The LocalDiscoveryServer is useful for networks where the host names can be discovered. However, this is typically not the case in large systems with multiple servers on multiple subnets. For this reason there is a need for an enterprise wide DiscoveryServer called a GlobalDiscoveryServer. The GlobalDiscoveryServer (GDS) is an OPC UA Server which allows Clients to search for Servers in the administrative domain. It provides methods that allow applications to register themselves and to search for other applications.
The essential element of a GlobalDiscoveryServer (GDS) is that it can provide the Certificate management services defined in Clause 7. These services can simplify Certificate management even in medium to small systems, therefore, a GDS can be deployed in smaller systems. Different implementations are expected. Some of them will likely provide a front-end to an existing DirectoryService such as LDAP (See Annex E). By standardizing on an OPC UA based interface, OPC UA Clients do not need to have knowledge of different DirectoryServices.
If an administrator registers a LocalDiscoveryServer with the GDS, then the GDS shall periodically update its database by calling FindServersOnNetwork or FindServers on the LDS. Figure 7 shows the relationship between a GDS and the LDS-ME or LDS.
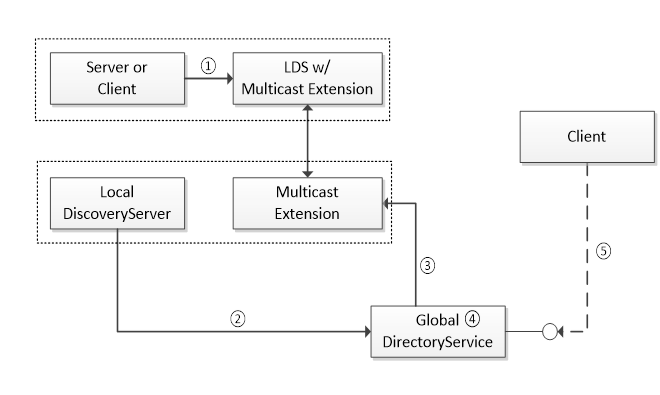
Figure 7 – The Relationship Between GDS and other components
The steps shown in Figure 7 are:
|
1 |
The Server calls RegisterServer2 on the LDS running on the same machine. |
|
2 |
The administrator registers LDS-ME installations with the GDS. |
|
3 |
The GDS calls FindServersOnNetwork on the LDS-ME to find all applications on the same MulticastSubnet. |
|
4 |
The GDS creates a record for each application returned by the LDS-ME. These records shall be approved before they are made available to Clients of the GDS. This approval can be obtained from an Administrator or the GDS can connect to the Server and verifies that it has a trusted Certfiicate. |
|
5 |
The Client calls QueryServers Method on the GDS to discover applications. |
The Information Model used for registration and discovery is shown in clause 6.2. Any Client shall be able to call the QueryServers Method to find applications known to GDS. The complete definitions for each of the types used are described in clause 7.5.
The discovery mechanisms defined in this standard are expected to be used in many different network architectures. The following three architectures are Illustrated:
- Single MulticastSubnet;
- Multiple MulticastSubnets;
- No MulticastSubnet (or multiple MulticastSubnets with exactly one host each);
A MulticastSubnet is a network segment where all hosts on the segment can receive multicast packets from the other hosts on the segment. A physical LAN segment is typically a MulticastSubnet unless the administrator has specifically disabled multicast communication. In some cases multiple physical LAN segments can be connected as a single MulticastSubnet
The Single MulticastSubnet Architecture is shown in Figure 8.
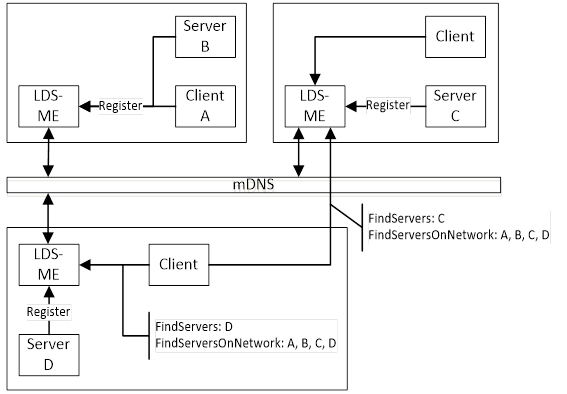
Figure 8 – The Single MulticastSubnet Architecture
In this architecture every host has an LDS-ME and uses mDNS to maintain a cache of the applications on the MulticastSubnet. A Client can call FindServersOnNetwork on any LDS-ME and receive the same set of applications. When a Client calls FindServers it only receives the applications running on the same host as the LDS.
