Errata exists for this version of the document.
The Client uses the “DomainDownload” Program to manage and monitor the download of a domain at the Server.
The basic state model for the DomainDownload Program is presented in Figure A.2. The Program has three primary states, Ready, Running, and Halted which are aligned with the standard states of a ProgramStateMachineType. Additionally, the DomainDownloadType extends the ProgramStateMachineType by defining subordinate State Machines for the Program’s Running and Halted states. The subordinate states describe the download operations in greater detail and allow the Client to monitor the activity of the download at a finer resolution.
An instance (Program Invocation) of a DomainDownload Program is created by the Client each time a download is to be performed. The instance exists until explicitly removed by the Client. The initial state of the Program is Ready and the terminal state is Halted. The DomainDownload can be temporarily suspended and then resumed or aborted. Once halted, the program may not be restarted.
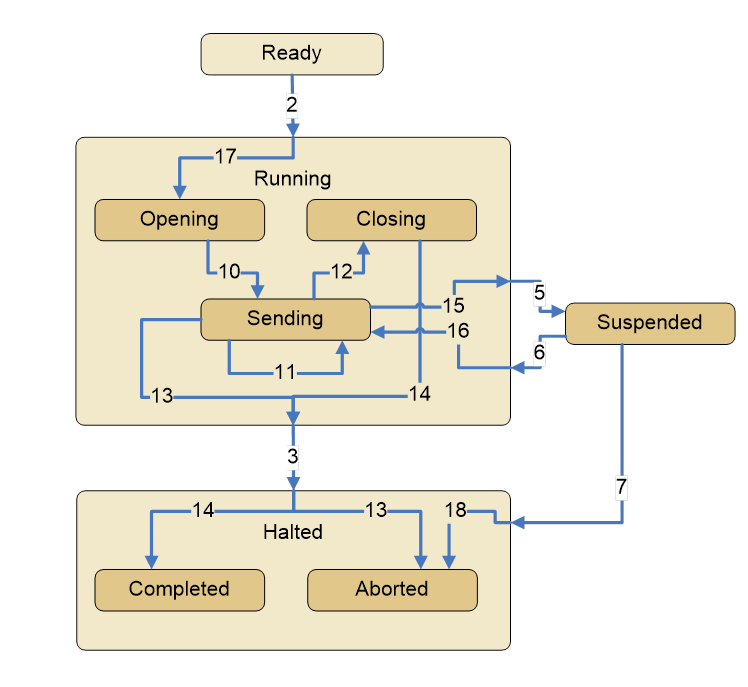
Figure A.2 – DomainDownload state diagram
The sequence of state transitions is illustrated in Figure A.2. Once the download is started, The Program progresses to the Opening state. After the source of the data is opened, a sequence of transfers occurs in the Sending state. When the transfer completes the Objects are closed in the Closing state. If the transfer is terminated before all of the data is downloaded or an error is encountered then the download is halted and the Program transitions to the Aborted state; otherwise the Program halts in the Completed state. The states are presented in Table A.1 along with the state transitions.
The valid state transitions specified for the DomainDownload Program are specified in Table A.1. Each of the transitions defines a start state and end state for the transition and is identified by a unique number. Five of the transitions are from the base ProgramStateMachineType and retain the transition identifier numbers specified for Programs. The additional transitions relate the base Program states with the subordinate states defined for the DomainDownload. These states have been assigned unique transition identifier numbers that distinguish them from the base Program transition identifiers. In cases where transitions occur between substates and the Program’s base states, two transitions are specified. One transition identifies the base state change and a second sub-state change. For example, Ready to Running and to Opening occurs at the same time.
The table also specifies the defined states, causes for the transitions, and the effects of each transition. Program Control Methods are used by the Client to “run” the DomainDownload. The Methods cause or trigger the specified transitions. The transition effects are the specified EventTypes which notify the Client of Program activity.
