileDirectoryType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:GetUpdateBehavior |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:ValidateFiles |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU FileSystem Loading |
|||||
The FileSystem Object is of type FileDirectoryType as it is defined in OPC 10000-5. It provides access to a hierarchy of directories and files of the device. The structure can be read and written by the Client however the device can restrict this for specific folders or files.
This Method can be used to check the specific update behavior for a set of files. The files are identified by the NodeId of their FileType instance in the FileSystem.
Signature
GetUpdateBehavior(
[in] 0:NodeId[] NodeIds,
[out] UpdateBehaviorUpdateBehavior);
Table 86 – GetUpdateBehavior Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
NodeIds |
NodeIds of the files to install. |
|
UpdateBehavior |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If one or more NodeIds are not found. |
Table 87 – GetUpdateBehavior Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:GetUpdateBehavior |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU FileSystem Loading |
|||||
This Method can be used to check if the specified set of files are valid and complete for an installation. This should also include dependency checks if appropriate.
Note: In case of Direct-Loading or Cached-Loading these checks should be part of the transfer and this method shall not be supported since it is part of the file transfer (e.g., in CloseAndCommit).
Signature
ValidateFiles(
[in] 0:NodeId[] NodeIds,
[out] 0:Int32 ErrorCode,
[out] 0:LocalizedTextErrorMessage);
Table 88 – ValidateFiles Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
NodeIds |
NodeIds of the files to validate. |
|
ErrorCode |
0 for success or device specific number for validation issues. |
|
ErrorMessage |
Message for the user that describes how to resolve the issue. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If one or more NodeIds are not found. |
Table 89 – ValidateFiles Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:ValidateFiles |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU FileSystem Loading |
|||||
The SoftwareVersionType identifies a concrete version of a software. It is used by the CachedLoadingType (8.4.5) and the DirectLoadingType (8.4.4) to store the version information.
The Description Attribute on the instances of the SoftwareVersionType should be used to provide additional information about the concrete version of the software to the user (e.g., change notes).
The SoftwareVersionType is illustrated in Figure 47 and formally defined in Table 90.
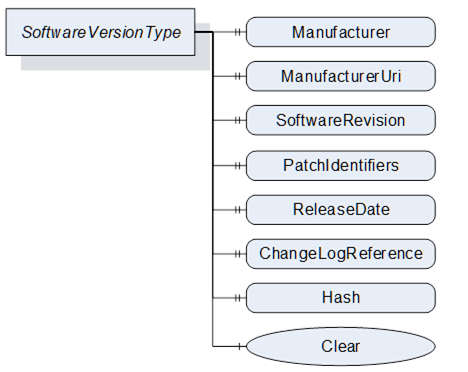
Figure 47 – SoftwareVersionType
Table 90 – SoftwareVersionType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:SoftwareVersionType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:Manufacturer |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:ManufacturerUri |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:SoftwareRevision |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:PatchIdentifiers |
0:String[] |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:ReleaseDate |
0:DateTime |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:ChangeLogReference |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:Hash |
0:ByteString |
0:PropertyType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Clear |
|
|
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
The read only Manufacturer Property provides the name of the company that created the software.
In case of the Pending Version this shall be empty if there is no pending software to install.
The read only ManufacturerUri Property provides a unique identifier for the manufacturer of the software.
In case of the Pending Version this shall be empty if there is no pending software to install.
The read only SoftwareRevision Property defines the version of the software. The format and semantics of the string is vendor-specific. SemanticVersionString (a sub-type of String defined in OPC 10000-5) can be used when using the Semantic Versioning format.
In case of the Pending Version this shall be empty if there is no pending software to install.
The read only PatchIdentifiers Property identifies the list of patches that are applied to a software version. The format and semantics of the strings are vendor-specific. The order of the strings shall not be relevant.
The read only ReleaseDate Property defines the date when the software is released. If the version information is about patches, this should be the date of the latest patch. It is additional information for the user.
The read only ChangeLogReference Property can optionally provide a URL to a web site with detailed information about the particular version of the software (change notes). In case of a patched software, the web site should also inform about the patches.
The optional read only Hash Property can be read by a Client to get the hash of a previously transferred Software Package. The hash value is calculated by the Server with the SHA-256 algorithm. It can be used to verify if the transferred package matches the one at the Client.
This optional Method can be used to delete the previously transferred software from the device. For Pending and Fallback Versions this often makes sense to free memory. For configuration objects it can be possible to clear the Current Version. This Method supports the use case in 8.2.2.1.
