The OPC UA systems architecture models Clients and Servers as interacting partners. Each system may contain multiple Clients and Servers. Each Client may interact concurrently with one or more Servers, and each Server may interact concurrently with one or more Clients. This model enables Clients to access data, invoke Services, and receive Events from Servers. An application can embody both Server and Client functionalities, allowing it to exchange information with other Servers and Clients as described in 5.3.7.
Clients and Servers are described in 5.2 and 5.3. Figure 2 illustrates the architecture that includes a combined Server and Client.
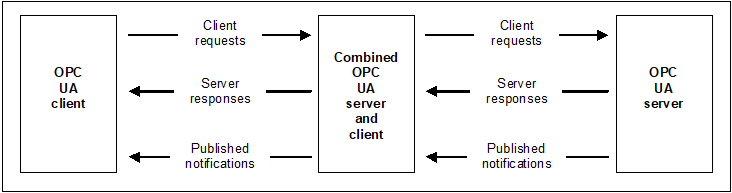
Figure 2 – OPC UA system architecture
The OPC UA Client architecture models the Client endpoint of ClientServer interactions. Figure 3 illustrates the major elements of a typical Client and how they relate to each other.
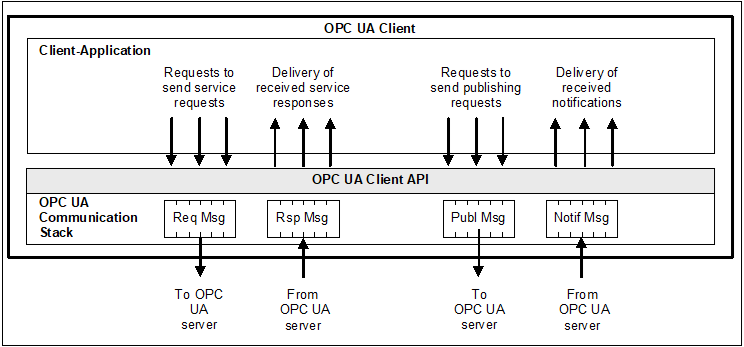
Figure 3 – OPC UA Client architecture
The Client Application utilizes a Client API to initiate OPC UA Service requests and receive responses from Servers. The Communication Stack handles the conversion of Client API calls into messages and manages the underlying communication with the Server. The Services defined for OPC UA are described in clause 6, and specified in OPC 10000-4.
Note that the “Client API” is an internal interface that isolates the Client application code from an OPC UA Communication Stack. The OPC UA Communication Stack converts Client API calls into Messages and sends them through the underlying communications entity to the Server at the request of the Client application. The OPC UA Communication Stack also receives response and NotificationMessages from the underlying communications entity and delivers them to the Client application through the Client API.
The OPC UA Server architecture models the Server endpoint of client/server interactions. Figure 4 illustrates the major elements of the Server and how they relate to each other.
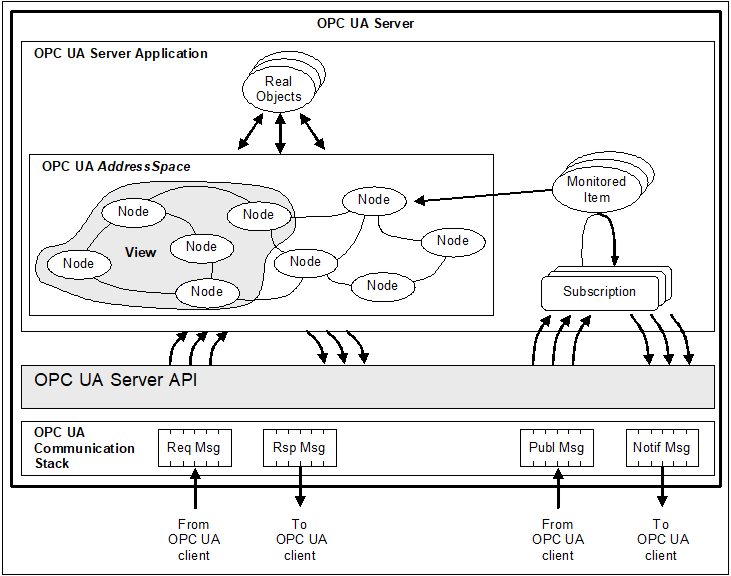
Figure 4 – OPC UA Server architecture
Real objects are physical or software objects that are accessible by the Server application or that it maintains internally. Examples include physical devices (e.g. sensors, actuators, motors) and diagnostics counters.