Table A.1 – DomainDownload states
|
No. |
Transition name |
Cause |
From State |
To State |
Effect |
|
2 |
ReadyToRunning |
Start Method |
Ready |
Running |
Report Transition 2 Event/Result |
|
3 |
RunningToHalted |
Halt Method/Error or Internal. |
Running |
Halted |
Report Transition 3 Event/Result |
|
5 |
RunningToSuspended |
Suspend Method |
Running |
Suspended |
Report Transition 5 Event/Result |
|
6 |
SuspendedToRunning |
Resume Method |
Suspended |
Running |
Report Transition 6 Event/Result |
|
7 |
SuspendedToHalted |
Halt Method |
Suspended |
Halted |
Report Transition 7 Event/Result |
|
10 |
OpeningToSending |
Internal |
Opening |
Sending |
Report Transition 10 Event/Result |
|
11 |
SendingToSending |
Internal |
Sending |
Sending |
Report Transition 11 Event/Result |
|
12 |
SendingToClosing |
Internal |
Sending |
Closing |
Report Transition 12 Event/Result |
|
13 |
SendingToAborted |
Halt Method/Error |
Opening |
Aborted |
Report Transition 13 Event/Result |
|
14 |
ClosingToCompleted |
Internal |
Closing |
Completed |
Report Transition 14 Event/Result |
|
15 |
SendingToSuspended |
Suspend Method |
Sending |
Suspended |
Report Transition 16 Event/Result |
|
16 |
SuspendedToSending |
Resume Method |
Suspended |
Sending |
Report Transition 17 Event/Result |
|
18 |
SuspendedToAborted |
Halt Method |
Suspended |
Aborted |
Report Transition 18 Event/Result |
|
17 |
ToOpening |
Internal |
Ready |
Opening |
Report Transition 19 Event/Result |
Four standard Program Methods are specified for running the DomainDownload Program, Start, Suspend, Resume, and Halt. No additional Methods are specified. The base behaviours of these Methods are defined by the ProgramStateMachineType. The Start Method initiates the download activity and passes the source and destination locations for the transfer. The Suspend Method is used to pause the activity temporarily. The Resume Method reinitiates the download, when paused. The Halt Method aborts the download. Each of the Methods causes a Program state transition and a sub state transition. The specific state transition depends on the current state at the time the Method is called. If a Method Call is made when the DomainDownload is in a state for which that Method has no associated transition, the Method returns an error status indicating invalid state for the Method.
The Start Method specifies three input arguments to be passed when it is called: Domain Name, DomainSource, and DomainDestination. The other Methods require no input arguments. No output arguments are specified for the DomainDownload Methods. The resultant error status for the Program is part of the Call Service.
A ProgramTransitionEventType is specified for each of the DomainDownload Program transitions. The EventTypes trigger a specific Event notification to the Client when the associated state transition occurs in the running Program Instance. The Event notification identifies the transition. The SendingToSending state transition also includes intermediate result data.
The SendingToSending Program transition Event relays intermediate result data to the Client along with the notification. Each time the transition occurs, data items describing the amount and percentage of data transferred are sent to the Client.
The DomainDownload Program retains final result data following a completed or aborted download. The data includes the total transaction time and the size of the domain. In the event of an aborted download, the reason for the termination is retained.
The UA model for the DomainDownload Program is presented in the following tables and figures. Collectively they define the components that constitute this Program. For clarity, the figures present a progression of portions of the model that complement the contents of the tables and illustrate the Program’s composition.
The type definition for the DomainDownload Program precisely represents the behaviour of the Program in terms of UA components. These components can be browsed by a Client to interpret or validate the actions of the Program.
The DomainDownloadType is a subtype derived from the ProgramStateMachineType. It specifies the use or non-use of optional ProgramStateMachineType components, valid extensions such as subordinate State Machines, and constrained attribute values applied to instances of DomainDownload Programs.