Signature
Clear();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
The version object is already cleared. |
The PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType can be used if the device requires to be prepared before the update. Another option is to delay the resuming of normal operation until all update actions are executed. This supports to prepare for update option of 8.3.4.2.
If a Server implements this state machine, a Client shall use it except if the UpdateBehavior indicates that this is not necessary for the transferred software. If preparation is required, the installation is only allowed if the PrepareForUpdateStateMachine is in the PreparedForUpdate state.
The state machine is illustrated in Figure 48, Figure 49 and formally defined in Table 91. The transitions are formally defined in Table 93.
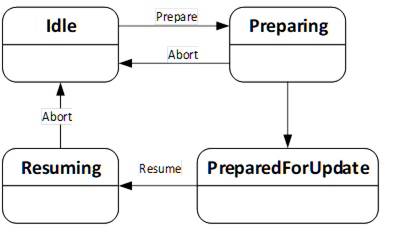
Figure 48 – PrepareForUpdate state machine
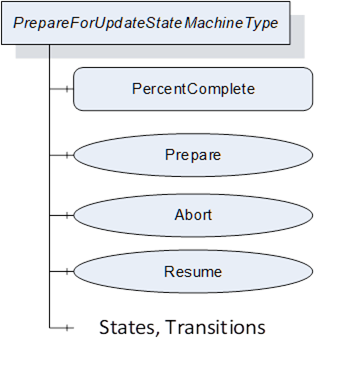
Figure 49 – PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType
Table 91 – PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:PercentComplete |
0:Byte |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Prepare |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Abort |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Resume |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Idle |
|
0:InitialStateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Preparing |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PreparedForUpdate |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Resuming |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:IdleToPreparing |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PreparingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PreparingToPreparedForUpdate |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:PreparedForUpdateToResuming |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:ResumingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU PrepareForUpdate |
|||||
The component Variables of the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 92.
Table 92 – 1:PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
12 |
||
|
21 |
||
|
23 |
||
|
34 |
||
|
41 |
Table 93 – 1:PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
|
|||
|
Transitions |
|||
|
1:IdleToPreparing |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Preparing |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Prepare |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:PreparingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Preparing |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Abort |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:PreparingToPreparedForUpdate |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Preparing |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:PreparedForUpdate |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:PreparedForUpdateToResuming |
0:FromState |
True |
1:PreparedForUpdate |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Resuming |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Resume |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:ResumingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Resuming |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Abort |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
This percentage is a number between 0 and 100 that informs about the progress in the Preparing or the Resuming States. It can be used whenever the activity takes longer and the user should be informed about the completion. If the state machine is in Idle or PreparedForUpdate State it shall have the value 0.
This information is for the user only. It shall not be used to detect completion of the transition.
The Prepare Method can be called to prepare a device for an update. This call transitions the device into the state Preparing.
After the preparation is complete the state machine can perform an automatic transition to the state PreparedForUpdate.
If the preparation cannot complete and the device does not get prepared for update the state machine transitions back to Idle. In this case a message with the reason should be provided to the user via the UpdateStatus.
Signature
Prepare();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType is not in Idle state. |
An update client can use the Abort Method to bring the state machine from Resuming or Preparing back to the Idle state. This can be necessary, if the preparation takes too long or does not complete at all because the required internal conditions are not met. This call transitions the device back to the Idle state.
Note: If the transition from Preparing to Idle cannot complete instantly a Client can subscribe for the events or the state variable of the PrepareForUpdateStateMachine.
Signature
Abort();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType is not in Preparing state. |
A call to the optional Resume Method transitions the device into the state Resuming. After the resuming is complete the state machine performs an automatic transition to the Idle state. If the method is not supported, the transitions to Resuming and back to Idle shall be done by the Server automatically. If the method is supported, there shall not be an automatic transition to Resuming. Supporting this method enables the Client to group several activities like backup, install, restore on a single device or group the update of multiple devices before the devices are allowed to Resume their operation again.
Signature
Resume();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the PrepareForUpdateStateMachineType is not in PreparedForUpdate state or if the InstallationStateMachine is still in the state Installing. |
The InstallationStateMachineType can be used if the device supports explicit installation (Cached-Loading or File System based Loading). This supports the installation option of 8.3.4.6. It is illustrated in Figure 50 and Figure 51 and formally defined in Table 94. The transitions are formally defined in Table 96.
