OPC UA is applicable to components in all industrial domains, such as industrial sensors and actuators, control systems, Manufacturing Execution Systems and Enterprise Resource Planning Systems, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Machine To Machine (M2M) and others. It is designed to enable seamless information exchange and to support command and control functionalities for diverse industrial processes, spanning from device-level communication to enterprise-wide and cloud integration.
OPC UA defines a common infrastructure model to facilitate this information exchange. OPC UA specifies the following:
- the information model to represent structure, behaviour and semantics;
- the message model to interact between applications;
- the communication model to transfer the data between end-points;
- the conformance model to guarantee interoperability between systems.
OPC UA is a platform-independent standard that enables various systems and devices to communicate securely and reliably. It employs mechanisms for authentication, encryption, and integrity checks to ensure the identity of OPC UA Applications as well as identification of users and protect against attacks.
Using the ClientServer model, OPC UA defines sets of Services that Servers provide, and it utilizes both OPC UA-defined and vendor-defined data types, along with flexible object models, to facilitate interoperability and dynamic information discovery by Clients. Supporting a variety of communication protocols and data encodings, such as TCP, HTTPS, WebSockets, XML/text, UA Binary, and JSON, OPC UA allows for trade-offs between portability and efficiency to suit different application requirements. Servers can provide access to both current and historical data, as well as Alarms and Events to notify Clients of important changes.
In addition to the ClientServer model, OPC UA also supports information transfer from Publishers to Subscribers using the PubSub model.
OPC UA provides a consistent, integrated AddressSpace and service model. This allows a single Server to integrate data, Alarms and Events, and history into its AddressSpace, and to provide access to them using an integrated set of Services. These Services also include an integrated security model.
OPC UA also allows Servers to provide Clients with type definitions for the Objects accessed from the AddressSpace. This allows Information Models to be used to describe the contents of the AddressSpace. OPC UA allows data to be exposed in many different formats, including binary structures and XML or JSON documents. The format of the data may be defined by OPC, other standard organizations or vendors. Through the AddressSpace, Clients can query the Server for the metadata that describes the format for the data. In many cases, Clients with no pre-programmed knowledge of the data formats will be able to determine the formats at runtime and properly utilize the data.
OPC UA adds support for many relationships between Nodes instead of being limited to just a single hierarchy. In this way, a Server may present data in a variety of hierarchies tailored to the way a set of Clients would typically like to view the data. This flexibility, combined with support for type definitions, makes OPC UA applicable to a wide array of problem domains. As illustrated in Figure 1, OPC UA is not targeted at just the SCADA, PLC and DCS interface, but also as a way to provide greater interoperability between higher level functions.
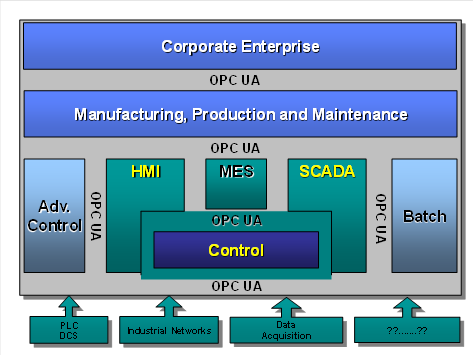
Figure 1 – OPC UA target applications
OPC UA is designed to provide robustness of published data. A major feature of all OPC servers is the ability to publish data and Event Notifications. OPC UA provides mechanisms for Clients to quickly detect and recover from communication failures associated with these transfers without having to wait for long timeouts provided by the underlying protocols.
OPC UA is designed to support a wide range of Servers, from plant floor PLCs to enterprise Servers. These Servers are characterized by a broad scope of size, performance, execution platforms and functional capabilities. Therefore, OPC UA defines a comprehensive set of capabilities, and Servers may implement a subset of these capabilities. To promote interoperability, OPC UA defines subsets, referred to as Profiles, to which Servers may claim conformance. Clients can then discover the Profiles of a Server, and tailor their interactions with that Server based on the Profiles. Profiles are defined in OPC 10000-7.
The OPC UA is layered to isolate the core design from the underlying computing technology and network transport. This allows OPC UA to be mapped to future technologies as necessary, without negating the basic design. Mappings and data encodings are described in OPC 10000-6. Several data encodings are defined:
- XML/text,
- UA Binary,
- JSON.
In addition, several protocols are defined:
- OPC UA TCP,
- HTTPS,
- WebSockets.
OPC UA Applications that support multiple transports and encodings will allow the end users to make decisions about trade-offs between performance and compatibility at the time of deployment, rather than having these trade-offs determined by the OPC vendor at the time of product definition.
OPC UA is designed as the migration path for OPC clients and servers that are based on Microsoft COM technology (OPC Classic). Care has been taken in the design of OPC UA so that existing data exposed by OPC COM servers (DA, HDA and A&E) can easily be mapped and exposed via OPC UA. Vendors may choose migrating their products natively to OPC UA or use external wrappers to convert from OPC COM to OPC UA and vice-versa. Each of the specifications of OPC Classic developed by OPC Foundation defined its own address space model and its own set of Services. OPC UA unifies the previous models into a single integrated address space with a single set of Services.
OPC UA PubSub opens new application fields for OPC UA. The following are some example uses for PubSub:
- Configurable peer to peer communication between controllers and between controllers and HMIs. The peers are not directly connected and do not even need to know about the existence of each other. The data exchange often requires a fixed time-window; it may be point-to-point or a multi-point connection.
- Asynchronous workflows. For example, an order processing application can place an order on a message queue or an enterprise service bus. From there it can be processed by one or more workers.
- Logging to multiple systems; for example, sensors or actuators can write logs to a monitoring system, an HMI, an archive application for later querying, and so on.