Table A.2 specifies the optional and extended components defined by the DomainDownload Type. Note the references to two sub State Machine Types, TransferStateMachine and FinishStateMachine. The DomainDownloadType omits references to the Reset Program Control Method and its associated state transition (HaltedToReady), which it does not support.
Table A.2 – DomainDownloadType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all non-optional attributes specified for the ProgramStateMachineType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DomainDownloadType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
TransferStateMachine |
|
StateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
FinishStateMachine |
|
StateMachineType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
ProgramDiagnostic |
|
ProgramDiagnostic2Type |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToRunning |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
RunningToHalted |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
RunningToSuspended |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToRunning |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToHalted |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Suspend |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Halt |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Resume |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
FinalResultData |
|
BaseObjectType |
Mandatory |
Table A.3 specifies the Transfer State Machine type that is a sub State Machine of the DomainDownload Program Type. This definition identifies the StateTypes that compose the sub states for the Program’s Running StateType.
Table A.3 – TransferStateMachineType
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all attributes specified for the FiniteStateMachineType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
TransferStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Opening |
|
StateType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Sending |
|
StateType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Closing |
|
StateType |
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToOpening |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
OpeningToSending |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SendingToClosing |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SendingToAborted |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SendingToSuspended |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
SuspendedToSending |
|
TransitionType |
-- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Suspend |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Halt |
|
|
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
Resume |
|
|
Mandatory |
Table A.3 specifies the StateTypes associated with the Transfer State Machine Type. All of these states are sub states of the Running state of the base ProgramStateMachineType.
The Opening state is the preparation state for the domain download.
The Sending state is the activity state for the transfer in which the data is moved from the source to destination.
The Closing state is the cleanup phase of the download.
Table A.4 defines the states of the TransferStateMachineType.
Table A.4 – Transfer State Machine – states
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target TypeDefinition |
NOTES |
|
States |
|||||
|
Opening |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
5 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OpeningToSending |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ToOpening |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
OpeningToSending |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sending |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
6 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OpeningToSending |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SendingToSending |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SendingToClosing |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
SendingToSuspended |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ToSending |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Closing |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
7 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
ClosingToCompleted |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
ToTransition |
ClosingToAborted |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
SendingToClosing |
|
TransitionType |
|
Table A.5 specifies the Finish State Machine Type that is a sub state machine of the DomainDownload ProgramStateMachineType. This definition identifies the StateTypes that compose the sub states for the Program’s Halted StateType.
Table A.5 – Finish State Machine Type
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all attributes specified for the FiniteStateMachineType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
TransferStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Completed |
|
StateType |
-- |
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
-- |
Table A.6 specifies the StateTypes associated with the Finish State Machine Type. Note these are final states and that they have no associated transitions between them.
Table A.6 – Finish State Machine – states
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target TypeDefinition |
NOTES |
|
States |
|||||
|
Aborted |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
8 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
OpeningToAborted |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ClosingToAborted |
|
TransitionType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Completed |
HasProperty |
StateNumber |
9 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
FromTransition |
ClosingToCompleted |
|
TransitionType |
|
The Aborted state is the terminal state that indicates an incomplete or failed domain download operation.
The Completed state is the terminal state that indicates a successful domain download.
Table A.7 specifies the constraining behaviour of a DomainDownload.
Table A.7 – DomainDownloadType Property Attributes variable values
|
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
Data Value |
Modelling Rule |
|
Variable |
Creatable |
Boolean |
True |
-- |
|
Variable |
Deletable |
Boolean |
True |
Mandatory |
|
Variable |
AutoDelete |
Boolean |
False |
Mandatory |
|
Variable |
RecycleCount |
Int32 |
0 |
Mandatory |
|
Variable |
InstanceCount |
UInt32 |
PropertyType |
-- |
|
Variable |
MaxInstanceCount |
UInt32 |
500 |
-- |
|
Variable |
MaxRecycleCount |
UInt32 |
0 |
-- |
A DomainDownload Program Invocation can be created and also destroyed by a Client. The Program Invocation will not delete itself when halted, but will persist until explicitly removed by the Client. A DomainDownload Program Invocation cannot be reset to restart. The Server will support up to 500 concurrent DomainDownload Program Invocations.
