The ConnectionConfigurationSetType is an ObjectType representing one or more Connection configurations. Connections are grouped in a set, for example, to allow sharing communication model configurations by multiple Connections; see 5.5.6.2.3 and 5.5.6.2.4 for appropriate use cases.
ConnectionConfigurationSets are generated and deployed to the ConnectionManager (see Figure 11, label 3). The ConnectionManager may expose the ConnectionConfigurationSets in its AddressSpace.
A ConnectionConfigurationSet exposes diagnostic information about the Connections as part of its Information Model. It also allows Connection configurations to be available for modification by standard Clients (see Figure 11, label 4), and it could provide an interface to trigger the processing of such Connection configurations.
A ConnectionConfigurationSet may only be modified by a standard Client as follows:
- The SelectionListType (see OPC 10000-5) is used to indicate where support for modifications is required. This type allows the generator of the ConnectionConfigurationSet to provide a list of Selections and an optional description of them. If the optional RestrictToList is set to TRUE, a Client changing the Variable is restricted to the provided Selections. If set to FALSE or missing, a Client may change the Variable to any value, including one of the Selections. For example, the value of PublishingInterval may be restricted to the values 2 ms, 4 ms, and 8 ms by adding these values to Selections and setting RestrictToList to TRUE. If the value is fixed, the SelectionListType value shall be the fixed value, the Selections list shall be populated with the same fixed value, and the RestrictToList shall be TRUE.
- Data that has been set to ReadWrite for specific users or in general. This can be determined by examining the AccessLevel and UserAccessLevel Attributes of the data.
With these mechanisms, the generator of the ConnectionConfigurationSet can specify and restrict the allowed changes.
For an overview of the ConnectionConfigurationSetType and its related types, see Figure 35. For examples, see Annex E.
The ConnectionConfigurationSetType is illustrated in Figure 37.
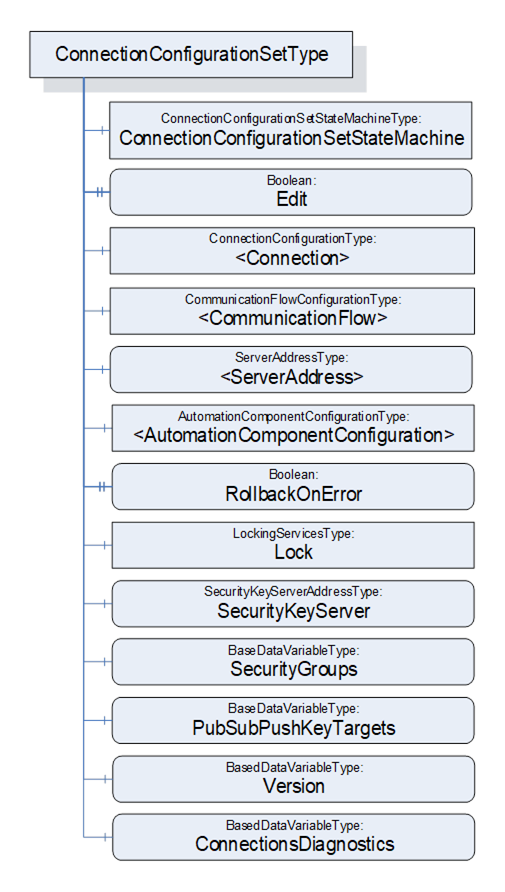
Figure 37 – ConnectionConfigurationSetType illustration
The ConnectionConfigurationSetType is formally defined in Table 89 and Table 90.
Table 89 – ConnectionConfigurationSetType definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
4:ConnectionConfigurationSetType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5 |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
4:ConnectionConfigurationSetStateMachine |
|
4:ConnectionConfigurationSetStateMachineType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
4:Edit |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
|
4:HasConnectionConfiguration |
Object |
4:<Connection> |
|
4:ConnectionConfigurationType |
MP |
|
4:HasCommunicationFlowConfiguration |
Object |
4:<CommunicationFlow> |
|
4:CommunicationFlowConfigurationType |
MP |
|
4:HasServerAddress |
Variable |
4:<ServerAddress> |
4:ServerAddressDataType |
4:ServerAddressType |
MP |
|
4:HasAutomationComponentConfiguration |
Object |
4:<AutomationComponentConfiguration> |
|
4:AutomationComponentConfigurationType |
MP |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
4:RollbackOnError |
0:Boolean |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
5:Lock |
|
5:LockingServicesType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
4:SecurityKeyServer |
4:SecurityKeyServerAddressDataType |
4:SecurityKeyServerAddressType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
4:SecurityGroups |
0:SecurityGroupDataType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
4:PubSubKeyPushTargets |
0:PubSubKeyPushTargetDataType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
4:Version |
0:UInt32 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
4:ConnectionsDiagnostics |
4:ConnectionDiagnosticsDataType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O, RO |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
UAFX ConnectionManager Base |
|||||
Table 90 – ConnectionConfigurationSetType additional references
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
IsForward |
TargetBrowsePath |
||
|
4:<ServerAddress> |
4:ToAutomationComponentConfiguration |
True |
4:<AutomationComponentConfiguration> |
||
|
4:<AutomationComponentConfiguration> |
4:ToConnectionEndpointConfiguration |
True |
|
||
|
4:<AutomationComponentConfiguration> |
4:ToConnectionEndpointConfiguration |
True |
|
ConnectionConfigurationSetStateMachine contains the current State of this ConnectionConfigurationSet. See 6.9 for a formal definition of the state machine.
