The following complex DataTypes have special mappings that are non-intuitive.
QualifiedName – The integer NamespaceIndex used in OPC UA is replaced by a NamespaceUri in AutomationML. In AutomationML, the full URI is always used, and there is never an index. Wherever NamespaceUri is used, the AutomationML datatype is always xs:anyURI.
LocalizedText – An xs:string AttributeType with contained attributes that derive from AutomationMLBaseAttributeTypeLib/LocalizedAttribute and follows the standard AutomationML rules.
NodeId – NodeIds in running OPC UA Servers are represented as an ID and a NamespaceIndex. In order to make reference to Nodes in the offline AutomationML file, a more flexible way to reference a Node is needed, both directly and indirectly, possibly long before the real Node is present in a running Server. The NodeId AML AttributeType is defined with four top-level attributes, as shown in Figure A.6
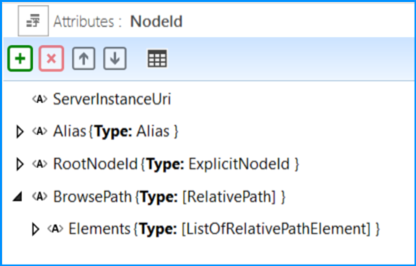
Figure A.6 – NodeId AttributeType definition
ServerInstanceUri – an optional attribute used to indicate the ServerInstanceUri of the Server containing the NodeId. If empty or missing, the context should be assumed to be the “local” Server. The type is xs:anyURI.
Alias – An indirect reference to a NodeId to be resolved by an alias Server at runtime. The Alias attribute type is defined in A.2.3.
RootNodeId – An ExplicitNodeId from which to traverse the BrowsePath in case the BrowsePath is not empty. The ExplicitNodeId attribute type is defined in A.2.3. If the BrowsePath is empty or not present, the node is identified by the RootNodeId or the NodeId resolved from the alias.
BrowsePath – An optional RelativePath to follow from either the RootNodeId or the NodeId resolved from the Alias. See the definition of the RelativePath structure in OPC 10000-4.
If a BrowsePath is present and not empty in a NodeId, then the RootNodeId should be a well-known NodeId like the NodeId of the Root Object (NS=UA, i=84) or the NodeId of the FxRoot Object (NS=UAFX, i=71).
Either the Alias attribute or the RootNodeId attribute shall be present. If both are present, the Alias attribute shall be ignored.
A typical use case for the BrowsePath in a Descriptor is to reference the corresponding variable in the AddressSpace from the PublishedData of a PublishedDataSet if the variable does not contain a real NodeId. The RootNodeId attribute of the NodeId AttributeType refers to the starting point of the BrowsePath, and the Elements of the BrowsePath direct to the target. Figure A.7 shows an example.

Figure A.7 – Example for the use of the BrowsePath
The formal definition of the BrowsePath is given in Table A.3.
Table A.3 – Formal definition of the BrowsePath
|
0 |
ReferenceTypeId |
NamespaceUri |
NumericId |
35 |
IncludeSubTypes |
False |
IsInverse |
False |
TargetName |
NamespaceUri |
Name |
ME_BottleMachineProject |
|
1 |
ReferenceTypeId |
NamespaceUri |
NumericId |
47 |
IncludeSubTypes |
False |
IsInverse |
False |
TargetName |
NamespaceUri |
Name |
FunctionalEntities |
|
2 |
ReferenceTypeId |
NamespaceUri |
NumericId |
35 |
IncludeSubTypes |
False |
IsInverse |
False |
TargetName |
NamespaceUri |
Name |
BottleMachineFE |
|
3 |
ReferenceTypeId |
NamespaceUri |
NumericId |
47 |
IncludeSubTypes |
False |
IsInverse |
False |
TargetName |
NamespaceUri |
Name |
OutputData |
|
4 |
ReferenceTypeId |
NamespaceUri |
NumericId |
35 |
IncludeSubTypes |
False |
IsInverse |
False |
TargetName |
NamespaceUri |
Name |
BottleIdOut |
ExpandedNodeId – ExpandedNodeId has the same definition as NodeId since NodeId can already express an ExpandedNodeId as well.