Figure A.3 presents a partial DomainDownloadType model that illustrates the association between the states and the DomainDownload, Transfer, and Finish State Machines. Note that the current state number for the sub state machines is only valid when the DomainDownload active base state references the sub state machine, Running for the Transfer current state and Halted for the Finish current state.
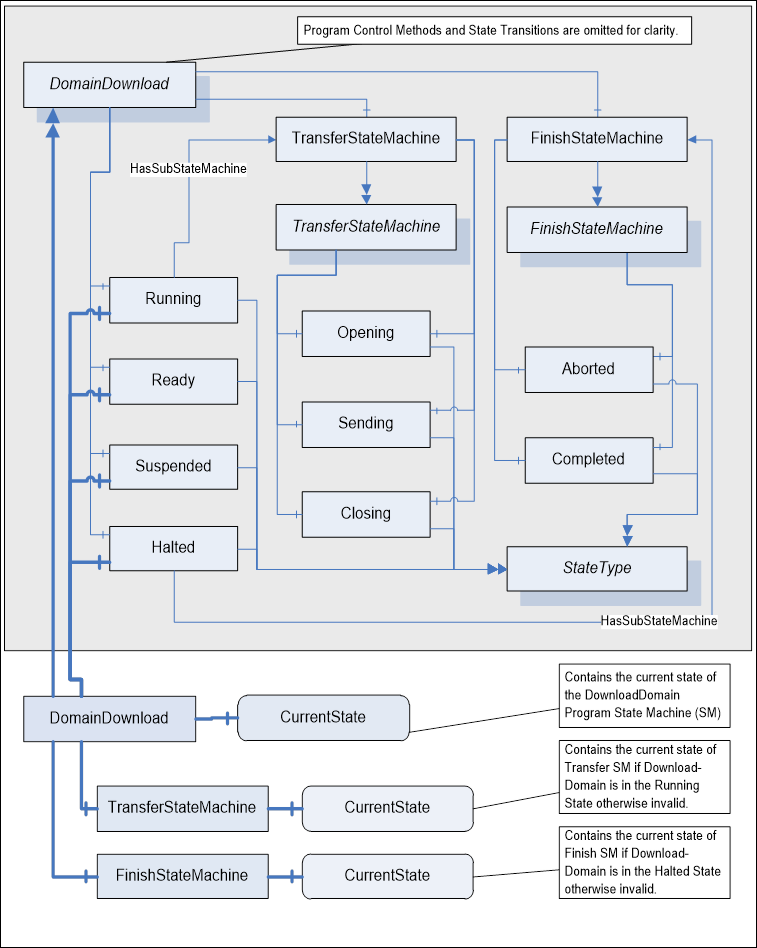
Figure A.3 – DomainDownloadType partial state model
Table A.8 specifies the ProgramTransitionTypes that are defined in addition to the ProgramTransitionTypes specified for Programs in Table 7. These types associate the Transfer and Finish sub state machine states with the states of the base Program.
Table A.8 – Additional DomainDownload transition types
|
BrowseName |
References |
Target BrowseName |
Value |
Target TypeDefinition |
NOTES |
|
Transitions |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ToSending |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
10 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Opening |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Start |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SendingToSending |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
11 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SendingToClosing |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
12 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Closing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SendingToAborted |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
13 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Halt |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ClosingToCompleted |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
14 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Completed |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Closing |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SendingToSuspended |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
15 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Suspend |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendedToSending |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
16 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Sending |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Resume |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SuspendedToAborted |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
18 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Aborted |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Suspended |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Halt |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ReadyToOpening |
HasProperty |
TransitionNumber |
17 |
PropertyType |
|
|
|
ToState |
Opening |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
FromState |
Ready |
|
StateType |
|
|
|
HasCause |
Start |
|
|
Method |
|
|
HasEffect |
ProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
HasEffect |
AuditProgramTransitionEventType |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure A.4 through Figure A.10 illustrate portions of the DomainDownloadType model. In each figure, the referenced tates, Methods, transitions, and EventTypes are identified for one or two state transitions.
