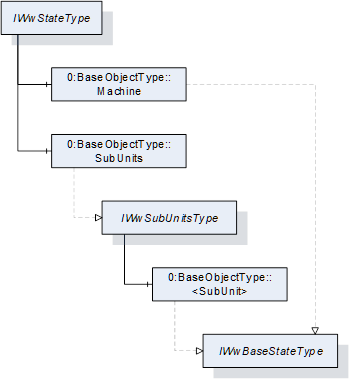
Figure 7 – Overview IWwStateType
The IWwStateType provides the machine state and is formally defined in Table 18.
Table 18 – IWwStateType Definiton
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
IWwStateType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the BaseInterfaceType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Machine |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
SubUnits |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
Woodworking SubUnits Monitoring |
|||||
|
Woodworking Unit State |
|||||
Each instance of an IWwStateType represents an instance of a machine state. In the simplest case, there is only the Machine Object. The SubUnits Object is used when a machine has multiple states. For example, a CNC machine can have several places where independent jobs are produced.
The Machine state does not summarize the SubUnits states. It does not have to be based on the SubUnits states. It is a decision of the machine manufacturer.
The KPI calculation has to be done individually based on the special machine instance and its states.
The units of the IWwStateType have additional subunits which are defined in Table 19.
Table 19 – IWwStateType Additional SubUnits
|
Source Path |
Reference |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
Machine |
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IWwBaseStateType |
|
|
|
|
SubUnits |
0:HasInterface |
ObjectType |
IWwSubUnitsType |
|
|
|