Clients define MonitoredItems to subscribe to data and Events. Each MonitoredItem identifies the item to be monitored and the Subscription to use to send Notifications. The item to be monitored may be any Node Attribute.
Notifications are data structures that describe the occurrence of data changes and Events. They are packaged into NotificationMessages for transfer to the Client. The Subscription periodically sends NotificationMessages at a user-specified publishing interval, and the cycle during which these messages are sent is called a publishing cycle.
Four primary parameters are defined for MonitoredItems that tell the Server how the item is to be sampled, evaluated and reported. These parameters are the sampling interval, the monitoring mode, the filter and the queue parameter. Figure 15 illustrates these concepts.
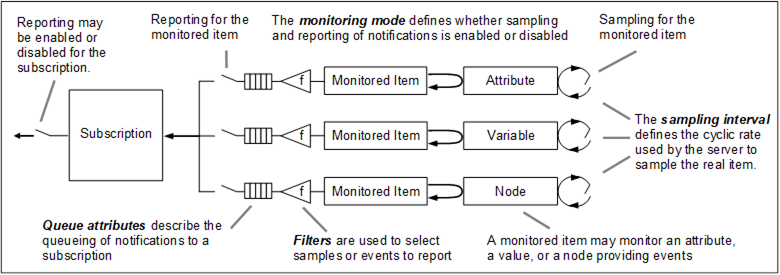
Figure 15 – MonitoredItem model
Attributes, other than the Value Attribute, are only monitored for a change in value. The filter is not used for these Attributes. Any change in value for these Attributes causes a Notification to be generated.
The Value Attribute is used when monitoring Variables. Variable values are monitored for a change in value or a change in their status. The filters defined in this document (see 7.22.2) and in OPC 10000-8 are used to determine if the value change is large enough to cause a Notification to be generated for the Variable.
Objects and views can be used to monitor Events. Events are only available from Nodes where the SubscribeToEvents bit of the EventNotifier Attribute is set. The filter defined in this document (see 7.22.3) is used to determine if an Event received from the Node is sent to the Client. The filter also allows selecting fields of the EventType that will be contained in the Event such as EventId, EventType, SourceNode, Time and Description.
OPC 10000-3 describes the Event model and the base EventTypes.
The Properties of the base EventTypes and the representation of the base EventTypes in the AddressSpace are specified in OPC 10000-5.
Each MonitoredItem created by the Client is assigned a sampling interval that is either inherited from the publishing interval of the Subscription or that is defined specifically to override that rate. A negative number indicates that the default sampling interval defined by the publishing interval of the Subscription is requested. The sampling interval indicates the fastest rate at which the Server should sample its underlying source for data changes.
A Client shall define a sampling interval of 0 if it subscribes for Events.
The assigned sampling interval defines a “best effort” cyclic rate that the Server uses to sample the item from its source. “Best effort” in this context means that the Server does its best to sample at this rate. Sampling at rates faster than this rate is acceptable, but not necessary to meet the needs of the Client. How the Server deals with the sampling rate and how often it actually polls its data source internally is a Server implementation detail. However, the time between values returned to the Client shall be greater or equal to the sampling interval.
The Client may also specify 0 for the sampling interval, which indicates that the Server should use the fastest practical rate. It is expected that Servers will support only a limited set of sampling intervals to optimize their operation. If the exact interval requested by the Client is not supported by the Server, then the Server assigns to the MonitoredItem the most appropriate interval as determined by the Server. It returns this assigned interval to the Client. The ServerCapabilities Object defined in OPC 10000-5 identifies the minimum sampling interval supported by the Server. The optional MinimumSamplingInterval Attribute defined in OPC 10000-3 identifies the minimum sampling interval supported for a Variable. If a Server uses a fixed set of sampling intervals, the intervals can be exposed using the SamplingIntervalDiagnosticsArray in the ServerDiagnostics Object defined in OPC 10000-5.
The Server may support data that is collected based on a sampling model or generated based on an exception-based model. The fastest supported sampling interval may be equal to 0, which indicates that the data item is exception-based rather than being sampled at some period. An exception-based model means that the underlying system does not require sampling and reports data changes.