The Multiple MulticastSubnet Architecture is shown in Figure 9.
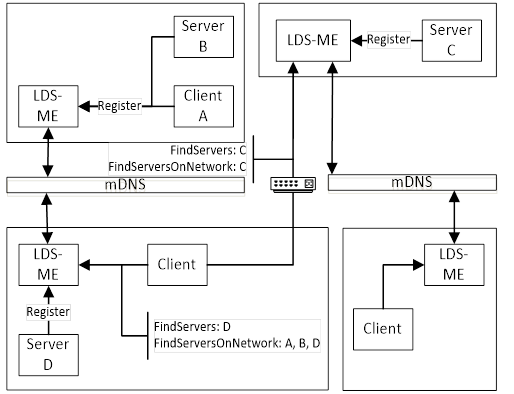
Figure 9 – The Multiple MulticastSubnet Architecture
This architecture is the same as the previous architecture except in this architecture the mDNS messages do not pass through routers connecting the MulticastSubnets. This means that a Client calling FindServersOnNetwork will only receive a list of applications running on the MulticastSubnets that the LDS-ME is connected to.
A Client that wants to connect to a remote MulticastSubnet shall use out of band discovery (i.e. manual entry) of a HostName or DiscoveryUrl. Once a Client finds an LDS-ME on a remote MulticastSubnet it can use FindServersOnNetwork to discover all applications on that MulticastSubnet.
The No MulticastSubnet Architecture is shown in Figure 10.
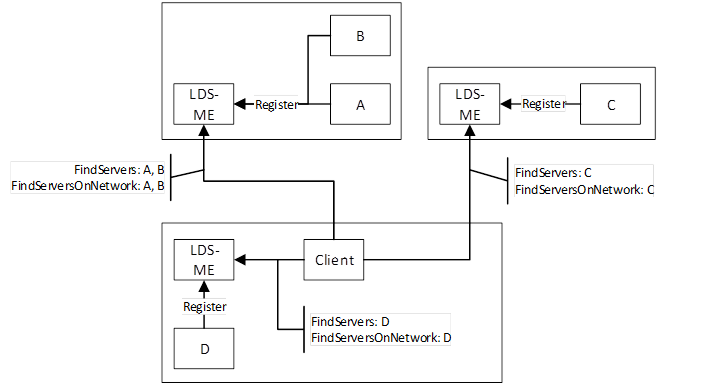
Figure 10 – The No MulticastSubnet Architecture
In this architecture the mDNS is not used at all because the Administrator has disabled multicast at a network level or by turning off multicast capabilities of each LDS-ME.
A Client that wants to discover a applications needs to use an out of band mechanism to find the HostName and call FindServers on the LDS of that host. FindServersOnNetwork may also work but it will never return more than what FindServers returns.
The mDNS specification requires that fully qualified domain name be annouced on the network. If a Server is not configured with a fully qualified domain name then mDNS requires that the ‘local’ top level domain be appended to the domain names. The ‘local’ top level domain indicates that the domain can only be consided to be unique within the subnet where the domain name was used. This means Clients need to be be aware that URLs received from any LDS-ME other than the one on the Client’s machine could contain ‘local’ domains which are not reachable or will connect to a different machine with the same domain name that happens to be on the same subnet as the Client. It is recommended that Clients ignore all URLs with the ‘local’ top level domain unless they are returned from the LDS-ME running on the same machine.
System administrators can eliminate this problem by configuring a normal DNS with the fully qualilfied domain names for all machines which need to be accessed by Clients outside the MulticastSubnet.
Servers configured with fully qualified domain names should specify the fully qualified domain name in its ApplicationInstance Certificate. Servers shall not specify domains with the ‘local’ top level domain in their Certificate. Clients using a URL returned from an LDS-ME shall ignore the ‘local’ top level domain when checking the domain against the Server Certificate.
Note that domain name validation is a necessary but not sufficient check against rogue Servers or man-in-the-middle attacks when Server Certificates do not contain fully qualified domain names. The Certificate trust relationship established by administrators is the primary mechanism used to protect against these risks.
The GlobalDiscoveryServer Information Model used for discovery is shown in Figure 11. Most of the interactions between the GlobalDiscoveryServer and Application administrator or the Client will be via Methods defined on the Directory folder.
