The SystemOperationStateMachineType represents the behaviour of a controller at the system level and can be used for monitoring and for external or direct operation. In robot systems, a distinction is typically made between external and direct operation, depending on the OperationalMode (see 7.7.2).
If the system takes a significant amount of time to transition from the Idle State to the Ready State, the Idle State can be extended by the sub state machine IdleSubstateMachine. Alternatively, a vendor/application specific Substate machine may also be used.
For certain stop modes, the transition from the Executing State to the Ready State can take a significant amount of time. In such cases, the Executing State can be extended by the sub state machine ExecutingSubstateMachine. Alternatively, an application or vendor specific Substate machine may also be used.
The Substate machines enable the client to get more information during the transition.
The SystemMonitor Server Facet supports monitoring of the activities performed by the operator or system internally. (e.g. monitor condition changes and base causes) The SystemOperation Server Facet extends on the SystemMonitor Server Facet and adds support to operate the system.
The overview of the SystemOperationStateMachine with the IdleSubstateMachine as Substate machine of Idle State and the ExecutingSubstateMachine as Substate machine of Executing State with all transitions is shown in Figure 8.
The transitions in this state machine can occur due to internal processes of the system or they may be triggered by a method call. In case the transition is triggered by a method call, the transition might not occur immediately (e.g. it will be delayed until internal conditions are met).
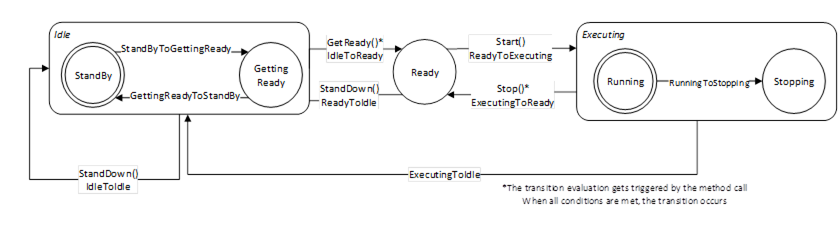
Figure 22 – SystemOperationStateMachine.
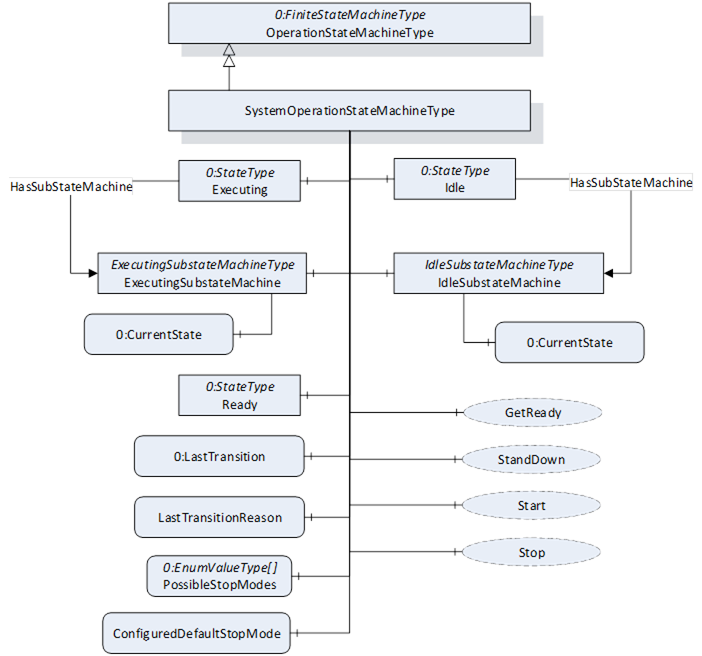
Figure 23 – SystemOperationStateMachineType.
The SystemOperationStateMachineType is formally defined in Table 45.
Table 45 – SystemOperationStateMachineType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SystemOperationStateMachineType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the OperationStateMachineType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleSubstateMachine |
|
IdleSubstateMachineType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingSubstateMachine |
|
ExecutingSubstateMachineType |
O |
|
Inherited from OperationStateMachineType |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransitionReason |
0:Int16 |
0:MultiStateValueDiscreteType |
M |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
PossibleStopModes |
0:EnumValueType[] |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
ConfiguredDefaultStopMode |
0:Int16 |
0:BaseDataVariableType |
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Idle |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Ready |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
Executing |
|
0:StateType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToReady |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ReadyToExecuting |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
ExecutingToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
IdleToIdle |
|
0:TransitionType |
|
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Start |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
Stop |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
StandDown |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Method |
GetReady |
|
|
O |
|
0:HasComponent |
Variable |
LastTransition |
0:LocalizedText |
0:FiniteTransitionVariableType |
M |
|
0:GeneratesEvent |
ObjectType |
TransitionEventType |
|
|
O |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob System Monitor |
|||||
|
Rob System Operation |
|||||
|
Rob System Events |
|||||
|
Rob System Idle Substate |
|||||
|
Rob System ExecutingSubstate |
|||||
The Idle State of SystemOperationStatemachineType has additional subcomponents which are defined in Table 46
Table 46 – SystemOperationStateMachineType Additional Subcomponents
|
Source Path |
Reference |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Idle |
0:HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
IdleSubstateMachine |
|
IdleSubstateMachineType |
O |
|
Executing |
0:HasSubStateMachine |
Object |
ExecutingSubstateMachine |
|
ExecutingSubstateMachineType |
O |
To acknowledge the state changes in a system the Conditions within the Conditions folder of SystemOperationType must be taken under consideration. A client might need to acknowledge them so that the robot system can be activated. (e.g. operational mode change requires acknowledgement to start the system)
Table 47 – SystemOperationStateMachineType State Descriptions
|
StateName |
Description |
|
Idle |
The system is available, but cannot be started because preparation is needed |
|
Ready |
The system is ready to start execution. |
|
Executing |
The system is executing. Typically, at least one task control is executing, however it is a system specific behaviour. |
Table 48 – SystemOperationStateMachine Transition Descriptions
|
TransitionName |
Description |
|
IdleToIdle |
Occurs in response to StandDown(), internal events, or when preparations to get the system ready are unsuccessful. |
|
IdleToReady |
Occurs in response to GetReady() or internal events, when preparations to get the system ready are successful. |
|
ReadyToIdle |
Occurs in response to StandDown() or internal events. |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
Occurs in response to Start() or internal events. |
|
ExecutingToReady |
Occurs in response to Stop() or internal events when the system has come to a stop |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
Occurs in response to internal events (typically in case of an error) |
The components of the SystemOperationStateMachineType have additional references which are defined in the table below.