The Client may use the revised sampling interval values as a hint for setting the publishing interval as well as the keep-alive count of a Subscription. If, for example, the smallest revised sampling interval of the MonitoredItems is 5 seconds, then the time before a keep-alive is sent should be longer than 5 seconds.
Note that, in many cases, the OPC UA Server provides access to a decoupled system and therefore has no knowledge of the data update logic. In this case, even though the OPC UA Server samples at the negotiated rate, the data might be updated by the underlying system at a much slower rate. In this case, changes can only be detected at this slower rate.
If the behaviour by which the underlying system updates the item is known, it will be available via the MinimumSamplingInterval Attribute defined in OPC 10000-3. If the Server specifies a value for the MinimumSamplingInterval Attribute it shall always return a revisedSamplingInterval that is equal or higher than the MinimumSamplingInterval if the Client subscribes to the Value Attribute.
Clients should also be aware that the sampling by the OPC UA Server and the update cycle of the underlying system are usually not synchronized. This can cause additional delays in change detection, as illustrated in Figure 16.
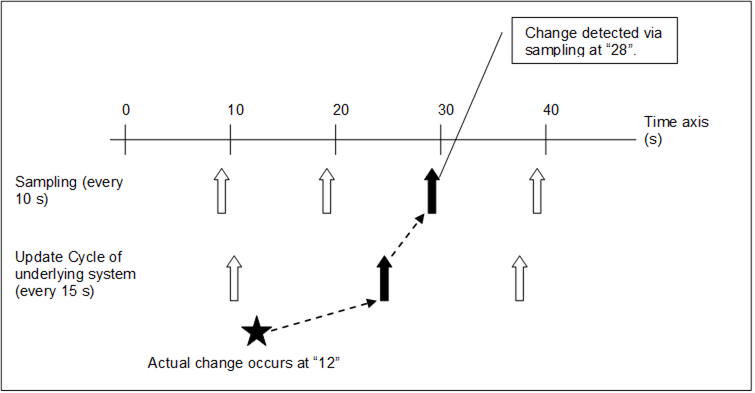
Figure 16 – Typical delay in change detection
The monitoring mode parameter is used to enable and disable the sampling of a MonitoredItem, and also to provide for independently enabling and disabling the reporting of Notifications. This capability allows a MonitoredItem to be configured to sample, sample and report, or neither. Disabling sampling does not change the values of any of the other MonitoredItem parameter, such as its sampling interval.
When a MonitoredItem is enabled (i.e. when the MonitoringMode is changed from DISABLED to SAMPLING or REPORTING) or it is created in the enabled state, the Server shall report the first sample as soon as possible and the time of this sample becomes the starting point for the next sampling interval.
Each time a MonitoredItem is sampled, the Server evaluates the sample using the filter defined for the MonitoredItem. The filter parameter defines the criteria that the Server uses to determine if a Notification should be generated for the sample. The type of filter is dependent on the type of the item that is being monitored. For example, the DataChangeFilter and the AggregateFilter are used when monitoring Variable Values and the EventFilter is used when monitoring Events. Sampling and evaluation, including the use of filters, are described in this document. Additional filters may be defined in other parts of OPC 10000.
If the sample passes the filter criteria, a Notification is generated and queued for transfer by the Subscription. The size of the queue is defined when the MonitoredItem is created. When the queue is full and a new Notification is received, the Server either discards the oldest Notification and queues the new one, or it replaces the last value added to the queue with the new one. The MonitoredItem is configured for one of these discard policies when the MonitoredItem is created. If a Notification is discarded for a DataValue and the size of the queue is larger than one, then the Overflow bit (flag) in the InfoBits portion of the DataValue statusCode is set. If discardOldest is TRUE, the oldest value gets deleted from the queue and the next value in the queue gets the flag set. If discardOldest is FALSE, the last value added to the queue gets replaced with the new value. The new value gets the flag set to indicate the lost values in the next NotificationMessage. Figure 17 illustrates the queue overflow handling.
