Several nodesets (see Figure 10) are defined to organise the address space. Figure 10 includes the nodeset name, the corresponding namespace URI and the file name containing the nodeset. All nodesets are based on the UA Base types. The nodeset AutomationML Base types (AML, see Chapter 6) defines all nodes and type definitions necessary for the modelling of AutomationML in OPC UA. This includes e.g. organisational nodes for the entry into the AutomationML folder for RoleClassLibs or AutomationML types (ObjectType CAEXFileType). One nodeset is defined for the standardised and informative AutomationML libraries (AMLLibs, see Chapter 6.4) coming from IEC62714-1, IEC62714-2, IEC62714-3, and IEC62714-4. And finally, one or more nodesets are used for the concrete AutomationML documents (Filename of each AutomationML document).
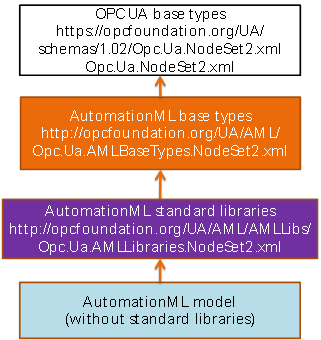
Figure 10 – Different nodesets for the usage of AutomationML in OPC UA information models
The main structure of an AutomationML file from Figure 7 is mapped into a slightly variant structure depicted in Figure 11. The InstanceHierarchies and libraries shall be stored in common folders (AutomationMLInstanceHierarchies, AutomationMLLibraries, AutomationMLSystemUnitClassLibs, AutomationMLRoleClassLibs, AutomationMLInterfaceClassLibs).
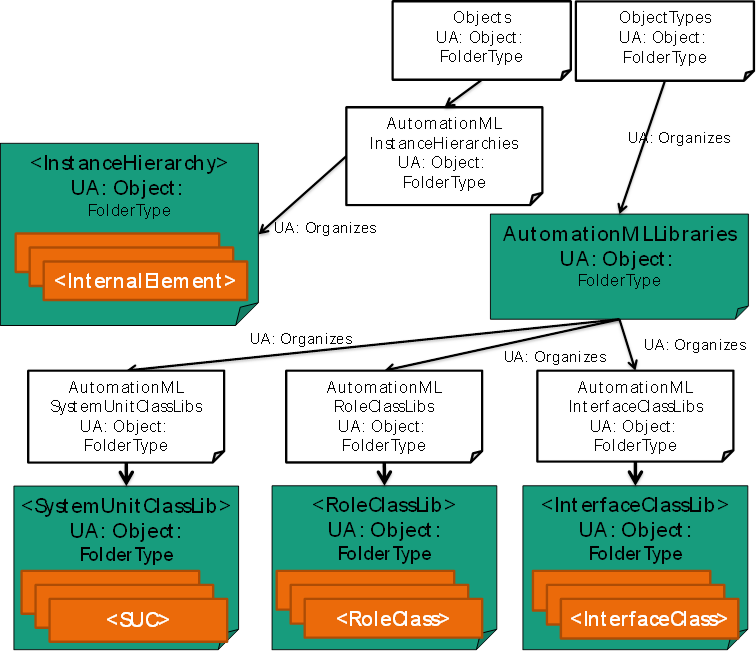
Figure 11 – CAEX file <-> OPC UA Types [1]
The AutomationML BaseElementTypes transformation into OPC UA Types is depicted in Figure 12, the transformation of AutomationML elements into OPC UA Types is depicted in Figure 13.
Figure 12 depicts the mapping of the relations between the main AutomationML elements (see Figure 8). The structure of the picture is not changed, so the mapping can be read directly from the graphic. Table 7 and Table 8 resume the mapping rules in a list. Basically, AutomationML InternalElements are represented by OPC UA Objects, AutomationML SystemUnitClasses and RoleClasses are represented by OPC UA ObjectTypes. Detailed definition of new ObjectTypes, ReferenceTypes and VariableTypes are given in Chapter 6.
ChildElement relations within class structures (SystemUnitClass, RoleClass) are mapped to the OPC UA ‘Organizes’ references. InternalElements which follow the ChildElement relation are referenced via ‘HasComponent’ references. The inheritance relations within SystemUnitClasses and RoleClasses are mapped to OPC UA ‘HasSubtype’ references. The internal structures of SystemUnitClasses are depicted by InternalElements which are connected via OPC UA ‘HasComponent’ references. The RefBaseClassPath relation of AutomationML is an OPC UA ‘HasTypeDefinition’ reference. The referencing of RoleClasses to InternalElements or SystemUnitClasses via SupportedRoleClass or RoleRequirement of AutomationML is done via OPC UA ‘HasAMLRoleReference’ references.