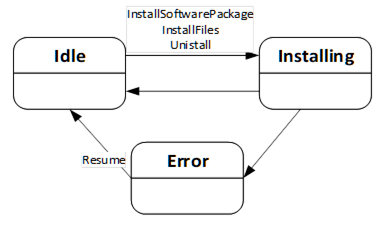
Figure 50 – Installation state machine
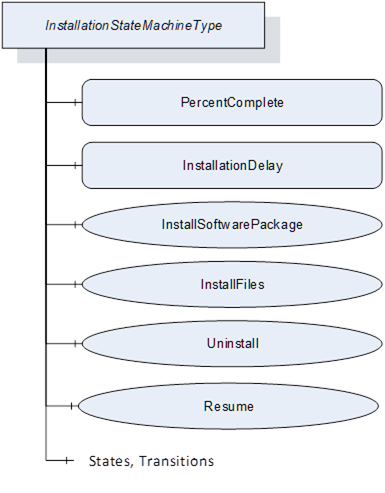
Figure 51 – InstallationStateMachine
Table 94 – InstallationStateMachineType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:InstallationStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:PercentComplete |
0:Byte |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:InstallationDelay |
0:Duration |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:InstallSoftwarePackage |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:InstallFiles |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Uninstall |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Resume |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Idle |
|
0:InitialStateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Installing |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:Error |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:IdleToInstalling |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:InstallingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:InstallingToError |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:ErrorToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
The component Variables of the InstallationStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 95.
Table 95 – 1:InstallationStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
12 |
||
|
21 |
||
|
23 |
||
|
31 |
Table 96 – 1:InstallationStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
|
|||
|
Transitions |
|||
|
1:IdleToInstalling |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Installing |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:InstallSoftwarePackage |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:InstallFiles |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Uninstall |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:InstallingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Installing |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:InstallingToError |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Installing |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Error |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:ErrorToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:Error |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:Idle |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Resume |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
This percentage is a number between 0 and 100 that informs the user about the progress of an installation or uninstallation. It should be used whenever an update activity takes longer and the user should be informed about the completion. If the state machine is in Idle State it shall have the value 0. In case of an error the last value should be kept until the Resume is called.
This information is for the user only. It shall not be used to detect completion of the installation.
The optional InstallationDelay can be set by a Client to delay the actual installation after the call to InstallSoftwarePackage or InstallFiles is returned by the Server. This can be used when the installation is started on several devices in parallel and there is a risk that a reboot of one device could harm the connection to other devices. With a delay the install methods can be called on all devices before the devices actually start the installation. The InstallationDelay does not delay the transition from Idle to Installing.
This value could be preconfigured. If a Client wants to set this value it has to be done before the install method is called.
The Server is expected to stay operational at least during the delay.
With this Method the Client requests the installation of a Software Package. The package can be either the previously transferred Pending Version or the alternative Fallback Version. To identify the version and to prevent conflicts with a second Client that transfers a different version, the InstallSoftwarePackage Method requires the ManufacturerUri, the SoftwareRevision and PatchIdentifiers Properties of the SoftwareVersionType.
Optionally an additional hash value can be passed to the Method. This hash could be calculated by the Client or taken from a trusted source. Before installation the Server can compare the hash against the calculated hash of the Software Package. This mechanism can be used if there is a risk that the Software Package is altered during the transfer to the device and if the Server has no other mechanism to ensure that the Software Package is from a trustworthy source.
If the installation succeeds but the software cannot run properly this should not be treated as an error of the installation. Instead, this should be indicated using the IDeviceHealthType Interface of the device / component.
This Method shall not return before the state has changed to the Installing state.
Signature
InstallSoftwarePackage(
[in] 0:String ManufacturerUri,
[in] 0:String SoftwareRevision,
[in] 0:String[] PatchIdentifiers,
[in] 0:ByteString Hash);
Table 97 – InstallSoftwarePackage Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
ManufacturerUri |
ManufacturerUri Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed. |
|
SoftwareRevision |
SoftwareRevision Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed. |
|
PatchIdentifiers |
PatchIdentifiers Property of either the Pending or Fallback SoftwareVersionType that should be installed (or empty array if not supported on the SoftwareVersionType instance). |
|
Hash |
Hash of the Software Package that should be installed (or empty if not used). |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the InstallationStateMachineType is not in Idle state or if the PrepareForUpdate Object is available and the PrepareForUpdate state machine is not in the state PreparedForUpdate. |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If the specified Software Package does not exist. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
If the Hash does not match the calculated hash of the Software Package. |
Table 98 – InstallSoftwarePackage Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:InstallSoftwarePackage |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
This Method can be called to request the installation of one or more files. The files are identified by the NodeId of their FileType instance in the FileSystem.
