The Condition model extends the Event model by defining the ConditionType. The ConditionType introduces the concept of states differentiating it from the base Event model. Unlike the BaseEventType, Conditions are not transient. The ConditionType is further extended into Dialog and AcknowledgeableConditionType, each of which has their own sub-types.
The Condition model is illustrated in Figure 10 and formally defined in the subsequent tables. It is worth noting that this figure, like all figures in this document, is not intended to be complete. Rather, the figures only illustrate information provided by the formal definitions.
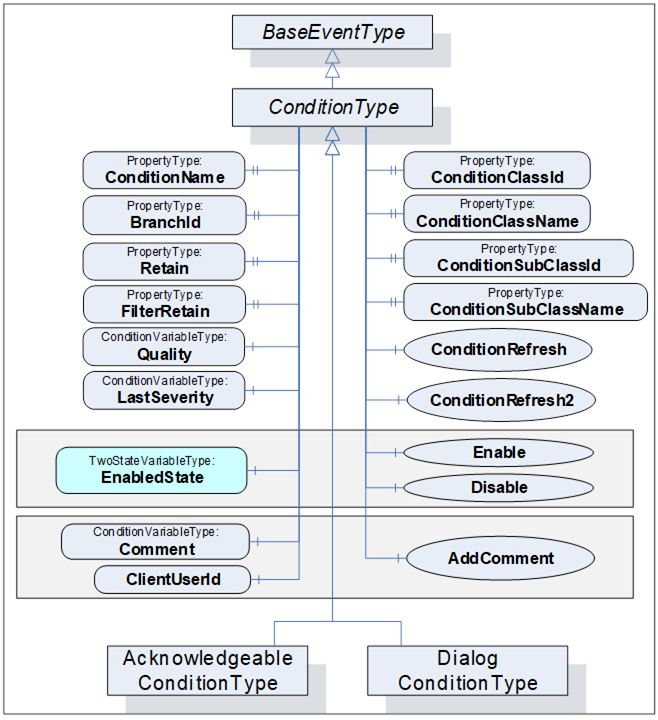
The ConditionType defines all general characteristics of a Condition. All other ConditionTypes derive from it. It is formally defined in Table 10 and Table 11. The False state of the EnabledState shall not be extended with a sub state machine.
Table 10 – ConditionType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ConditionType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
Subtype of the BaseEventType defined in 10000-5 |
|||||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
DialogConditionType |
Defined in Clause 5.6.2 |
||
|
HasSubtype |
ObjectType |
AcknowledgeableConditionType |
Defined in Clause 5.7.2 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ConditionClassId |
NodeId |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ConditionClassName |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ConditionName |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
BranchId |
NodeId |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
Retain |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
SupportsFilteredRetain |
Boolean |
PropertyType |
|
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
EnabledState |
LocalizedText |
TwoStateVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Quality |
StatusCode |
ConditionVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
LastSeverity |
UInt16 |
ConditionVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
Comment |
LocalizedText |
ConditionVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
ClientUserId |
String |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Disable |
Defined in Clause 5.5.4 |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Enable |
Defined in Clause 5.5.5 |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
AddComment |
Defined in Clause 5.5.6 |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
ConditionRefresh |
Defined in Clause 5.5.7 |
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
ConditionRefresh2 |
Defined in Clause 5.5.8 |
|
|
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Basic |
|||||
Table 11 – ConditionType Additional Subcomponents
|
BrowsePath |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
EnabledState |
HasProperty |
Variable |
TrueState |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
|
|
EnabledState |
HasProperty |
Variable |
FalseState |
LocalizedText |
PropertyType |
|
The empty “Others” column indicates that no ModellingRule applies.
The ConditionType inherits all Properties of the BaseEventType. Their semantic is defined in 10000-5. SourceNode Property identifies the ConditionSource. See 5.12 for more details. If the ConditionSource is not a Node in the AddressSpace, the NodeId is set to NULL. The SourceNode Property is the Node, which the Condition is associated with, it may be the same as the InputNode for an Alarm, but it may be a separate node. For example, a motor, which is a Variable with a Value that is an RPM, may be the ConditionSource for Conditions that are related to the motor as well as a temperature sensor associated with the motor. In the former the InputNode for the High RPM Alarm is the value of the Motor RPM, while in the later the InputNode of the High Alarm would be the value of the temperature sensor that is associated with the motor.
