The EncryptedSecret uses an extensible format which has the TypeId of a DataType Node as a prefix as defined for the ExtensionObject encoding in OPC 10000-6. The general layout of the EncryptedSecret is shown in Figure 39.
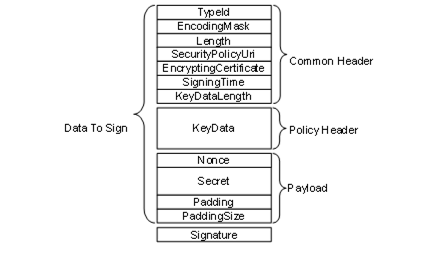
Figure 39 – EncryptedSecret layout
The TypeId specifies how the EncryptedSecret is serialized and secured. For example, the RsaEncryptedSecret requires that the KeyData be encrypted with the public key associated with the EncryptingCertificate before it is serialized.
The SecurityPolicyUri is used to determine what algorithms were used to encrypt and sign the data. Valid SecurityPolicyUris are defined in OPC 10000-7.
The payload is always encrypted using the symmetric encryption algorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. The KeyData provides the keys needed for symmetric encryption. The structure of the KeyData depends on the EncryptedSecret DataType.
The EncryptedSecret is secured and serialized as follows:
- Serialize the common header;
- Serialize the KeyData;
- If required, encrypt the KeyData and append the result to the common header;
- Update the KeyDataLength with the length of the encrypted KeyData;
- Append the Nonce and the Secret to the encrypted KeyData;
- Calculate padding required on the payload and append after the Secret;
- Encrypt the payload;
- Calculate a Signature;
- Append the Signature.
Individual fields are serialized using the UA Binary encoding (see OPC 10000-6) for the DataType specified in Table 187. The Padding is used to ensure there is enough data to fill an integer multiple of encryption blocks. The size of the encryption block depends on the encryption algorithm. The total length of the Padding, not including the PaddingSize, is encoded as a UInt16. The individual bytes of the Padding are set to the least significant byte of the PaddingSize.
The EncryptedSecret is deserilized and validated as follows:
- Deserialize the common header;
- Verify the Signature if the KeyData is not encrypted;
- Decrypt the KeyData and verify the Signature if the KeyData is encrypted;
- Decrypt the payload;
- Verify the padding on the payload;
- Extract the Secret;
The fields in the EncryptedSecret are described in Table 187. The first three fields TypeId, EncodingMask and Length belong to the ExtensionObject encoding defined in OPC 10000-6.
Table 187 – EncryptedSecret layout
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
TypeId |
NodeId |
|
|
EncodingMask |
Byte |
This value is always 1. |
|
Length |
Int32 |
The length of the data that follows including the Signature. |
|
SecurityPolicyUri |
String |
The URI for the SecurityPolicy used to apply security. |
|
Certificate |
ByteString |
The signing and/or encrypting Certificate. |
|
SigningTime |
DateTime |
When the Signature was created. |
|
KeyDataLength |
UInt16 |
The length, in bytes, of the KeyData that follows If the KeyData is encrypted this is the length of the encrypted data; Otherwise, it is the length of the unencrypted data. |
|
KeyData |
Byte [*] |
The key data used to create the keys needed for decrypting and verifying the payload using the SymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. Each EncryptedSecret DataType describes how the key data is structured for different SecurityPolicies. |
|
Nonce |
ByteString |
This is the last serverNonce returned in the CreateSession or ActivateSession Response when a UserIdentityToken is passed with the ActivateSession Request. If used outside of an ActivateSession call, the Nonce is created by the sender and its length shall be between 32 and 128 bytes inclusive. |
|
Secret |
ByteString |
The secret to protect. The password when used with UserNameIdentityTokens. The tokenData when used with IssuedIdentityTokens. |
|
PayloadPadding |
Byte[*] |
Additional padding added to ensure the size of the encrypted payload is an integer multiple of the InitializationVectorLength specified by the SecurityPolicyUri. If the InitializationVectorLength is less than 16 bytes then 16 bytes are used instead. The value of each byte is the least significant byte of the PayloadPaddingSize. |
|
PayloadPaddingSize |
UInt16 |
The size of the padding added to the payload. |
|
Signature |
Byte[*] |
The Signature calculated after all encryption is applied. Each EncryptedSecret DataType describes how the Signature is calculated for different SecurityPolicies. |
The PayloadPaddingSize adjusted with the following formula:
If (Secret.Length + PayloadPaddingSize < InitializationVectorLength) Then
PayloadPaddingSize = PayloadPaddingSize + InitializationVectorLength
Where the InitializationVectorLength is specified by the SymmetricEncryptionAlgorithm.
The currently available EncryptedSecret DataTypes are defined in Table 188.
Table 188 – EncryptedSecret DataTypes
|
Type Name |
When to Use |
|
RsaEncryptedSecret |
Used when the SecurityPolicy requires the use of RSA cryptography. It is described in 7.41.2.4. |
|
EccEncryptedSecret |
Used when the SecurityPolicy requires the use of ECC cryptography.It is described in 7.41.2.5. |