The Server application is the code that implements the function of the Server. It uses the Server API to send and receive OPC UA Messages from Clients. Note that the “Server API” is an internal interface that isolates the Server application code from an OPC UA Communication Stack.
The AddressSpace is modelled as a set of Nodes accessible by Clients using OPC UA Services (interfaces and methods). Nodes in the AddressSpace are used to represent real objects, their definitions and their References to each other.
OPC 10000-3 contains the details of the meta model “building blocks” used to create an AddressSpace out of interconnected Nodes in a consistent manner. Servers are free to organize their Nodes within the AddressSpace as they choose. The use of References between Nodes permits Servers to organize the AddressSpace into hierarchies, a full mesh network of Nodes, or any possible mix.
OPC 10000-5 defines OPC UA Nodes and References and their expected organization in the AddressSpace. Some Profiles will not require that all of the UA Nodes be implemented.
A View is a subset of the AddressSpace. Views are used to restrict the Nodes that the Server makes visible to the Client, thus restricting the size of the AddressSpace for the Service requests submitted by the Client. The default View is the entire AddressSpace. Servers may optionally define other Views. Views hide some of the Nodes or References in the AddressSpace. Views are visible via the AddressSpace and Clients are able to browse Views to determine their structure. Views are often hierarchies, which are easier for Clients to navigate and represent in a tree.
The OPC UA AddressSpace supports Information Models. This support is provided through:
- Node References that allow Objects in the AddressSpace to be related to each other.
- ObjectType Nodes that provide semantic information for real Objects (type definitions).
- ObjectType Nodes to support subclassing of type definitions.
- Data type definitions exposed in the AddressSpace that allow industry specific data types to be used.
- Industry groups can define how their specific information models are to be represented in Server AddressSpace.
MonitoredItems are entities in the Server created by the Client that monitor AddressSpace Nodes and, indirectly, their real-world counterparts. When they detect a data change or an event/alarm occurrence, they generate a Notification that is transferred to the Client by a Subscription.
A Subscription is an endpoint in the Server that publishes Notifications to Clients. Clients control the rate at which publishing occurs by sending Publish Messages.
The Services defined for OPC UA are described in clause 6, and specified in OPC 10000-4.
Request/response Services are Services invoked by the Client through the OPC UA Service Interface to perform a specific task on one or more Nodes in the AddressSpace and to return a response.
The Publish Service is invoked through the OPC UA Service Interface for the purpose of periodically sending Notifications to Clients. Notifications include Events, Alarms, data changes and Program outputs.
Server to Server interactions in the ClientServer model are interactions in which one Server acts as a Client of another Server. Server to Server interactions allow for the development of servers that:
- exchange information with each other on a peer-to-peer basis, this could include redundancy or remote Servers that are used for maintaining system wide type definitions (see Figure 5),
are chained in a layered architecture of Servers to provide:
aggregation of data from lower-layer Servers,
higher-layer data constructs to Clients, and
concentrator interfaces to Clients for single points of access to multiple underlying Servers.
Figure 5 illustrates interactions between Servers.
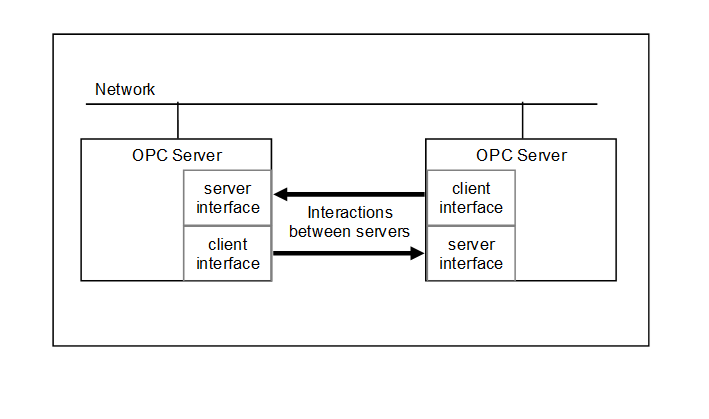
Figure 5 – Peer-to-peer interactions between Servers
Similar peer-to-peer interactions can also be accomplished using the OPC UA PubSub model where each peer Application is both a Publisher and a Subscriber.
Figure 6 extends the previous example and illustrates the chaining of Servers together for vertical access to data in an enterprise.