ConditionClassId, ConditionClassName, ConditionSubClassId and ConditionSubClassName originally defined in ConditionType are now defined in the BaseEventType (from which this type is derived). They are optional in the BaseEventType, but ConditionClassId, and ConditionClassName are Mandatory in ConditionType and thus listed(to update the modelling rule).
ConditionName identifies the Condition instance that the Event originated from. It can be used together with the SourceName in a user display to distinguish between different Condition instances. If a ConditionSource has only one instance of a ConditionType, and the Server has no instance name, the Server shall supply the name element of the BrowseName of the ConditionType.
BranchId is NULL for all Event Notifications that relate to the current state of the Condition instance. If BranchId is not NULL, it identifies a previous state of this Condition instance that still needs attention by an Operator. If the current ConditionBranch is transformed into a previous ConditionBranch then the Server needs to assign a non-NULL BranchId. An initial Event for the branch will generated with the values of the ConditionBranch and the new BranchId. The ConditionBranch can be updated many times before it is no longer needed. When the ConditionBranch no longer requires Operator input the final Event will have Retain set to False. The retain bit on the current Event is True, as long as any ConditionBranches require Operator input. See 4.2 for more information about the need for creating and maintaining previous ConditionBranches and Clause B.1 for an example using branches. The BranchId DataType is NodeId although the Server is not required to have ConditionBranches in the AddressSpace. The use of a NodeId allows the Server to use simple numeric identifiers, strings or arrays of bytes.
Retain when True describes a Condition (or ConditionBranch) as being in a state that is interesting for a Client wishing to synchronize its state with the Server’s state. The logic to determine how this flag is set is Server specific. Typically, all Active Alarms would have the Retain flag set; however, it is also possible for inactive Alarms to have their Retain flag set to True.
In normal processing when a Client receives an Event with the Retain flag set to False, the Client should consider this as a ConditionBranch that is no longer of interest, in the case of a “current Alarm display” the ConditionBranch would be removed from the display.
SupportsFilteredRetain Property is only provided on the ConditionType. When this Property is set to True on the Type, then the Server provides a Client specific Retain flag value taking into account any Client provided filter. When the property is False on the ConditionType then the Server does not provide a Client specific the value of the Retain flag. For example, if a Client applies a filter to exclude Alarms that are shelved, and the SupportsFilteredRetain is set to True, the Client receives an Alarm (it is not shelved, Retain is true). The Client (or another Client) shelves the Alarm. At this point the Alarm no longer passes the filter, but since the previous event was sent, this event is transmitted with Retain = False. For an example see B.1.4
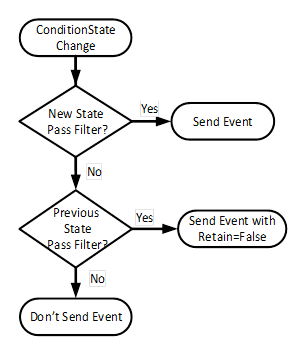
Figure 11 - SupportsFilteredRetain process
Figure 11 provides an illustration of the processing a Server shall follow for processing Retain flag when SupportsFilteredRetain flag is set to True.
EnabledState indicates whether the Condition is enabled. EnabledState/Id is True if enabled, False otherwise. EnabledState/TransitionTime defines when the EnabledState last changed. Recommended state names are described in A.1.
A Condition’s EnabledState effects the generation of Event Notifications and as such results in the following specific behaviour:
- When the Condition instance enters the Disabled state, the Retain Property of this Condition shall be set to False by the Server to indicate to the Client that the Condition instance is currently not of interest to Clients. This includes all ConditionBranches if any branches exist.
- When the Condition instance enters the enabled state, the Condition shall be evaluated and all of its Properties updated to reflect the current values. If this evaluation causes the Retain Property to transition to True for any ConditionBranch, then an Event Notification shall be generated for that ConditionBranch.