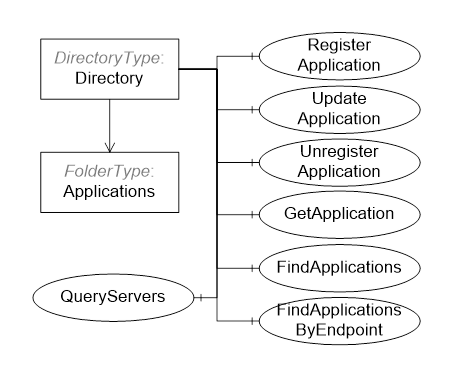
Figure 11 – The Address Space for the GDS
This Object is the root of the GlobalDiscoveryServer AddressSpace and it is the target of an Organizes reference from the Objects folder defined in OPC 10000-5. It organizes the information that can be accessed into subfolders. The implementation of a GDS can customize and organize the folders in any manner it desires. For example folders may exist for information models, or for optional services or for various locations in an administrative domain. It is defined in Table 2.
Table 2 – Directory Object Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
Directory |
||||
|
Namespace |
GDS (see 3.3) |
||||
|
TypeDefinition |
DirectoryType defined in 6.3.3. |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
DirectoryType is the ObjectType for the root of the GlobalDiscoveryServer AddressSpace. It organizes the information that can be accessed into subfolders It also provides methods that allow applications to register or find applications. It is defined in Table 3.
Table 3 – DirectoryType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
DirectoryType |
||||
|
Namespace |
GDS (see 3.3) |
||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Modelling Rule |
|
Subtype of the FolderType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|||||
|
HasComponent |
Object |
Applications |
- |
FolderType |
Mandatory |
|
HasComponent |
Method |
FindApplications |
Defined in 6.3.4. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
RegisterApplication |
Defined in 6.3.6. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
UpdateApplication |
Defined in 6.3.7. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
UnregisterApplication |
Defined in 6.3.8. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
GetApplication |
Defined in 6.3.9. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
QueryApplications |
Defined in 6.3.10. |
Mandatory |
|
|
HasComponent |
Method |
QueryServers |
Defined in 6.3.11. |
Mandatory |
|
The Applications folder may contain Objects representing the Applications known to the GDS. These Objects may be organized into subfolders as determined by the GDS. Some characteristics for organizing applications are the networks, the physical location, or the supported profiles. The QueryServers Method can be used to search for OPC UA Applications based on various criteria.
A GDS is not required to expose its Applications as browsable Objects in its AddressSpace, however, each Application shall have a unique NodeId which can be passed to Methods used to administer the GDS.
The FindApplications Method returns the Applications associated with an ApplicationUri. It can be called by any Client application.
The RegisterApplication Method is used to add a new Application to the GDS. It requires administrative privileges.
The UpdateApplication Method is used to update an existing Application in the GDS. It requires administrative privileges.
The UnregisterApplication Method is used to remove an Application from the GDS. It requires administrative privileges.
The QueryApplications Method is used to find Client or Server applications that meet the criteria provided. This Method replaces the QueryServers Method.
The QueryServers Method is used to find Servers that meet the criteria specified. It can be called by any Client application. This Method has been replaced by the QueryApplications Method
FindApplications is used to find the ApplicationId for an OPC UA Application known to the GDS. In normal situations the list of records returned will not have more than one entry, however, system configuration errors can create situations where the GDS has multiple entries for a single ApplicationUri. If this happens a human will likely have to look at records to determine which record is the true match for the ApplicationUri.
If the returned array is null or zero length then the GDS does not have an entry for the ApplicationUri.
Signature
FindApplications(
[in] String applicationUri
[out] ApplicationRecordDataType[] applications
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationUri |
The ApplicationUri that identifies the Application of interest. |
|
applications |
A list of application records that match the ApplicationUri. The ApplicationRecordDataType is defined in 6.3.5. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 4 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the FindApplications Method.
Table 4 – FindApplications Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
FindApplications |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This type defines a DataType which represents a record in the GDS.
Table 5 – ApplicationRecordDataType Structure
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
ApplicationRecordDataType |
Structure |
Subtype of the Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
|
applicationId |
NodeId |
The unique identifier assigned by the GDS to the record. |
|
applicationUri |
String |
The URI for the Application associated with the record. |
|
applicationType |
ApplicationType |
The type of application. This type is defined in OPC 10000-4. |
|
applicationNames |
LocalizedText[] |
One or more localized names for the application. The first element is the default ApplicationName for the application when a non-localized name is needed. |
|
productUri |
String |
A globally unique URI for the product associated with the application. This URI is assigned by the vendor of the application. |
|
discoveryUrls |
String[] |
The list of discovery URLs for an application. The first element is the default if a Client needs to choose one URL. The first HTTPS URL specifies the domain used as the Common Name of HTTPS Certificates. If the ApplicationType is Client then all of the URLs shall have the ‘inv+’ prefix which indicates they support reverse connect. |
|
serverCapabilities |
String[] |
The list of server capability identifiers for the application. The allowed values are defined in Annex D. |
Its representation in the AddressSpace is defined in Table 5a.