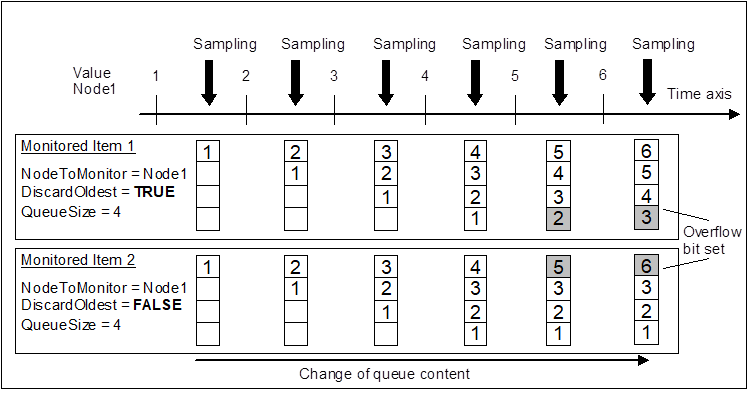
Figure 17 – Queue overflow handling
If the queue size is one, the queue becomes a buffer that always contains the newest Notification. In this case, if the sampling interval of the MonitoredItem is faster than the publishing interval of the Subscription, the MonitoredItem will be over sampling and the Client will always receive the most up-to-date value. The discard policy is ignored if the queue size is one.
On the other hand, the Client may want to subscribe to a continuous stream of Notifications without any gaps, but does not want them reported at the sampling interval. In this case, the MonitoredItem would be created with a queue size large enough to hold all Notifications generated between two consecutive publishing cycles. Then, at each publishing cycle, the Subscription would send all Notifications queued for the MonitoredItem to the Client. The Server shall return Notifications for any particular item in the same order they are in the queue.
The Server may be sampling at a faster rate than the sampling interval to support other Clients; the Client should only expect values at the negotiated sampling interval. The Server may deliver fewer values than dictated by the sampling interval, based on the filter and implementation constraints. If a DataChangeFilter is configured for a MonitoredItem, it is always applied to the newest value in the queue compared to the current sample.
If, for example, the AbsoluteDeadband in the DataChangeFilter is “10”, the queue could consist of values in the following order:
- 100
- 111
- 100
- 89
- 100
Queuing of data may result in unexpected behaviour when using a Deadband filter and the number of encountered changes is larger than the number of values that can be maintained. The new first value in the queue may not exceed the Deadband limit of the previous value sent to the Client.
The queue size is the maximum value supported by the Server when monitoring Events. In this case, the Server is responsible for the Event buffer. If Events are lost, an Event of the type EventQueueOverflowEventType is placed in the queue. This Event is generated when the first Event is discarded on a MonitoredItem subscribing for Events. It is put into the Queue of the MonitoredItem in addition to the size of the Queue defined for this MonitoredItem without discarding any other Event. If discardOldest is set to TRUE it is put at the beginning of the queue and is never discarded, otherwise at the end. An aggregating Server shall not pass on such an Event. It shall be handled like other connection error scenarios using the SystemStatusChangeEventType with the ServerState COMMUNICATION_FAULT.
For any fatal error during event processing like out of memory situations, the Server should queue an SystemStatusChangeEventType event with the ServerState COMMUNICATION_FAULT and the source set to the Server Object. If there are no resources available at the time the error happens, the Server should flag an error internally until there are resources to further process Events for the MonitoredItem.
The MonitoredItems Service allows the addition of items that are reported only when some other item (the triggering item) triggers. This is done by creating links between the triggered items and the items to report. The monitoring mode of the items to report is set to sampling-only so that it will sample and queue Notifications without reporting them. Figure 18 illustrates this concept.
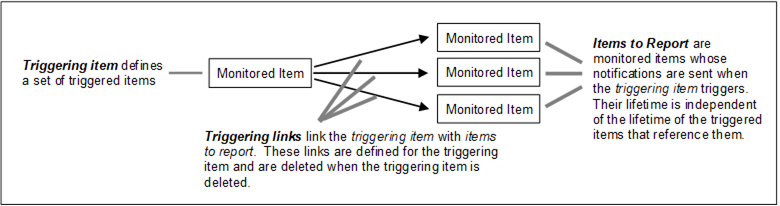
The triggering mechanism is a useful feature that allows Clients to reduce the data volume on the wire by configuring some items to sample frequently but only report when some other Event happens.