PortableNodeId – The identifier field of PortableNodeId has the same definition as NodeId. The NamespaceUri information of the PortableNodeId is already present in the identifier and, therefore, redundant.
RelativePathElement – This attribute type is created using the standard mapping rules, except the ReferenceTypeId attribute is of type ExplicitNodeId defined in A.2.3, rather than NodeId. Table A.4 indicates the default value to use if the indicated attribute is missing.
Table A.4 – Default Values for RelativePathElement
|
attribute |
Default value used if attribute is missing |
|
ReferenceTypeId |
nsu=http://opcfoundation.org/UA/;i=22 (i.e. HierarchicalReferences) |
|
IsInverse |
FALSE |
|
IncludeSubtypes |
TRUE |
Guid – An xs:string AttributeType where the string shall be formatted in the standard notation for UUIDs per ISO/IEC 9834-8.
Byte – Where the UA DataType Byte is used in builtInType fields, the AML AttributeType is changed to derive from ATL_OpcAmlMetaModel/BuiltInType with constraints to match the enumeration as shown in Figure A.8.
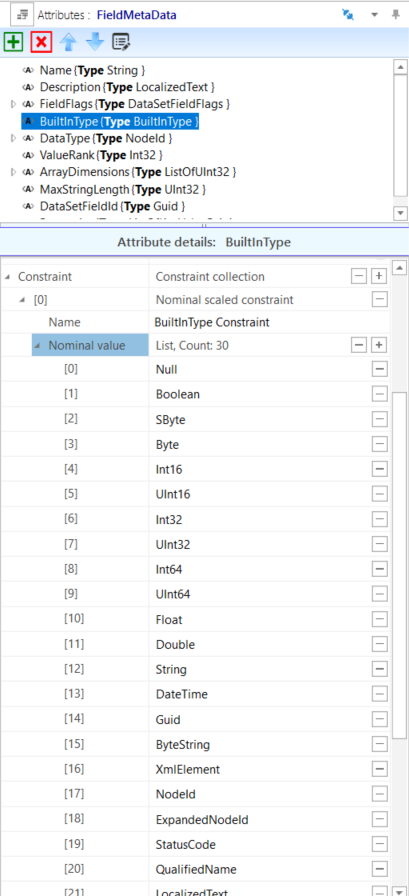
Figure A.8 – BuiltInType enumeration
IntegerId – Where the UA DataType IntegerId is used in fields named “AttributeId”, the AML AttributeType is changed to derive from ATL_OpcAmlMetaModel/AttributeId with constraints to match the enumeration as shown in Figure A.9.
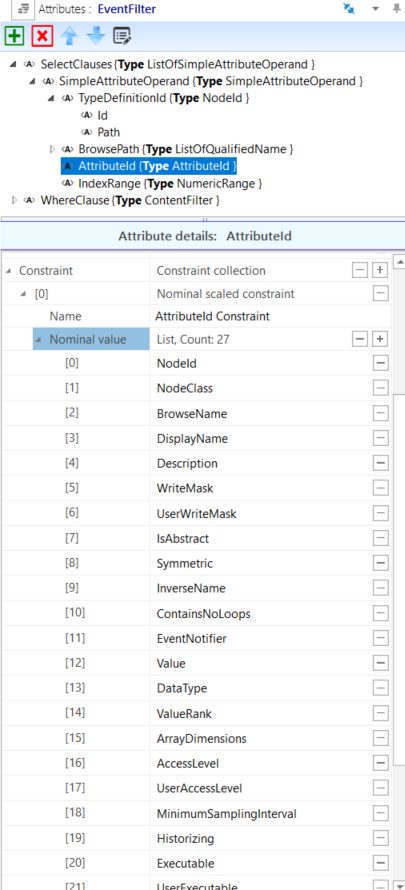
Figure A.9 – AttributeId enumeration