There are different standards for Device Authentication which do not meet the complete set of requirements described in this specification. However, an OwnerOperator may have reasons to use one of these other mechanisms (i.e. they have the infrastructure and wish to reuse it).
In some cases, the OwnerOperator have a complete solution that manages the entire life cycle of the Certificates installed on the Device. In these cases, the onboarding mechanisms described in this specification are not used and it is responsibility of the alternate mechanism to issue and renew Application Instance Certificates to all Applications running on the Device and to maintain their Trust Lists.
In other cases, the alternate mechanism will only authenticate the Device and install a single Certificate. In these cases, the mechanism described in this specification takes over and manages the life cycle of Application Instance Certificates and the Trust Lists. This pull management version of this case is illustrated in Figure 8.
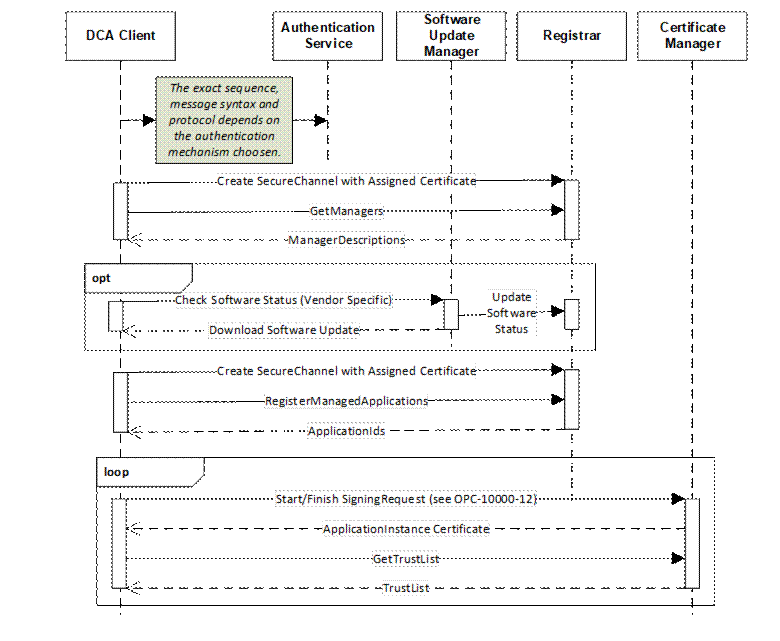
Figure 8 – Alternate Authentication Models with Pull Management
In this case, it is responsibility of the Authentication Service to verify the authenticity of the Device and supply a Certificate to the DCA that is trusted by the Registrar, SoftwareUpdateManager and CertificateManager. This Certificate shall also contain a ProductInstanceUri (see 5.2) which uniquely identifies the Device.
If a software update check is required the DCA needs the Endpoint for the SoftwareUpdateManager. If the Authentication Service cannot supply this Endpoint, the DCA can get it from the Registrar which may be discovered with mDNS and then calling the GetManagers Method. Once any software update is completed, the DCA calls RegisterManagedApplications on the Registrar to get permission to request Certificates and TrustLists on behalf of those Applications.
The location of the CertificateManager is returned by the GetManagers Method. The DCA can use the mechanisms defined in OPC 10000-12 to request the Certificates and TrustLists for all of the Applications which it is authorized to manage.
The Authentication Service may also provide a DCA Certificate to a Server which would then annouce its presence via mDNS. The Registrar would then follow the process described in 7.3 to discover the Applications managed by the DCA and providing their Certificates and TrustLists.