The following triggering behaviours are specified.
- If the monitoring mode of the triggering item is SAMPLING, then it is not reported when the triggering item triggers the items to report.
- If the monitoring mode of the triggering item is REPORTING, then it is reported when the triggering item triggers the items to report.
- If the monitoring mode of the triggering item is DISABLED, then the triggering item does not trigger the items to report.
- If the monitoring mode of the item to report is SAMPLING, then it is reported when the triggering item triggers the items to report.
- If the monitoring mode of the item to report is REPORTING, this effectively causes the triggering item to be ignored. All notifications of the items to report are sent after the publishing interval expires.
- If the monitoring mode of the item to report is DISABLED, then there will be no sampling of the item to report and therefore no notifications to report.
- The first trigger shall occur when the first notification is queued for the triggering item after the creation of the link.
Clients create and delete triggering links between a triggering item and a set of items to report. If the MonitoredItem that represents an item to report is deleted before its associated triggering link is deleted, the triggering link is also deleted, but the triggering item is otherwise unaffected.
Deletion of a MonitoredItem should not be confused with the removal of the Attribute that it monitors. If the Node that contains the Attribute being monitored is deleted, the MonitoredItem generates a Notification with a StatusCode Bad_NodeIdUnknown that indicates the deletion, but the MonitoredItem is not deleted.
This Service is used to create and add one or more MonitoredItems to a Subscription. A MonitoredItem is deleted automatically by the Server when the Subscription is deleted. Deleting a MonitoredItem causes its entire set of triggered item links to be deleted, but has no effect on the MonitoredItems referenced by the triggered items.
Calling the CreateMonitoredItems Service repetitively to add a small number of MonitoredItems each time may adversely affect the performance of the Server. Instead, Clients should add a complete set of MonitoredItems to a Subscription whenever possible.
When a MonitoredItem is added, the Server performs initialization processing for it. The initialization processing is defined by the Notification type of the item being monitored. Notification types are specified in this document and in the Access Type Specification parts of OPC 10000, such as OPC 10000-8. See OPC 10000-1 for a description of the Access Type Parts. Clients may receive Notifications for added MonitoredItems before the CreateMonitoredItems Response is received. Clients set the ClientHandle for the MonitoredItem in the CreateMonitoredItems Request and are therefore able to process the Notifications received before the CreateMonitoredItems Response is received.
When a user adds a monitored item that the user is denied read access to, the add operation for the item shall succeed and the bad status Bad_NotReadable or Bad_UserAccessDenied shall be returned in the Publish response. This is the same behaviour for the case where the access rights are changed after the call to CreateMonitoredItems. If the access rights change to read rights, the Server shall start sending data for the MonitoredItem. The same procedure shall be applied for an IndexRange that does not deliver data for the current value but could deliver data in the future. Servers should return all other errors as CreateMonitoredItems results but all possible errors are allowed to be returned in the Publish response.
Monitored Nodes can be removed from the AddressSpace after the creation of a MonitoredItem. This does not affect the validity of the MonitoredItem but a Bad_NodeIdUnknown shall be returned in the Publish response. It is possible that the MonitoredItem becomes valid again if the Node is added again to the AddressSpace and the MonitoredItem still exists.
If a NodeId is known to be valid by a Server but the corresponding Node Attributes are currently not available, the Server may allow the creation of a MonitoredItem and return an appropriate Bad StatusCode in the Publish response.
The return diagnostic info setting in the request header of the CreateMonitoredItems or the last ModifyMonitoredItems Service is applied to the Monitored Items and is used as the diagnostic information settings when sending Notifications in the Publish response.
Illegal request values for parameters that can be revised do not generate errors. Instead the Server will choose default values and indicate them in the corresponding revised parameter.