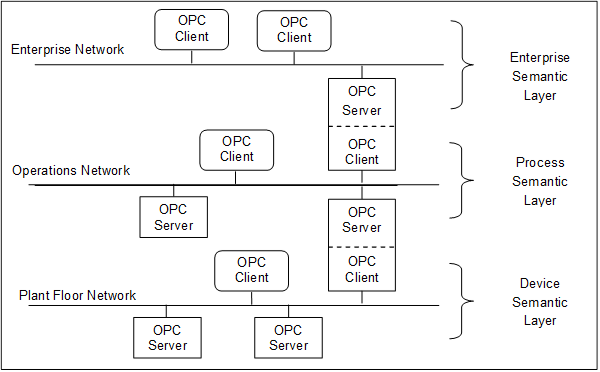
Figure 6 – Chained Server example
OPC UA provides the data structures and services by which Redundancy may be achieved in a standardized manner. Redundancy may be used for high availability, fault tolerance and load balancing. OPC 10000-4 formally defines Client, Server and Network Redundancy. Whether and what Redundancy is supported by an OPC UA Application is defined by its Profiles. Profiles are described in OPC 10000-7.
Required Client and Server behaviours are associated with two distinct modes of Server Redundancy, transparent and non-transparent. The Client and Server responsibilities when using either transparent or non-transparent redundancy are defined in OPC 10000-4.
Servers that support non-transparent redundancy can also support client-controlled load balancing. The health of a Server including its ability to Service requests is collectively defined as ServiceLevel. See OPC 10000-5 for a formal definition of ServiceLevel. OPC 10000-4 defines four distinct ServiceLevel sub-ranges and example usage.
The Publish-Subscribe (PubSub) communication model in OPC UA offers an alternative to the ClientServer model, enabling efficient and/or decoupled communication. With PubSub, OPC UA Applications do not directly exchange requests and responses. Instead, Publishers send messages to a Message Oriented Middleware, without knowledge of what, if any, Subscribers there may be. Similarly, Subscribers express interest in specific types of data, and process messages that contain this data, without knowledge of what Publishers there are.
Message Oriented Middleware is software or hardware infrastructure supporting sending and receiving messages between distributed systems. It depends on the Message Oriented Middleware how this distribution is implemented.
To cover a large number of use cases, OPC UA PubSub supports two largely different Message Oriented Middleware variants. These are:
- A broker-less form, where the Message Oriented Middleware is the network infrastructure that is able to route datagram-based messages. Subscribers and Publishers use datagram protocols like UDP multicast.
- A broker-based form, where the Message Oriented Middleware is a Broker. Subscribers and Publishers use standard messaging protocols like AMQP or MQTT to communicate with the Broker. All messages are published to specific queues (e.g. topics, nodes) that the Broker exposes and Subscribers can listen to these queues. The Broker may translate messages from the formal messaging protocol of the Publisher to the formal messaging protocol of the Subscriber.
PubSub is used to communicate messages between different system components without these components having to know each other’s identity.
A Publisher is pre-configured with what data to send. There is no connection establishment between Publisher and Subscriber.
The knowledge about who Subscribers are and the forwarding of published data to the Subscribers is off-loaded to the Message Oriented Middleware. The Publisher does not know or even care if there is one or many Subscribers. Effort and resource requirements for the Publisher are predictable and do not depend on the number of Subscribers.
OPC 10000-14 describes the details of the OPC UA PubSub model.
OPC UA PubSub and ClientServer models are complementary and can be combined and used synergistically. The OPC UA Information Model is the foundation for both. A typical scenario involves using ClientServer interactions for configuration, control, and on-demand data access, while PubSub is used for efficient, high-speed dissemination of real-time data. For instance, a Client application might use ClientServer to configure a Server and set up PubSub connections. Subsequently, the Server/Publisher publishes real-time data updates using PubSub, and the Client/Subscriber subscribes to this data stream for continuous monitoring.
OPC PubSub can easily be integrated into Servers and Clients. Quite typically, a Publisher will be a Server (the owner of information) and a Subscriber is often a Client. Above all, the PubSub Information Model for configuration promotes the configuration of Publishers and Subscribers using the OPC UA ClientServer model.
Figure 7 depicts a single OPC UA Application that acts as both a Server and a Publisher.