Table 5a – ApplicationRecordDataType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
ApplicationRecordDataType |
|||||
|
Namespace |
GDS (see 3.3) |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
False |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
Other |
|
|
Subtype of the Structure DataType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
RegisterApplication is used to register a new Application Instance with a GlobalDiscoveryServer.
This Method shall only be invoked by authorized users.
Servers that support transparent redundancy shall register as a single application and pass the DiscoveryUrls for all available instances and/or network paths.
RegisterApplication will create duplicate records if the ApplicationUri already exists since misconfiguration of applications can result in different applications having the same ApplicationUri. Before calling this Method the Client shall call FindApplications to check if a record for the application it is using already exists. If records are found which appear to belong to different applications (e.g. the DiscoveryUrls are different) then the Client shall report a warning before continuing.
If registration was successful and auditing is supported, the GDS shall generate the ApplicationRegistrationChangedAuditEventType (see 6.3.12).
Signature
RegisterApplication(
[in] ApplicationRecordDataType application
[out] NodeId applicationId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
application |
The application that is to be registered with the GlobalDiscoveryServer. |
|
applicationId |
A unique identifier for the registered Application. This identifier is persistent and is used in other Methods used to administer applications. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The application or one of the fields of the application record is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 6 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the RegisterApplication Method.
Table 6 – RegisterApplication Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
RegisterApplication |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
UpdateApplication is used to update an existing Application in a GlobalDiscoveryServer.
This Method shall only be invoked by authorized users.
If the update was successful and auditing is supported, the GDS shall generate the ApplicationRegistrationChangedAuditEventType (see 6.3.12).
Signature
UpdateApplication(
[in] ApplicationRecordDataType application
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
application |
The application that is to be updated in the GDS database. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The applicationId is not known to the GDS. |
|
Bad_InvalidArgument |
The application or one of the fields of the application record is not valid. The text associated with the error shall indicate the exact problem. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 7 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the UpdateApplication Method.
Table 7 – UpdateApplication Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
UpdateApplication |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
UnregisterApplication is used to remove an Application from a GlobalDiscoveryServer.
This Method shall only be invoked by authorized users.
A Server Application that is unregistered may be automatically added again if the GDS is configured to populate itself by calling FindServersOnNetwork and the Server Application is still registering with its local LDS.
If un-registration was successful and auditing is supported, the GDS shall generate the ApplicationRegistrationChangedAuditEventType (see 6.3.12).
Signature
UnregisterApplication(
[in] NodeId applicationId
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The identifier assigned by the GDS to the Application. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The ApplicationId is not known to the GDS. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 8 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the UnregisterApplication Method.
Table 8 – UnregisterApplication Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
UnregisterApplication |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
GetApplication is used to find an OPC UA Application known to the GDS.
Signature
GetApplication(
[in] NodeId applicationId
[out] ApplicationRecordDataType application
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
applicationId |
The ApplicationId that identifies the Application of interest. |
|
application |
The application record that matches the ApplicationId. The ApplicationRecordDataType is defined in6.3.5 |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_NotFound |
The no record found for the specified ApplicationId. |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 9 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the GetApplication Method.
Table 9 – GetApplication Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
GetApplication |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
QueryApplications is used to find Client or Server applications that meet the specified filters. The only Clients returns are those that support the reverse connection capability described in OPC 10000-6.
QueryApplications returns ApplicationDescriptions instead of the ServerOnNetwork Structures returned by QueryServers. This is more useful to some Clients because it matches the return type of FindServers.
Any Client is able to call this Method, however, the set of results returned may be restricted based on the Client’s user credentials.
The applications returned shall pass all of the filters provided (i.e. the filters are combined in an AND operation). The capabilities parameter is an array and an application will pass this filter if it supports all of the specified capabilities.
Each time the GDS creates or updates an application record it shall assign a monotonically increasing identifier to the record. This allows Clients to request records in batches by specifying the identifier for the last record received in the last call to QueryApplications. To support this the GDS shall return records in order starting from the lowest record identifier. The GDS shall also return the last time the counter was reset. If a Client detects that this time is more recent than the last time the Client called the Method it shall call the Method again with a startingRecordId of 0.