It is strongly recommended by OPC UA that a Client reuses a Subscription after a short network interruption by activating the existing Session on a new SecureChannel as described in 6.7. If a Client called CreateMonitoredItems during the network interruption and the call succeeded in the Server but did not return to the Client, then the Client does not know if the call succeeded. The Client may receive data changes for these monitored items but is not able to remove them since it does not know the Server handle for each monitored item. There is also no way for the Client to detect if the create succeeded. To delete and recreate the Subscription is also not an option since there may be several monitored items operating normally that should not be interrupted. To resolve this situation, the Server Object provides a Method GetMonitoredItems that returns the list of Server and client handles for the monitored items in a Subscription. This Method is defined in OPC 10000-5. The Server shall verify that the Method is called within the Session context of the Session that owns the Subscription.
Table 69 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 69 – CreateMonitoredItems Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.33 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
subscriptionId |
IntegerId |
The Server-assigned identifier for the Subscription that will report Notifications for this MonitoredItem (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). |
|
timestampsToReturn |
Enum Timestamps ToReturn |
An enumeration that specifies the timestamp Attributes to be transmitted for each MonitoredItem. The TimestampsToReturn enumeration is defined in 7.40. When monitoring Events, this applies only to Event fields that are of type DataValue. |
|
itemsToCreate [] |
MonitoredItem CreateRequest |
A list of MonitoredItems to be created and assigned to the specified Subscription. This structure is defined in-line with the following indented items. |
|
itemToMonitor |
ReadValueId |
Identifies an item in the AddressSpace to monitor. To monitor for Events, the attributeId element of the ReadValueId structure is the id of the EventNotifier Attribute. The ReadValueId type is defined in 7.29. |
|
monitoringMode |
Enum MonitoringMode |
The monitoring mode to be set for the MonitoredItem. The MonitoringMode enumeration is defined in 7.23. |
|
requestedParameters |
Monitoring Parameters |
The requested monitoring parameters. Servers negotiate the values of these parameters based on the Subscription and the capabilities of the Server. The MonitoringParameters type is defined in 7.21. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
Response Header |
Common response parameters (see 7.34 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
results [] |
MonitoredItem CreateResult |
List of results for the MonitoredItems to create. The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the itemsToCreate request parameter. This structure is defined in-line with the following indented items. |
|
statusCode |
StatusCode |
StatusCode for the MonitoredItem to create (see 7.39 for StatusCode definition). |
|
monitoredItemId |
IntegerId |
Server-assigned id for the MonitoredItem (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). This id is unique within the Subscription, but might not be unique within the Server or Session. This parameter is present only if the statusCode indicates that the MonitoredItem was successfully created. |
|
revisedSampling Interval |
Duration |
The actual sampling interval that the Server will use. This value is based on a number of factors, including capabilities of the underlying system. The Server shall always return a revisedSamplingInterval that is equal or higher than the requested samplingInterval. If the requested samplingInterval is higher than the maximum sampling interval supported by the Server, the maximum sampling interval is returned. |
|
revisedQueueSize |
Counter |
The actual queue size that the Server will use. |
|
filterResult |
Extensible Parameter MonitoringFilterResult |
Contains any revised parameter values or error results associated with the MonitoringFilter specified in requestedParameters. This parameter may be null if no errors occurred. The MonitoringFilterResult parameter type is an extensible parameter type specified in 7.22. |
|
diagnosticInfos [] |
DiagnosticInfo |
List of diagnostic information for the MonitoredItems to create (see 7.12 for DiagnosticInfo definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the itemsToCreate request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 70 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 182.
Table 70 – CreateMonitoredItems Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyOperations |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TimestampsToReturnInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
Table 71 defines values for the operation level statusCode parameter that are specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 183.
Table 71 – CreateMonitoredItems Operation Level Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_MonitoringModeInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_NodeIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_NodeIdUnknown |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_AttributeIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_IndexRangeInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_IndexRangeNoData |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. If the ArrayDimensions have a fixed length that cannot change and no data exists within the range of indexes specified, Bad_IndexRangeNoData is returned in CreateMonitoredItems. Otherwise if the length of the array is dynamic, the Server shall return this status in a Publish response for the MonitoredItem if no data exists within the range. |
|
Bad_DataEncodingInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_DataEncodingUnsupported |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemFilterInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemFilterUnsupported |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_FilterNotAllowed |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyMonitoredItems |
The Server has reached its maximum number of monitored items. |
This Service is used to modify MonitoredItems of a Subscription. Changes to the MonitoredItem settings shall be applied immediately by the Server. They take effect as soon as practical but not later than twice the new revisedSamplingInterval.