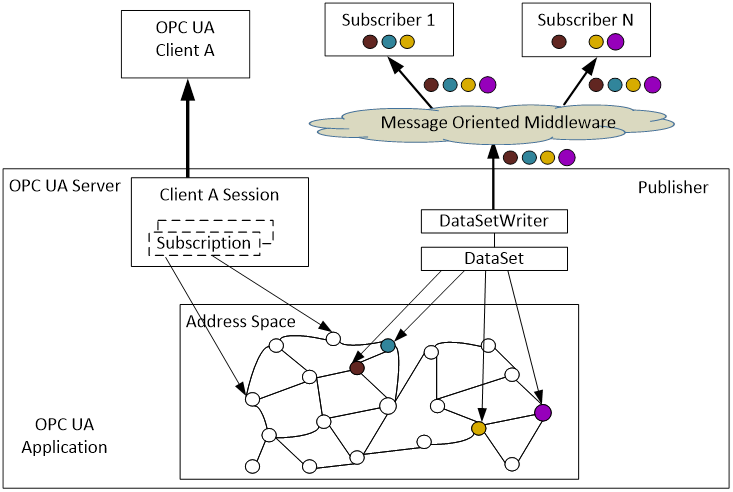
Figure 7 – Integrated ClientServer and PubSub models
Nevertheless, the PubSub communication does not require such a role dependency. I.e., Clients can be Publishers and Servers can be Subscribers. In fact, there is no necessity for Publishers or Subscribers to be either a Server or a Client to participate in PubSub communications.
OPC Unified Architecture is highly decentralized and is mostly concerned with the standardization of the independent interactions between UA Applications (i.e. between Clients and Servers and between Publishers and Subscribers). However, as the number of Applications in a given system grows, there are advantages to having some information centralized and interactions that are uniform among all Applications in a system. For example, if a system consists of one Server and one or more Clients, it is reasonable for the Server to be configured with the usernames and passwords of all users that can access the Server. If instead a system has hundreds of Servers, then it becomes unmanageable for each Server to independently store and maintain the usernames and passwords for all users of the system. For scenarios like this, the Unified Architecture includes certain centralized, global components to provide consistency and alleviate administration burden.
Ideally all Applications should work with all the defined global services when they are present in a system, but Applications that wish to utilize a particular global service need to be designed and built to do so. Keep in mind that the use of the global services in a system is always optional, so Applications should not be written to require their presence.
Discovery Services enable OPC UA Applications to locate other OPC UA Applications. For example, a Client application can use a Local Discovery Server (LDS) to find Servers on the local network. In a larger, more complex network, a Global Discovery Server (GDS) might be used to discover Servers across different network segments. The Client sends a Discovery request, and the Discovery Server responds with a list of available Servers and their connection details.
OPC UA defines three levels of dedicated Discovery Servers:
- Local Discover Servery (LDS)
- Local Discovery Server with multicast extension (LDS-ME)
- Global Discovery Server (GDS)
OPC 10000-12 describes how to use the Discovery services with dedicated Discovery Servers.
OPC UA Applications rely on Digital (X.509) Certificates as the basis for trust. In systems it is highly desirable to assign and manage the Certificates used by the Applications centrally as they all need periodic maintenance (e.g., updates to trust lists and revocation lists, Certificate renewals, etc.). OPC 10000-12 describes the centralize Certificate management services.
Some OPC UA Applications may need to access external entities (e.g. authorization services, Brokers, etc.) that require an identifier and a secret (called a “key credential”) to be presented for access. The assignment and management of key credentials can be centralized using the services described in OPC 10000-12.
The authorization services described in OPC 10000-12 allows OPC UA Applications to delegate the user authentication, user management and the assignment of users to roles (see OPC 10000-18) to an external central entity (e.g. an OAuth2 server).
Historically, devices with network connectivity have been allowed to communicate as soon as they are plugged into the network. For enhanced security, many networks will now require that physical network devices be uniquely identified and authorized to communicate on the network before any additional network based provisioning can be done. For example, the assignment of a Certificate using the Certificate management services as described in 5.7.3.
OPC 10000-21 defines a standard process for devices to be allowed to communicate on the network so that OPC UA Applications can be installed, updated, and provisioned with Certificates over the network.
In large systems unique well-known names are often assigned to a piece of equipment, a measurement, or a control artifact. Such user-assigned names are often referred to as “Tag Names”. When a Node in a Server represents an entity with an assigned Tag Name, the Tag Name is often used as the Name or Description attribute for that Node, but short of browsing all Nodes in all Servers, there is no easy way to find a Node with a particular Name or Description. OPC 10000-17 defines a mechanism to assign a well-known name called an “alias name” to any Node in a Server and a centralized way to look up that Node by its alias name.
OPC UA Publishers and Subscribers utilize a security key service (SKS) to secure the messages sent between them. The SKS is responsible for managing the keys used to publish or consume the secured messages. The SKS may be implemented directly by a Publisher, or it may be centralized where a single SKS is used by a group of Publishers and Subscribers in a system. The SKS is described in OPC 10000-14.