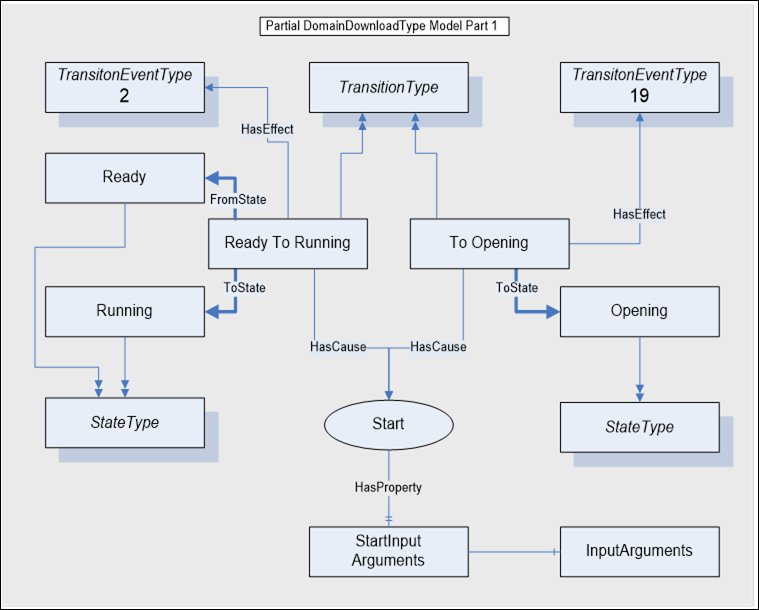
Figure A.4 – Ready To Running model
Figure A.4 illustrates the model for the ReadyToRunning Program transition. The transition is caused by the Start Method. The Start Method requires three input arguments. The Method Call service is used by the Client to invoke the Start Method and pass the arguments. When successful, the Program Invocation enters the Running state and the subordinate Transfer Opening state. The Server issues two Event notifications, ReadyToRunning (2), and ToOpening (19).
Table A.9 – Start Method additions
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
Start |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
-- |
|
Table A.9 specifies that the Start Method for the DomainDownloadType requires input arguments. Table A.10 identifies the Start Arguments required.
|
Name |
Type |
Value |
|
Argument 1 |
structure |
|
|
name |
String |
SourcePath |
|
dataType |
NodeId |
StringNodeId |
|
valueRank |
Int32 |
-1 (-1 = scalar) |
|
arrayDimensions |
UInt32[] |
null |
|
description |
LocalizedText |
The source specifier for the domain |
|
Argument 2 |
structure |
|
|
Name |
String |
DestinationPath |
|
dataType |
NodeId |
StringNodeId |
|
valueRank |
Int32 |
-1 (-1 = scalar) |
|
arrayDimensions |
UInt32[] |
null |
|
description |
LocalizedText |
The destination specifier for the domain |
|
Argument 3 |
structure |
|
|
name |
String |
DomainName |
|
dataType |
NodeId |
StringNodeId |
|
arrayDimensions |
UInt32[] |
null |
|
valueRank |
Int32 |
-1 (-1 = scalar) |
|
description |
LocalizedText |
The name of the domain |
|
|
|
|
Figure A.5 illustrates the model for the Opening To Sending and the Sending to Closing Program transitions. As specified in the transition table, these state transitions require no Methods to occur, but rather are driven by the internal actions of the Server. Events are generated for each state transition (10 to 12), when they occur.