If the installation succeeds but the software cannot run properly this should not be treated as an error of the installation. Instead, this should be indicated using the IDeviceHealthType Interface of the device / component.
Signature
InstallFiles(
[in] 0:NodeId[] NodeIds);
Table 99 – InstallFiles Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
NodeIds |
NodeIds of the files to install. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the InstallationStateMachineType is not in Idle state or if the PrepareForUpdate Object is available and the PrepareForUpdate state machine is not in the state PreparedForUpdate. |
|
Bad_NotFound |
If one or more NodeIds are not found. |
Table 100 – InstallFiles Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:InstallFiles |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Software Update |
|||||
The Uninstall Method can be called to request the uninstallation of the current software. This can be necessary e.g. for a project when uncommissioning a device or before deleting an application or configuration from the device (see SoftwareFolderType in 8.4.12.2).
The signature and specific result codes of this Method are specified below.
Signature
Uninstall();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the InstallationStateMachineType is not in Idle state or if the PrepareForUpdate Object is available and the PrepareForUpdate state machine is not in the state PreparedForUpdate. |
This Method can be called to resume from the Error state. The Error state can be reached if there are issues during the installation. The state machine remains in this state until the Client calls the Resume Method to get back to the Idle state immediately.
Signature
Resume();
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the InstallationStateMachineType is not in Error state. |
The PowerCycleStateMachineType is used to inform the user to perform a manual power cycle.
When the server requires a manual power cycle it indicates that to the client by changing the state to WaitingForPowerCycle. After restart of the Device, it transitions to NotWaitingForPowerCycle automatically.
There are no methods, all transitions originate from the installation process. The state machine is illustrated in Figure 52 and formally defined in Table 101. The transitions are formally defined in Table 103.
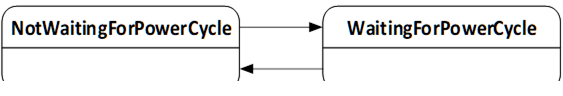
Figure 52 – PowerCycle state machine
Table 101 – PowerCycleStateMachineType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:PowerCycleStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:NotWaitingForPowerCycle |
|
0:InitialStateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:WaitingForPowerCycle |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:NotWaitingForPowerCycleToWaitingForPowerCycle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:WaitingForPowerCycleToNotWaitingForPowerCycle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Manual Power Cycle |
|||||
The component Variables of the PowerCycleStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 102.
Table 102 – 1:PowerCycleStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
12 |
||
|
21 |
Table 103 – 1:PowerCycleStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
|
|||
|
Transitions |
|||
|
1:NotWaitingForPowerCycleToWaitingForPowerCycle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:NotWaitingForPowerCycle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:WaitingForPowerCycle |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
1:WaitingForPowerCycleToNotWaitingForPowerCycle |
0:FromState |
True |
1:WaitingForPowerCycle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:NotWaitingForPowerCycle |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
The ConfirmationStateMachineType is used to prove a valid Client – Server connection after a restart of the OPC UA Server. This supports the confirmation option of 8.3.4.9.
If several instances of this state machine are provided on a device (due to several instances of the SoftwareUpdateType), all instances should behave as if it is only a single instance. In particular it is sufficient to call one of the confirm methods after reboot.
The ConfirmationStateMachineType is illustrated in Figure 53 and Figure 54 and formally defined in Table 104. The transitions are formally defined in Table 106.

Figure 53 – Confirmation state machine
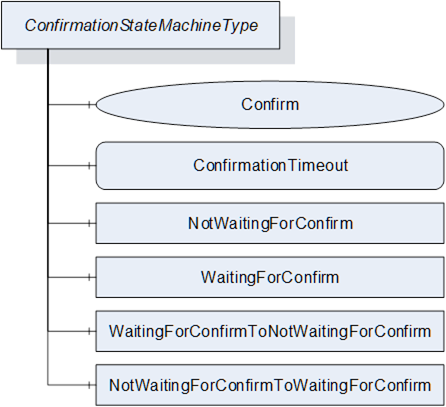
Figure 54 – ConfirmationStateMachineType
Table 104 – ConfirmationStateMachineType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:ConfirmationStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Confirm |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
1:ConfirmationTimeout |
0:Duration |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:NotWaitingForConfirm |
|
0:InitialStateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:WaitingForConfirm |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:NotWaitingForConfirmToWaitingForConfirm |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
1:WaitingForConfirmToNotWaitingForConfirm |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU Update Confirmation |
|||||
The component Variables of the ConfirmationStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 105.
