OPC UA provides a framework that can be used to represent complex information as Objects in an AddressSpace which can be accessed with standard services. These Objects consist of Nodes connected by References. Different classes of Nodes convey different semantics. For example, a Variable Node represents a value that can be read or written. The Variable Node has an associated DataType that can define the actual value, such as a string, float, structure etc. It can also describe the Variable value as a variant. A Method Node represents a function that can be called. Every Node has a number of Attributes including a unique identifier called a NodeId and non-localized name called as BrowseName. An Object representing a ‘Reservation’ is shown in Figure 4.
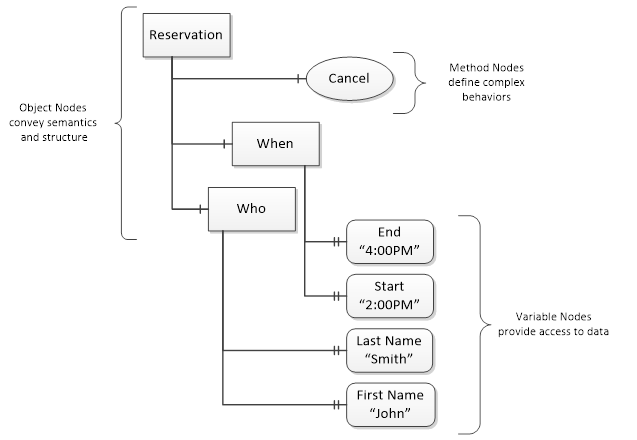
Figure 4 – A Basic Object in an OPC UA Address Space
Object and Variable Nodes represent instances and they always reference a TypeDefinition (ObjectType or VariableType) Node which describes their semantics and structure. Figure 5 illustrates the relationship between an instance and its TypeDefinition.
The type Nodes are templates that define all of the children that can be present in an instance of the type. In the example in Figure 5 the PersonType ObjectType defines two children: First Name and Last Name. All instances of PersonType are expected to have the same children with the same BrowseNames. Within a type the BrowseNames uniquely identify the children. This means Client applications can be designed to search for children based on the BrowseNames from the type instead of NodeIds. This eliminates the need for manual reconfiguration of systems if a Client uses types that multiple Servers implement.
OPC UA also supports the concept of sub-typing. This allows a modeller to take an existing type and extend it. There are rules regarding sub-typing defined in OPC 10000-3, but in general they allow the extension of a given type or the restriction of a DataType. For example, the modeller may decide that the existing ObjectType in some cases needs an additional Variable. The modeller can create a subtype of the ObjectType and add the Variable. A Client that is expecting the parent type can treat the new type as if it was of the parent type. Regarding DataTypes, subtypes can only restrict. If a Variable is defined to have a numeric value, a sub type could restrict it to a float.
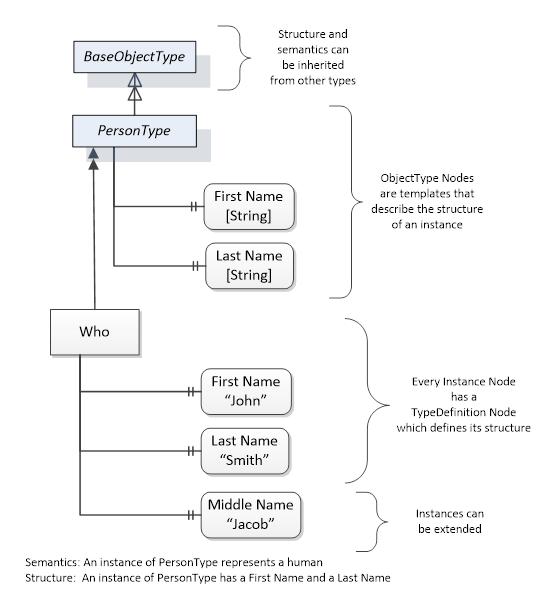
Figure 5 – The Relationship between Type Definitions and Instances
References allow Nodes to be connected in ways that describe their relationships. All References have a ReferenceType that specifies the semantics of the relationship. References can be hierarchical or non-hierarchical. Hierarchical references are used to create the structure of Objects and Variables. Non-hierarchical are used to create arbitrary associations. Applications can define their own ReferenceType by creating subtypes of an existing ReferenceType. Subtypes inherit the semantics of the parent but may add additional restrictions. Figure 6 depicts several References, connecting different Objects.
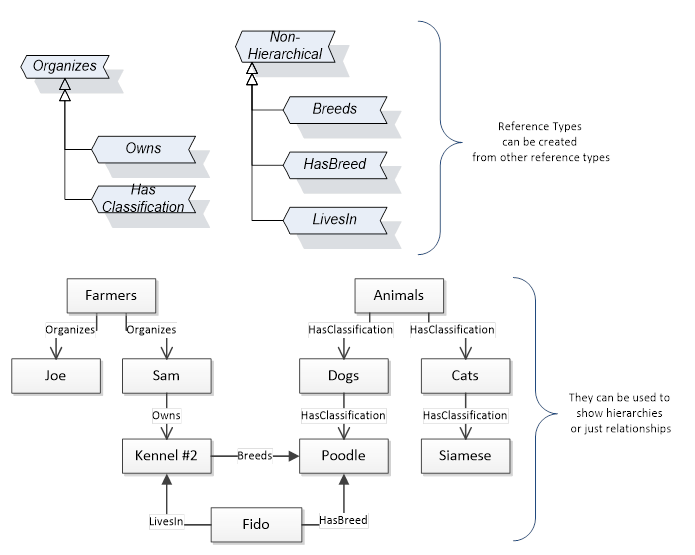
Figure 6 – Examples of References between Objects
The figures above use a notation that was developed for the OPC UA specification. The notation is summarized in Figure 7. UML representations can also be used; however, the OPC UA notation is less ambiguous because there is a direct mapping from the elements in the figures to Nodes in the AddressSpace of an OPC UA Server.
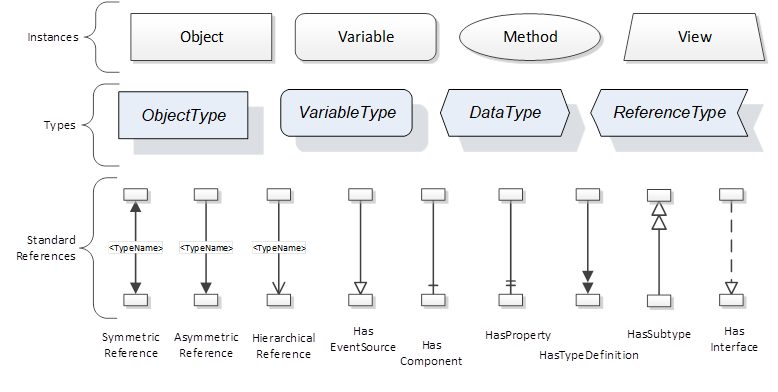
Figure 7 – The OPC UA Information Model Notation
A complete description of the different types of Nodes and References can be found in OPC 10000-3 and the base structure is described in OPC 10000-5.
OPC UA specification defines a very wide range of functionality in its basic information model. It is not required that all Clients or Servers support all functionality in the OPC UA specifications. OPC UA includes the concept of Profiles, which segment the functionality into testable certifiable units. This allows the definition of functional subsets (that are expected to be implemented) within a companion specification. The Profiles do not restrict functionality, but generate requirements for a minimum set of functionalities (see OPC 10000-7)