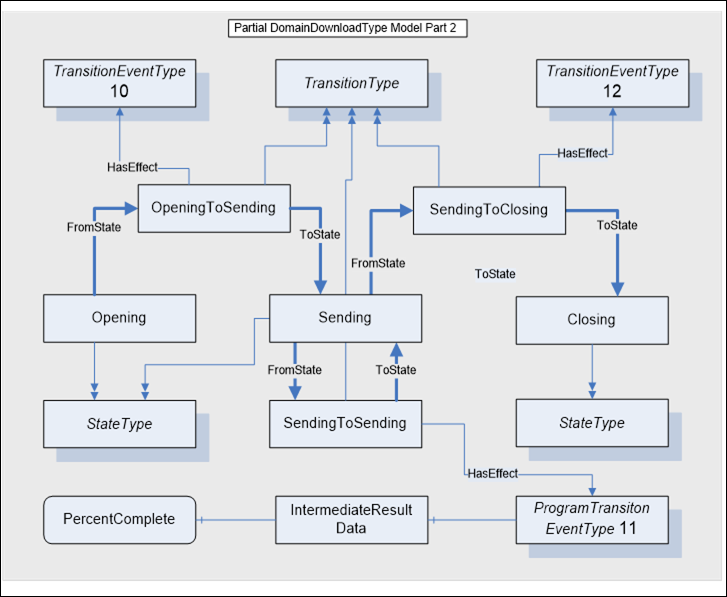
Figure A.5 – Opening To Sending To Closing model
Notice that a state transition can initiate and terminate at the same state (Sending). In this case the transition serves a purpose. The ProgramTransitionEventType effect referenced by the SendingToSending state transition has an IntermediateResultData Object Reference. The IntermediateResultData Object serves to identify two Variables whose values are obtained each time the state transition occurs. The values are sent to the Client with the Event notification. Table A.11 defines the IntermediateResults ObjectType and Table A.13 defines the Variables of the ObjectType.
Table A.11 – IntermediateResults Object
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all attributes specified for the ObjectType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IntermediateResults |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
AmountTransferred |
Long |
VariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
PercentageTransferred |
Long |
VariableType |
Mandatory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table A.12 – Intermediate result data Variables
|
Intermediate Result Variables |
Type |
Value |
|
Variable 1 |
Structure |
|
|
Name |
String |
AmountTransferred |
|
dataType |
NodeId |
StringNodeId |
|
description |
LocalizedText |
Bytes of domain data transferred. |
|
Variable 2 |
Structure |
|
|
Name |
String |
PercentageTransferred |
|
dataType |
NodeId |
StringNodeId |
|
description |
LocalizedText |
Percentage of domain data transferred. |
The model for the Running To Suspended state transition is illustrated in Figure A.6. The cause for this transition is the Suspend Method. The Client can pause the download of domain data to the control. The transition from Running to Suspended invokes the Event generation for TransitionEventTypes 5 and 16. Note that there is no longer a valid current state for the Transfer State Machine.
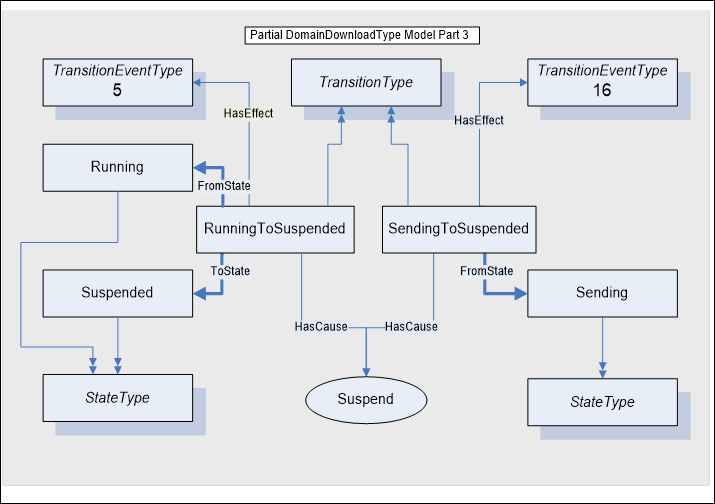
Figure A.6 – Running To Suspended model
The model for the SuspendedToRunning state transition is illustrated in Figure A.7. The cause for this transition is the Resume Method. The Client can resume the download of domain data to the control. The transition from Suspended to Running generates the Event for TransitionEventTypes 6 and 17. Now that the Running state is active, the Sending state of the Transfer State Machine is again specified for the CurrentStateNumber.
