Applications shall never communicate with another application that they do not trust. An Application decides if another application is trusted by checking whether the Application Instance Certificate for the other application is trusted. A Certificate is only trusted if its chain can be validated.
Applications shall rely on lists of Certificates provided by the Administrator to determine trust. There are two separate lists: a list of trusted Certificates and a list of issuer Certificates (i.e. CAs). The list of trusted Certificates may contain a Certificate issued to another Application or it may be a Certificate belonging to a CA. The list of issuer Certificates contains CA Certificates needed for chain validation that are not in the list of trusted Certificates.
When building a chain each Certificate in the chain shall be validated back to a CA with a self-signed Certificate (a.k.a. a root CA). If any validation error occurs then the trust check fails. Some validation errors are non-critical which means they can be suppressed by a user of an Application with the appropriate privileges. Suppressed validation errors are always reported via auditing (i.e. an appropriate Audit event is raised).
Determining trust requires access to all Certificates in the chain. These Certificates may be stored locally or they may be provided with the application Certificate. Processing fails with Bad_SecurityChecksFailed if an element in the chain cannot be found. A Certificate is trusted if the Certificate or at least one of the Certificates in the chain are in the list of trusted Certificates for the Application and the chain is valid.
Table 106 specifies the steps used to validate a Certificate in the order that they shall be followed. These steps are repeated for each Certificate in the chain. Each validation step has a unique error status and audit event type that shall be reported if the check fails. The audit event is in addition to any audit event that was generated for the particular Service that was invoked. The Service audit event in its message text shall include the audit EventId of the AuditCertificateEventType (for more details, see 6.5). Processing halts if an error occurs, unless it is non-critical and it has been suppressed.
ApplicationInstanceCertificates shall not be used in a Client or Server until they have been evaluated and marked as trusted. This can happen automatically by a PKI trust chain or in an offline manner where the Certificate is marked as trusted by an administrator after evaluation.
Table 106 – Certificate validation steps
|
Step |
Error/AuditEvent |
Description |
|
Certificate Structure |
Bad_CertificateInvalid Bad_SecurityChecksFailed AuditCertificateInvalidEventType |
The Certificate structure is verified. This error may not be suppressed. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. |
|
Build Certificate Chain |
Bad_CertificateChainIncomplete Bad_SecurityChecksFailed AuditCertificateInvalidEventType |
The trust chain for the Certificate is created. An error during the chain creation may not be suppressed. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. |
|
Signature |
Bad_CertificateInvalid Bad_SecurityChecksFailed AuditCertificateInvalidEventType |
A Certificate with an invalid signature shall always be rejected. A Certificate signature is invalid if the Issuer Certificate is unknown. A self-signed Certificate is its own issuer. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. |
|
Security Policy Check |
Bad_CertificatePolicyCheckFailed Bad_SecurityChecksFailed AuditCertificateInvalidEventType |
A Certificate signature shall comply with the CertificateSignatureAlgorithm, MinAsymmetricKeyLength and MaxAsymmetricKeyLength requirements for the used SecurityPolicy defined in OPC 10000-7. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. This error may be suppressed. |
|
Trust List Check |
Bad_CertificateUntrusted Bad_SecurityChecksFailed AuditCertificateUntrustedEventType |
If the Application Instance Certificate is not trusted and none of the CA Certificates in the chain is trusted, the result of the Certificate validation shall be Bad_CertificateUntrusted. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. |
|
Validity Period |
Bad_CertificateTimeInvalid Bad_CertificateIssuerTimeInvalid AuditCertificateExpiredEventType |
The current time shall be after the start of the validity period and before the end. This error may be suppressed. |
|
Host Name |
Bad_CertificateHostNameInvalid AuditCertificateDataMismatchEventType |
The HostName in the URL used to connect to the Server shall be the same as one of the HostNames specified in the Certificate. This check is skipped for CA Certificates. This check is skipped for Server side validation. This error may be suppressed. |
|
URI |
Bad_CertificateUriInvalid AuditCertificateDataMismatchEventType |
Application and Software Certificates contain an application or product URI that shall match the URI specified in the ApplicationDescription provided with the Certificate. This check is skipped for CA Certificates. This error may not be suppressed. The gatewayServerUri is used to validate an Application Certificate when connecting to a Gateway Server (see 7.2). |
|
Certificate Usage |
Bad_CertificateUseNotAllowed Bad_CertificateIssuerUseNotAllowed AuditCertificateMismatchEventType |
Each Certificate has a set of uses for the Certificate (see OPC 10000-6). These uses shall match use requested for the Certificate (i.e. Application, Software or CA). This error may be suppressed unless the Certificate indicates that the usage is mandatory. |
|
Find Revocation List |
Bad_CertificateRevocationUnknown Bad_CertificateIssuerRevocationUnknown AuditCertificateRevokedEventType |
Each CA Certificate may have a revocation list. This check fails if this list is not available (i.e. a network interruption prevents the application from accessing the list). No error is reported if the Administrator disables revocation checks for a CA Certificate. This error may be suppressed. Bad_SecurityChecksFailed should be reported back to the Client. |
|
Revocation Check |
Bad_CertificateRevoked Bad_CertificateIssuerRevoked AuditCertificateRevokedEventType |
The Certificate has been revoked and may not be used. This error may not be suppressed. If this check fails on the Server side, the error Bad_SecurityChecksFailed shall be reported back to the Client. |
Certificates are usually placed in a central location called a CertificateStore. Figure 20 illustrates the interactions between the Application, the Administrator and the CertificateStore. The CertificateStore could be on the local machine or in some central server. The exact mechanisms used to access the CertificateStore depend on the application and PKI environment set up by the Administrator.
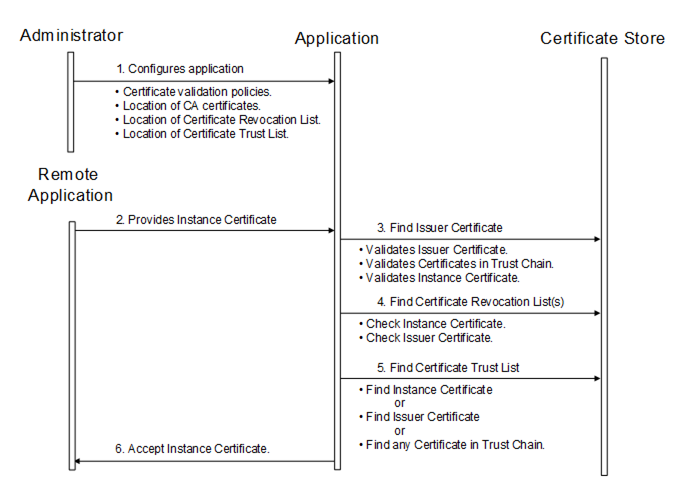
Figure 20 – Determining if an Application Instance Certificate is trusted