Signature
QueryApplications(
[in] UInt32 startingRecordId
[in] UInt32 maxRecordsToReturn
[in] String applicationName
[in] String applicationUri
[in] UInt32 applicationType
[in] String productUri
[in] String[] capabilities
[out] DateTime lastCounterResetTime
[out] UInt32 nextRecordId
[out] ApplicationDescription[] applications
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
INPUTS |
|
|
startingRecordId |
Only records with an identifier greater than this number will be returned. Specify 0 to start with the first record in the database. |
|
maxRecordsToReturn |
The maximum number of records to return in the response. 0 indicates that there is no limit. |
|
applicationName |
The ApplicationName of the applications to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. The filter is only applied to the default ApplicationName. |
|
applicationUri |
The ApplicationUri of the applications to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. |
|
applicationType |
A mask indicating what types of applications are returned. The mask values are: 0x1 – Servers; 0x2 – Clients; : If the mask is 0 then all applications are returned. |
|
productUri |
The ProductUri of the applications to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. |
|
capabilities |
The capabilities supported by the applications returned. The applications returned shall support all of the capabilities specified. If no capabilities are provided this filter is not used. |
|
OUTPUTS |
|
|
lastCounterResetTime |
The last time the counters were reset. |
|
nextRecordId |
The identifier of the next record. It is passed as the startingRecordId in subsequent calls to QueryApplications to fetch the next batch of records. It is 0 if there are no more records to return. |
|
applications |
A list of Applications which meet the criteria. The ApplicationDescription structure is defined in OPC 10000-4. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 11 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the QueryApplications Method.
Table 10 – QueryApplications Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
QueryApplications |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
QueryServers is used to find Server applications that meet the specified filters.
Any Client is able to call this Method, however, the set of results returned may be restricted based on the Client’s user credentials.
The applications returned shall pass all of the filters provided (i.e. the filters are combined in an AND operation). The serverCapabilities parameter is an array and an application will pass this filter if it supports all of the specified capabilities.
Each time the GDS creates or updates an application record it shall assign a monotonically increasing identifier to the record. This allows Clients to request records in batches by specifying the identifier for the last record received in the last call to QueryServers. To support this the GDS shall return records in order starting from the lowest record identifier. The GDS shall also return the last time the counter was reset. If a Client detects that this time is more recent than the last time the Client called the Method it shall call the Method again with a startingRecordId of 0.
Signature
QueryServers(
[in] UInt32 startingRecordId
[in] UInt32 maxRecordsToReturn
[in] String applicationName
[in] String applicationUri
[in] String productUri
[in] String[] serverCapabilities
[out] DateTime lastCounterResetTime
[out] ServerOnNetwork[] servers
);
|
Argument |
Description |
|
INPUTS |
|
|
startingRecordId |
Only records with an identifier greater than this number will be returned. Specify 0 to start with the first record in the database. |
|
maxRecordsToReturn |
The maximum number of records to return in the response. 0 indicates that there is no limit. |
|
applicationName |
The ApplicationName of the Applications to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. The filter is only applied to the default ApplicationName. |
|
applicationUri |
The ApplicationUri of the Servers to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. |
|
productUri |
The ProductUri of the Servers to return. Supports the syntax used by the LIKE FilterOperator described in OPC 10000-4. Not used if an empty string is specified. |
|
serverCapabilities |
The applications returned shall support all of the server capabilities specified. If no server capabilities are provided this filter is not used. |
|
OUTPUTS |
|
|
lastCounterResetTime |
The last time the counters were reset. |
|
servers |
A list of Servers which meet the criteria. The ServerOnNetwork structure is defined in OPC 10000-4. |
Method Result Codes (defined in Call Service)
|
Result Code |
Description |
|
Bad_UserAccessDenied |
The current user does not have the rights required. |
Table 11 specifies the AddressSpace representation for the QueryServers Method.
Table 11 – QueryServers Method AddressSpace Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
||||
|
BrowseName |
QueryServers |
||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
InputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
|
HasProperty |
Variable |
OutputArguments |
Argument[] |
PropertyType |
Mandatory |
This event is raised when the RegisterApplication, UpdateApplication or UnregisterApplication Methods are called.
Its representation in the AddressSpace is formally defined in Table 12.
Table 12 – ApplicationRegistrationChangedAuditEventType Definition
|
Attribute |
Value |
|||||
|
BrowseName |
ApplicationRegistrationChangedAuditEventType |
|||||
|
Namespace |
GDS (see 3.3) |
|||||
|
IsAbstract |
True |
|||||
|
References |
NodeClass |
BrowseName |
DataType |
TypeDefinition |
ModellingRule |
|
|
Subtype of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType defined in OPC 10000-5. |
||||||
This EventType inherits all Properties of the AuditUpdateMethodEventType. Their semantics are defined in OPC 10000-5.