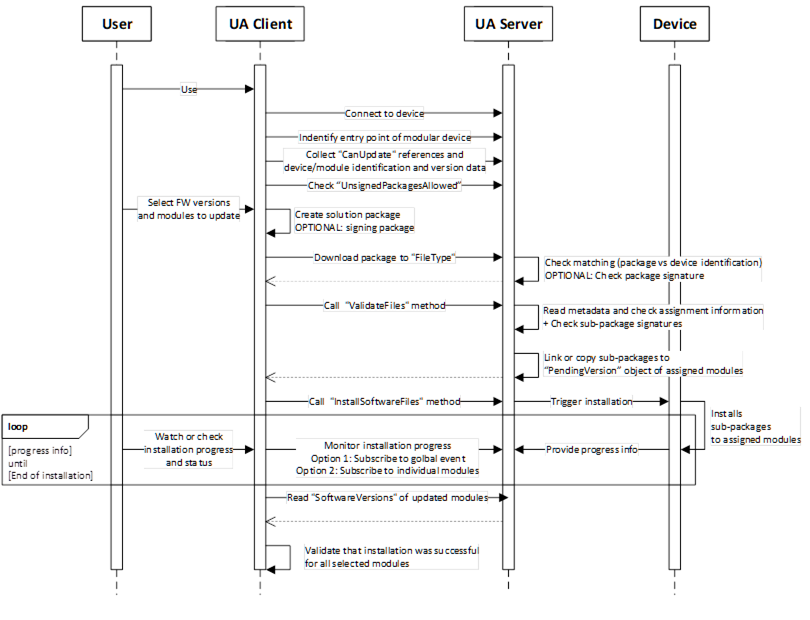
Figure B.14: Update sequence for a modular device using a solution package.
Steps of the workflow:
- Connect to the device via the UA server.
- The client finds the entry point of the modular device, that can happen by:
- Knowing the structure such as UADI:DeviceType or UAFX:AssetType
- Finding the object with software class “Solution” behind,
- In cases of a sever hosting multiple devices, the user selects the right one or the client knows the identification of the target device.
- Browse the references CanUpdate of the “Solution” object to know devices can be updated via a solution package. Afterwards read the identification of the linked modules.
- Check the flag “UnsignedPackagesAllowed” to know if a solution package is required to be signed.
- User selects the FW version or config/application and modules/targets that should be updated.
- Client creates a new solution package with the selected content. It includes:
- Creating of the solution package and pack the sub-packages into it.
- Creating a package metadata file that contains the assignment information.
- Optionally sign the solution package with a customer provided certificate or service.
- Client downloads the solution package to the device.
- Device is doing an overall check on the package level if its valid and intended for this device.
- Optional checking the package signature
- Client calls ValidateFiles to trigger a check of the metadata data about assignments
- For the successful matched elements, the sub-packages are copied or linked to the SoftwareUpdate instances of each device into the PendingVersion.
- Server is returning the info which elements are ready for update and which are not supported
- Client tiggers the installation process by calling InstallSoftwareFiles. This triggers the real installation process on the device side.
- Device is installing the selected version. That can happen in parallel or sequential or combined way depending on the device capabilities. This is up to the devices.
- Client is subscribing to [a] or/and [b] to get progress and status of the installation process.
- A global event (aggregates all progress and status updates via the module and update ID, so that the client can see the details on module is referred)
- Each individual module
- Device is sending the progress and status information.
- After client received the message for end of installation, he is reading the module identification with software revision to check if installation was really successful.