The return diagnostic info setting in the request header of the CreateMonitoredItems or the last ModifyMonitoredItems Service is applied to the Monitored Items and is used as the diagnostic information settings when sending Notifications in the Publish response.
Illegal request values for parameters that can be revised do not generate errors. Instead the Server will choose default values and indicate them in the corresponding revised parameter.
Table 72 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 72 – ModifyMonitoredItems Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.33 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
subscriptionId |
IntegerId |
The Server-assigned identifier for the Subscription used to qualify the monitoredItemId (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). |
|
timestampsToReturn |
Enum Timestamps ToReturn |
An enumeration that specifies the timestamp Attributes to be transmitted for each MonitoredItem to be modified. The TimestampsToReturn enumeration is defined in 7.40. When monitoring Events, this applies only to Event fields that are of type DataValue. |
|
itemsToModify [] |
MonitoredItemModifyRequest |
The list of MonitoredItems to modify. This structure is defined in-line with the following indented items. |
|
monitoredItemId |
IntegerId |
Server-assigned id for the MonitoredItem. |
|
requestedParameters |
Monitoring Parameters |
The requested values for the monitoring parameters. The MonitoringParameters type is defined in 7.21. If the number of notifications in the queue exceeds the new queue size, the notifications exceeding the size shall be discarded following the configured discard policy. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
Response Header |
Common response parameters (see 7.34 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
results [] |
MonitoredItemModifyResult |
List of results for the MonitoredItems to modify. The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the itemsToModify request parameter. This structure is defined in-line with the following indented items. |
|
statusCode |
StatusCode |
StatusCode for the MonitoredItem to be modified (see 7.39 for StatusCode definition). |
|
revisedSampling Interval |
Duration |
The actual sampling interval that the Server will use. The Server returns the value it will actually use for the sampling interval. This value is based on a number of factors, including capabilities of the underlying system. The Server shall always return a revisedSamplingInterval that is equal or higher than the requested samplingInterval. If the requested samplingInterval is higher than the maximum sampling interval supported by the Server, the maximum sampling interval is returned. |
|
revisedQueueSize |
Counter |
The actual queue size that the Server will use. |
|
filterResult |
Extensible Parameter MonitoringFilter Result |
Contains any revised parameter values or error results associated with the MonitoringFilter specified in the request. This parameter may be null if no errors occurred. The MonitoringFilterResult parameter type is an extensible parameter type specified in 7.22. |
|
diagnosticInfos [] |
DiagnosticInfo |
List of diagnostic information for the MonitoredItems to modify (see 7.12 for DiagnosticInfo definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the itemsToModify request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 73 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 182.
Table 73 – ModifyMonitoredItems Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyOperations |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TimestampsToReturnInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
Table 74 defines values for the operation level statusCode parameter that are specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 183.
Table 74 – ModifyMonitoredItems Operation Level Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemFilterInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemFilterUnsupported |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_FilterNotAllowed |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
This Service is used to set the monitoring mode for one or more MonitoredItems of a Subscription. Setting the mode to DISABLED causes all queued Notifications to be deleted.
Table 75 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 75 – SetMonitoringMode Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.33 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
subscriptionId |
IntegerId |
The Server-assigned identifier for the Subscription used to qualify the monitoredItemIds (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). |
|
monitoringMode |
Enum MonitoringMode |
The monitoring mode to be set for the MonitoredItems. The MonitoringMode enumeration is defined in 7.23. |
|
monitoredItemIds [] |
IntegerId |
List of Server-assigned ids for the MonitoredItems. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
Response Header |
Common response parameters (see 7.34 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
results [] |
StatusCode |
List of StatusCodes for the MonitoredItems to enable/disable (see 7.39 for StatusCode definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the monitoredItemIds request parameter. |
|
diagnosticInfos [] |
DiagnosticInfo |
List of diagnostic information for the MonitoredItems to enable/disable (see 7.12 for DiagnosticInfo definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the monitoredItemIds request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 76 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 182.