|
AutomationML |
OPC UA |
|
InternalElement |
Object |
|
SystemUnitClass |
ObjectType |
|
RoleClass |
ObjectType |
|
AutomationML Source |
AutomationML Target |
AutomationML Relation |
OPC UA Reference |
Description |
|
InternalElement |
RoleClass |
SupportedRoleClass |
HasAMLRoleReference |
Semantic similar to HasTypeDefinition |
|
InternalElement |
RoleClass |
RoleRequirement |
HasAMLRoleReference |
Semantic similar to HasTypeDefinition |
|
InternalElement |
SystemUnitClass |
RefBaseClassPath |
HasTypeDefinition |
|
|
InternalElement |
InternalElement |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
SystemUnitClass |
RoleClass |
SupportedRoleClass |
HasAMLRoleReference |
Semantic similar to HasTypeDefinition |
|
SystemUnitClass |
InternalElement |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
SystemUnitClass |
SystemUnitClass |
|
Organizes |
ChildElement |
|
SystemUnitClass |
SystemUnitClass |
RefBaseClassPath |
HasSubtype |
|
|
RoleClass |
RoleClass |
|
Organizes |
ChildElement |
|
RoleClass |
RoleClass |
RefBaseClassPath |
HasSubtype |
|
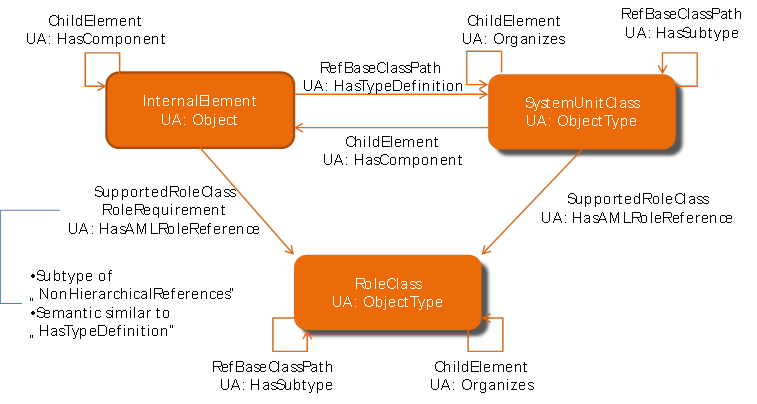
Figure 12 – AutomationML BaseElementTypes and the OPC UA Types [1]
The mappings of the AutomationML object details (see Figure 9) are depicted in Figure 13. The analogy between the two figures is obvious. Table 9 and Table 10 summarize the mapping rules in a list. AutomationML Attributes become OPC UA Variables. AutomationML InterfaceClasses are transformed into OPC UA ObjectTypes and the corresponding AutomationML ExternalInterface elements are modelled by OPC UA Objects.
The Attributes and ExternalInterfaces are referenced via ‘HasComponent’ references. The InterfaceClass is the type definition of the ExternalInterface therefore it is assigned via ‘HasTypeDefinition’ reference. Similarly to the RoleClasses and SystemUnitClasses, the relations between InterfaceClasses are mapped to ‘Organizes’ references within the XML tree structure and to ‘HasSubtype’ references concerning inheritance relation. Relations between ExternalInterfaces (AutomationML InternalLinks) are assigned via ‘HasAMLInternalLink’ reference. Details are given in Chapter 6.
|
AutomationML |
OPC UA |
|
InternalElement |
Object |
|
SystemUnitClass |
ObjectType |
|
RoleClass |
ObjectType |
|
InterfaceClass |
ObjectType |
|
Attribute |
Variable |
|
ExternalInterface |
Object |
|
AutomationML Source |
AutomationML Target |
AutomationML Relation |
OPC UA Reference |
Description |
|
InternalElement |
Attribute |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
SystemUnitClass |
Attribute |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
RoleClass |
Attribute |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
InternalElement |
ExternalInterface |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
SystemUnitClass |
ExternalInterface |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
RoleClass |
ExternalInterface |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
ExternalInterface |
ExternalInterface |
InternalLink |
HasAMLInternalLink |
|
|
ExternalInterface |
Attribute |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
ExternalInterface |
InterfaceClass |
RefBaseClassPath |
HasTypeDefinition |
|
|
InterfaceClass |
Attribute |
|
HasComponent |
ChildElement |
|
InterfaceClass |
InterfaceClass |
RefBaseClassPath |
HasSubtype |
|
|
InterfaceClass |
InterfaceClass |
|
Organizes |
ChildElement |
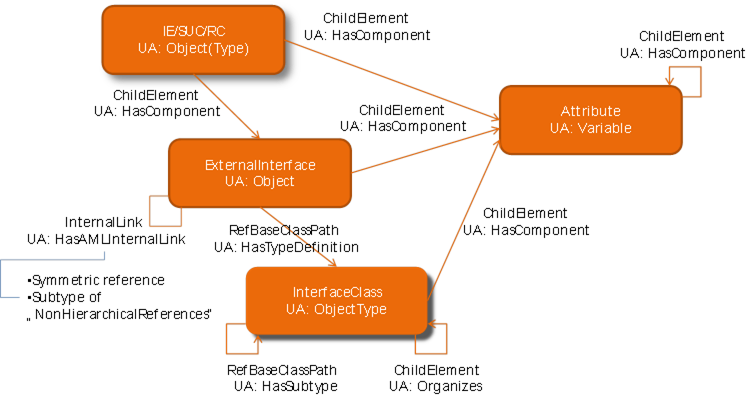
Figure 13 – AutomationML Element and the OPC UA Types [1]