- The Server may choose to continue to test for a Condition instance while it is Disable d. However, no Event Notifications will be generated while the Condition instance is disabled.
- For any Condition that exists in the AddressSpace the Attributes and the following Variables will continue to have valid values even in the Disable d state; EventId, Event Type, Source Node, Source Name, Time, and EnabledState. Other Properties may no longer provide current valid values. All Variables that are no longer provided shall return a status of Bad_ConditionDisabled. The Event that reports the Disabled state should report the Properties as NULL or with a status of Bad_ConditionDisabled.
When enabled, changes to the following Variables shall cause a ConditionType Event Notification:
- Quality
- Severity (inherited from BaseEventType)
- Comment
This may not be the complete list. Subtypes of ConditionType may define additional Variables that trigger Event Notifications. In general, changes to Variables of the types TwoStateVariableType, ConditionVariableType, StateMachineType or any of their subtypes trigger Event Notifications and are not explicitly described in subtypes.
In the event of a restart of an AlarmManager, the AlarmManager shall recover the Enabled/Disabled states of all current conditions. If the system can not determine if the Condition is Enabled or Disabled, it shall be Enabled.
Quality reveals the status of process values or other resources that this Condition instance is based upon. If, for example, a process value is “Uncertain”, the associated “LevelAlarm” Condition is also questionable. Values for the Quality can be any of the OPC StatusCodes defined in 10000-8 as well as Good, Uncertain and Bad as defined in 10000-4. These StatusCodes are similar to but slightly more generic than the description of data quality in the various field bus specifications. It is the responsibility of the Server to map internal status information to these codes. A Server that supports no quality information shall return Good. This quality can also reflect the communication status associated with the system that this value or resource is based on and from which this Alarm was received. For communication errors to the underlying system, especially those that result in some unavailable Event fields, the quality shall be Bad_NoCommunication error.
Events are only generated for Conditions that have their Retain field set to True and for the initial transition of the Retain field from True to False.
LastSeverity provides the previous severity of the ConditionBranch. Initially this Variable contains a zero value; it will return a value only after a severity change. The new severity is supplied via the Severity Property, which is inherited from the BaseEventType.
Comment contains the last comment provided for a certain state (ConditionBranch) of a Condition. It may have been provided by an AddComment Method, some other Method or in some other manner. Any change in this field, shall trigger a new event to be generated. The initial value of this Variable is NULL, unless it is provided in some other manner.
ClientUserId is related to the Comment field and contains the identity of the user who inserted the most recent Comment. The logic to obtain the ClientUserId is defined in 10000-5.
The NodeId of the Condition instance is used as ConditionId. It is not explicitly modelled as a component of the ConditionType. However, it can be requested with the following SimpleAttributeOperand (see Table 12) in the SelectClause of the EventFilter: See 10000-4 for a detailed definition of the SelectClause in an Event Subscription.
Table 12 – ConditionId SimpleAttributeOperand Illustration
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
SimpleAttributeOperand |
|
|
|
typeId |
NodeId |
NodeId of the ConditionType Node |
|
browsePath[] |
QualifiedName |
empty |
|
attributeId |
IntegerId |
Id of the NodeId Attribute |
Conditions are Objects which have a state which changes over time. Each Condition instance has a ConditionId as an identifier which uniquely identifies it within the Server. This Condition (and it representative ConditionId) follows the same rules associated with Nodes (and their representative NodeIds) in the AddressSpace (see 10000-3). Therefore, once a Condition is created in a system that does not expose instances, any time that Condition is active it shall always have the same ConditionId. This allows higher level alarm management systems to operate on Conditions and to perform analysis of them.
A Condition instance may be an Object that appears in the Server Address Space. If this is the case the ConditionId shall be the NodeId for the Object.
The state of a Condition instance at any given time is the set values for the Variables that belong to the Condition instance. If one or more Variable values change the Server generates an Event with a unique EventId.
If a Client calls Refresh the Server will report the current state of a Condition instance by re-sending the last Event (i.e. the same EventId and Time is sent).