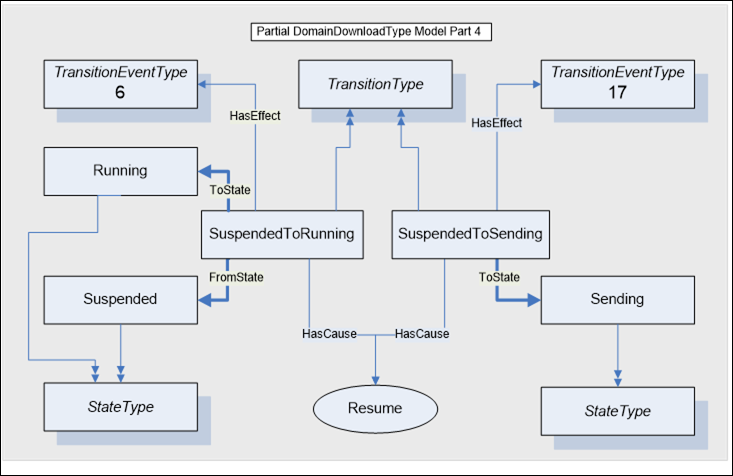
Figure A.7 – Suspended To Running model
The model for the Running To Halted state transition for an abnormal termination of the domain download is illustrated in Figure A.8. The cause for this transition is the Halt Method. The Client can terminate the download of domain data to the control. The transition from Running To Halted generates the Event for TransitionEventTypes 3 and 15. The TransitionEventType 15 indicates the transition from the Sending state as the Running State ends and then to the Aborted state as the Halted state is entered.
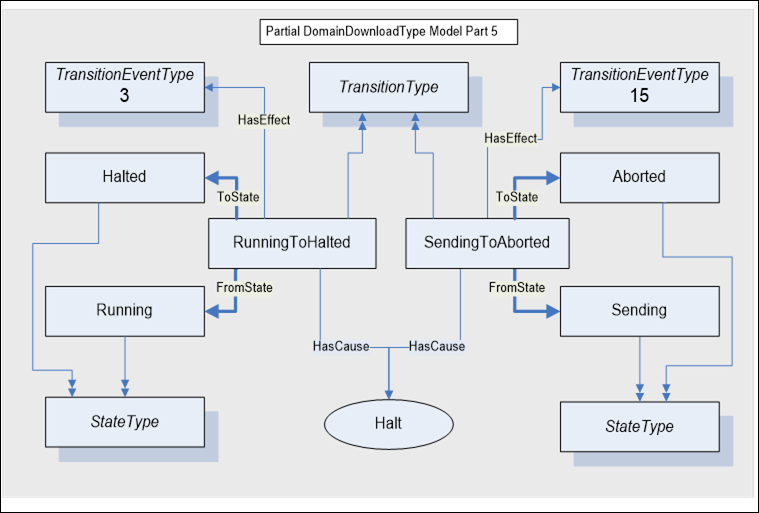
Figure A.8 – Running To Halted – Aborted model
Figure A.9 illustrates the model for the Suspended To Halted state transition for an abnormal termination of the domain download. The cause for this transition is the Halt Method. The Client can terminate the download of domain data to the control while it is suspended. The transition from SuspendedToHalted invokes the Event notifiers for TransitionEventTypes 7 and 18.