Table 105 – 1:ConfirmationStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
12 |
||
|
21 |
Table 106 – 1:ConfirmationStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
|
|
||||
|
Transitions |
||||
|
1:NotWaitingForConfirmToWaitingForConfirm |
0:FromState |
True |
1:NotWaitingForConfirm |
|
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:WaitingForConfirm |
|
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
|
1:WaitingForConfirmToNotWaitingForConfirm |
0:FromState |
True |
1:WaitingForConfirm |
|
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
1:NotWaitingForConfirm |
|
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
1:Confirm |
|
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
0:TransitionEventType |
|
The ConfirmationTimeout can be set by a Client to a value other then 0 to enable the confirmation feature. If the value is not 0 and the Client – Server connection is lost, the ConfirmationTimeout represents the maximum time that the Client is required to reconnect and call the Confirm Method. The Server shall automatically reset the value to 0 when the installation is complete.
After a reboot and with a ConfirmationTimeout other than 0 a Client shall call this Method to inform the Server that it has successfully reconnected. If this Method is not called after a lost connection the Server shall regard the update as unsuccessful and shall revert it. A Client is required to react within the time specified in the ConfirmationTimeout Variable.
Signature
Confirm();
The SoftwareFolderType is a subtype of FolderType. It allows adding and removing its items via the Add and Delete methods. With the SoftwareClass Variable the server exposes whether the folder holds a collection of applications or a collection of configurations. The ObjectType of the items is server specific, but the items shall at least support the SoftwareUpdate AddIn. They are identified by SoftwareSubclass and SoftwareName which is provided with the Add Method. After adding a new item, the SoftwareUpdate AddIn is used to transfer the initial software. After that it can be used to install updates. The SoftwareUpdate AddIn of each item shall support SoftwareClass, SoftwareSubclass and SoftwareName. SoftwareFolderType is defined in Table 107 and its usage is illustrated in Figure 55.
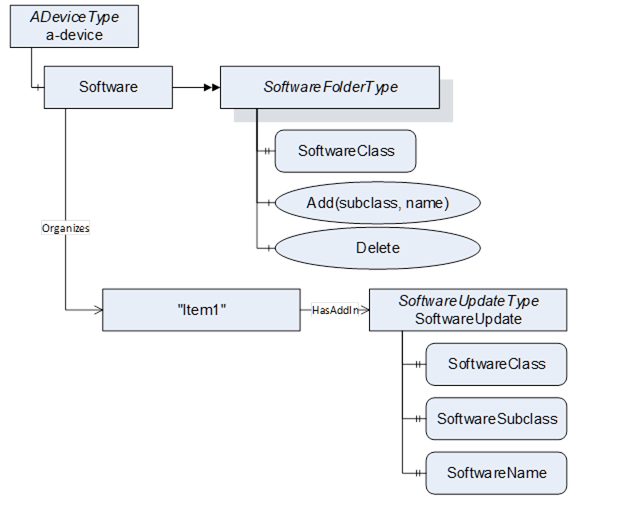
Figure 55 – Example use of SoftwareFolderType
Table 107 – SoftwareFolderType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:SoftwareFolderType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
1:SoftwareClass |
1:SoftwareClass |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Add |
|
|
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
1:Delete |
|
|
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU SoftwareFolder |
|||||
The SoftwareClass Property is a SoftwareClass enumeration. It declares what items are managed by the folder. The value shall either be Application or Configuration.
The Add Method can be used to add a new item to the folder. The parameters Subclass and Name are exposed at the attached SoftwareUpdate AddIn as SoftwareSubclass and SoftwareName Properties. The Name shall be unique within the SoftwareFolderType.
Signature
Add(
[in] 0:String Subclass,
[in] 0:String Name);
Table 108 – Add Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Subclass |
Subclass of the new item. |
|
Name |
Name of the new item. |
Table 109 – Delete Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:Add |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU SoftwareFolder |
|||||
The Delete Method can be used to delete an item from the folder. The Delete can require a call to Uninstall at the InstallationStateMachine (see 8.4.9).
Signature
Delete(
[in] 0:NodeId ObjectToDelete);
Table 110 – Delete Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
ObjectToDelete |
NodeId of the item to delete. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The specified item does not exist. |
|
Bad_InvalidState |
If the item shall be uninstalled before deletion. (see InstallationStateMachineType 8.4.9). |
Table 111 – Delete Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
1:Delete |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
DI SU SoftwareFolder |
|||||