Table 49 – SystemOperationStateMachineType Additional References
|
SourceBrowsePath |
Reference Type |
Is Forward |
TargetBrowsePath |
|
IdleToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasCause |
True |
StandDown |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
IdleToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Idle |
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
0:HasCause |
True |
GetReady |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
|
|
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
|
|
0:HasCause |
True |
StandDown |
|
|
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ReadyToExecuting |
0:FromState |
True |
Ready |
0:ToState |
True |
Executing |
0:HasCause |
True |
Start |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToIdle |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Idle |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
|
ExecutingToReady |
0:FromState |
True |
Executing |
0:ToState |
True |
Ready |
0:HasCause |
True |
Stop |
0:HasEffect |
True |
TransitionEventType |
The component Variables of the SystemOperationStateMachineType have additional Attributes defined in the table below.
Table 50 – SystemOperationStateMachineType Attribute values for child Nodes
|
BrowsePath |
Value Attribute |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
4 |
||
|
5 |
||
|
6 |
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Start (
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The Start Method is called by a Client to start execution of the system that is represented by the state machine. If the method is successfully called, the method should return with a Good or Uncertain result code.
The Start Method allows an authorized Client to command the system to the Executing State.
Table 51 – Start Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the Method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 52
Table 52 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The system level operation succeeded |
|
Uncertain |
The value is uncertain. A concrete reason is defined in the Status Output-Argument. |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The Method could not be called due to an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The Start Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 53.
Table 53 – Start Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Start |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob System Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
Stop (
[in]0:Int64 StopMode
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The Stop Method allows an authorized Client to command the system to stop executing and leave the Executing state.
In conjunction with the usage of this method, the transient states can be expressed with Substate machines within the Executing state (e.g. the ExecutingSubstateMachine in 7.14)
The input argument StopMode must be either 0 or one of those listed in the PossibleStopModes Variable (see Table 31). If not, then a Bad_InvalidArgument Result Code is returned.
Table 54 – Stop Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
StopMode |
must either be 0 or one of those listed in the PossibleStopModes Variable (see Table 31) |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the Method call <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 55
Table 55 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The system level operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The system level operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The input argument is invalid |
The Stop Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 56
Table 56 – Stop Method AddressSpace definition.
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Stop |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:InputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob System Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
GetReady (
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The GetReady Method allows an authorized Client to request the system to transition from the Idle state to the Ready state. Internally the system prepares to get started in the next step (e.g. switching on the intermediate circuit). If the internal preparations for this transition are successful, the system will transition from Idle to Ready. If the internal preparations are unsuccessful then the IdleToIdle transition occurs.
In conjunction with the usage of this method, the transient states can be expressed with Substate machines within the Idle state (e.g. the IdleSubstateMachine in 7.13)
Table 57 – GetReady Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the Method call 3 – E_ActiveAlarm – An Active Alarm prevents the system start 4 – E_AcknowledgeRequired – Condition needs to be acknowledged <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 58
Table 58 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The system level operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The system level operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The Start Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 59.
Table 59 – GetReady Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetReady |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob System Operation |
|||||
The signature of this Method is specified below.
Signature
StandDown (
[out]0:Int32Status
);
The StandDown method allows an authorized Client to request the system to:
- transition from the Ready state to the Idle state or
- cancel an ongoing preparation of the system and causes the IdleToIdle transition.
Table 60 – StandDown Method Arguments
|
Argument |
Description |
|
Status |
0 – OK – Everything is OK 1 – E_SystemState – The system is not in correct state for this operation 2 – E_UnexpectedError – Unexpected Error during the Method call <0 – shall be used for vendor-specific errors. >0 – are reserved for errors defined by this and future standards |
In conjunction with the usage of this method, the transient states can be expressed with Substate machines within the Idle state (e.g. the IdleSubstateMachine in 7.13)
The possible Method result codes are formally defined in Table 61.
Table 61 – Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Good |
The system level operation succeeded |
|
Bad_InternalError |
The system level operation failed because of an internal error |
|
Bad_ResourceUnavailable |
The Method is locked by another Client/Clientgroup |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The caller is not allowed to call this Method. |
The StandDown Method representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 62.
Table 62 – StandDown Method AddressSpace definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
StandDown |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
0:OutputArguments |
0:Argument[] |
0:PropertyType |
M |
|
ConformanceUnits |
|||||
|
Rob System Operation |
|||||