- Servers representing services or devices can stream data to applications hosted in the cloud. For example, backend servers, big data analytics for system optimization and predictive maintenance.
PubSub is not bound to a particular messaging system. Rather it can be mapped to various different systems as illustrated with two examples:
- PubSub with UDP may be well-suited in production environments for frequent transmissions of small amounts of data. It also allows data exchange in one-to-one and one-to-many configurations.
- The use of established messaging protocols (e.g. the ISO/IEC AMQP 1.0 protocol or the MQTT 5.0 protocol) with JSON data encoding supports the cloud integration path and readily allows handling of the information in modern stream and batch analytics systems.
OPC UA security is concerned with the authentication of Clients and Servers, the authentication of users, the integrity and confidentiality of their communications, and the verifiability of claims of functionality. It does not specify the circumstances under which various security mechanisms are required. That specification is crucial, but it is made by the designers of the system at a given site and may be specified by other standards.
Rather, OPC UA provides a security model, described in OPC 10000-2, in which security measures can be selected and configured to meet the security needs of a given installation. This model includes security mechanisms and parameters. In some cases, the mechanism for exchanging security parameters is defined, but the way that applications use these parameters is not. This framework also defines a minimum set of security Profiles that all OPC UA Applications support, a subset of which can be enabled in each installation. Profiles are defined in OPC 10000-7.
Application level security relies on a secure communication channel that is active for the duration of the application Session and ensures the integrity of all Messages that are exchanged. This means users need to be authenticated only once, when the application Session is established. The mechanisms for discovering Servers and establishing secure communication channels and application Sessions are described in OPC 10000-4 and OPC 10000-6. Additional information about the Discovery process is described in OPC 10000-12.
When a Session is established, the Client and Server applications negotiate a secure communications channel. Digital (X.509) Certificates are utilized to identify the Client and Server. The Server further authenticates the user and authorizes subsequent requests to access Objects in the Server.
OPC UA includes support for security audit trails with traceability between Client and Server audit logs. If a security-related problem is detected at the Server, the associated Client audit log entry can be located and examined. OPC UA also provides the capability for Servers to generate Event Notifications that report auditable Events to Clients capable of processing and logging them. OPC UA defines security audit parameters that can be included in audit log entries and in audit Event Notifications. OPC 10000-5 defines the data types for these parameters. Not all Servers and Clients provide all of the auditing features. Profiles, found in OPC 10000-7, indicate which features are supported.
OPC UA security complements the security infrastructure provided by most web service capable platforms.
Transport level security can be used to encrypt and sign Messages. Encryption and signatures protect against disclosure of information and protect the integrity of Messages. Encryption capabilities are provided by the underlying communications technology used to exchange Messages between OPC UA Applications. OPC 10000-7 defines the encryption and signature algorithms to be used for a given Profile.
The set of Objects and related information that the Server makes available to Clients is referred to as its AddressSpace. The OPC UA AddressSpace represents its contents as a set of Nodes connected by References.
Primitive characteristics of Nodes are described by Attributes. Attributes are the only elements of a Server that have data values. Data types that define attribute values may be simple or complex.
Nodes in the AddressSpace are typed according to their use and their meaning. NodeClasses define the metadata for the OPC UA AddressSpace. OPC 10000-3 defines the OPC UA NodeClasses.
The Base NodeClass defines Attributes common to all Nodes, allowing identification, classification, and naming. Each NodeClass inherits these Attributes and may additionally define its own Attributes.
To promote interoperability of Clients and Servers, the OPC UA AddressSpace is structured hierarchically with the top levels the same for all Servers. Although Nodes in the AddressSpace are typically accessible via the hierarchy, they may have References to each other, allowing the AddressSpace to represent an interrelated network of Nodes. The model of the AddressSpace is defined in OPC 10000-3.
Servers may subset the AddressSpace into Views to simplify Client access. Subclause 5.3.4.3 describes AddressSpace Views in more detail.
The OPC UA Object Model provides a consistent, integrated set of NodeClasses for representing Objects in the AddressSpace. This model represents Objects in terms of their Variables, Events and Methods, and their relationships with other Objects. OPC 10000-3 describes this model.
The OPC UA object model allows Servers to provide type definitions for Objects and their components. Type definitions may be subclassed. They also may be common or they may be system-specific. ObjectTypes may be defined by standards organizations, vendors, or end-users.
This model allows data, Alarms and Events, and their history to be integrated into a single Server. For example, Servers are able to represent a temperature transmitter as an Object that is composed of a temperature value, a set of alarm parameters, and a corresponding set of alarm limits.
The interface between Clients and Servers is defined as a set of Services. These Services are organized into logical groupings called Service Sets. Service Sets are discussed in clause 6 and specified in OPC 10000-4.
OPC UA Services provide two capabilities to Clients. They allow Clients to issue requests to Servers and receive responses from them. They also allow Clients to subscribe to Servers for Notifications. Notifications are used by the Server to report occurrences such as Alarms, data value changes, Events, and Program execution results.
OPC UA Messages may be encoded as text (XML or JSON) or in binary format for efficiency purposes. They may be transferred using multiple underlying transports, for example TCP or HTTP. Servers may provide different encodings and transports as defined by OPC 10000-6.
OPC UA ClientServer interaction requires a stateful model. The state information is maintained inside an application Session. Examples of state-information are Subscriptions, user credentials and continuation points for operations that span multiple requests.
Sessions are defined as logical connections between Clients and Servers. Servers may limit the number of concurrent Sessions based on resource availability, licensing restrictions, or other constraints. Each Session is independent of the underlying communications protocols. Failures of these protocols do not automatically cause the Session to terminate. Sessions terminate based on Client or Server request, or based on inactivity of the Client. The inactivity time interval is negotiated during Session establishment.