A ConditionBranch is a copy of the Condition instance state that can change independently of the current Condition instance state. Each Branch has an identifier called a BranchId which is unique among all active Branches for a Condition instance. Branches are typically not visible in the Address Space and this standard does not define a standard way to make them visible.
The Disable Method is used to change a Condition instance to the Disabled state. Normally, the NodeId of the object instance as the ObjectId is passed to the Call Service. However, some Servers do not expose Condition instances in the AddressSpace. Therefore, all Servers shall allow Clients to call the Disable Method by specifying ConditionId as the ObjectId. The Method cannot be called with an ObjectId of the ConditionType Node. Since Condition instances may not be defined in the AddressSpace, the MethodId that is passed in the Call Service shall be the NodeId of the Disable Method on the ConditionType.
Signature
Disable();
Method Result Codes in Table 13 (defined in Call Serv ice)
Table 13 – Disable result codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_ConditionAlreadyDisabled |
See Table 137 for the description of this result code. |
Table 14 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the Disable Method.
Table 14 – Disable Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Disable |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
AuditConditionEnableEventType |
Defined in 5.10.2 |
||
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Enable |
|||||
If Auditing is supported, this Method shall generate an Event of AuditConditionEnableEventType for all invocations of the Method.
The Enable Method is used to change a Condition instance to the enabled state. Normally, the NodeId of the object instance as the ObjectId is passed to the Call Service. However, some Servers do not expose Condition instances in the AddressSpace. Therefore, all Servers shall allow Clients to call the Enable Method by specifying ConditionId as the ObjectId. The Method cannot be called with an ObjectId of the ConditionType Node. If the Condition instance is not exposed, then it may be difficult for a Client to determine the ConditionId for a disabled Condition. Since Condition instances may not be defined in the AddressSpace, the MethodId that is passed in the Call Service shall be the NodeId of the Enable Method on the ConditionType.
Signature
Enable();
Method result codes in Table 15 (defined in Call Serv ice)
Table 15 – Enable result codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_ConditionAlreadyEnabled |
See Table 137 for the description of this result code. |
Table 16 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the Enable Method.
Table 16 – Enable Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Enable |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
AuditConditionEnableEventType |
Defined in 5.10.2 |
||
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Enable |
|||||
If Auditing is supported, this Method shall generate an Event of AuditConditionEnableEventType for all invocations of the Method.
The AddComment Method is used to apply a comment to a specific state of a Condition instance. Normally, the NodeId of the Object instance is passed as the ObjectId to the Call Service. However, some Servers do not expose Condition instances in the AddressSpace. Therefore, all Servers shall also allow Clients to call the AddComment Method by specifying ConditionId as the ObjectId. The Method cannot be called with an ObjectId of the ConditionType Node.
Signature
AddComment(
[in] ByteString EventId
[in] LocalizedText Comment
);
The parameters are defined in Table 17
Table 17 – AddComment arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
EventId |
EventId identifying a particular Event Notification where a state was reported for a Condition. |
|
Comment |
A localized text to be applied to the Condition. |
Method result codes in Table 18 (defined in Call Service)
Table 18 – AddComment result codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_MethodInvalid |
The MethodId provided does not correspond to the ObjectId provided. See 10000-4 for the general description of this result code. |
|
Bad_EventIdUnknown |
See Table 137 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_NodeIdInvalid |
Used to indicate that the specified ObjectId is not valid or that the Method was called on the ConditionType Node. See 10000-4 for the general description of this result code. |
Comments
Comments are added to Event occurrences identified via an EventId. EventIds where the related EventType is not a ConditionType (or subtype of it) and thus does not support Comments are rejected.
A ConditionEvent – where the Comment Variable contains this text – will be sent for the identified state. If a comment is added to a previous state (i.e. a state for which the Server has created a branch), the BranchId and all Condition values of this branch will be reported. If the comment field is NULL (both locale and text are empty) it will be ignored and any existing comments will remain unchanged. If the comment is to be reset, an empty text with a locale shall be provided.
