The OperationStateMachineType provides an abstract state machine for operation. The state machine can be used for entities whose states can be represented by Idle, Ready or Executing and which can be started and stopped.
At the system and task control levels, concrete state machine types are derived from the OperationStateMachineType. The states of these state machines can be further enhanced with Substate machines.
The overview of the state machine with all transitions is shown in Figure 19.
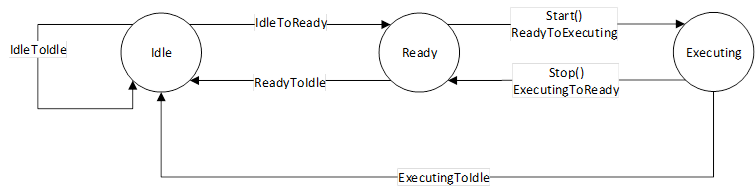
Figure 19 – OperationStateMachine.
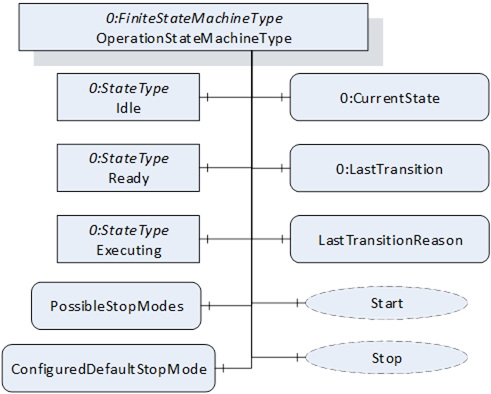
Figure 20 – The OperationStateMachineType
Figure 20 shows the OPC UA representation of the OperationStateMachineType, the transitions between the states have not been shown for the sake of simplicity. The OperationStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 65.
Table 27 – OperationStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
OperationStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the FiniteStateMachineType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransitionReason |
0:Int16 |
0:MultiStateValueDiscreteType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
PossibleStopModes |
0:EnumValueType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ConfiguredDefaultStopMode |
0:Int16 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Idle |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Ready |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Executing |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToExecuting |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Stop |
|
|
O |
|
Inherited from FiniteStateMachineType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransition |
0:LocalizedText |
0:FiniteTransitionVariableType |
M |
|
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
TransitionEventType |
|
|
O |
The states of the OperationStateMachineType are described in Table 28.
The component Variables of the OperationStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 30.
Table 28 – OperationStateMachineType State Descriptions
|
StateName |
Description |
|
Idle |
Entity is not in a condition to start execution. |
|
Ready |
Entity is in a condition to start execution. |
|
Executing |
Entity is in a condition of execution. |
The Variable LastTransitionReason provides the reason for the LastTransition. The EnumValue and ValueAsText of this 0:MultiStateValueDiscreteType are described in Table 29. This specification does not define an explicit error state. The LastTransitionReason indicates if a state change was caused due to an error.
Table 29 – Values for LastTransitionReason
|
EnumValue |
ValueAsText |
Description |
|
0 |
Unknown |
Caused by an unknown reason |
|
1 |
External |
Caused by external operation |
|
2 |
Direct |
Caused by direct operation |
|
3 |
System |
Caused by system specific behaviour |
|
4 |
Error |
Caused by an error |
|
5 |
Application |
Caused explicitly by end user program logic |
The component Variables of the OperationStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in Table 30.
Table 30 – OperationStateMachineType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
||
|
[ {"Value":0,"DisplayName":"Unknown","Description":"Caused by an unknown reason"}, {"Value":1,"DisplayName":"External","Description":"Caused by external operation"}, {"Value":2,"DisplayName":"Direct","Description":"Caused by direct operation"}, {"Value":3,"DisplayName":"System","Description":"Caused by system specific behavior"}, {"Value":4,"DisplayName":"Error", "Description": "Caused by an error"}, {"Value":5,"DisplayName":"Application","Description":"Caused explicitly by end user program logic"} ] |
|
LastTransitionReason EnumValues 1 and 2 describe where an operation was initiated, which reasoned the last transition. External means that the operation was initiated by a control station, which is not part of the robot system, e.g a cell PLC. Direct means that the operation was initiated by a control station, which is part of the robot system, e.g. the teach pendant.