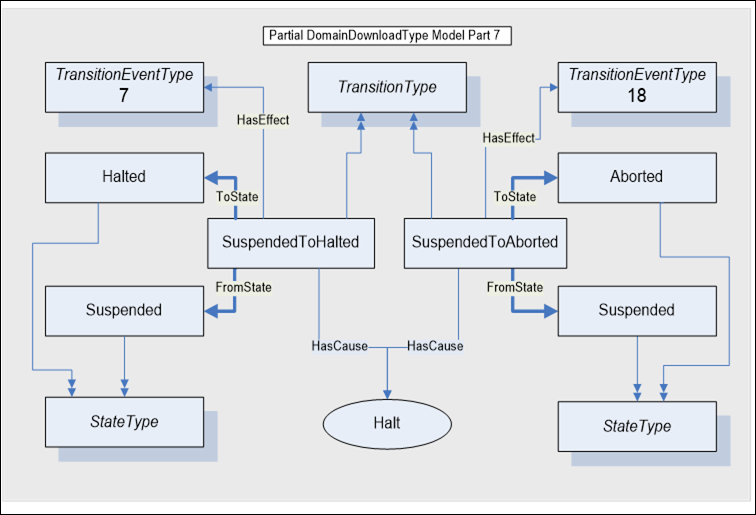
Figure A.9 – Suspended To Aborted model
The model for the Running To Completed state transition for a normal termination of the domain download is illustrated in Figure A.10. The cause for this transition is internal. The transition from Closing To Halted generates the Event for TransitionEventTypes 3 and 14. The TransitionEventType 14 indicates the transition from the Closing state as the Running state ends and then to the Completed state as the Halted state is entered.
The DomainDownloadType includes a component reference to a FInalResultData Object. This Object references Variables that persists information about the domain download once it has completed. This data can be read by Clients who are not subscribed to Event notifications. The result data is described in Table A.13.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
|
Includes all attributes specified for the ObjectType |
||||
|
BrowseName |
FinalResultData |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
Data Type |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
DownloadPerformance |
Double |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Variable |
FailureDetails |
String |
BaseDataVariableType |
Mandatory |
The Domain Download net transfer data rate and detailed reason for aborted downloads is retained as final result data for each Program Invocation.
DownloadPerformance provides the data rate in seconds for domain data transferred.
FailureDetails provides a descriptive reason for an abort.
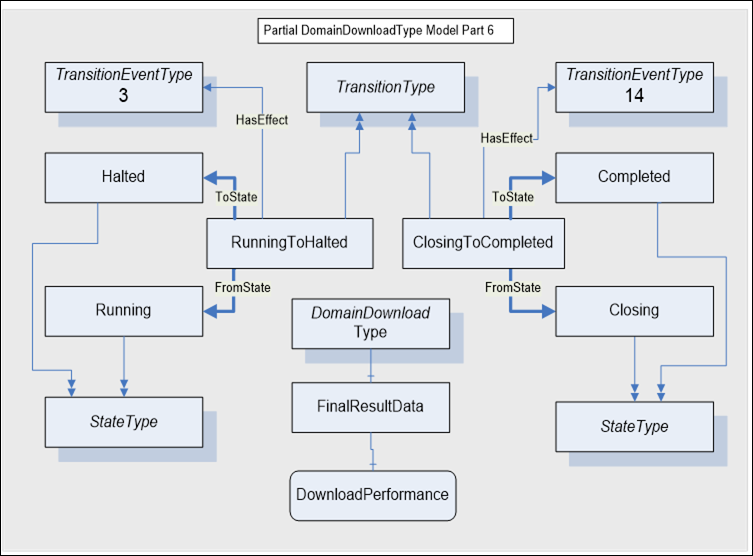
Figure A.10 – Running To Completed model
Figure A.11 illustrates a normal sequence of service exchanges between a Client and Server that would occur during the life cycle of a DomainDownloadType Program Invocation.

Figure A.11 – Sequence of operations
____________