Table 19 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the AddComment Method.
Table 19 – AddComment Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AddComment |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
AuditConditionCommentEventType |
Defined in 5.10.4 |
||
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Comment |
|||||
If Auditing is supported, this Method shall generate an Event of AuditConditionCommentEventType for all invocations of the Method.
ConditionRefresh allows a Client to request a Refresh of all Condition instances that currently are in an interesting state (they have the Retain flag set). This includes previous states of a Condition instance for which the Server maintains Branches. A Client would typically invoke this Method when it initially connects to a Server and following any situations, such as communication disruptions, in which it would require resynchronization with the Server. This Method is only available on the ConditionType. To invoke this Method, the call shall pass the well-known MethodId of the Method on the ConditionType and the ObjectId shall be the well-known NodeId of the ConditionType ObjectType.
Signature
ConditionRefresh(
[in] IntegerId SubscriptionId
);
The parameters are defined in Table 20
Table 20 – ConditionRefresh parameters
|
Argument |
Description |
|
SubscriptionId |
A valid Subscription Id of the Subscription to be refreshed. The Server shall verify that the SubscriptionId provided is part of the Session that is invoking the Method. |
Method result codes in Table 21 (defined in Call Serv ice)
Table 21 – ConditionRefresh result codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See 10000-4 for the description of this result code |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
The ConditionRefresh Method was called on a SubscriptionId that has no event MonitoredItems. |
|
Bad_RefreshInProgress |
See Table 137 for the description of this result code |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The Method was not called in the context of the Session that owns the Subscription See 10000-4 for the general description of this result code. |
Comments
Sub clause 4.5 describes the concept, use cases and information flow in more detail.
The input argument provides a Subscription identifier indicating which Client Subscription shall be refreshed. If the Subscription is accepted the Server will react as follows:
- The Server issues an event of RefreshStartEventType (defined in 5.11.2) marking the start of Refresh. A copy of the instance of RefreshStartEventType is queued into the Event stream for every Notifier MonitoredItem in the Subscription. Each of the Event copies shall contain the same EventId.
- The Server issues Event Notifications of any Retained Conditions and Retained Branches of Conditions that meet the Subscriptions content filter criteria. Note that the EventId for such a refreshed Notification shall be identical to the one for the original Notification, the values of the other Properties are Server specific, in that some Servers may be able to replay the exact Events with all Properties/Variables maintaining the same values as originally sent, but other Servers might only be able to regenerate the Event. The regenerated Event might contain some updated Property/Variable values. For example, if the Alarm limits associated with a Variable were changed after the generation of the Event without generating a change in the Alarm state, the new limit might be reported. In another example, if the HighLimit was 100 and the Variable is 120. If the limit were changed to 90 no new Event would be generated since no change to the StateMachine, but the limit on a Refresh would indicate 90, when the original Event had indicated 100.
- The Server may intersperse new Event Notifications that have not been previously issued to the Notifier along with those being sent as part of the Refresh request. Clients shall check for multiple Event Notifications for a ConditionBranch to avoid overwriting a new state delivered together with an older state from the Refresh process.
- The Server issues an instance of RefreshEndEventType (defined in 5.11.3) to signal the end of the Refresh. A copy of the instance of RefreshEndEventType is queued into the Event stream for every Notifier MonitoredItem in the Subscription. Each of the Events copies shall contain the same EventId.
It is important to note that if multiple Event Notifiers are in a Subscription all Event Notifiers are processed. If a Client does not want all MonitoredItems refreshed, then the Client should place each MonitoredItem in a separate Subscription or call ConditionRefresh2 if the Server supports it.
If more than one Subscription is to be refreshed, then the standard call Service array processing can be used.
As mentioned above, ConditionRefresh shall also issue Event Notifications for prior states if they still need attention. In particular, this is True for Condition instances where previous states still need acknowledgement or confirmation.
Table 22 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ConditionRefresh Method.
