All SecurityProtocols shall implement the OpenSecureChannel and CloseSecureChannel services defined in OPC 10000-4. These Services specify how to establish a SecureChannel and how to apply security to Messages exchanged over that SecureChannel. The Messages exchanged and the security algorithms applied to them are shown in Figure 10.
SecurityProtocols shall support three SecurityModes: None, Sign and SignAndEncrypt. If the SecurityMode is None then no security is used and the security handshake shown in Figure 10 is not required. However, a SecurityProtocol implementation shall still maintain a logical channel and provide a unique identifier for the SecureChannel. The handshake shown also applies when using Session-less Service invocations, however the CreateSession steps are omitted.
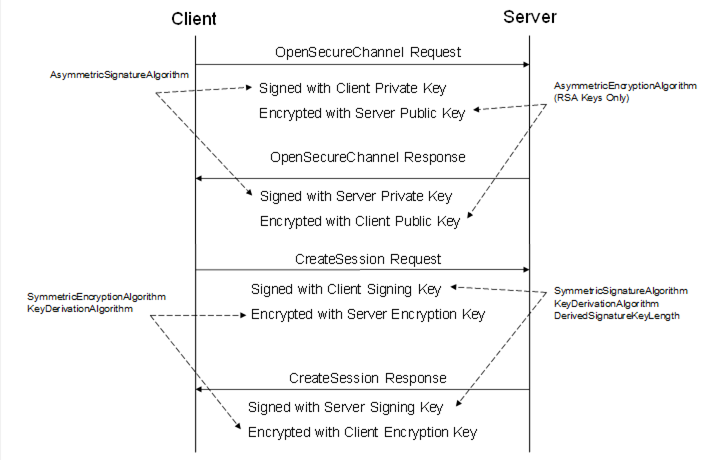
Figure 10 – Security handshake when Creating a Session
Each SecurityProtocol mapping specifies exactly how to apply the security algorithms to the Message. A set of security algorithms that shall be used together during a security handshake is called a SecurityPolicy. OPC 10000-7 defines standard SecurityPolicies as parts of the standard Profiles which OPC UA applications are expected to support. OPC 10000-7 also defines a URI for each standard SecurityPolicy. The latest versions of all SecurityPolicies are available in the online Profiles website. OPC 10000-7 defines the link to this website.
A Stack is expected to have built in knowledge of the SecurityPolicies that it supports. Applications specify the SecurityPolicy they wish to use by passing the URI to the Stack.
Table 48 defines the contents of a SecurityPolicy. Each SecurityProtocol mapping specifies how to use each of the parameters in the SecurityPolicy. A SecurityProtocol mapping may not make use of all of the parameters.
|
Name |
Description |
|
PolicyUri |
The URI assigned to the SecurityPolicy. |
|
SymmetricSignatureAlgorithm |
The symmetric signature algorithm to use. |
|
SymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm |
The symmetric encryption algorithm to use. |
|
AsymmetricSignatureAlgorithm |
The asymmetric signature algorithm to use. |
|
AsymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm |
The asymmetric encryption algorithm to use. |
|
MinAsymmetricKeyLength |
The minimum length, in bits, for an asymmetric key. |
|
MaxAsymmetricKeyLength |
The maximum length, in bits, for an asymmetric key. |
|
KeyDerivationAlgorithm |
The key derivation algorithm to use. |
|
DerivedSignatureKeyLength |
The length in bits of the derived key used for Message authentication. |
|
CertificateSignatureAlgorithm |
The asymmetric signature algorithm used to sign certificates. |
|
CertificateKeyAlgorithm |
The algorithm used to create asymmetric key pairs used with Certificates. |
|
EphemeralKeyAlgorithm |
The algorithm used to create asymmetric key pairs used for EphemeralKeys. |
|
SecureChannelNonceLength |
The length, in bytes, of the Nonces used when opening a SecureChannel. |
|
InitializationVectorLength |
The length, in bits, of the data used to initialize the symmetric algorithm. |
|
SymmetricSignatureLength |
The length, in bits, of the symmetric signature. |
|
LegacySequenceNumbers |
If TRUE, the 1024 based SequenceNumber rules apply to the SecurityPolicy; If FALSE, the 0 based SequenceNumber rules apply. See 6.7.2.4. |
The KeyDerivationAlgorithm is used to create the keys used to secure Messages sent over the SecureChannel. The length of the keys used for encryption is implied by the SymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm. The length of the keys used for creating Signatures is specified by the DerivedSignatureKeyLength.
The MinAsymmetricKeyLength and MaxAsymmetricKeyLength are constraints that apply to all Certificates (including Issuers in the chain). In addition, the key length of issued Certificates shall be less than or equal to the key length of the issuer Certificate. See 6.2.6 for information on Certificate chains.
The CertificateKeyAlgorithm and EphemeralKeyAlgorithm are used to generate new asymmetric key pairs used with Certificates and during the SecureChannel handshake. OPC 10000-7 specifies the algorithms that need to be supported for each SecurityPolicy.
The CertificateSignatureAlgorithm applies the Certificate and all Issuer Certificates. If a CertificateSignatureAlgorithm allows for more than one algorithm then the algorithms are listed in order of increasing priority. Each Issuer in a chain shall have an algorithm that is the same or higher priority than any Certificate it issues.
The SecureChannelNonceLength specifies the length of the Nonces exchanged when establishing a SecureChannel (see 6.7.4).