The MachineToolIdentificationType of the Machine Tools information model holds static data which shall uniquely identify a machine tool among a pool of the machine tool operating entity. It is a subtype of the 3:MachineIdentificationType defined in OPC 40001-1, so it inherits all InstanceDeclarations specified there.
The MachineToolIdentificationType is formally defined in Table 12.
Table 12 – MachineToolIdentificationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
MachineToolIdentificationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 3:MachineIdentificationType defined in OPC 40001-1 i.e. inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasComponent |
Object |
SoftwareIdentification |
|
0:BaseObjectType |
O |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
MachineTool Identification SoftwareInformation |
|||||
|
MachineTool Identification Machinery additional |
|||||
SoftwareIdentification contains a list of instances of the SoftwareIdentificationType (see Table 14). This list contains the machine tool’s software identification information. It allows to add multiple software items, e.g., one for each of PLC, NC and HMI.
2:SoftwareRevision inherited from the 3:MachineIdentificationType shall contain an overall software patch level of the machine tool. Individual software revision numbers may be given using SoftwareIdentification.
For the 2:DeviceClass inherited from the 3:MachineIdentificationType, the values in Table 13 should be used but might be extended by specifications using OPC 40501-1. The most appropriate value, based on the main machine tool technology shall be chosen.
Additive manufacturing machines are not defined in the source mentioned. They include every additive technology currently available.
Table 13 – DeviceClasses for Machine Tools
|
DeviceClasses for Machine Tools |
|||
|
Additive manufacturing machine |
Forming machine |
Mill-turn machining centre |
Shaping machine |
|
Additive manufacturing hybrid machine |
Gear cutting machine |
Nibbling machine |
Shearing machine |
|
Beading machine |
Grinding machine |
Other |
Slotting machine |
|
Bending machine |
Hammer machine |
Planer |
Straightening machine |
|
Broaching machine |
Hardening machine |
Planing machine |
Testing machine |
|
Copy milling machine |
Honing machine |
Plasma cutting machine |
Thermal deburring machine (TEM) |
|
Curling machine |
Lapping machine |
Polishing machine |
Transfer machine |
|
Deburring machine |
Laser ablation machine |
Press |
Trimming machine |
|
Drawing machine |
Laser cutting machine |
Profiling machine |
Turn-mill machining centre |
|
Drilling / Boring machine |
Laser drilling machine |
Punch laser machine |
Turning machine |
|
Electrical discharge machine (EDM) |
Laser texturing machine |
Punching machine |
Water jet cutting machine |
|
Electro chemical machine (ECM) |
Laser welding machine |
Riveting machine |
|
|
Finishing machine |
Machining centre |
Rolling machine |
|
|
Flanging machine |
Machining centre (other) |
Rotary transfer machine |
|
|
Folding machine |
Measuring machine |
Sawing machine |
|
|
Forging machine |
Milling machine |
Seaming machine |
|
All other properties of the MachineToolIdentificationType are defined in OPC 40001-1 and are intended to be used as indicated there.
Table 14 – MachineToolIdentificationType Additional Subcomponents
|
BrowsePath |
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Others |
|
SoftwareIdentification |
0:HasComponent |
Object |
<SoftwareItem> |
|
SoftwareIdentificationType |
MP |
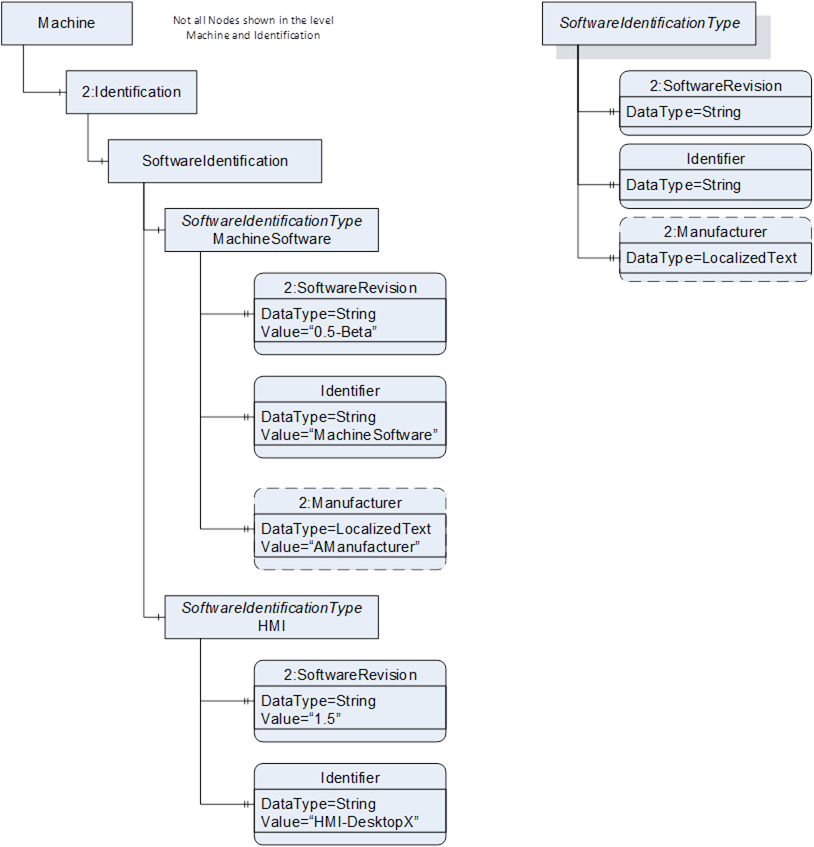
Figure 13 – Example Instance of SoftwareIdentification in a Machine Tools Server
The SoftwareIdentificationType holds information about the specific software in operation in the machine tool. Almost all modern machine tools operate on several software system components, this shall enable presentation of software components (NC Kernel, HMI base system, etc.). Figure 13 shows an example instance of the application of this type within the 2:Identification component of the MachineToolType.
The SoftwareIdentificationType is formally defined in Table 15.
Table 15 – SoftwareIdentificationType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
SoftwareIdentificationType |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
Node Class |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
Subtype of the 0:BaseObjectType defined in OPC 10000-5 i.e. inheriting the InstanceDeclarations of that Node. |
|||||
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:SoftwareRevision |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
M, RO |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
Identifier |
0:String |
0:PropertyType |
M, RO |
|
0:HasProperty |
Variable |
2:Manufacturer |
0:LocalizedText |
0:PropertyType |
O, RO |
|
Conformance Units |
|||||
|
MachineTool Identification SoftwareInformation |
|||||
In most cases, machine tools consist of several software components. A software component can be an individual application, or plugin of an application involved in controlling the machine tool.
2:SoftwareRevision provides a string representation of the version or revision level of the software component, the software/firmware of a hardware component. Examples are: “PLL01 1.10.0.3”, “V05.01.01.15”, “3.1 R1293”, “70.0.1”.
The Identifier Property provides an identifier to distinguish the software component.
2:Manufacturer refers to the manufacturer/producer of the software.