Table 22 – ConditionRefresh Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ConditionRefresh |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
RefreshStartEventType |
Defined in 5.11.2 |
||
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
RefreshEndEventType |
Defined in 5.11.3 |
||
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Refresh |
|||||
ConditionRefresh2 allows a Client to request a Refresh of all Condition instances that currently are in an interesting state (they have the Retain flag set) that are associated with the given Monitored item. In all other respects it functions as ConditionRefresh. A Client would typically invoke this Method when it initially connects to a Server and following any situations, such as communication disruptions where only a single MonitoredItem is to be resynchronized with the Server. This Method is only available on the ConditionType. To invoke this Method, the call shall pass the well-known MethodId of the Method on the ConditionType and the ObjectId shall be the well-known NodeId of the ConditionType ObjectType.
This Method is optional and as such Clients must be prepared to handle Servers which do not provide the Method. If the Method returns Bad_MethodInvalid, the Client shall revert to ConditionRefresh.
Signature
ConditionRefresh2(
[in] IntegerId SubscriptionId
[in] IntegerId MonitoredItemId
);
The parameters are defined in Table 23
Table 23 – ConditionRefresh2 parameters
|
Argument |
Description |
|
SubscriptionId |
The identifier of the Subscription containing the MonitoredItem to be refreshed. The Server shall verify that the SubscriptionId provided is part of the Session that is invoking the Method. |
|
MonitoredItemId |
The identifier of the MonitoredItem to be refreshed. The MonitoredItemId shall be in the provided Subscription. |
Method result codes in Table 24(defined in Call Serv ice)
Table 24 – ConditionRefresh2 result codes
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See 10000-4 for the description of this result code |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See 10000-4 for the description of this result code |
|
Bad_RefreshInProgress |
See Table 137 for the description of this result code |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The Method was not called in the context of the Session that owns the Subscription See 10000-4 for the general description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MethodInvalid |
See 10000-4 for the description of this result code |
Comments
Sub clause 4.5 describes the concept, use cases and information flow in more detail.
The input argument provides a Subscription identifier and MonitoredItem identifier indicating which MonitoredItem in the selected Client Subscription shall be refreshed. If the Subscription and MonitoredItem is accepted the Server will react as follows:
- The Server issues a RefreshStartEvent (defined in 5.11.2) marking the start of Refresh. The RefreshStartEvent is queued into the Event stream for the Notifier MonitoredItem in the Subscription.
- The Server issues Event Notifications of any Retained Conditions and Retained Branches of Conditions that meet the Subscriptions content filter criteria. Note that the EventId for such a refreshed Notification shall be identical to the one for the original Notification, the values of the other Properties are Server specific, in that some Servers may be able to replay the exact Events with all Properties/Variables maintaining the same values as originally sent, but other Servers might only be able to regenerate the Event. The regenerated Event might contain some updated Property/Variable values. For example, if the Alarm limits associated with a Variable were changed after the generation of the Event without generating a change in the Alarm state, the new limit might be reported. In another example, if the HighLimit was 100 and the Variable is 120. If the limit were changed to 90 no new Event would be generated since no change to the StateMachine, but the limit on a Refresh would indicate 90, when the original Event had indicated 100.
- The Server may intersperse new Event Notifications that have not been previously issued to the notifier along with those being sent as part of the Refresh request. Clients shall check for multiple Event Notifications for a ConditionBranch to avoid overwriting a new state delivered together with an older state from the Refresh process.
- The Server issues a RefreshEndEvent (defined in 5.11.3) to signal the end of the Refresh. The RefreshEndEvent is queued into the Event stream for the Notifier MonitoredItem in the Subscription.
If more than one MonitoredItem or Subscription is to be refreshed, then the standard call Service array processing can be used.
As mentioned above, ConditionRefresh2 shall also issue Event Notifications for prior states if those states still need attention. In particular, this is True for Condition instances where previous states still need acknowledgement or confirmation.
Table 25 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the ConditionRefresh2 Method.
Table 25 – ConditionRefresh2 Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
ConditionRefresh2 |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
RefreshStartEventType |
Defined in 5.11.2 |
||
|
AlwaysGeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
RefreshEndEventType |
Defined in 5.11.3 |
||
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
A & C Refresh2 |
|||||