The AlternativeUnitType describes alternative units to a ServerUnit. It is required to specify a conversion method for a value from the ServerUnit to this AlternativeUnit. It is formally defined in Table 42.
The use of conversions enables that a server and a client can work with different units and even in different systems of units. E.g. a server works with imperial units and a client uses metric units.
As a single server can distribute values to a number of clients with different needs the actual conversion has to be performed at client side.
Table 42 – AlternativeUnitType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
AlternativeUnitType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the UnitType |
|||||
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
LinearConversion |
LinearConversionDataType |
PropertyType |
O |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
MathMLConversion |
String |
PropertyType |
O |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
MathMLInverseConversion |
String |
PropertyType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Data Access Alternative Units |
|||||
The Server shall provide either a LinearConversion or a MathMLConversion together with a corresponding MathMLInverseConversion. It can provide Linear and MathML conversions in parallel.
The optional Property LinearConversion represents a simple conversion according to the following formula. The values (a, b, c, d) are given in a Structure as defined in the LinearConversionDataType in chapter 6.6.2. The value x is published by the Server in the named server unit and y is the value converted into the named alternative unit.
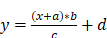
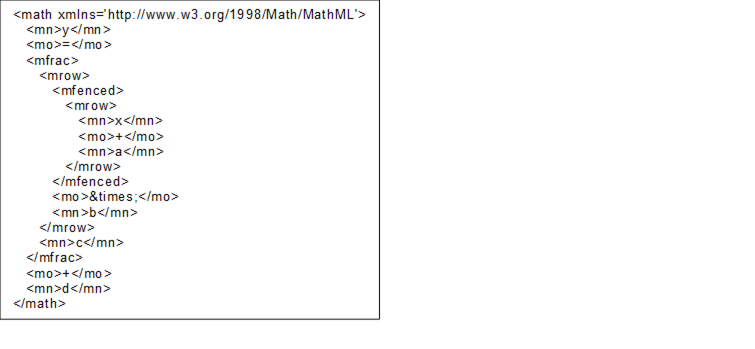
Figure 10 – MathML example linear conversion
This also defines the inverse conversion to be used if a Client wants to write a value to the Server. The values (a, b, c, d) are given in a Structure as defined in the LinearConversionDataType in chapter 6.6.2. The value y1 is the value that the Client wants to write to the Server in the named alternative unit and x1 is the value the Client actually has to write to the Server instead
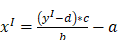

Figure 11 – MathML example inverse linear conversion
The optional Property MathMLConversion allows the specification of all kinds of conversion methods. The MathML syntax is used for this. Within the MathML expression X always stands for the value at the server side and Y for the value at the client side. An example (formula of the LinearConversion) looks as follows.