If Edit is present, the ConnectionConfigurationSet supports editing. If Edit is TRUE, the ConnectionConfigurationSet is currently being edited by a Client. See 6.7.4 on editing a ConnectionConfigurationSet.
<Connection> represents one or more instances of ConnectionConfigurationType, which defines Connection configurations to be established. For a formal definition, see 6.10.
<CommunicationFlow > represents one or more instances of CommunicationFlowConfigurationType, which defines communication model-specific configuration to apply to a Connection. For a formal definition, see 6.13. There may be fewer instances of this type than ConnectionConfigurations.
<ServerAddress> represents one or more instances of ServerAddressType, which defines addressing information for AutomationComponents. For a formal definition, see 9.2. There may be fewer instances of this type than ConnectionConfigurations.
<AutomationComponentConfiguration> represents one or more AutomationComponents. In addition, it holds the parameters used for Asset verification. For a formal definition, see 6.14.
RollbackOnError indicates the behaviour that should be followed when there is an error with Connection establishment. If this Property is TRUE and an error occurs during the Connection establishment sequence, establishing the set shall stop, and all established Connections that are part of this set shall be closed (see 6.7.3.2).
It is recommended that the system integrator Client use the well-known Role ConfigureAdmin, as defined in Clause 5.9, for accessing this Object. It is recommended that the modifiable content of the ConnectionConfigurationSet has the write privilege for the well-known Role ConfigureAdmin as defined in Clause 5.9.
Lock is an instance of LockingServicesType, defined in OPC 10000-100, which provides the basic locking functionality. A ConnectionConfigurationSet that is not in editable mode shall be locked to the ConnectionManager and blocked from any changes (the Client is set to the NodeId of the ConnectionManager, and the user is set to “CM”). A Client can call the EditConnectionConfigurationSets Method on a ConnectionManager to release the Lock from the ConnectionManager and assign it to the Client that issued the EditConnectionConfigurationSets Method Call (for additional details, see 6.7.4).
SecurityKeyServerAddress defines the location of the SKS to be used for PubSub security configuration of this ConnectionConfigurationSet. For a formal definition, see 9.3.
NOTE 1 Depending on the environment, the list could contain the address of a GDS acting as SKS, the address of the ConnectionManager itself if providing SKS functionality, or other SKS within the network.
SecurityGroups and PubSubPushKeyTargets define the configuration information to be applied to the SKS for PubSub security configuration of the ConnectionConfigurationSet.
NOTE 2 For an overview of how to configure the SKS, see E.5.
Version shall be a monotonically increasing number. It shall be incremented by 1 on each change to a given ConnectionConfigurationSet, no matter the source of the change. Its ServerTimestamp shall be set to the time of the change. When a ConnectionConfigurationSet is added or replaced (i.e., new NodeId), Version shall be set to 1. Changes could occur via the CloseAndUpdate Method defined in F.3.3, via the EditConnectionConfigurationSets Method, or via vendor-specific means.
NOTE 3 Version allows a Client to detect changes on a ConnectionConfigurationSet due to editing. Clients could detect a replacement of a ConnectionConfigurationSet by having a different NodeId.
ConnectionsDiagnostics provides an array of diagnostic information for Connections included in this ConnectionConfigurationSet. There shall be one element in this array for each <Connection > instance in the ConnectionConfigurationSet. The Name field of the ConnectionDiagnosticsType provides a linkage between an array element and a specific <Connection >. The value of this Variable shall be updated every time the ConnectionManager finishes processing the ConnectionConfigurationSet. If a ConnectionManager monitors ConnectionEndpoints, it shall also update the value when it acquires new information about the status of the Connections. See 10.19 and 10.20 for details on how to update the value.
The ToAutomationComponentConfiguration Reference is used to link a ServerAddress to AutomationComponentConfiguration (see 6.14). The ServerAddress provides the Connection information to address the referenced AutomationComponent.
The ToConnectionEndpointConfiguration Reference is used to link an AutomationComponentConfiguration to ConnectionEndpointConfigurations (see 6.11).
The ToOutboundFlow Reference is used to link a ConnectionEndpointConfiguration to a PubSubCommunicationFlowConfiguration (see 6.13.3). This Reference defines the PubSub- specific configuration to be used for the transmission of output data related to this ConnectionEndpoint. It shall be present if an outbound PubSub flow is configured.
The ToInboundFlow Reference is used to link a ConnectionEndpointConfiguration to a SubscriberConfiguration (see 6.13.3.3). This Reference defines the PubSub- specific configuration to be used for the reception of input data related to this ConnectionEndpoint. It shall be present if an inbound PubSub flow is configured.
A ConnectionEndpointConfiguration shall have at most one ToOutboundFlow and at most one ToInboundFlow Reference.
The References used to link a ConnectionEndpointConfiguration to Client Server-specific communication configuration will be defined in a later version of this document.
NOTE 4 For an overview of how to configure the various Connection types, see Annex E.