Table 76 – SetMonitoringMode Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyOperations |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoringModeInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
Table 77 defines values for the operation level results parameter that are specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 183.
Table 77 – SetMonitoringMode Operation Level Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
This Service is used to create and delete triggering links for a triggering item. The triggering item and the items to report shall belong to the same Subscription.
Each triggering link links a triggering item to an item to report. Each link is represented by the MonitoredItem id for the item to report. An error code is returned if this id is invalid.
See 5.13.1.6 for a description of the triggering model.
Table 78 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 78 – SetTriggering Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
Request Header |
Common request parameters (see 7.33 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
subscriptionId |
IntegerId |
The Server-assigned identifier for the Subscription that contains the triggering item and the items to report (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). |
|
triggeringItemId |
IntegerId |
Server-assigned id for the MonitoredItem used as the triggering item. |
|
linksToAdd [] |
IntegerId |
The list of Server-assigned ids of the items to report that are to be added as triggering links. The list of linksToRemove is processed before the linksToAdd. |
|
linksToRemove [] |
IntegerId |
The list of Server-assigned ids of the items to report for the triggering links to be deleted. The list of linksToRemove is processed before the linksToAdd. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
Response Header |
Common response parameters (see 7.34 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
addResults [] |
StatusCode |
List of StatusCodes for the items to add (see 7.39 for StatusCode definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the linksToAdd parameter specified in the request. |
|
addDiagnosticInfos [] |
Diagnostic Info |
List of diagnostic information for the links to add (see 7.12 for DiagnosticInfo definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the linksToAdd request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
|
removeResults [] |
StatusCode |
List of StatusCodes for the items to delete. The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the linksToRemove parameter specified in the request. |
|
removeDiagnosticInfos [] |
Diagnostic Info |
List of diagnostic information for the links to delete. The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the linksToRemove request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 79 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in 7.39.
Table 79 – SetTriggering Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyOperations |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
Table 80 defines values for the results parameters that are specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 183.
Table 80 – SetTriggering Operation Level Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |
This Service is used to remove one or more MonitoredItems of a Subscription. When a MonitoredItem is deleted, its triggered item links are also deleted.
Successful removal of a MonitoredItem, however, might not remove Notifications for the MonitoredItem that are in the process of being sent by the Subscription. Therefore, Clients may receive Notifications for the MonitoredItem after they have received a positive response that the MonitoredItem has been deleted.
Table 81 defines the parameters for the Service.
Table 81 – DeleteMonitoredItems Service Parameters
|
Name |
Type |
Description |
|
Request |
|
|
|
requestHeader |
RequestHeader |
Common request parameters (see 7.33 for RequestHeader definition). |
|
subscriptionId |
IntegerId |
The Server-assigned identifier for the Subscription that contains the MonitoredItems to be deleted (see 7.19 for IntegerId definition). |
|
monitoredItemIds [] |
IntegerId |
List of Server-assigned ids for the MonitoredItems to be deleted. |
|
|
|
|
|
Response |
|
|
|
responseHeader |
Response Header |
Common response parameters (see 7.34 for ResponseHeader definition). |
|
results [] |
StatusCode |
List of StatusCodes for the MonitoredItems to delete (see 7.39 for StatusCode definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the monitoredItemIds request parameter. |
|
diagnosticInfos [] |
DiagnosticInfo |
List of diagnostic information for the MonitoredItems to delete (see 7.12 for DiagnosticInfo definition). The size and order of the list matches the size and order of the monitoredItemIds request parameter. This list is empty if diagnostics information was not requested in the request header or if no diagnostic information was encountered in processing of the request. |
Table 82 defines the Service results specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 182.
Table 82 – DeleteMonitoredItems Service Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_NothingToDo |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_TooManyOperations |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
|
Bad_SubscriptionIdInvalid |
See Table 182 for the description of this result code. |
Table 83 defines values for the results parameter that are specific to this Service. Common StatusCodes are defined in Table 183.
Table 83 – DeleteMonitoredItems Operation Level Result Codes
|
Symbolic Id |
Description |
|
Bad_MonitoredItemIdInvalid |
See Table 183 for the description of this result code. |