The Units model describes the relations between UnitType, ServerUnitType and AlternativeUnitType.
The UnitType is the base class and defines details that are relevant of all derived types.
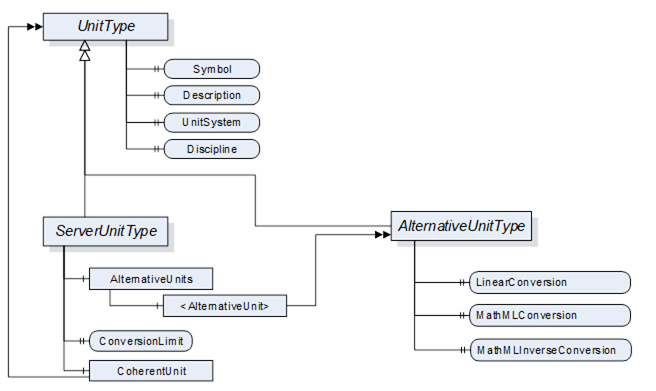
The Units model describes the relations between UnitType, ServerUnitType and AlternativeUnitType.
The UnitType is the base class and defines details that are relevant of all derived types.