The Variable PossibleStopModes is an array of EnumValueType, which contains a list of supported stop modes (see Table 31).
Table 31 – PossibleStopMode Array Values
|
Nr. |
Stop Mode |
Description |
|
1 |
OnPath |
Stop program execution in a controlled manner along the programmed path. |
|
2 |
EndOfCycle |
Stop program execution when the current production cycle has been finished. |
|
3 |
ProcessStop |
Application dependent stop instruction that stops program execution at a "favourable" point for the application, e.g. at the end of a paint stroke or sealing bead. |
|
4 |
QuickStop |
This stop is performed by ramping down motion as fast as possible using optimum motor performance. The robot may not stay on the path. |
|
5 |
EndOfInstruction |
This stop can be used to stop the program execution when the current instruction is completed. |
|
>=1000 |
|
Reserved for other OPC UA Companion Specifications |
|
>=2000 |
|
Used for vendor specific stop modes |
Table 32 – OperationStateMachineType Attribute values for child nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
Description Attribute |
|
PossibleStopModes |
[ {"Value": 1, "DisplayName": "OnPath", "Description": "Stop program execution in a controlled manner along the programmed path"}, {"Value": 2, "DisplayName": "EndOfCycle", "Description": "Stop program execution when the current production cycle has been finished"}, {"Value": 3, "DisplayName": "ProcessStop", "Description": "Application dependent stop instruction that stops program execution at a favourable point for the application, e.g. at the end of a paint stroke or sealing bead"}, {"Value": 4, "DisplayName": "QuickStop", "Description": "This stop is performed by ramping down motion as fast as possible using optimum motor performance. The robot may not stay on the path”}, {"Value": 5, "DisplayName": "EndOfInstruction", "Description": "This stop can be used to stop the program execution when the current instruction is completed"} ] |
|
The Variable ConfiguredDefaultStopMode is an integer, which contains the value of the configured stop mode for this system. This shall be one of the values in the PossibleStopModes array.
The Variable LastTransition, inherited from the FiniteStateMachineType, is defined as mandatory in the OperationStateMachineType.
The transitions of the OperationStateMachineType are described in Table 33.
Table 33 – OperationStateMachineType Transition Descriptions
|
TransitionName |
Description |
|
IdleToReady |
Changes from Idle to Ready. |
|
IdleToIdle |
Changes from Idle to Idle. |
|
ReadyToIdle |
Changes from Ready to Idle. |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
Changes from Ready to Executing. |
|
ExecutingToReady |
Changes from Executing to Ready. |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
Changes from Executing to Idle. |
The components of the OperationStateMachineType have additional references which are defined in Table 69.
Table 34 – OperationStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
IdleToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
IdleToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
0:ToState |
True |
Executing |
0:HasCause |
True |
Start |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
0:HasCause |
True |
Stop |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
The component Variables of the OperationStateMachine have additional Attributes defined in the table below.
Table 35 – OperationStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Start (
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The Start Method is called by a Client to start execution of the entity which is represented by the state machine.
Table 36 – Start Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK Values > 0 are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards. Values < 0 shall be used for application-specific errors. |
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 37.
Table 37 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method cannot be executed because a required resource is locked. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to execute this Method. |
The Start Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in table below.
Table 38 – Start Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Start |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
0:Mandatory |
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Stop (
[in]0:Int64 StopMode
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The Stop Method is called by a Client to stop execution of the entity which is represented by the state machine.
Table 39 – Stop Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
StopMode |
provides a way to differentiate between different stop modes. This parameter should correspond to one of the values in the PossibleStopModes array. |
|
Status |
0 – OK Values > 0 are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards. Values < 0 shall be used for application-specific errors. |
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 40.
Table 40 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The Stop Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in the table below.
Table 41 – Stop Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Stop |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |